Fluid Balance 216A
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
0.5-1ml/kg/h
how much urine per hour
220lbs
if the patient weighs 100 kg how many pounds does the patient weigh
body fluid
60% is h2o
where is water in the body?
ICF (40%) in cells, intracellular fluid
ECF (plasma 20%):
interstitial 16% plasma 4%
travelling cells, in circulation (stay there = edema)
continuous movement of water
need good lymph circulation
5L blood
plasma 3L only part of volume
hypotension
low blood volume
CNS injury
disability to regulate vitals
fluid regulation
homeostasis
baroreceptors
senses BP in hypothalamus -in glomerulus of kidney, knows to keep water or not and doesn’t fx w/out inflammation
-triggers vasomotor center in medulla
vasomotor center in medulla
baroreceptors trigger this (low perfusion activates SNS which releases norepinephrine)
norepinephrine
triggers vasoconstriction -this is released from the adrenal glands -in response to low BP to help raise it
-also lungs dilate
kidneys
these detect the drop in perfusion pressure and they release renin
renin
converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
angiotensin I
converted to angiotensin II by ACE in the lungs
angiotensin II
causes vasoconstriction which raises bp and stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
aldosterone
tells kidneys to reabsorb sodium and water and excrete potassium which raises blood volume and pressure
hypothalamus
detects low bp and signals posterior pituitary to release ADH
ADH
causes water reabsorption and less urine output = increasing blood volume and BP
I&O
intake should be greater than or equal to output
oliguria
<o.2ml/kg/h -low output of urine
creatinine clearance
check kidney function by checking this bloodwork
electrolytes to fx
sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride
patients that experience fluid balance issues or losses
GI patients, and any crucial organ dysfunction
osmolality
dependent on number of dissolved solutes in a fluid
