THE CYTOPLASM & NUCLEUS | A & P
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
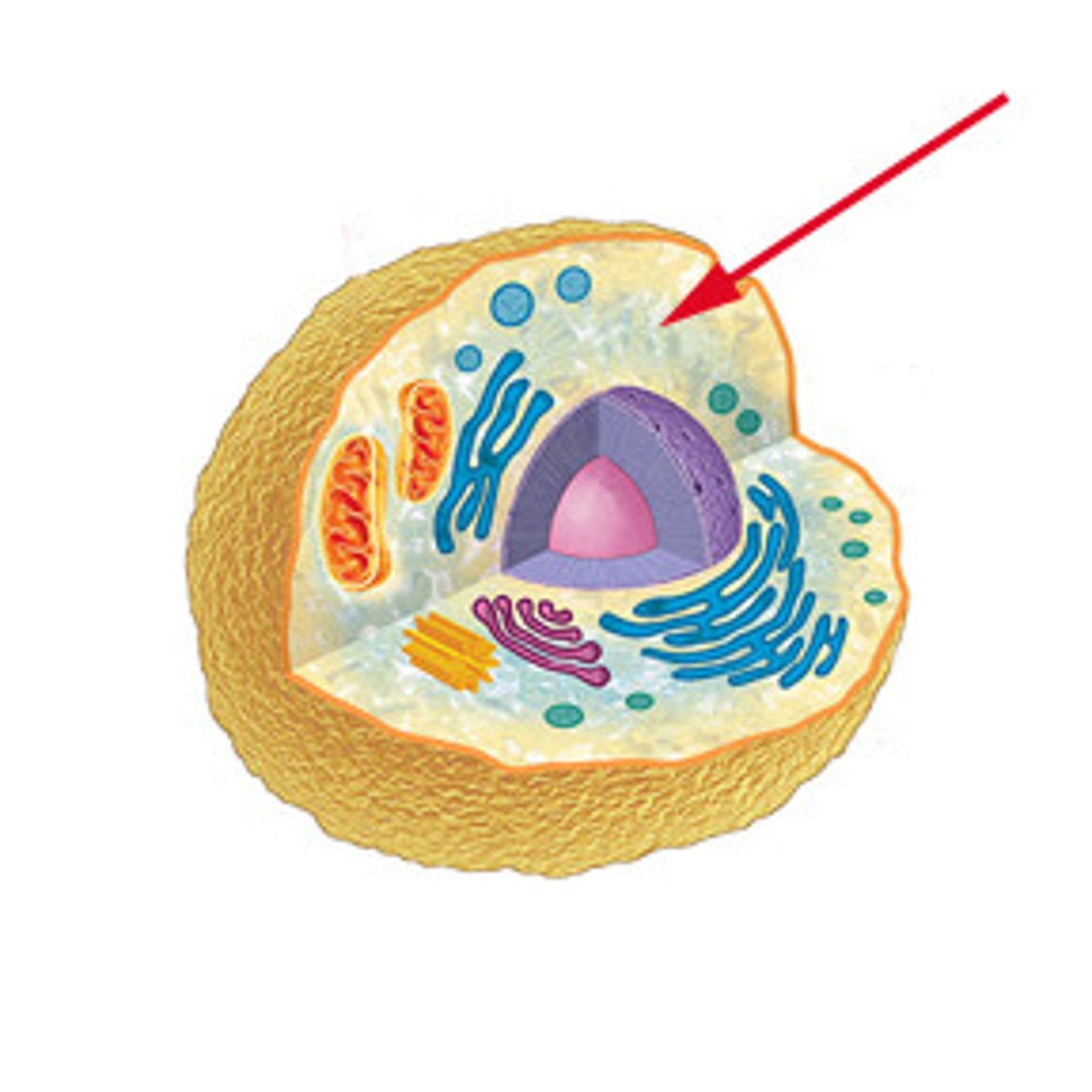
cytoplasm
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus.
