Human Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam
1/697
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
698 Terms
Levels of Structural Organization in the Body
chemical→ Cellular→Tissue→Organ→Organ system→Organism
Nervous System
brain, spinal cord, nerves; regulates body function, provides for sensation, movement, automatic functions, and higher mental functions via nerve impulses
Endocrine System
pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, thymus gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovaries (female)/testes (male); regulates body functions, regulates the functions of muscles, glands, and other tissues through the secretion of hormones
Cardiovascular System
blood vessels, heart; pumps and delivers oxygen-poor blood to the lungs and oxygen-rich blood to the tissues, removes waste from tissues, transports cells, nutrients and other substances
Lymphatic System
tonsils, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, lymphatic vessels; returns excess tissue fluid to the cardiovascular system, provides immunity
Respiratory System
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs; delivers oxygen to blood, removes CO2 from the body, maintains the acid-base balance of the body
Digestive System
mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, liver, stomach, gallbladder, pancreas, large intestine, small intestine; digests food, absorbs nutrients into blood, removes waste, maintains fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance
Integumentary System
hair, skin, nails; protects body from external environment, produces vitamin D, retains water, regulates body temperature
Skeletal System
bones, joints; supports the body, protects internal organs, provides leverage for movement, produces blood cells, stores calcium salts
Muscular System
skeletal muscles; produces movement, controls body openings, generates heat
Urinary System
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra; removes metabolic waste from the blood, maintains fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance, stimulates blood cell production
Male Reproductive System