-like sodium, glucose, urea
measured osmolality
275-295 mOsm/kgH20
changes in osmolality
can cause water to move to different compartments via osmosis
-cells, interstitial fluids, plasma
dehydration
increases osmolality
-high electrolytes compared to water
overhydration
decreases osmolality
-low electrolytes compared to water
can lead to cell swelling (edema)
occurs when replacing water but not electrolytes
IV fluid admin
aims to maintain homeostasis and correct fluid imbalance
osmosis
mov’t of H2O from low solute to high solute (dilutes)
-how IV fluid works
-the correct iv fluid will achieve the desired shift
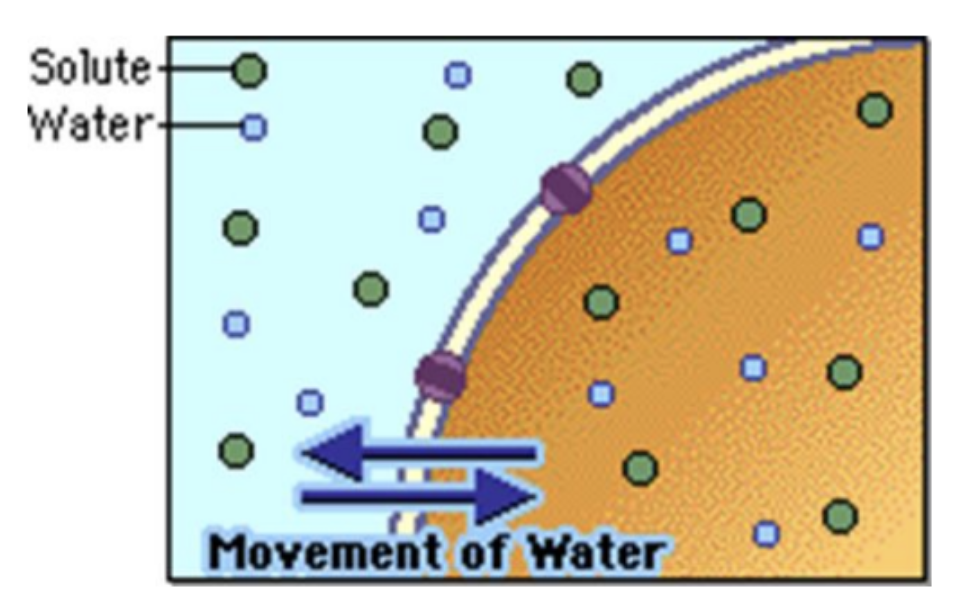
tonicity
clinical application of osmolality
-a relative (to blood) measurement of IV fluid’s osmolality
-relates osmolality of the fluid to that of plasma
all iv fluids
are dispensed according to their ‘tonicity’
dictates movement of fluid
tonicity dictates fluid movement btw compartments
sodium and dextrose
iv fluids tonicity’s main solutes
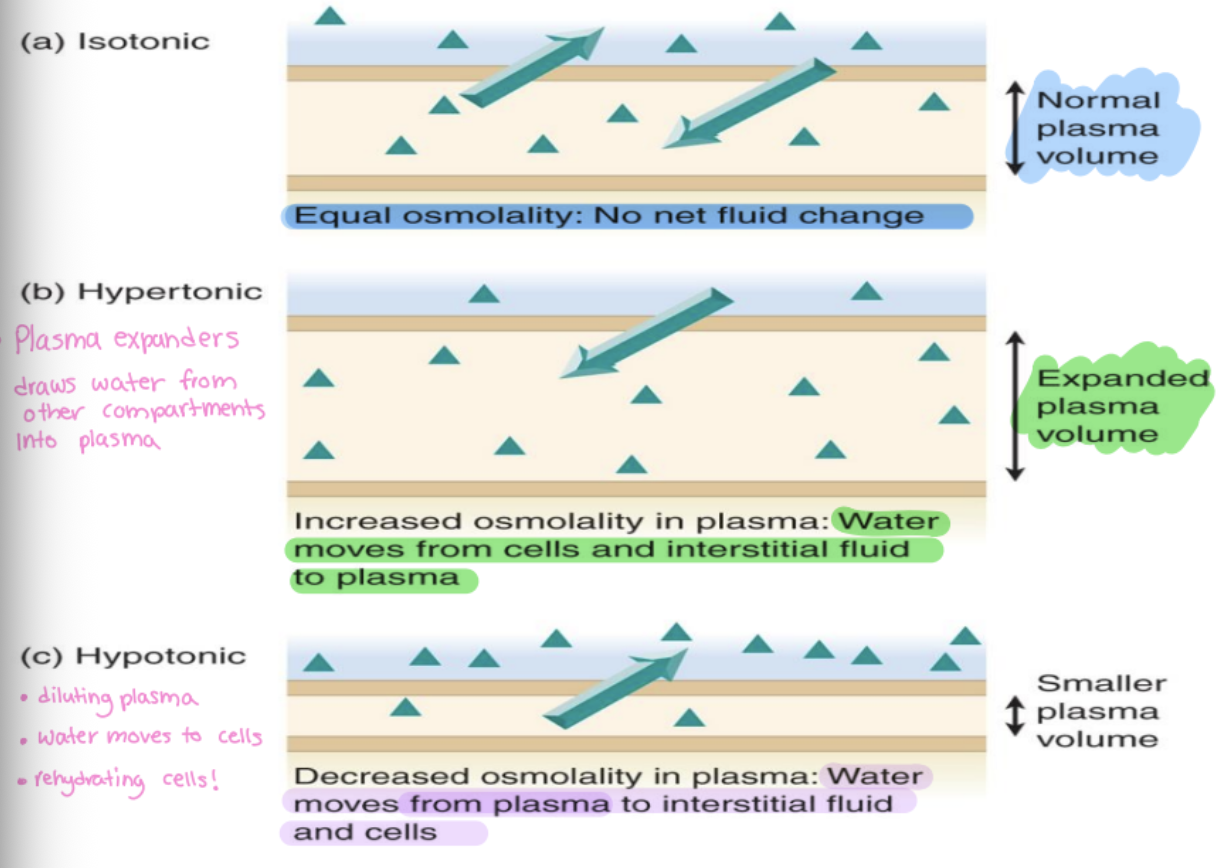
isotonic fluid
same as plasma (same osmolality)
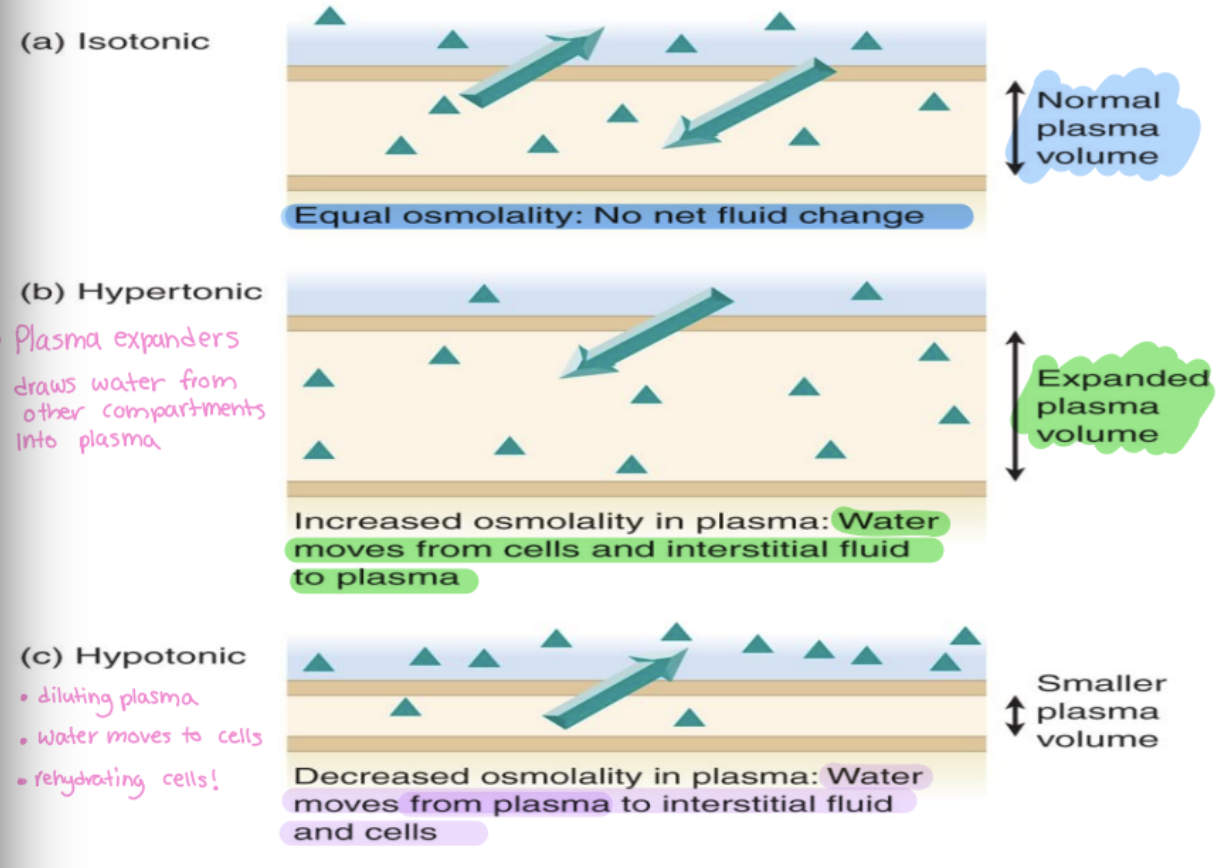
hypertonic fluid
higher than plasma
-plasma expanders, draws water from other compartments into plasma
-increased osmolality in plasma
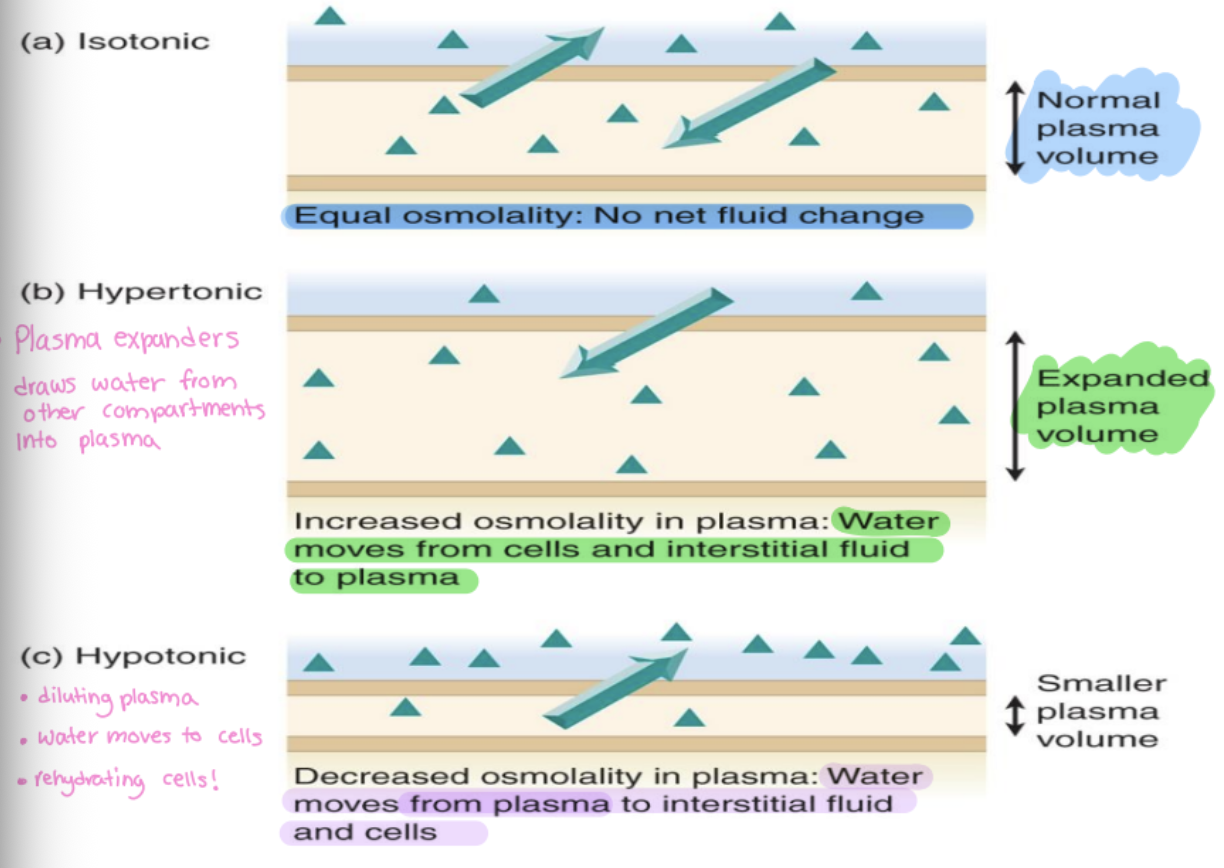
hypotonic fluid
lower than plasma
-diluting plasma, water moves to cells and interstitial fluid
-rehydrating cells
-smaller plasma volume
iv fluid categories
colloids and crystalloids
colloids
-protein based iv fluid
-stay in circulation (can’t cross membranes)
-aka plasma expanders: bring water to plasma
tx of hypovolemic shock
-colloids
-contra. in most other cases (not first line)
due to no pass via capillaries and high renal workload (need high kidney fx and high strain)
-plasbumin, alburex
iv fluid colloids
plasbumin and alburex
crystalloids
most common iv fluids
-H2O + electrolytes + other solutes (ex. glucose)
-easily move btw ECF & ICF
