Really understandig basics of international law
1/323
Earn XP
Description and Tags
the foundation and glue in the big spiderweb of international law
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
324 Terms
How does the transparency of state practice affect the crystallization of customary international law (CIL)?
Countries with detailed records of state practice contribute significantly to the crystallization of customs by providing clear evidence of practice and opinio juris. Transparent states, like those in the West, help accelerate the formation of CIL, as their legal practices are publicly accessible and easy to monitor. This leads to a faster and clearer recognition of norms.
ILC?
International Law Commision. established bu UNGA. 44 members. term 5 years
How is members chosen for ILC
elected by GA, upon suggestion of member states. Each region has a certain number of members.
6th committee of general assembly
legal committee of UN
When: Russian war on agression
24 February 2022
Role of ILC in the Vienna Convention
ILC drafted the law on treaties. The ILC developed the core principles found in the VCLT, such as treaty formation, validity, interpretation, suspension, and termination.
Draft articles by ICL
Safest way to identify customary rules
Read case law by international courts and tribunal, the judge know the law. (If fx ICJ rule based on asuch a custom it is safe to presume that such a custom exist)
What is a 'treaty' in international law?
A treaty is a formal agreement between two or more states, or between a state and an international organization
What is the positivist approach to international law?
Positivism emphasizes that international law is derived from the consent of states, through treaties and custom
Pacta sunt servanda
agreements must be kept → underpins entire system of treaty law
Scott criticism of RBIO
RBIO can be used offensively to promote particular geopolitical interests, as compared to an international law-based order
what is the Lotus Principle
The so-called Lotus principle is that 'restrictions upon the independence of States cannot therefore be presumed', or, as it has been construed, 'whatever is not prohibited is permitted in international law'
What is the problem of 'fragmentation' of international law?
Due to its horizontal structure, it is possible for several legal regimes (ie foreign investment law and human rights law) to exist and develop in isolation of each other, ultimately culminating in the production of divergent rules of international law.
What is the major difference between naturalism and positivism?
On the one hand, naturalism is based on a set of rules that are of universal and objective scope and on the other hand, positivism is based on a structured and coherent legal system that is created by States in light of their interests and desires correct
What is jus cogens?
They are peremptory norms of international law, from which no derogations are allowed and which can never be altered even with the consent of the States correct
Which rule of jus cogens was the first to be accepted explicitly as such by the ICJ?
the prohibition of Genocide
Are the peremptory norms of international law the only norms that set out obligations erga omnes?
No, even though all peremptory norms set out obligations erga omnes, the latter may also spring from treaties regulating objective regimes or unilateral acts
formal sources of IL
treaties, Custom and general principle of law.
Which treaties are considered as 'source of international law' under article 38 ICJ Statute?
only the treaties that are in force and binding upon the parties to the dispute
kind of state practise required in creation of ICL
Widespread, consistent and uniform practice, consisting both of acts and omissions
Who is a 'persistent objector'?
The State which persistently and publicly objects to the formation of a rule of customary law from its outset
Where do we find the 'general principles of law recognized by civilized nations' (article 38 ICJ Statute)?
Look for established principle of law, common to all major legal system
What is the value of the Resolutions of the UN General Assembly in terms as a 'source' of international law?
GA Resolutions are considered as material source, in the sense that they may enunciate statements of customary law
How can customary law be related to treaty provisions?
Treaties may 1) codify customary law, 2) 'crystallise' customary law, 3) lead to the emergence of customary law
What is 'unilateral acts'?
They are acts creating unilateral legal obligations to the acting State
Formal sources of IL
article 38(1) ICJ: Treaties, customary general principles of law (Subsidary: Judicial rulings and Academic work)
Why is Article 38(1) ICJ statute so important?
Since there are no legislative organ, states have determined in advance on those sources from which a binding international norm may emerge
three additional sources of Law not included in art 38(1)
SC res
Unilateral declerations (act)
Jus Cogens Norm (conts.)
what does art. 38(1) tell us about the basics of IL?
IL is the result of consent between states
Is soft law a sorce of law?
No it’s a source of governance
In practice, ICJ may refer to it for ligitimization
it contributes to international legal system
Why do states use soft law?
process is simpler, faster and potentially more inclusive
Easier to reach agreement
Easier to supplement, amend or replace
States can avoid domestic treaty ratification process (public support)
More immediate evidence of international consensus.
Is soft law good or bad?
Has to be used strategically, can:
Provide good Starting point
Hold back binding agreements
Compliment/ amplify treaties
What does “interpretation” refer to in IL?
The attempt to find the menaning of a treaty provision when applied to a particular probleL
Where is treaty interpretation regulated?
VCLT 31, 32 - Reflect CIL
The ILC based Articles 31 and 32 on pre-existing state practice and legal principles, intending them to codify rather than create new law.
