Regional Climates and Weathers
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
Different types of air masses
They don’t mix
Warm and cold will be separate → atmospheric features
\
Maritime - wetter
Continental - less moisture
Tropical - influenced by warm
Maritime tropical - necessary for formation of hurricanes
\
Source of moisture from oceans → control of air masses and regional climate patterns
Warm and cold will be separate → atmospheric features
\
Maritime - wetter
Continental - less moisture
Tropical - influenced by warm
Maritime tropical - necessary for formation of hurricanes
\
Source of moisture from oceans → control of air masses and regional climate patterns
2
New cards
Monsoons
Switching of air direction as ITCZ moves north and south throughout the year
\
Dry monsoon season
Wet monsoon season
\
Largest and most intense is in Asia (east Asian and Indian Monsoon)
\
Also in Australia and Sub-Saharan Africa
\
1/2 global pop influenced by process
\
Dry monsoon season
Wet monsoon season
\
Largest and most intense is in Asia (east Asian and Indian Monsoon)
\
Also in Australia and Sub-Saharan Africa
\
1/2 global pop influenced by process
3
New cards
Monsoon formation
Land warms faster than ocean so in summer land warms more than ocean
Land warms and air rises so cools and condenses into rainfall
Low pressure over land and high over ocean with cold air
Causes circulation pattern
Winter this reverses and it rains over the ocean
\
In some regions there is himalaya region and plateau which keep air rising → keep circulation pattern going
Land warms and air rises so cools and condenses into rainfall
Low pressure over land and high over ocean with cold air
Causes circulation pattern
Winter this reverses and it rains over the ocean
\
In some regions there is himalaya region and plateau which keep air rising → keep circulation pattern going
4
New cards
Asian Monsoon
Winter high in asia → dry outflowing winds
\
Summer ITCZ moves north causing winds to reverse and winds are drawn up to the continent from the sea causing precipitation
\
Summer ITCZ moves north causing winds to reverse and winds are drawn up to the continent from the sea causing precipitation
5
New cards
Summer Monsoon
Brings huge amounts of seasonal rain (e.g. up to 12m)
\
Very important bc large pop depends on it and supports rain-fed agriculture
50% India pop relies on agriculture for income
\
Growth season rains for natural ecosystems
\
Important for snowfall in Himalayas and important water store for rest of the year when it melts
\
Therefore understanding of how it works and could change is vital
\
Very important bc large pop depends on it and supports rain-fed agriculture
50% India pop relies on agriculture for income
\
Growth season rains for natural ecosystems
\
Important for snowfall in Himalayas and important water store for rest of the year when it melts
\
Therefore understanding of how it works and could change is vital
6
New cards
Australian Droughts
Caused by a number of factors
\
South Australia should get rain from westerlies but winter 2019 wind was further south so little precipitation
\
North and East Australia should get monsoon but impacted by ENSO
\
South Australia should get rain from westerlies but winter 2019 wind was further south so little precipitation
\
North and East Australia should get monsoon but impacted by ENSO
7
New cards
ENSO
El Nino - reversal of atmospheric conditions in equatorial pacific. Caused by changes in sea surface temps impacting atmosphere. Convection in middle of pacific so less over Aus. Tends to cause who earth to increase in temps during El Nino years
\
La Nina - strengthening of normal conditions. tends to cool the earth
\
La Nina - strengthening of normal conditions. tends to cool the earth
8
New cards
El Nino Conditions
Warm pool shifts east
\
Cooler water and higher pressure in west
\
Reduced precipitation over eastern Australia
\
Cooler water and higher pressure in west
\
Reduced precipitation over eastern Australia
9
New cards
Normal Conditions in ENSO system
Warm sea surface in west pacific
\
Upwelling of cool waters off South America
\
Winds blow to the west
\
Upwelling of cool waters off South America
\
Winds blow to the west
10
New cards
La Nina conditions
Warm than normal sea surface in west pacific
\
Cooler than normal in East Pacific
\