-tonicity directs fluid movement
isotonic in the ‘bag’
although it is this in the bag, it will be hypertonic in the body due to protein content
-water moves towards, protein can’t move -eg Albumin 5%
hypertonic in bag
if dextrose is the solute making it ‘this’ in the bag, once in the body dextrose is quickly utilized = the remainder fluid will become more isotonic or even hypotonic
-D5 ½ NS (mildy hypertonic in bag d/t dextrose)
fluid maintenance
meeting body requirements
-oral intake (eating/feeding tube); IV infusion; SC infusion
-or intake may not work for GI due to SNS stimulation, can be switched to IV
fluid resuscitation
replacing deficits
-PO if minor; IV if concerning
-goal: adequate perfusion → rescue intravascular volume
fluid restriction
restricted fluid intake
NPO
nothing by mouth, all fluids given IV
skin is big hint
organ not vital to life, lack perfusion when SNS stimulated
adult fluid calculation
35ml/kg/day of water
-electrolytes (potassium, sodium, chloride)
dextrose adult fluid calc
50-100 g/day of glucose to limit ‘starvation’ ketosis
-need minimum
if NPO adult
> 3 days, consider IV fluid content and additional nutrition
paediatric fluid calc
4/2/1 rule
-4ml/kg/hr for 1st 10kg of body weight
-2ml/kg/hr for 2nd 10kg of body weight
-1ml/kg/hr for the remaining kgs
common isotonic crystalloids
-normal saline 0.9%
-lactated ringer’s (LR or RL)
-plasma-lyte A
-D5W (5g of dextrose in water)
plasma lyte a
has components turn into bicarb
-alkylizes
-normal blood ph = 7.35-7.45, need to consider, shouldn’t use when in homeostasis
common isotonic colloids
-isotonic in bag, hypertonic in body
-5% albumin
-dextran 40
-hydroxyethyl starch 6% (higher in hypertonic) (tetrastarch, heptastarch - rescue not first choice)
NS 0.9% contents
154 mEq Na
154 mEq Cl
NS tonicity
isotonic
-#1 resuscitation fluid
adults ns
500 ml bolus, reassess, keep adding and reassess
paediatrics ns
15ml/kg, reassess, switch to D5 ½ NS (77mEq)
ns s/e
if prolonged use (>2days)