prostate gland, ductus deferens, testes, penis; produces and transports sperm, secretes hormones, sexual function
Female Reproductive System
mammary glands, uterine tube, ovary, uterus, vagina; produces and transports oocytes, site of fetal development, nourishment, childbirth, and lactation, secretes hormones, sexual function
Anterior (Ventral)
toward the front
Posterior (Dorsal)
toward the back
Superior (Cranial)
toward the head
Inferior (Caudal)
toward the tail
Proximal
closer to the point of origin
Distal
farther from the point of origin
Medial
closer to the midline
Lateral
farther from the midline
Superficial
toward the surface
Deep
farther below the surface
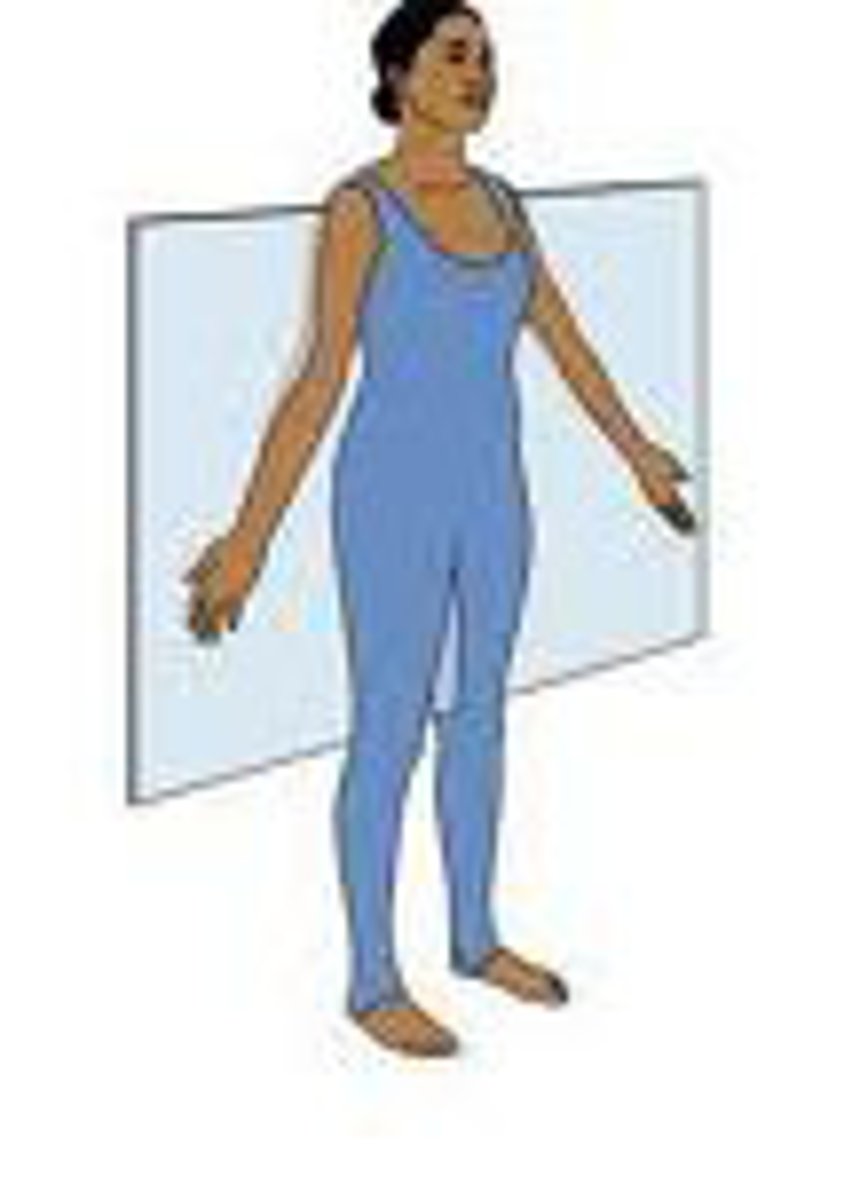
Sagittal Plane
divides the body into left and right
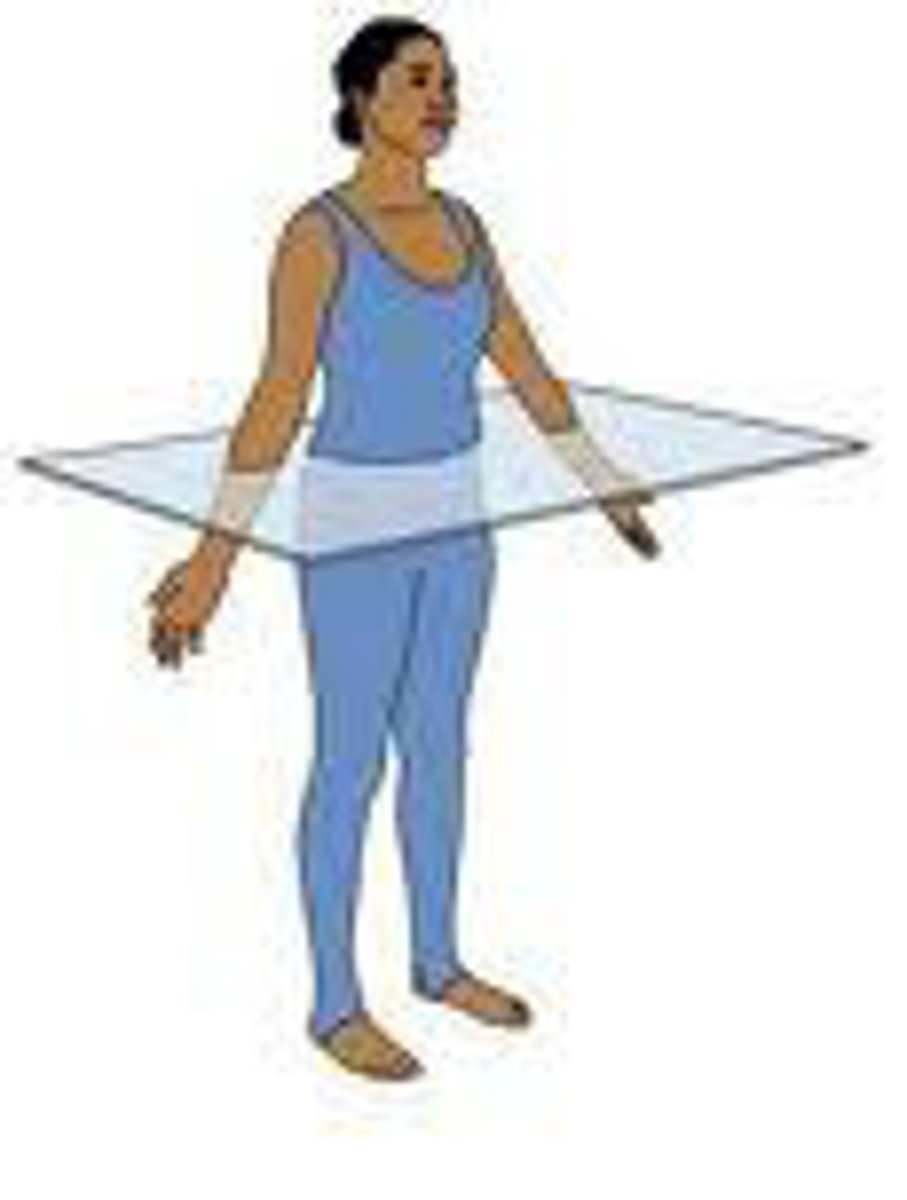
Transverse Plane
divides the body into top and bottom
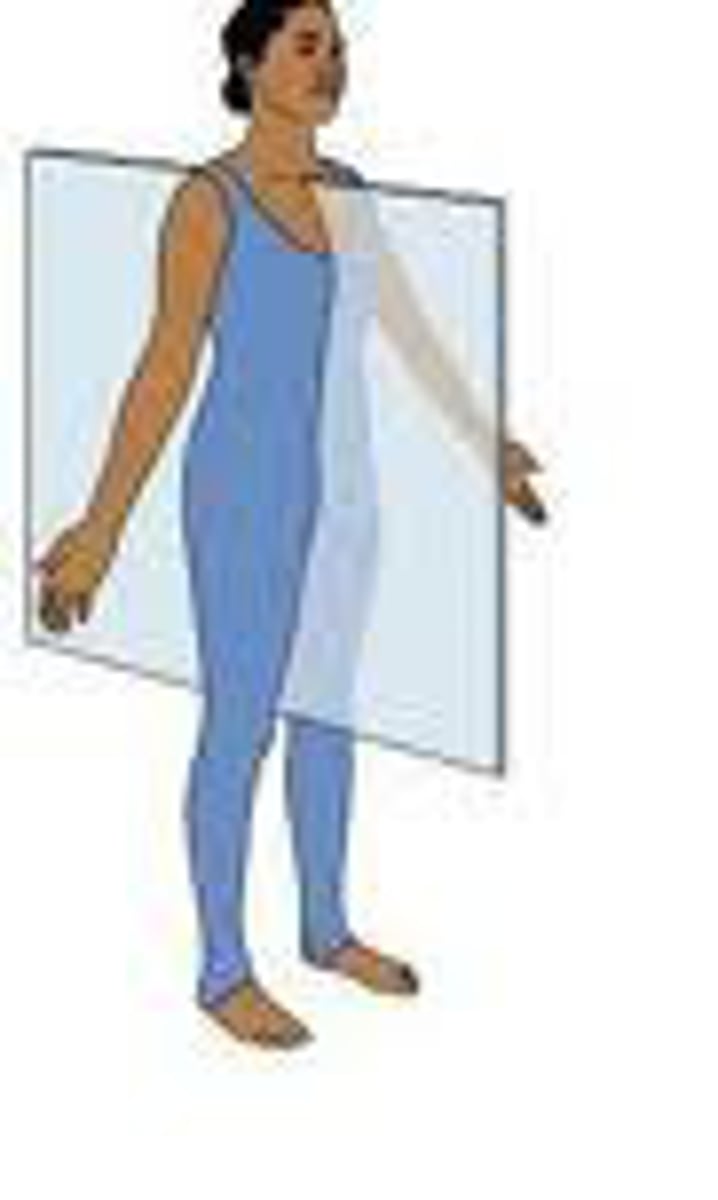
Frontal Plane
divides the body into front and back

Posterior Body Cavity
contains the cranial and vertebral or spinal cavities (CSF filled)
Anterior Body Cavity
contains the thoracic cavity
-pleural cavity (lungs)
-pericardial cavity (heart)
-mediastinum
abdominopelvic cavity
-pelvic cavity
-peritoneal cavity (abdominal)
Abdominopelvic Quadrants

Abdominopelvic Regions
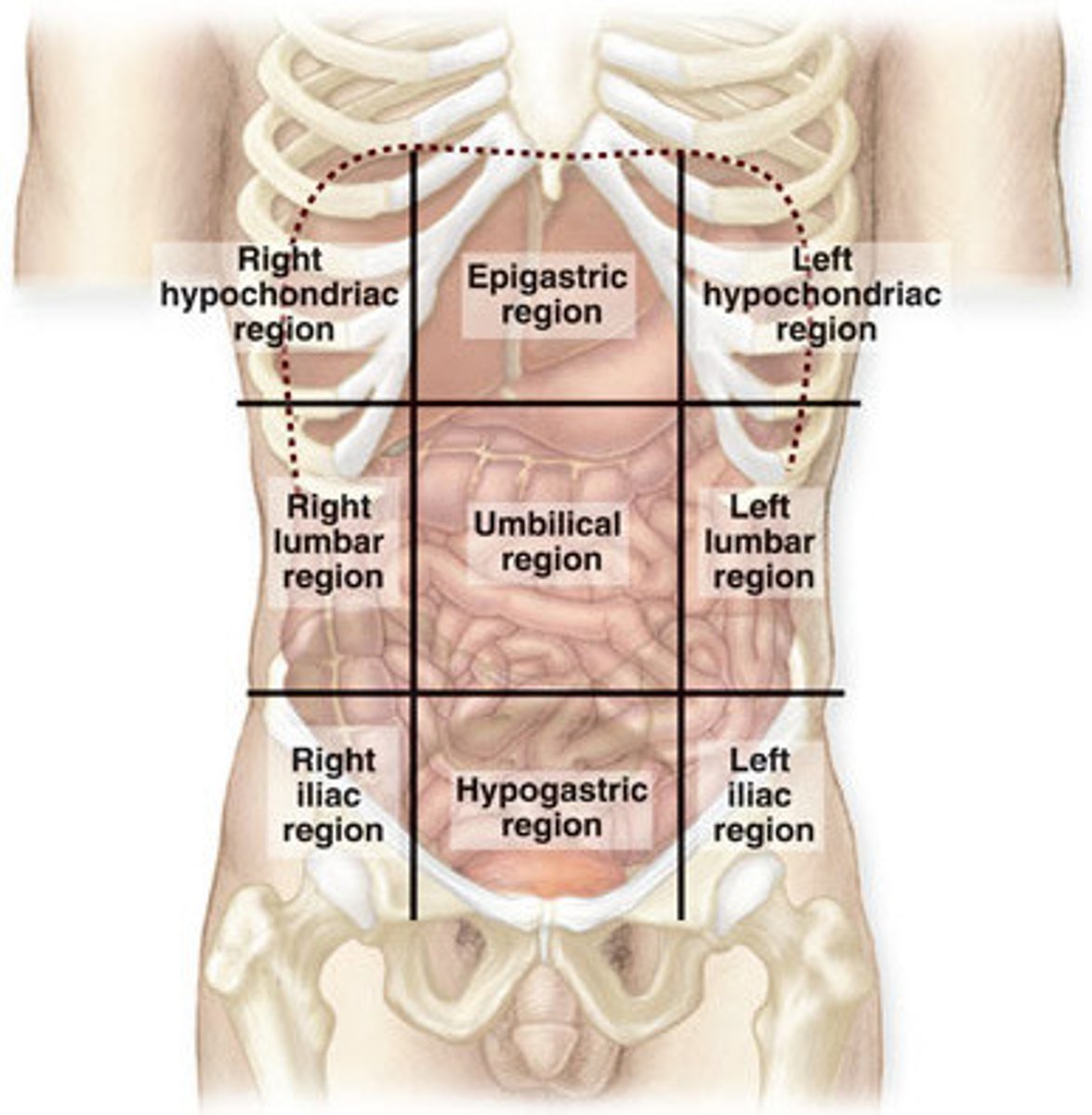
Core Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
feedback loops, structure and function, gradients, cell-cell communication
Negative Feedback
move in the opposite direction of the stimulus, and the effector's activity decreases when the variable returns to the normal range.
Positive Feedback
feature an escalating response that amplifies a stimulus
Isotope
an element that has the same atomic number as another element but a different mass number, due to a different number of neurons
Radioscope
certain high energy isotopes are unstable and will release energy in the form of radiation, this energy release, called radioactive decay, allows the isotope to assume a more stable form
Compound
a molecule composed of 2+ atoms of different elements
Macromolecule
very large compounds composed of many atoms
Solution
