Brainstem, Cranial Nerves, and Autonomic Nervous System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Cranial Nerves
Nerves that emerge directly from the brain, primarily responsible for sensory and motor functions of the head and neck.
Brainstem
The part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord and controls vital functions.
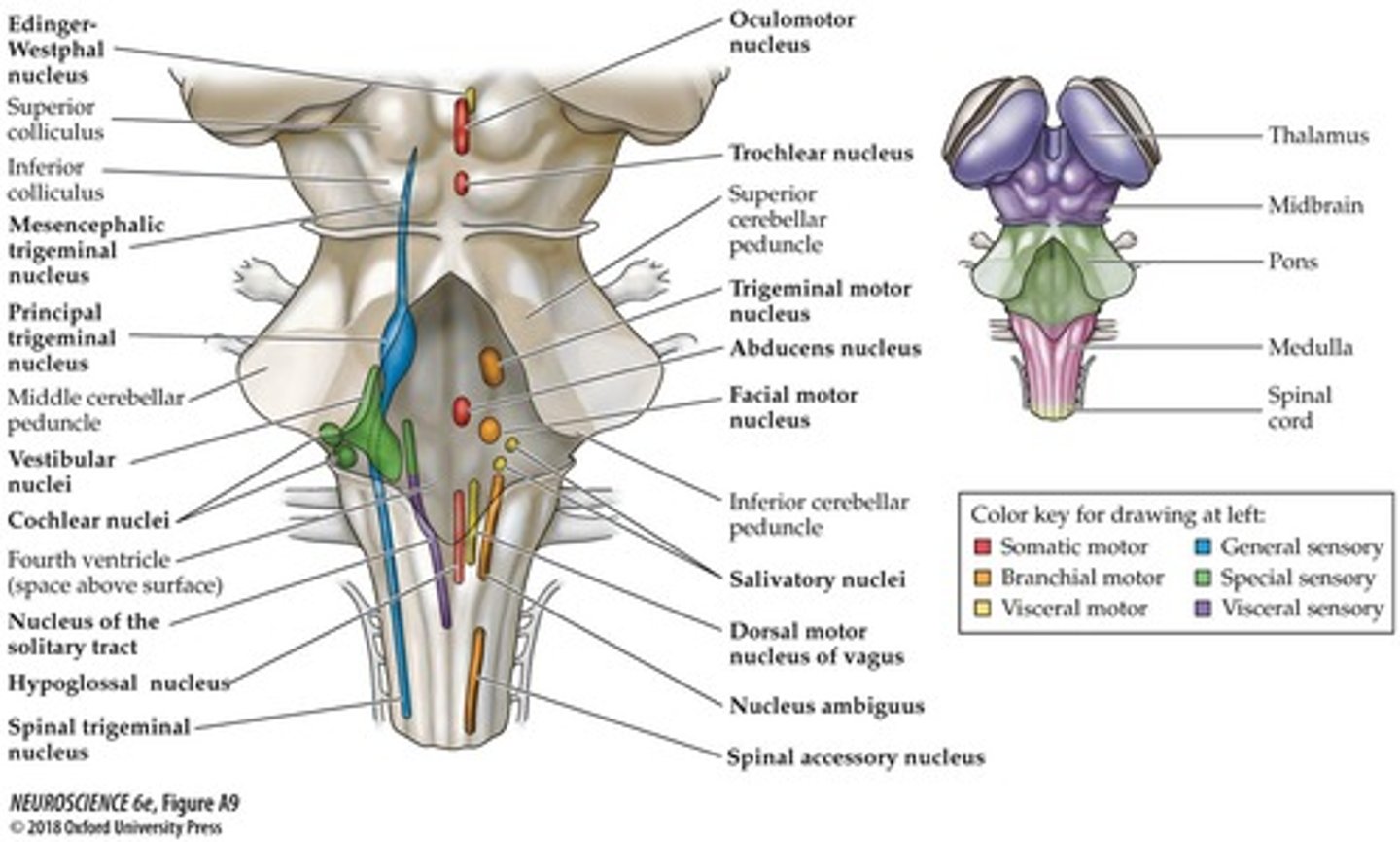
Rule 1
There are 2 cranial nerves in the midbrain, 4 in the pons, and 4 in the medulla.
Rule 3
The 4 motor medially located nuclei in the brainstem are numbers that divide by 12.