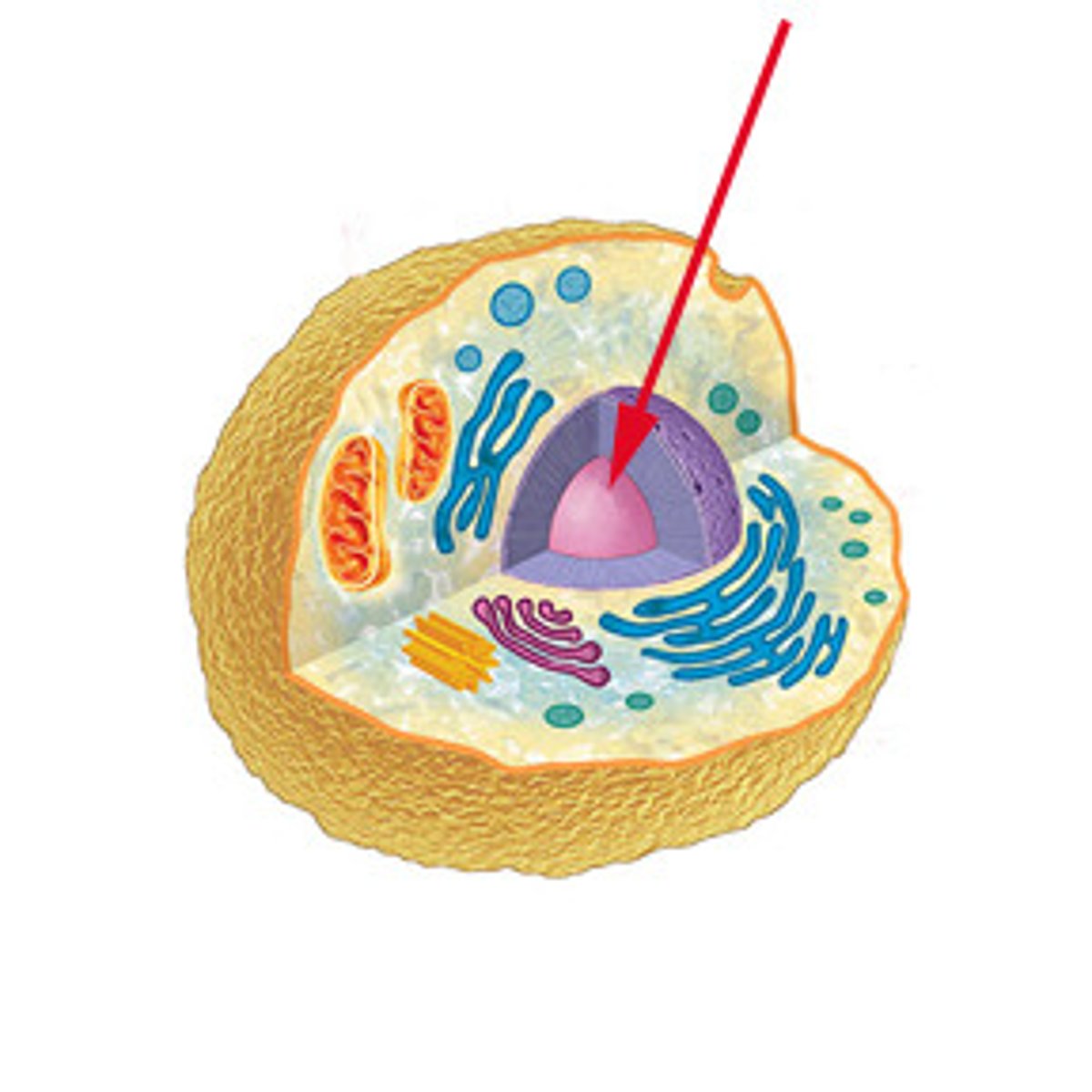
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
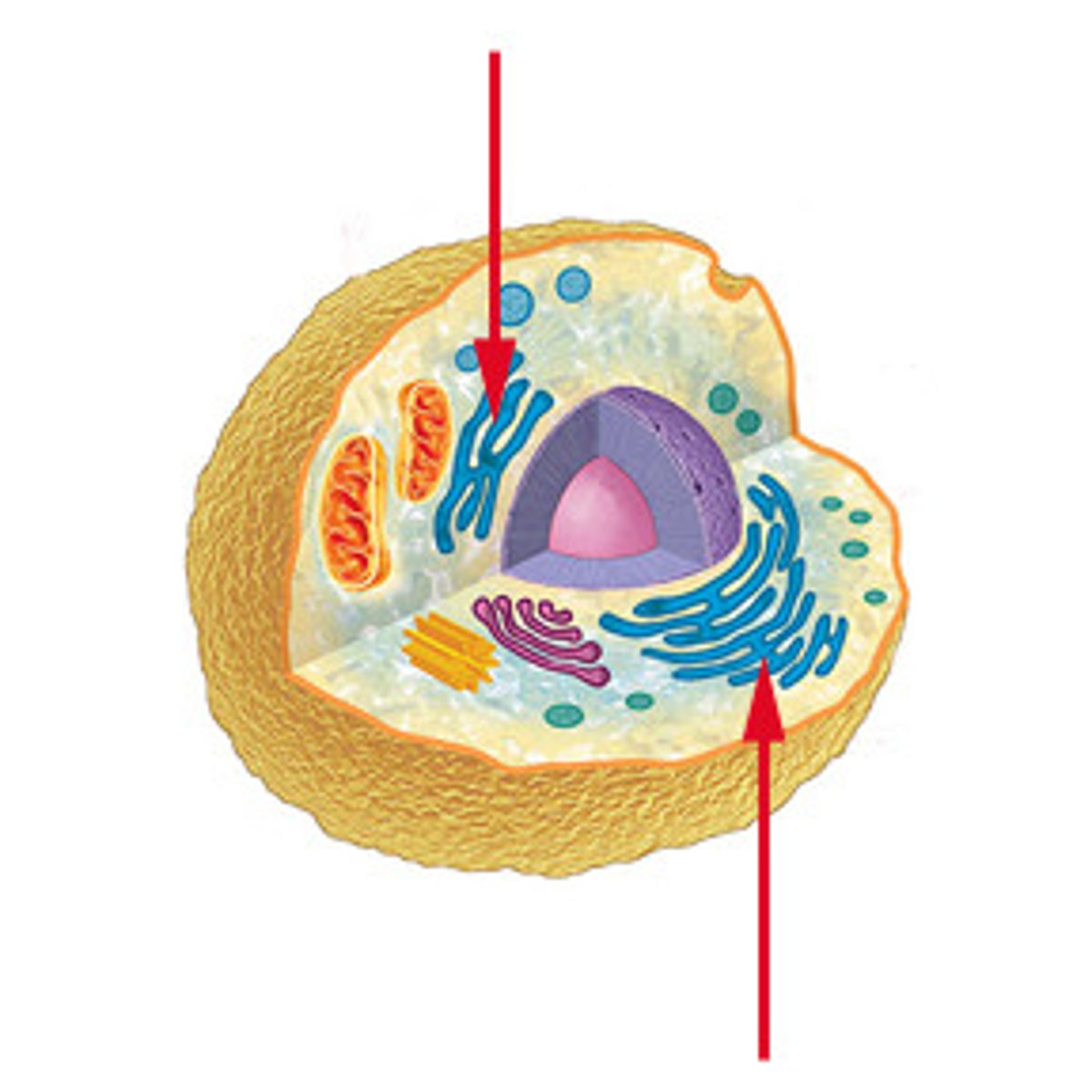
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