one dissolves another, smallest, transparent, solute and solvent, solubility, don't settle out, ex. saline, glucose, blood contains small dissolved molecules
Solute
the substance that is dissolved
Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
Ion
a charged particle that has lost or gained 1+ electrons
Cation
a positive ion with more protons than electrons
Anion
a negative ion with more electrons than protons
Ionic Bonds
results when electrons are transferred between a metal atom and a nonmetal atom; ex. sodium-chloride bond
Covalent Bonding
chemical bonding resulting from the sharing of electrons between 2 nonmetals or a nonmetal and a hydrogen
Single Bond
only one electron pair is shared
Double Bond
2 electron pairs are shared
Triple Bond
3 electron pairs are shared
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally among the atoms in the bond
Polar Covalent Bond
a covalent bond in which electrons spend more time around the more electronegative atom(s) which results in the formation of a dipole
Hydrogen Bond
weak attractions between partially positive hydrogen atoms of one compound or functional group and partially negative atoms of another compound or functional group
Reactant
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
Product
a substance that forms in a chemical reaction
Endergonic Reaction
a reaction in which the products have more energy than the reactants and require an input of energy
Exergonic Reactions
the excess energy stored in the reactants is released, leaving the products of the reaction with less energy than the reactants
Catabolic Reaction/Decomposition
breaking down the products into smaller, less complex molecules
Anabolic Reactions/Synthesis
combining molecules into a larger, more complex molecule
Enzymes
increase the rate at which a reaction takes place by lowering the activation energy, highly specific for individual substrates and reactions, do not alter the chemicals, not permanently altered in the reaction
Activation Energy
all chemical reactions require the input of some amount of energy to overcome the repulsion of the atoms' electrons, and to allow adequately strong collisions to take place
Why is water a good solvent?
