1. Heart, neck, vasculature/peripheral, vascular, lymphatic system
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Heart wall has numerous layers: pericardium
tough, fibrous, double-walled sac that surrounds and protects heart
Heart wall has numerous layers: myocardium
muscular wall of heart
Heart wall has numerous layers: endocardium
thin layer of endothelial tissue that lines inner surface of heart chambers and valves
Heart is ___ pumps separated by septum
2
Each side of the heart has an ____ and a _____
atrium and ventricle
Atrium
thin-walled reservoir for holding blood
Ventricle
thick-walled, muscular pumping chamber
Left ventricle
workload of the heart
Tricuspid valve
right AV valve
Bicuspid, or mitral valve
left AV valve
Valves thin leaflets are anchored by collagenous fibers ____ to papillary muscles embedded in ventricle floor
chordae tendineae
Pulmonic valve
SL valve in right side of heart
Aortic valve
SL valve in left side of the heart
Systole ventricle
heart depolarization
contraction
Diastole ventricle: 3 R’s
repolarize
refill with blood
rest
Diastole
ventricles relax and fill with blood; 2/3 of cardiac cycle
Prodiastolic filling
early passive phase
Presystole or atrial systole
atrial kick
Systole
heart’s contraction
blood pumped from ventricles fills pulmonary and systemic arteries; 1/3 of cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle: note that atrial systole occurs during ventricular diastole:
for a very brief moment, all four valves are closed, and ventricular walls undergo:
isometric contraction
isometric (or isovolumic) relaxation
Isometric contraction
contraction against closed system works to build high level pressure in ventricles
Isometric (or isovolumic) relaxation
all four valves closed, and ventricles relax
Aortic valve
2nd right intercostal space
Pulmonic valve
2nd left intercostal space
Nursing cardiovascular assessment: areas of auscultation
apply so-called Z pattern
aortic valve
pulmonic valve
erb’s point
tricuspid valve
mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
left lower sternal border
Mitral valve
5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
Areas of auscultation technique: S1
the so-called first heart sound
due to atroventricular (AV) valve
denotes start of systole
heard loudest at the apex of the heart
occurs simultaneously with a patients carotid artery pulse in a healthy adult
S1 stated another way..
atria relaxation
ventricle contraction
Where is the apex of the heart?
the inferior aspect or so-called bottom of the heart or base of the heart
Areas of auscultation technique: S2
the so-called second heart sound
due to semilunar (SL) valve closure
valves included
aortic valve
pulmonic valve
most audible at base of heart
What is occurring from a physiology standpoint during S2?
the ventricles are relaxing and filling with blood as the atria contract
stated another way
atria contraction
ventricle relaxation
Heart sound abnormalities: bruit
turbulent blood flow, can occur within the carotid artery
Heart sound abnormalities: murmur
so-called swooshing and blowing sound of turbulent blood flow in the heart/great vessels
Heart sound abnormalities: murmur characteristics
loudness
grading system of loudness
score grade (1-6)
timing
pitch
high, medium, low
pattern
crescendo, decrescendo
quality
location
radiation
Heart sound abnormalities: stenosis
refers to a narrowing of a blood vessel
Heart sound abnormalities: regurgitation
backflow of blood, so-called “leaky valves”
decreases cardiac output efficency
higher risk of blood clots
heart workload is increased to maintain homeostasis
Heart sound abnormalities: S3
so-called third heart sound
sound of ventricular filling
timing: early diastole
dull, soft and low-pitch sound
“distant thunder”
may be physiologic in pediatric patients/young adults
Heart sound abnormalities: S4
so-called fourth heart sound
vibrations that occur when blood pushed from atria into a ventricle that resists filling with blood
timing: so-called presystole, i.e. end of diastole
may be physiologic or pathologic
so-called atrial gallop, S4 gallop
Heart sound abnormalities: pericardial friction rub
may occur as result of pericardial inflammation
high pitched, scratchy, compared to sandpaper friction
Neck vessels palpation and auscultation: palpate carotid artery
palpate only ONE artery at a time
to avoid compromising arterial blood to brain
note contour and amplitude of pulse, normal strength 2+
normal finding is the same bilaterally
assess for bruit
Precordium abnormalities: thrill
abnormal pulsation palpated along the bilateral 2nd and 3rd intercostal spaces
note anatomical location
Precordium abnormalities: right-sided thrill
associated with systemic hypertension and severe aortic stenosis
Precordium abnormalities: left-sided thrill
associated with pulmonic hypertension and stenosis
Precordium abnormalities: heave (lift)
abnormal left lower sternal border pulsation
may occur which chronic lung disease, pulmonic hypertension, and valve disease
Pulse
a so-called pressure wave that occurs as the heart beats
What does generating a pulse accomplish for the human body?