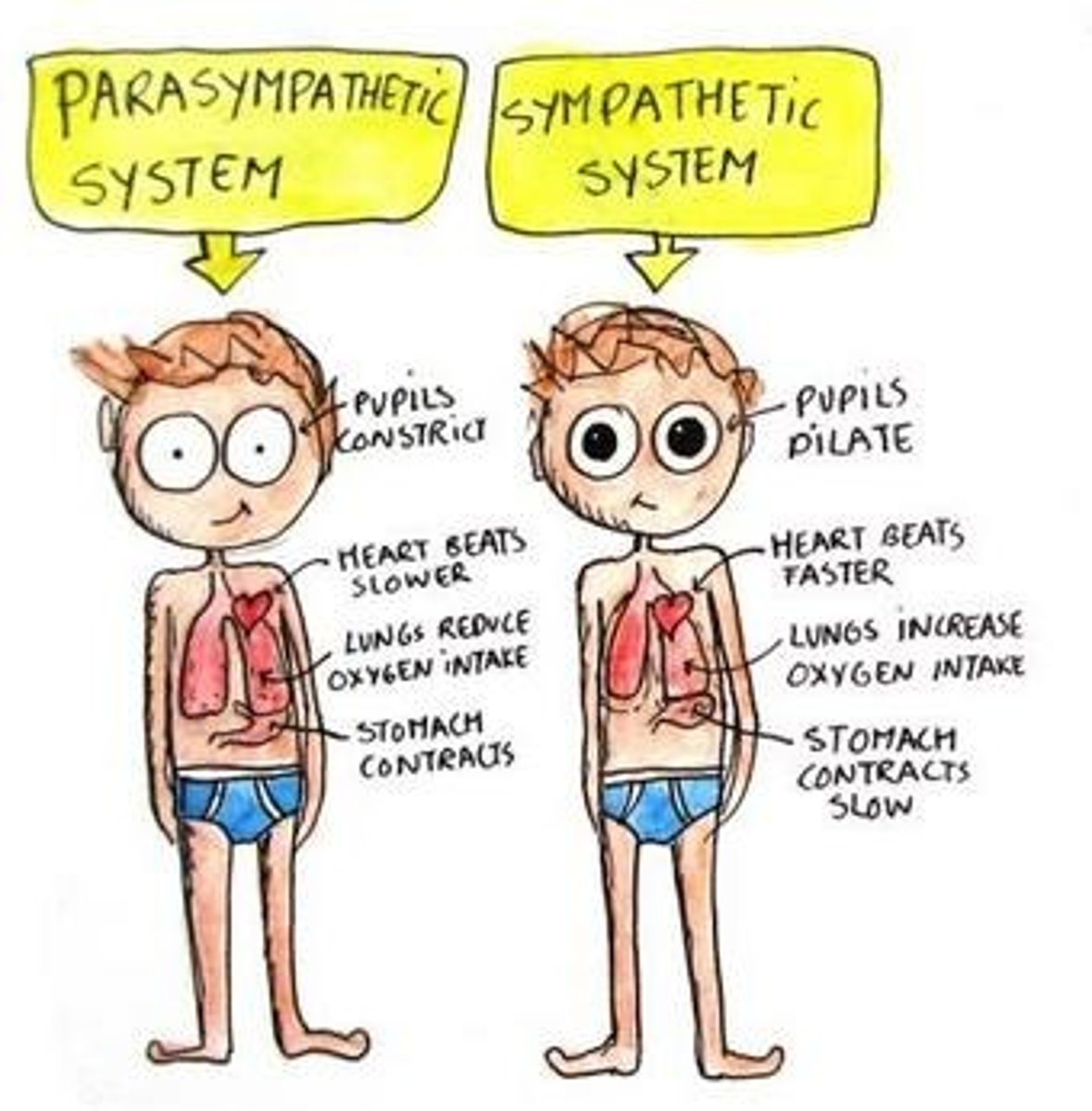
Autonomic Nervous System
A part of the nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate and digestion.