-hypokalemia (no potassium)
-no dextrose
LR contents
per L:
-Na 130 mEq
-Potassium 4 mEq
-Calcium 2.7 mEq
-Chloride 109 mEq
-Lactate 28mEq (alkyline, not an issue for acidosis patients)
LR
isotonic tonicity
-side effects: hyperkalemia, no dextrose -pediatric contraindication: high electrolytes
common hypertonic fluids
-fluid out of cells, tonicity high plasma
-high glucose &/or high sodium
-D5NS (may be isotonic in body bc demand is high)
-D5LR
-D10W (dextrose 10% in water)
-D5 0.45%NS (D5 ½ NaCl; D5.45 NS) (hypertonic in bag = becomes isotonic quickly)
-3% NaCl
-25% Albumin (colloid)
3% NaCl
high sodium, give small dose and reassess
-tx for head injury to lower ICP (cerebral edema) (shrink cells - water into plasma)
-hypertonic fluid
-crystalloid
25% albumin
colloid
-5% = isotonic
-tx: resuscitation fluid option, watch fluid shift
-common hypertonic fluid
D5.45 NS content per L
50g dextrose
77 mEq Na
77 mEq Cl
D5.45 ns
hypertonic (mildly)
1st choice paediatric maintenance fluid (+consider adding KCl); during interventions; if dextrose req’d
-s/e hyponatremia (low Na in blood)
25% Albumin contents
per L:
250g albumin
130-160 mEq Na
25% albumin
hypertonic tonicity
colloid
biologic - from donors (heat treated to eliminate pathogens)
-plasma volume expander extreme!
3.5 times it volume of additional fluid into circulation in minutes (infuzed volume, 100 ml → acts like 350ml)
common hypotonic fluids
fluid into cells, low nacl or low dextrose
-0.45% ns (1/2 ns)
-3.3% dextrose 0.3% sodium (2/3 1/3) short term not maintenance
-D5 0.2% NS (good dextrose, less na)
hypotonic application
dehydrated patient with high serum solute “hypernatremic dehydration'‘ → water loss > solute loss, high na in blood
-h20 shifting into ECF (circulation) need fluid back into cells
-administer hypotonic fluids to shift some fluid back into cells
GI bleed upper
PUD, esophageal varices (barrets esophagus), esophagitis
lower gi bleed
tumors, inflammatory bowel disease
