Plant sexual reproduction
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
production of flower gametes
anthers
produce pollen containing male gametes
diploid cells inside anther divide by meiosis to produce 4 haploid cells, each develops into pollen grain
nucleus inside pollen grain divides by mitosis to produce male gametes
ovules
ovoid structures inside the ovary
one cell in center of ovule grows particularly large and divides by meiosis
1 of the haploid nuclei produced divides 3 times by mitosis producing 8 haploid nuclei, one of which becomes female gamete
process of sexual reproduction in flower
pollination
transfer of pollen from anther to stigma, either by wind or animal
fertilisation
happens inside an ovule
each pollen grain that lands on stigma grows a tube from the grain down to the style to the ovary
male nuclei travel down the tube to the ovule and digest a route into it
male gametes are released fusing with female gamete, fertilisation occurs, producing a zygote
embryo development
zygote divides repeatedly by mitosis and cells produced develop into a seed
many flowers are hermaphrodite (have male and female parts) so can act as both male and female parent, so reproduction is sexual
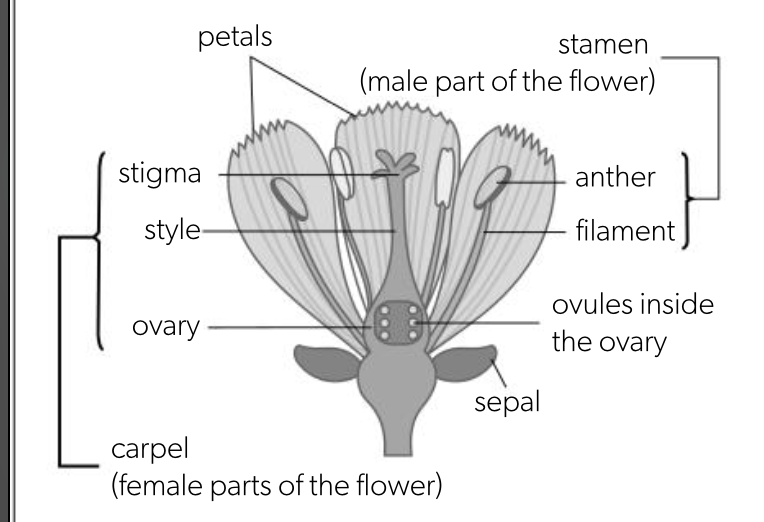
diagram of flower
sepal
protect developing flower
petal
large brightly coloured to attract insects
anther
part of stamen that produces male gametes
firmly attached to brush against insects
pollen
contains male nuclei for fertilisation
large and spiky so stick to visiting insect
filament
stalk of stamen that holds up anther
stigma
top of carpel, female part of flower, pollen lands here
sticky so pollen grains stick to it when insects brushes past
style
part of cartel that supports stigma
ovary
contains ovules
ovule
chamber within ovary where female gametes develop
increasing cross pollination
cross pollination: transfer of pollen from anther of one flower to stigma of another flower. leads to fusion of male and female gametes from diff plants so promotes genetic variation & therefore evolution
outside agent required to transfer pollen
most plants can self pollinate bc they’re hermaphrodites, but inbreeding increases chance of rare recessive allele in one ancestor being inherited twice by an individual, causing genetic disorder
natural selection therefore favours plants that reproduce by cross pollination, and mechanisms exist to promote it
separate male and female plants so anthers and carpels are on diff plants
separate male and female flowers on the same plant so anthers and carpels are on diff flowers
stigmas and pollen on anthers mature at diff times
self incompatibility mechanisms
sometimes self pollination does occur despite adaptations to reduce the chances
in many plants this pollen fails to germinate, or pollen tube stops growing before reaching ovary, this is self incompatibility and it has a genetic basis
plants with the same self-incompatibility alleles cannot produce offspring together
dispersal and germination of seeds
seeds often transported long distances from the parent plants
helps to spread the species and reduces competition between offspring and parent
the function of the fruit that develops from the ovary of the flower
germination follows seed dispersal
happens when conditions are suitable: oxygen, water, warmth
food reserves inside seed are mobilised by being digested and transferred to growing embryo