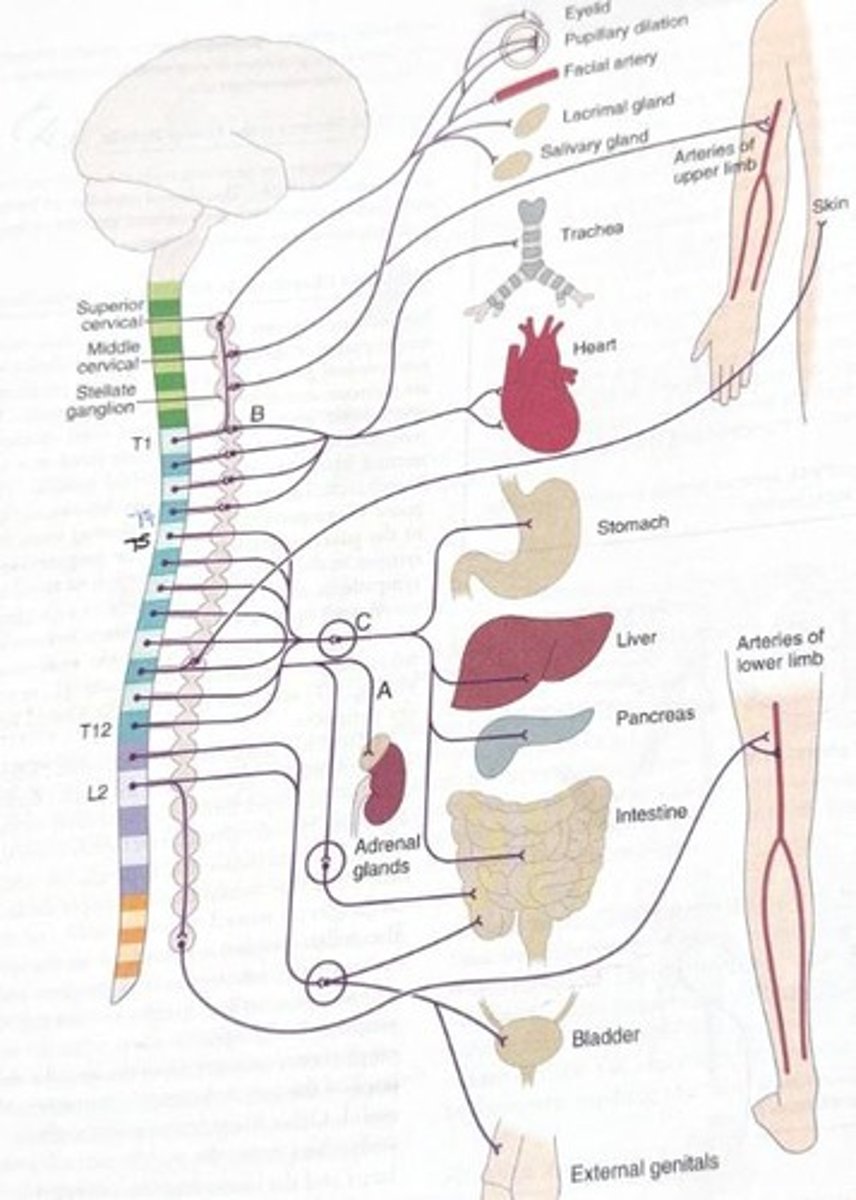
Sympathetic tract
Not modified.
Spinothalamic
Does not cross in the BS.
DCML
Decussates in medulla.
Spinocerebellar
Axons leave BS and enter Cerebellum via cerebellar peduncles.
Spinoreticular
Ends in the reticular formation.
Corticospinal
Lateral decussates in medulla.
Corticobulbar
Axons synapse with cranial nerves.
Reticulospinal
Originates in reticular formation.
Vestibulospinal
Originates in reticular formation.
Superior Cerebral Peduncles
Connect midbrain to cerebellum, efferent.
Substantia Nigra & PPN neurons
Basal ganglia circuit.
Red Nucleus
Part of cognitive motor circuit.
Periaqueductal gray
Coordinates somatic and autonomic reactions to nociceptive input, threats and emotions.
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor
Motor: eye up, down, medially, raises eyelid; Parasympathetic: constricts pupil, adjusts shape of lens.
Cranial Nerve IV: Trochlear
Motor: moves eye medially and down.
Middle Cerebral Peduncle
Connects pons to cerebellum, afferent.
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
Motor: chewing; Sensory: somatosensation from face, eyeball, temporomandibular joint.
Cranial Nerve VI: Abducens
Motor: abducts eye.
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial
Motor: facial expression, closes eye, protects hearing; Sensory: taste; Parasympathetic: tears, salivation.
Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear
Sensory: sensation of head position relative to gravity and head movements; hearing.
Pyramids
Pyramidal motor pathway.