absorbs heat without changing significantly in temperature itself, carries hear with it when it changes from liquid to gas, cushions and protects the body's structures, acts as a lubricant between two adjacent surfaces
What dissolves in water?
hydrophilic substances easily dissolve in water, partially or fully charged ends
Acid
a compound that releases one or more hydrogen ions when placed in water, pH<7
Base
a compound that accepts a hydrogen ion from an acid, pH>7
Buffer
chemical systems that resist changes in pH and prevent large swings
pH Scale
a logarithmic scale that represents the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
Electrolyte
cations and anions that result when ionic compounds are placed in a solution, these ions will conduct an electrical current
Carbohydrates
monosaccharides- glucose, fructose
disaccharides- sucrose, lactose
polysaccharides- glycogen, starch, cellulose
Glycogen
a polysaccharide that is the storage form of glucose in animals, mainly found in the liver and skeletal muscles
Fatty Acids
a lipid with a hydrocarbon chain bound to a carboxylic acid group
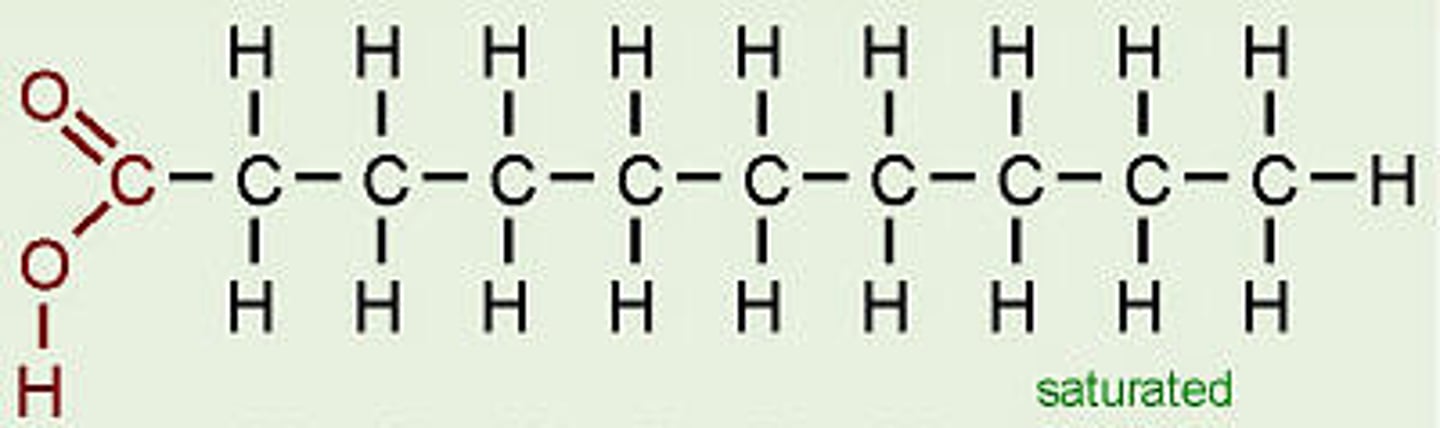
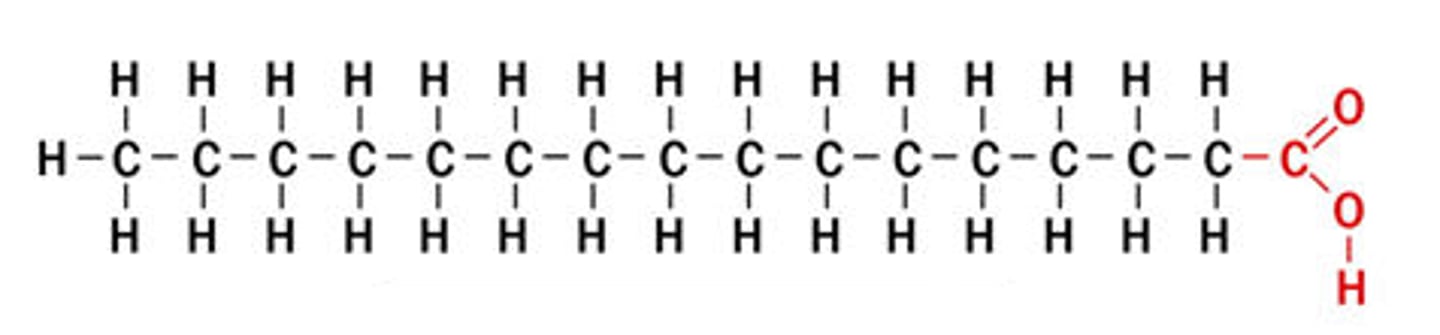
Saturated Fatty Acid
a FA with no double bonds between any carbon atoms
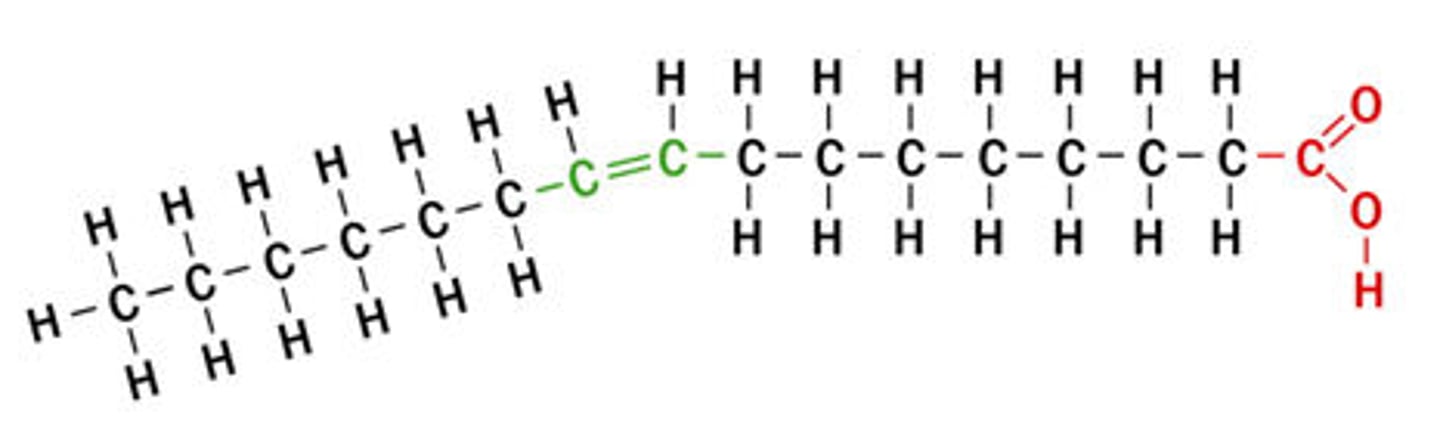
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
a FA with double bond(s) between carbon atoms
Essential Fatty Acid
fats needed by the body that must be consumed in the diet because the human body cannot manufacture them
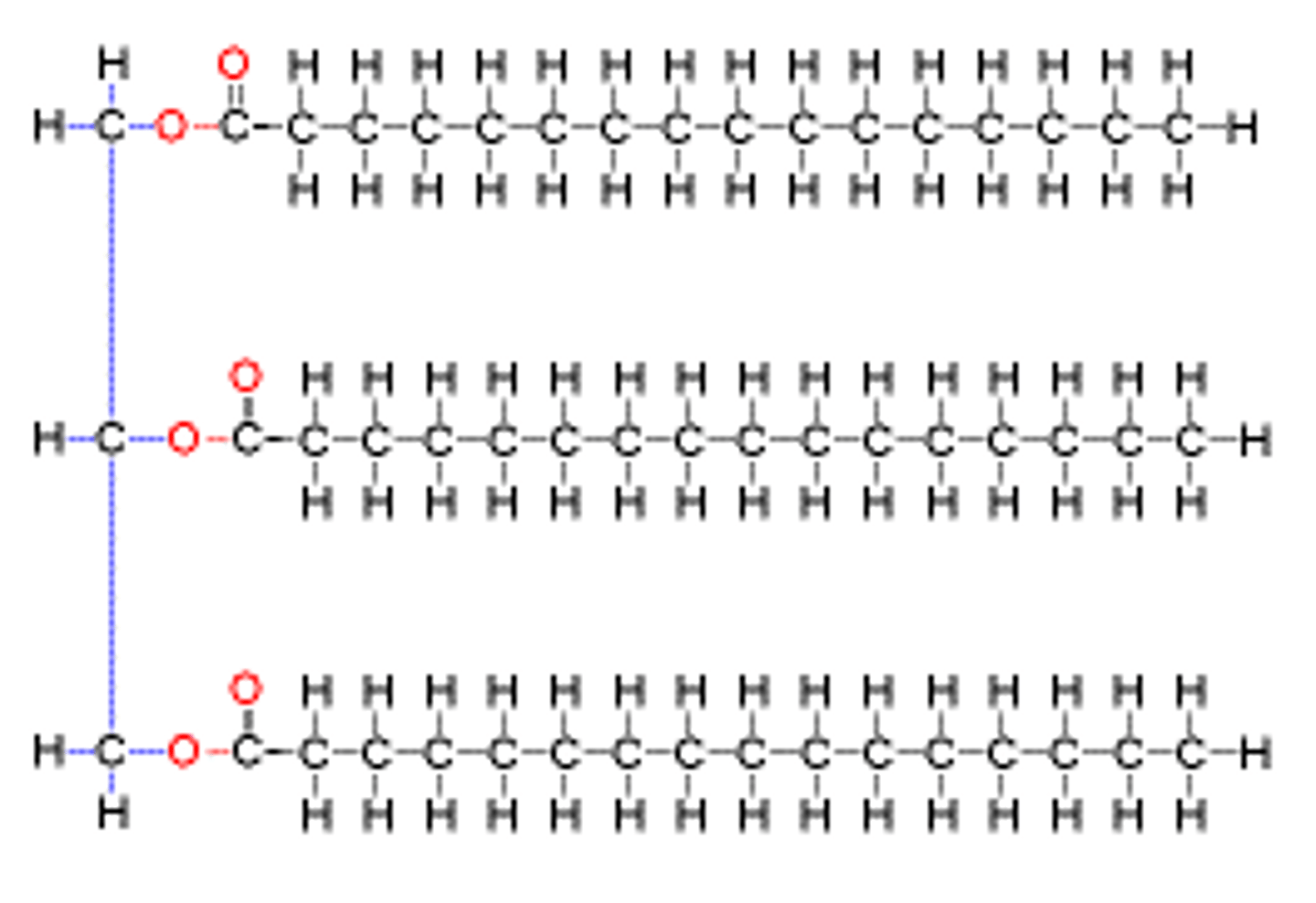
Triglycerides
consist of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids
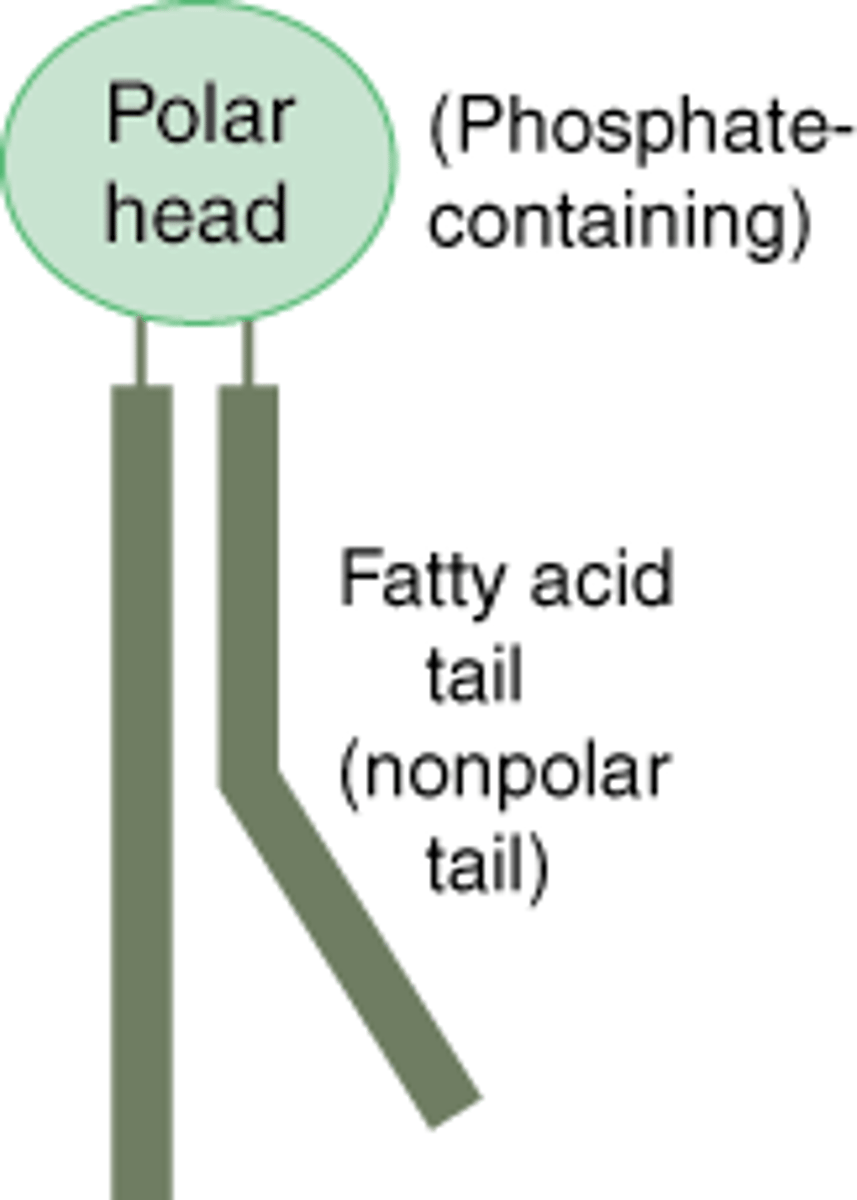
Phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
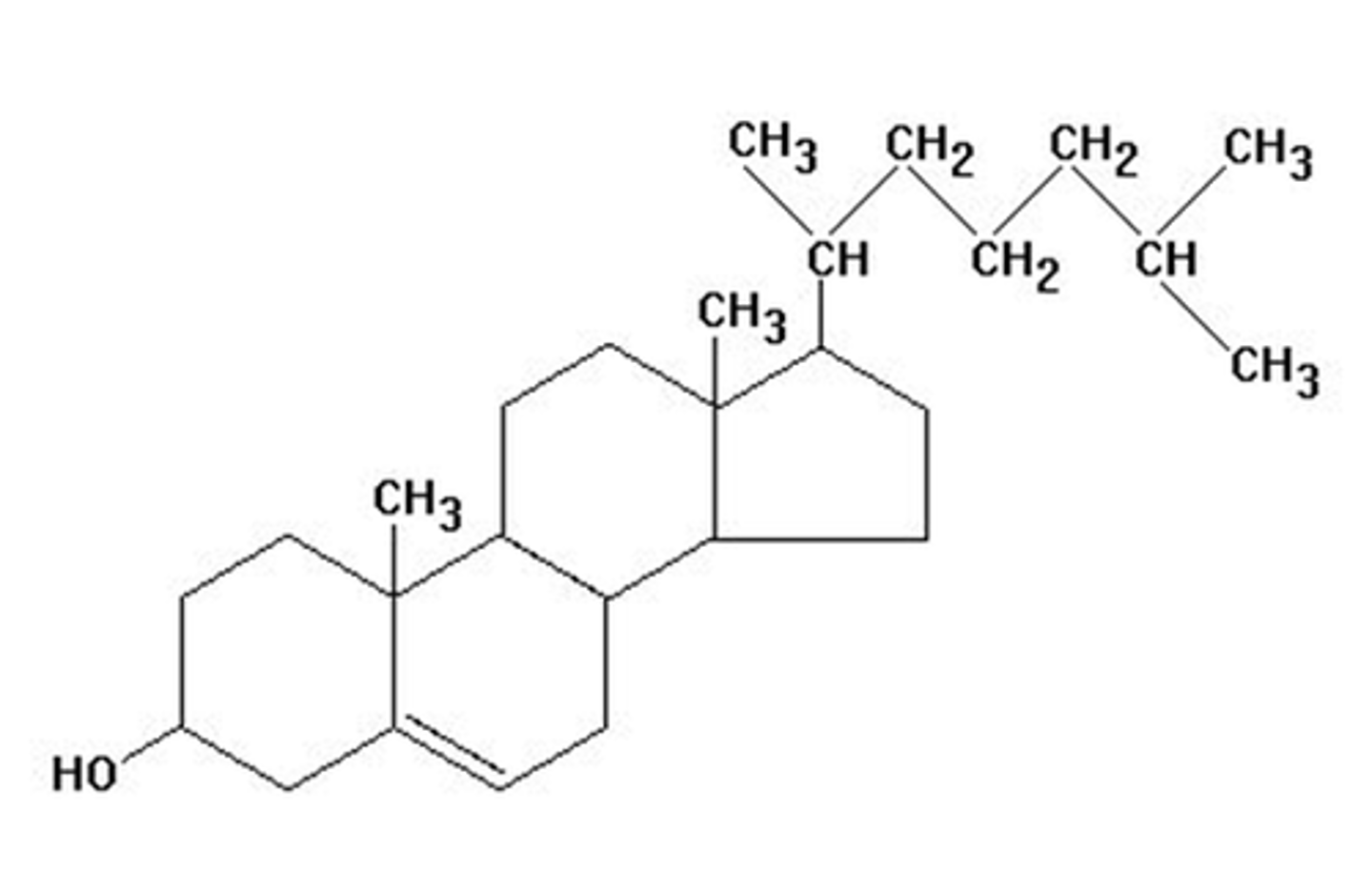
Steroid
a lipid consisting of a core of four hydrocarbon rings attached to another chemical group