Convection and rain affect Eastern Australia
\
Cooler than normal in East Pacific
\
Convection and rain affect Eastern Australia
11
New cards
ENSO cycle
Is a cyclical thing
\
USually in one or the other only being in normal during transition between them
\
Generally switches every 2-7 years
\
Has happened for thousands if not millions of years
\
USually in one or the other only being in normal during transition between them
\
Generally switches every 2-7 years
\
Has happened for thousands if not millions of years
12
New cards
Recent ENSO
Have had quite unusual frequency of La Nina (currently 3 in a row)
\
Currently in La Nina but probably going to switch to El Nino by July via neutral
\
Currently in La Nina but probably going to switch to El Nino by July via neutral
13
New cards
Fronts
Occur on different scales and can be warm/cold etc,
\
When air masses collide
\
Cold into warm → squashes warm and pushes it upwards. Warm air moves upwards → condenses → rainfall → frontal storms
\
When air masses collide
\
Cold into warm → squashes warm and pushes it upwards. Warm air moves upwards → condenses → rainfall → frontal storms
14
New cards
Thunderstorms
Can occur in frontal storms
\
Heating at surface and unstable conditions because of air masses leading to rising air and cloud formation
\
Falling rain evaporates and causes sinking air (downdraft)
\
Also causes wind shear which separates up and down drafts → allows storms to be maintained. Also bad for planes
\
often gets hail forming bc rain falls and is so high it turns to ice → falls → updraft → more rain → cycle repeats → big hailstones
\
Lightning distribution - areas with frontal storms have more lightning
Not in antartica bc not enough energy in system to produce bc cold
\
Heating at surface and unstable conditions because of air masses leading to rising air and cloud formation
\
Falling rain evaporates and causes sinking air (downdraft)
\
Also causes wind shear which separates up and down drafts → allows storms to be maintained. Also bad for planes
\
often gets hail forming bc rain falls and is so high it turns to ice → falls → updraft → more rain → cycle repeats → big hailstones
\
Lightning distribution - areas with frontal storms have more lightning
Not in antartica bc not enough energy in system to produce bc cold
15
New cards
Tornadoes
Warm moist air rises rapidly and is spinning
\
Often at cold front and in humid subtropical areas
\
Similar to thunderstorms but at different scale
Able to spin bc of the wind shear creating spinning and then sustaining it and going down to the ground once it reaches enough speed
\
Often at cold front and in humid subtropical areas
\
Similar to thunderstorms but at different scale
Able to spin bc of the wind shear creating spinning and then sustaining it and going down to the ground once it reaches enough speed
16
New cards
Hurricanes, Cyclones, Typhoons
Require sustained winds of at least 74mph and sea surface temps of >27°C
\
Spin anti-clockwise in NH and anti-clockwise in SH
\
None at the equator bc not enough coriolis effect isn’t enough to create deflection of winds
\
Sea surface temps in South Atlantic are usually too cold for them to form. Only ones that have formed are in marine heatwaves
\
Formed similar to thunderstorms but because of the energy caused by warm oceans and spin they can sustain themselves forming a tropical depression and then a cyclone H
\
Spin anti-clockwise in NH and anti-clockwise in SH
\
None at the equator bc not enough coriolis effect isn’t enough to create deflection of winds
\
Sea surface temps in South Atlantic are usually too cold for them to form. Only ones that have formed are in marine heatwaves
\
Formed similar to thunderstorms but because of the energy caused by warm oceans and spin they can sustain themselves forming a tropical depression and then a cyclone H
17
New cards
Hurricane Eye
Still conditions
\
Only a few km wide
\
Eye has no rain and then massive rain bands in eye wall
Intense precipitation all the way out
\
Only a few km wide
\
Eye has no rain and then massive rain bands in eye wall
Intense precipitation all the way out
18
New cards
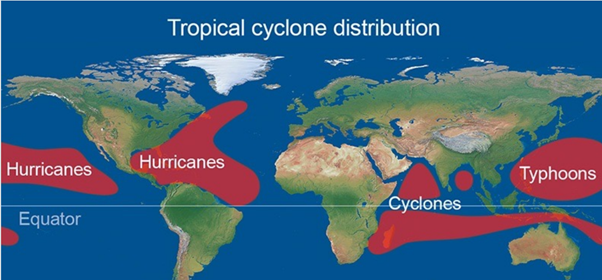
Tropical cyclone name distribution
West Pacific - Hurricanes
Atlantic - Hurricanes
Indian - Cyclones
East Pacific - Typhoons
Atlantic - Hurricanes
Indian - Cyclones
East Pacific - Typhoons