Olives
Inferior olivary nucleus.
Inferior Cerebral Peduncle
Connects medulla to cerebellum, afferent & efferent.
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
Motor: constricts pharynx; Sensory: sensation from pharynx, posterior tongue, middle ear, taste, afferent for gag & swallowing reflex; Parasympathetic: salivation; Autonomic: blood pressure and chemistry from carotid.
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Motor: regulates swallowing and speech, efferent for gag and swallowing reflex; Sensory: sensation from pharynx, larynx, skin in external ear canal; Parasympathetic: regulates viscera; Autonomic: regulates viscera.
Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory
Motor: elevates shoulders, turns head.
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal
Motor: moves tongue.
Reticular Formation
Integrates sensory and cortical info, regulates somatic motor activity, autonomic function and consciousness, modulates nociceptive info.
Neurotransmitters
Dopamine, GABA, Serotonin, Glutamate, Acetylcholine, Norepinephrine.
Vertebral Arteries
Supplies blood to the brain.
Basilar Artery
Supplies blood to the brain.
Brainstem Lesions
Affect vital functions.
4 Ds
Dysphagia, Dysarthria, Diplopia, Dysmetria.
Cranial Nerve Disorders
Include Bell's Palsy and Facial Synkinesis.
Case Study
52 yr old, referred to therapy due to Bell's Palsy, 5 months onset of symptoms. Left facial paralysis, pain on left side of face and increased loudness of sound in left ear.
Left facial paralysis
Loss of muscle function on the left side of the face.
Pain on left side of face
Discomfort or pain experienced on the left side of the facial region.
Increased loudness of sound in left ear
Heightened perception of sound intensity in the left ear.
Gradual onset of paralysis
Progressive development of muscle weakness over a period of time.
Lack of nociceptive and temperature info from right side of body
Absence of pain and temperature sensation on the right side of the body.
Lack of somatosensation of left side of face
Inability to perceive sensory stimuli on the left side of the facial region.
Ataxia on the left side of body
Lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements on the left side.
Paralysis of muscles of facial expressions on the left side
Loss of movement in muscles responsible for facial expressions on the left side.
Loss of corneal reflex on the left side
Inability to blink in response to stimulation of the cornea on the left side.
Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement that can affect balance and coordination.
Vertigo
A sensation of spinning or dizziness, often related to inner ear issues.
Nausea and vomiting when turning head
Feeling sick and potentially vomiting as a result of head movement.
Cranial nerves
Nerves that emerge directly from the brain and brainstem.
CN IV- midbrain
Cranial Nerve IV, also known as the Trochlear nerve, is associated with the midbrain.
Vestibulocochlear- medulla
Cranial Nerve VIII, responsible for hearing and balance, associated with the medulla.
CN V- pons
Cranial Nerve V, known as the Trigeminal nerve, associated with the pons.
CN IX- medulla
Cranial Nerve IX, known as the Glossopharyngeal nerve, associated with the medulla.
Knowledge of intended movements
Information about planned movements that reach the cerebellum.
The superior cerebellar peduncle
A structure that carries information from the cerebellum to the midbrain.
The contralateral pons
The pons on the opposite side of the body that transmits information to the cerebellum.
Climbing fibers originating in the inferior olivary nucleus
Fibers that provide input to the cerebellum from the inferior olivary nucleus.
Proprioceptors traveling in the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and cuneocerebellar tract
Sensory receptors that convey information about body position to the cerebellum.
Bell's palsy
A condition characterized by damage to the facial motor nucleus or facial nerve resulting in ipsilateral facial weakness.
Difficulty raising the eyelid
Inability to lift the eyelid, often associated with facial nerve injury.
Absence of taste to the entire tongue
Loss of taste sensation across the whole tongue due to nerve damage.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for the body's 'fight or flight' response.
Regulation of body temperature
Mechanisms that maintain the body's temperature within a normal range.
Regulation of blood flow to skeletal muscles
Control of blood distribution to muscles during physical activity.
Sympathetic control in the head
Regulation of physiological responses in the head region by the sympathetic nervous system.
Regulation of viscera
Control of internal organs' functions by the autonomic nervous system.
Metabolism
The chemical processes that occur within a living organism to maintain life.
Epinephrine increases metabolic rate
Epinephrine, a hormone, boosts the rate of metabolism in the body.
Norepinephrine stimulates precapillary sphincters
Norepinephrine causes contraction of precapillary sphincters, reducing heat loss.