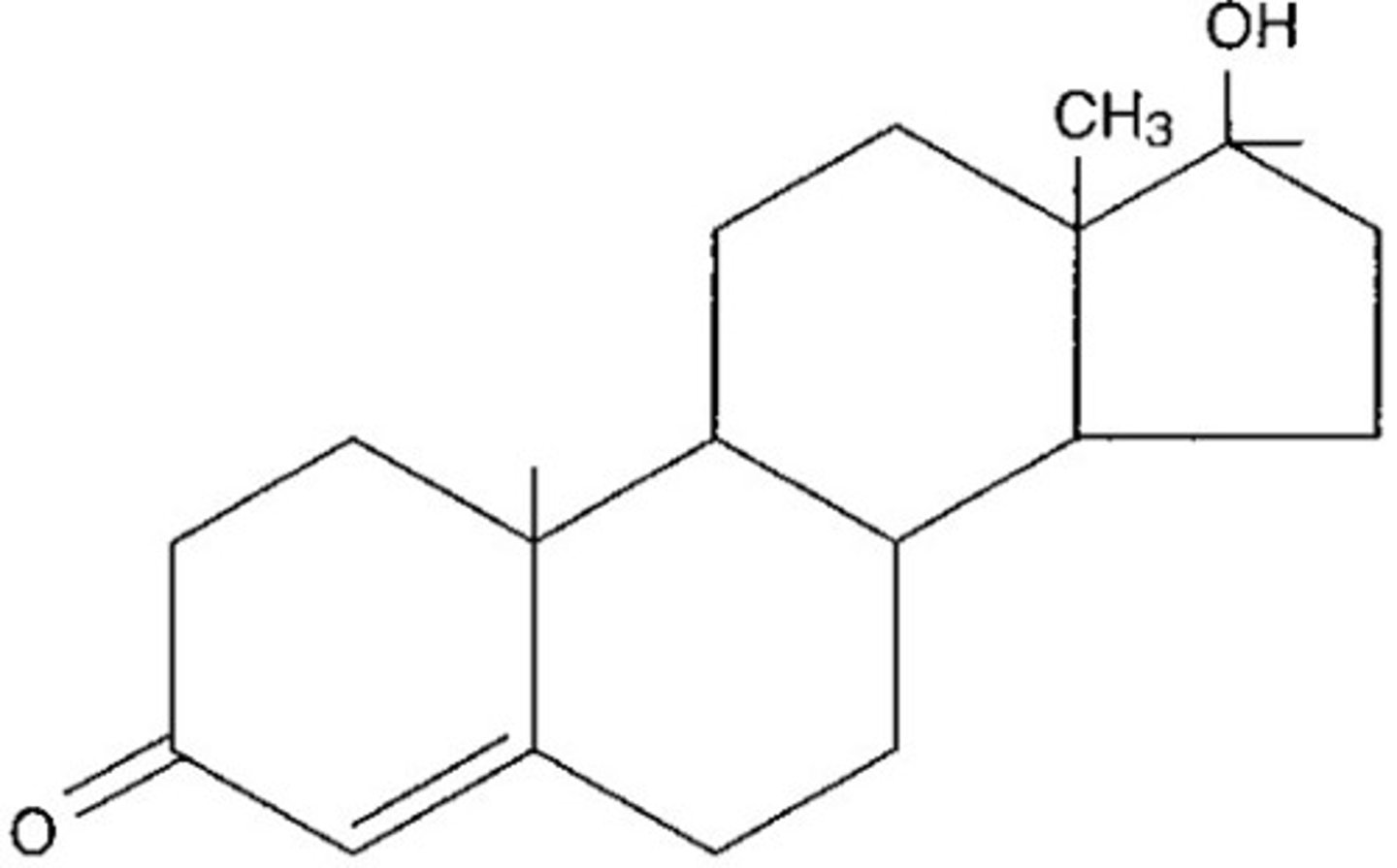
Cholesterol
most common steroid in the body
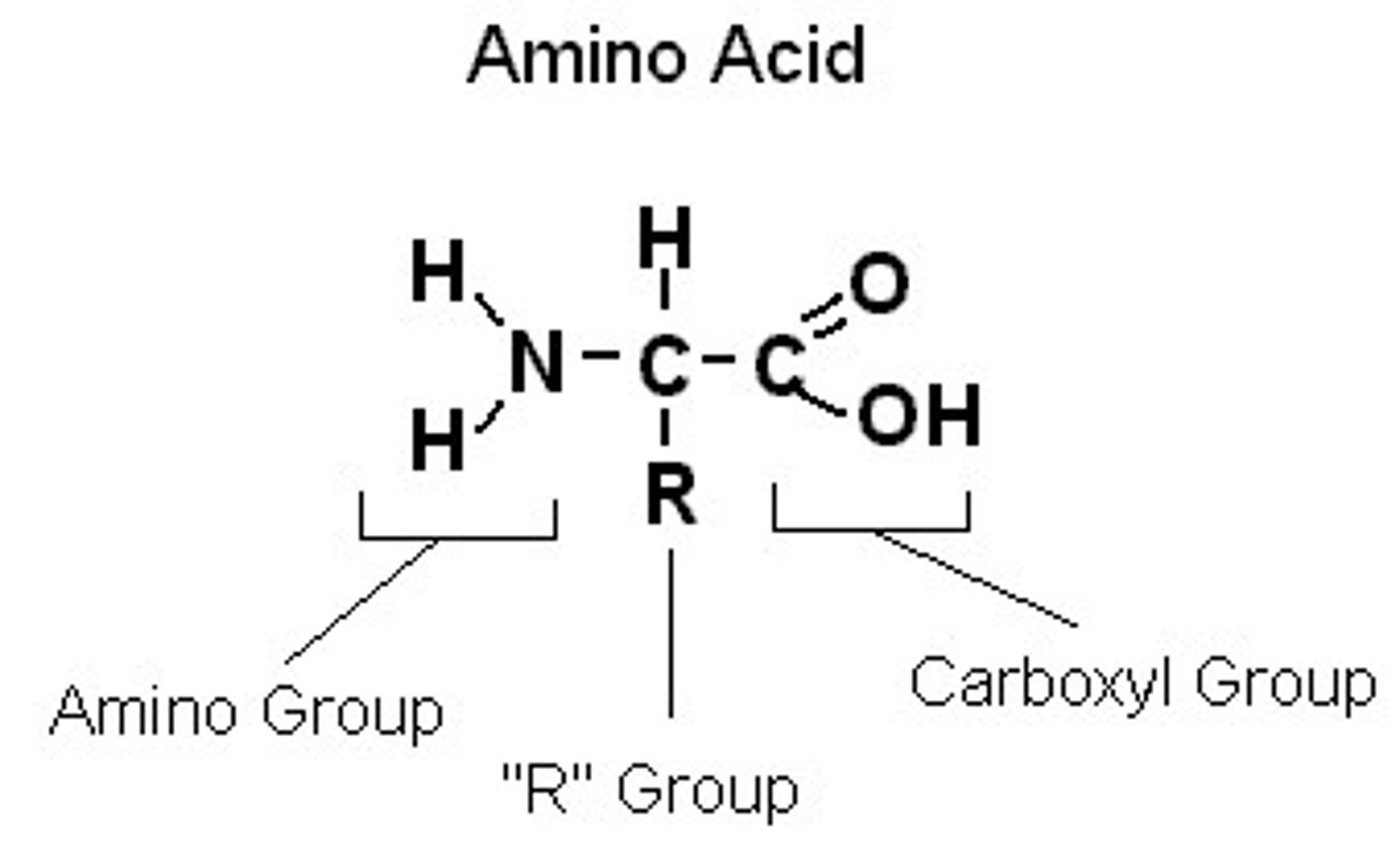
Amino Acid
protein monomer
Peptide Bond
a covalent bond between the amino acid group of one amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of a second amino acid
Denaturation
the destruction of the 3D structure of a protein and the subsequent loss of its function
Enzyme Substrate
the reactant that an enzyme acts on
Enzyme Active Site
site of the enzyme surface where substrate molecules binds
Enzyme Product
thing that is made after catalyzed reaction is complete
ATP
main energy currency of human cells
Nucleic Acids
DNA, RNA
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
the fluid portion of the cytoplasm that makes up about half of the cell's total volume. It is a watery gel with many proteins, different forms of RNA, and dissolved solutes
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