gi bleed need to stop
stop taking
NSAIDs
drugs which decrease clotting (antiplatelets, anticoagulants, thrombolytics)
tx for gi bleed
iv fluids resuscitation &/or maintenance
-blood products (electrolytes, RBC (CBC))
-abx if caused by pathogen
adjunct: PPIs (symptom relief)
assess for gi bleed
VS (map), peripheral pulses, dx to tx cause, endoscopt or colonoscopy, bw, pathogen specific
blood results
rbc count (need to replenish?)
differential
c-reactive protein (chrons, after tx, level drops, general inflammation marker)
pathogen specific PRN (c diff, h. pylori)
maturation of rbcs
erythropoietin produced in kidney, triggered by low O2 to speed maturation
erythropoietin
stimulates red bone marrow to enhanced erythropoiesis increases rbc count
isotonic iv fluids and hemorrhaging
complication if administering only isotonic IV fluids to a hemorrhaging patient is possible diluting of clotting factors leading to worsened bleeding. -replacing fluid and not electrolytes
PRBCs
packed red blood cells, improve o2 carrying capacity
whole blood
need to find blood type, o neg universal
platelets
not in prbc but in whole blood
FFP
fresh frozen plasma
-proteins, clotting factors, immunoglobulins
-when considering clotting and proteins
cryoprecipitate
cryo - for serious hemmorhage
-portion of plasma made from FFP
-fibrinogen (F8+10 in clotting), clotting factors
electrolytes
positively or negatively charged inorganic molecules
-essential for cellular fx, nerve conduction, water balance
hyponatremia
<135mEq/L
-common cause: loss of Na via GI, diaphoresis, diuretic drugs
-tx: D5NS
hypernatermia
>145mEq/L
-common cause: renal disease, high Na intake
-tx: restrict salt intake, diuretic meds to remove Na, if IV fluid → low in Na
hypokalemia
<3.5 mEq/L
-common cause: loss of K via GI, potassium wasting diuretic drugs
-tx: KCL (IV or PO)
hyperkalemia
>5 mEq/L
-common cause: potassium sparing diuretics, renal disease
-tx: Kayexalate (PO, NG) binds K for excretion