Norepinephrine
Causes vasodilation of certain vessels.
Dilation of pupil
Effect of sympathetic nervous system on the eyes.
Elevating eyelid
Effect of sympathetic nervous system on the eyes.
Salivary glands
Affected by sympathetic nervous system.
Heart rate increase
Occurs due to norepinephrine, regulated by T1-T4.
Dilation of airways
: Caused by norepinephrine and epinephrine, regulated by T1-T4.
Slowing down GI
Involves contracting sphincters (L1-L2), decreasing blood flow, and decreasing peristalsis (T5-T12).
Decreasing bowel and bladder
Involves contracting internal sphincters and decreasing wall contractions (L1-L2).
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Functions to conserve energy, decrease cardiac activity, facilitate digestion, and increase secretions in lungs, eyes, mouth, and sexual organs.
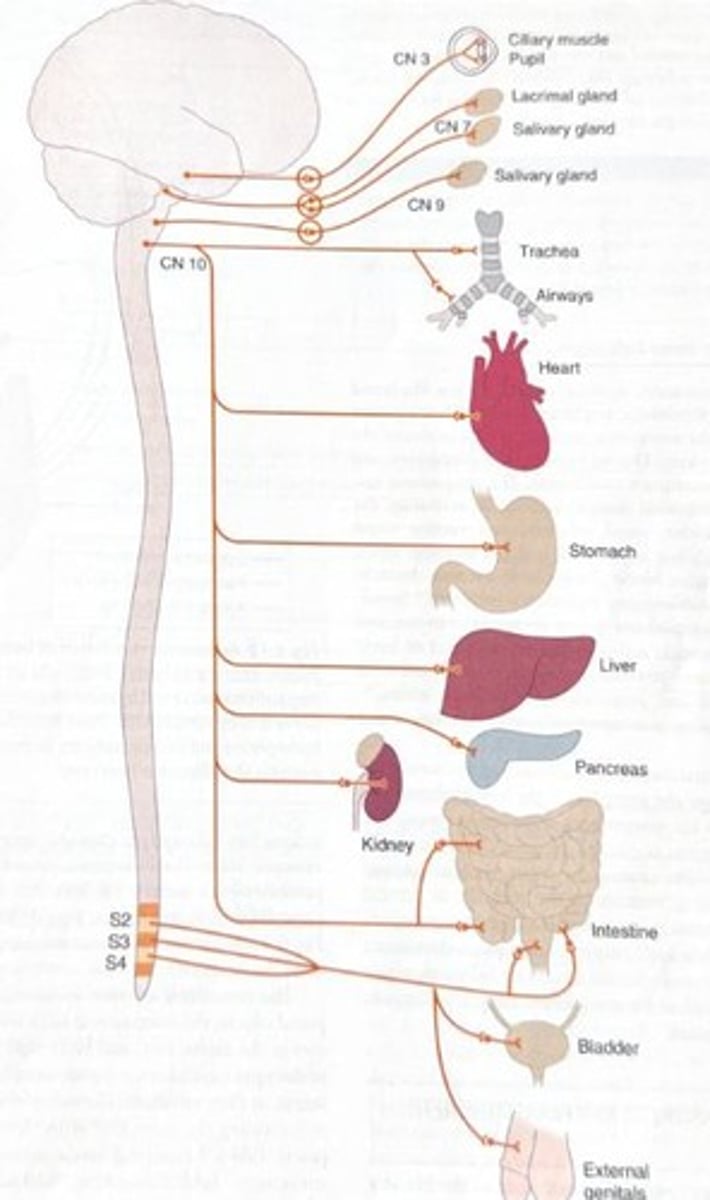
Erection of reproductive organs
A function of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Brainstem
Area of the brain involved in the parasympathetic nervous system.
CN X
Cranial nerve involved in parasympathetic functions.
CN III: Oculomotor
Cranial nerve responsible for constricting the pupil.
Bradycardia
Slowed heart rate, a function of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Increased convexity of lens
Effect of parasympathetic nervous system on airways.
Increased peristalsis
Effect of CN VII: Facial & IX: Glossopharyngeal on the stomach.
Glycogen synthesis
Function of the liver, pancreas, and kidney in the parasympathetic nervous system.
Bowel and bladder emptying
Function regulated by the sacrum (S2-S4).
Wall contractions
Involved in bowel and bladder emptying.