ribosome
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
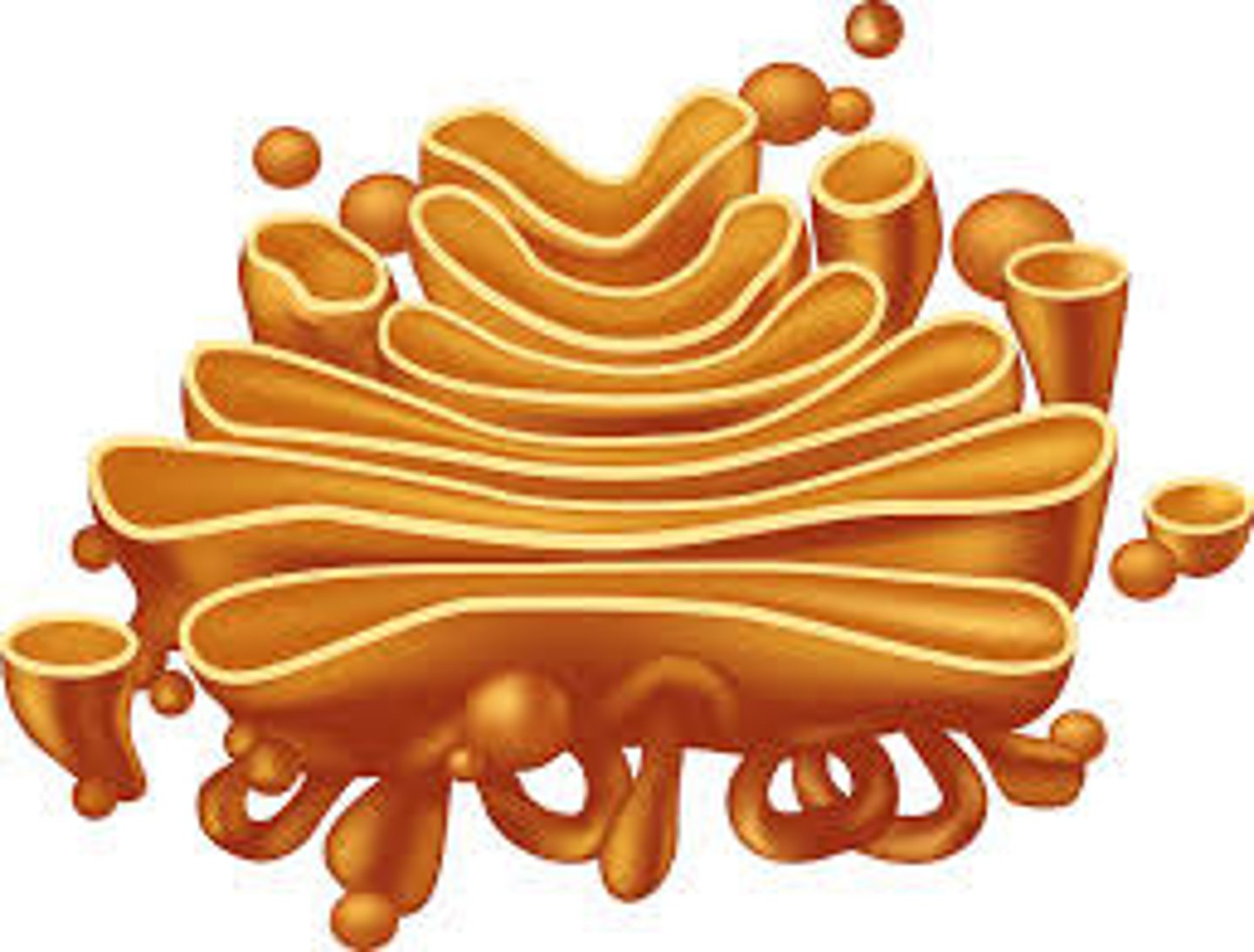
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell

lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
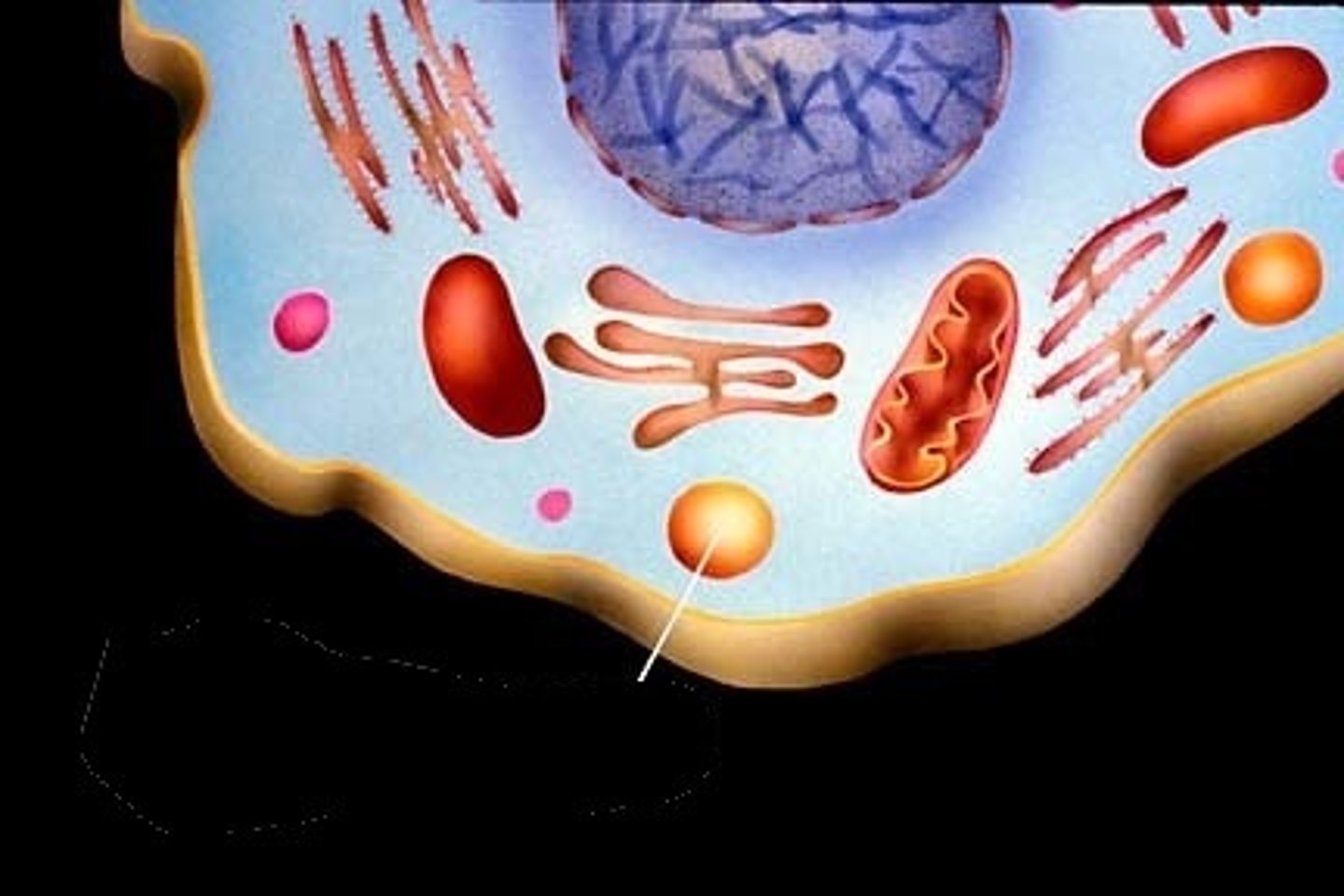
autophagy
A process in which lysosomes decompose damaged organelles to reuse their organic monomers
autolysis
the spontaneous breakdown of cells as they self-digest
Mitochondrion
A membrane‐bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells; site of cellular respiration.