maintenance of cardiac output
oxygen delivery
tissue perfusion
carbon dioxide venous return to the lungs
oxygen - carbon dioxide gas exhange
Ischemia
insufficient amount of oxygenated blood in a tissue
What is the cause of ischemia?
blood vessel obstruction, commonly associated with atherosclerosis
Artery
carry oxygenated blood away from heart to distal tissues
high pressure
Vein
return carbon dioxide-rich (deoxygenated) and waste product blood back → heart and lungs
low pressure
Lymphatic system: hydrostatic pressure
vessel system managing fluid excess and plasma using a pressure gradient
Lymphatic system: lymph nodes
tissue-dense areas found which filter fluid and pathogens
superficial and may be inspected and palpated
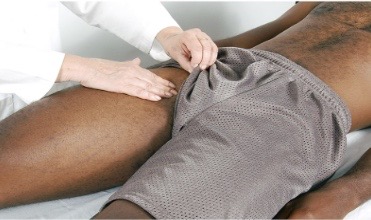
Palpation of lower leg: femoral artery
palpate below inguinal ligament halfway between pubis and anterior superior iliac spines
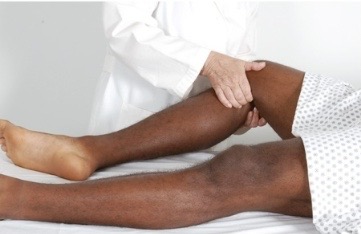
Palpation of lower leg: popliteal pulse
with leg extended but relaxed, anchor your thumbs on knee, and curl your fingers around into popliteal fossa
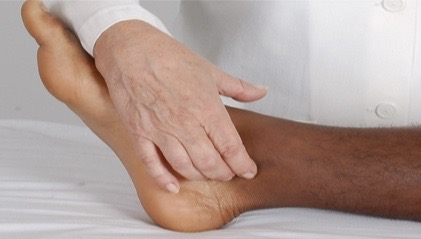
Palpation of lower leg: posterial tibial
curve your fingers around medial malleolus and palpate groove between malleolus and achilles tendon
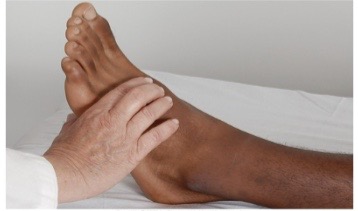
Palpation of lower leg: dorsalis pedis
typically lateral to and parallel with extensor tendon of big toe
Pretibial edema: check for this
firmly depress skin over tibia or medial malleolus for 5 seconds and release
grading of pitting edema
perform standing assessment
Pretibial edema: grading of pitting edema
1+ mild pitting, slight indentation, no perceptible swelling
2+ moderate pitting, indentation subsides rapidly
3+ deep pitting, indentation remains, leg looks swollen
4+ very deep pitting, indentation lasts long time, leg grossly swollen and distorted
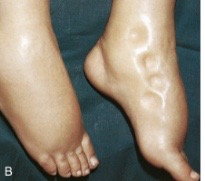
Which health conditions are commonly associated with this figure?
heart failure (HF) and peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
Nursing assessment: evaluation of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
well’s score
higher score = greater risk
score of 0 or less indicates low probability
score 1 or 2 indicates moderate probability
score 3 points or higher indicates high probability
What health conditions places a patient at risk of foot ulcers and neuropathy?
poorly controlled diabetes mellitus
maintain quality foot hygiene
assess for infection or pain of the fingers and toes
perform range of motion exercises of your extremities
periodic mobility as tolerated
use appropriately fitting shoes
Peripheral vascular disease: raynaud phenomenon
progressive pathology
finger pallor
progression to cyanosis (blue) coloration
advanced disease red (rubor) of hand heel area
Raynaud phenomenon: symptoms
pain, numbness, cold sensation