Relaxation of sphincter
Facilitates bowel and bladder emptying.
Erection of penis or clitoris
Function of external genitals in the parasympathetic nervous system.
Voluntary Bladder Emptying
Involves three key centers: frontal cortex, pons, and sacral spinal cord.
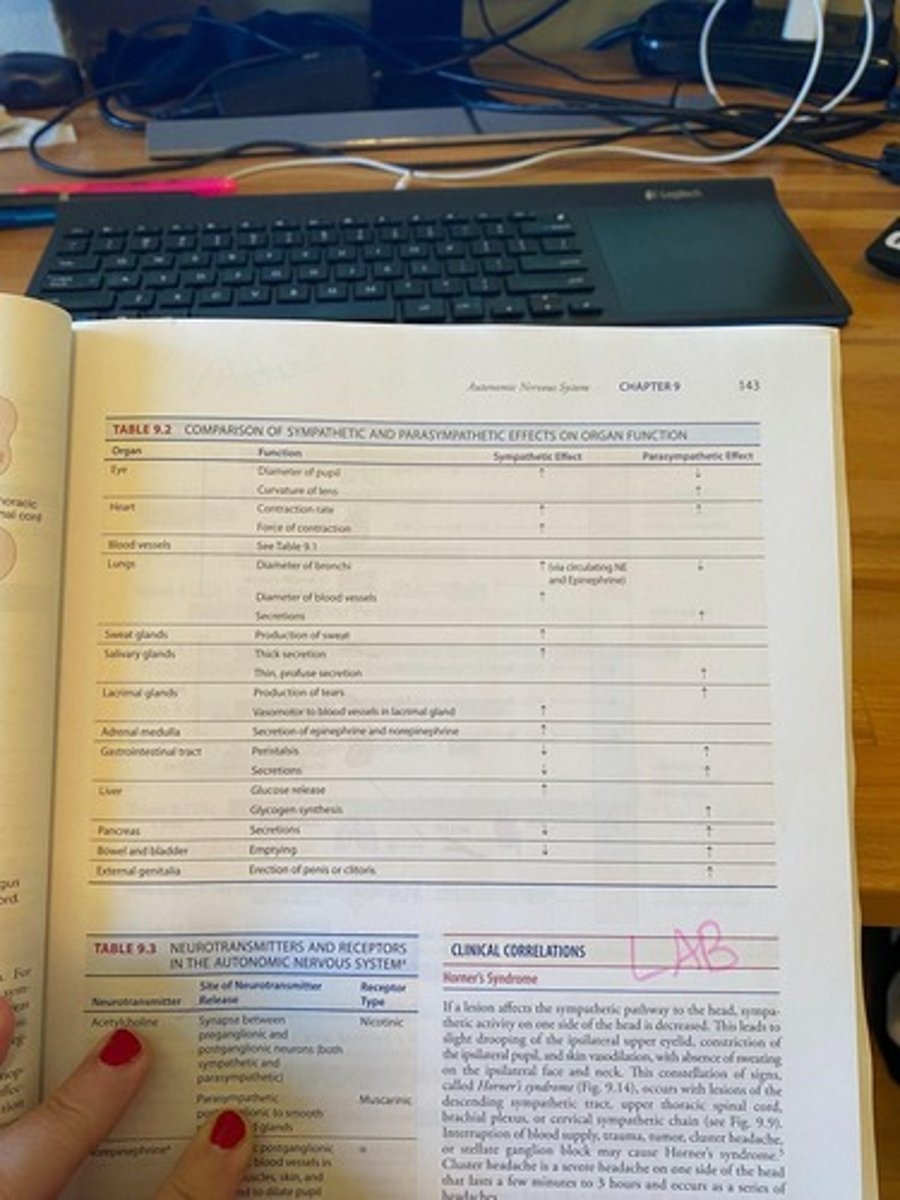
Horner's Syndrome
A clinical correlation for the autonomic nervous system.
Trophic Changes in skin
A clinical correlation for the autonomic nervous system.
Autonomic regulation of the heart
Dependent on parasympathetic fibers of the Vagus nerve and sympathetic fibers from the Thoracic level.
Normal autonomic function of the urinary bladder
Sympathetic efferents maintain relaxation of bladder and facilitate contraction of internal sphincter while parasympathetic efferents control bladder contractions and relaxation of internal sphincter.
Sympathetic control of the bladder
Comes from spinal cord levels L1-L2.