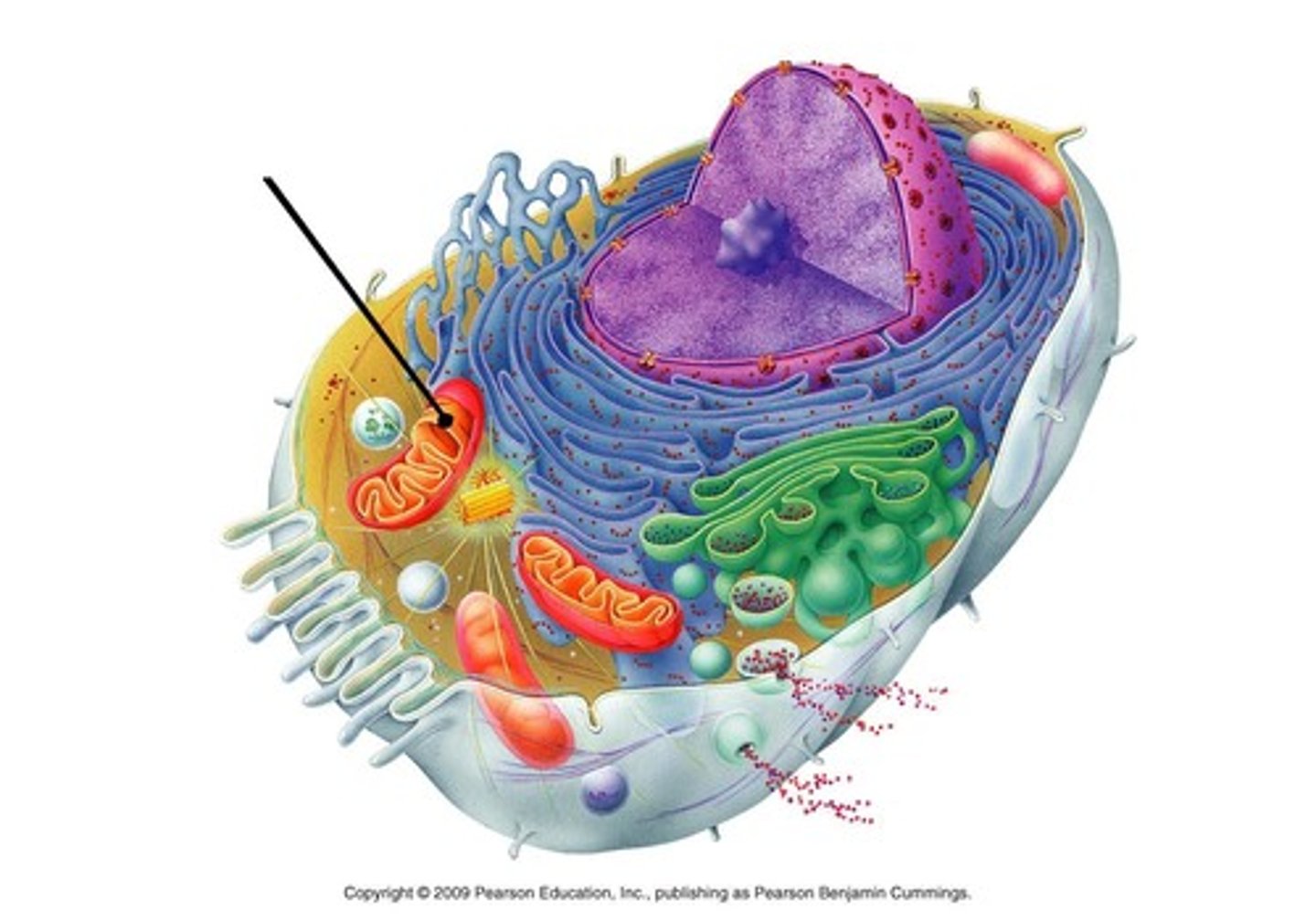
peroxisome
A microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing and then degrading hydrogen peroxide.