fluid located in the space between cells
Cytosol
filled with ICF, the site of many critical cellular processes such as protein synthesis, also where glycolytic catabolism, or glycolysis, take place
Plasma Membrane
outside border of the cell, phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid Bilayer
semipermeable, hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails in the middle; 98% of the molecules are lipids, 75% of the lipids are phospholipids, 20% of the lipids are cholesterol, 5% of the lipids are glycolipids
Fluid-Mosaic Model
defines the plasma membrane as a structure with multiple parts whose arrangement is dynamic, meaning that it changes from moment to moment
Integral Proteins/Transmembrane
typically span the entire width of the membrane; when they do reach both sides of the membrane
Peripheral Proteins
found on only one side of the membrane
Function of Membrane Proteins
carry out many of the membrane's functions and give different cell types some of their unique properties
Glycoprotein
consist of carbohydrate chains (polysaccharides) covalently attached to either membrane lipids or proteins, found on the outside of the plasma membrane and function in cell recognition
Selectively Permeable
has "gates" that allow some things through but not others
Active Transport
against a gradient that requires energy expenditure in the form of ATP from the cell
Passive Transport
uses a gradient that does not require energy expenditure in the form of ATP from the cell; filtration, simple diffusion, osmosis
Simple Diffusion
solutes move through a membrane or fluid from high to low solute concentration without any aid
Osmosis
a type of passive transport in which solvent, usually water moves through a selectively permeable membrane from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
Hypertonic Solution
cell loses water, more solute particles