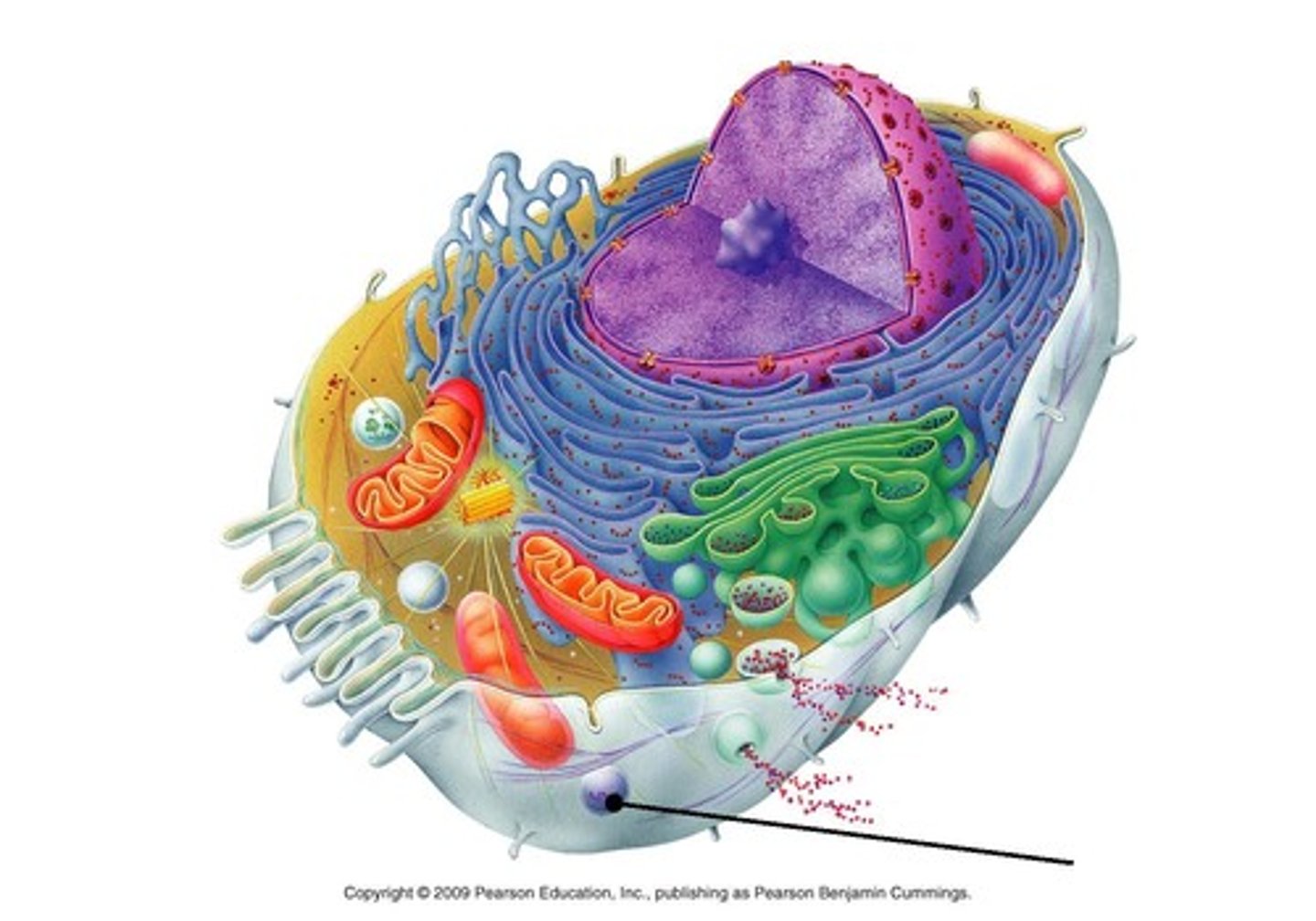
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
a group of extremely reactive peroxides and oxygen-containing radicals that may contribute to cellular damage
mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement
microtubule
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells and is found in cilia and flagella.
cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
flagellum
A long, whiplike structure that helps a cell to move
centriole
structure in an animal cell that helps to organize cell division
microfilament
a fiber found inside eukaryotic cells that is composed mainly of the protein actin and that has a role in cell structure and movement
intermediate filament
A component of the cytoskeleton that includes filaments intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments.
nuclear envelope
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
nuclear pore
a protein-lined channel in the nuclear envelope that regulates the transportation of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
chromatin
dna and proteins that condenses to make up chromosomes
chromosome
Any of the usually linear bodies in the cell nucleus that are made up of DNA and proteins and are visible during cell division
gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA
DNA polymerase
principle enzyme involved in DNA replication
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
triplet code
3 bases of DNA that code for a single amino acid
protein synthesis
the formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA
transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
RNA polymerase
principle enzyme involved in transcription
codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
translation
the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
anticodon
a sequence of three nucleotides forming a unit of genetic code in a transfer RNA molecule, corresponding to a complementary codon in messenger RNA.