VCLT influences other sources than treaties
how do you do interpretation?
single combined operation of all elements
Good faith
Wording
Context
Object and purpose
What are the difficulties of treaty interpretation?
ambiguity in treaty language
Evolutionalry interpretation
Fragmentation of IL
what speaks in favor or against referring to the drafting history of a norm when interpreting it?
In favor
A way of expliciting a party's of the norms intended purpose
Make interpretation "make more sense"
Conviniently allows to defend one's own position
Against
often contradictatory and unclear
”results matter” = the treaty, not the negotations are decisive
binds also new member states who did not participate in the drafting
What is State Practice composed of? (CIL)
widespread
representetative
consistent
What is Opinio Juris?
Treaties do not have to assume a particular form or designated as such
The VCLT does not require that a treaty assume any particular form or be designated as such. What matters is whether its terms are binding upon the parties
Who has the authority to conclude a treaty on the part of States?
Treaties are concluded by the competent representatives of States. Heads of States, heads of governments, ministers of foreign affairs and heads of diplomatic missions are presumed to have such authority
When a reservation is considered as invalid under the law of treaties?
A reservation is invalid when it is incompatible with the object and purpose of the treaty (article 19 of VCLT)
What is 'material breach' of the treaty?
'Material breach' is the repudiation or a significant violation of the treaty and serves as a ground for the unilateral termination of the treaty
What does the 'fundamental change of circumstances' entail for the treaty?
A fundamental change of the circumstances which constituted an essential basis of the consent of the parties to be bound by the treaty and which was not foreseen by the parties, may be invoked as a ground for terminating or withdrawing from the treaty
why is states as the actors of IL being challenged?
Globalization
Non-state actors
IOs
Can countries rely on their domestic law as an excuse to violate their obligations under international law?
This matter is regulated by international law, not domestic law. Obligations under international law prevail over those under domestic law.
What is the meaning of international legal personality?
It means having rights and duties under international law and a capacity to enforce these by or against the relevant actor
What are the criteria for statehood under the 1933 Montevideo Convention?
It requires a permanent population, a defined territory, a government and a capacity to enter into foreign relations
which rights come with statehood? (5)
Protection through sovereignty
Exclusive access to resources within the state's territory
The ability to conclude treaties and contribute to customary international law
Membership in international organizations
Access to international courts
What constitutes a state under IL
No universal decleration. It’s the whole system not just territory
Montevideo element provide framework
additional → recognition
How Do You Become a State Under International Law?
Declaration theory -> state exist independent of recognition
The Constitutive Theory is dominant: Recognition by other states determines statehood.
Practice: Recognition often depends on political processes and how other states interact with the new entity.
Example: Kosovo demonstrates an evolving norm, often referred to as "compensatory independence."
Alternative Pathways:
Successor states: Example: South Sudan
Unilateral acts of secession: Not explicitly prohibited in international law, but practice is traditionally silent.
The lack of explicit prohibition allows for the emergence of new states.
Who decide Statehood
International law operates within a decentralized system of state recognition.
UN - P5 can block membership - strong signal to get UN membership
Why Is Recognition Important for Catalonia, Kosovo, and Palestine?
The constitutive effect of recognition establish formal relationships with other states -> statehood. It is especially critical when a state's factual existence is uncertain.
article 53 VCLT
a treaty is void if it's violate Jus Cogens
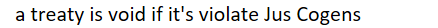
Who decide what is Jus Cogens Norms?
broad acceptance by the international community.
Why is prohibition on torture considered Jus Cogens norm
widespread legal commitment
States, even those accused of practicing torture, often deny or justify their actions, demonstrating opinio juris—a belief that the prohibition of torture is legally binding.
Security Council Resolution 242 (1967)
Followed the Six-Day War, reinforced the inadmissibility of acquiring territory by force and called for the withdrawal of Israeli forces from occupied territories.
right to self-determination does not automatically -
confer a right to secession
Can territory be aqusitioned though conquest?
no not since 1945, menaing state does not loose de jure posession
Why can Israel not obtain title over those parts of Palestine that it occupies?
bc of the prohibition against forceful territory aquisitions, as also recognised by Israel Supreme court (except Eat jerusalem and Golan heights)
UN Charter article 105
States and international organizations are granted certain immunities and protections, such as diplomatic immunity and inviolability of premises.
Legal argument against Palestines right to self-determination
UN Charter, Article 2(4) & Territorial Integrity: The principle of self-determination must be balanced against the prohibition in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter, which forbids actions that threaten the "territorial integrity or political independence" of existing states. Since Palestine’s statehood claim overlaps with territory claimed by Israel, which is an existing UN member state, unilateral self-determination may conflict with the principle of maintaining territorial integrity.
Where is right to self-determination established?
has referred to it as an "essential" principle of contemporary international law. + UN Charter article 1. Human right covenants
what is the principle of speciality regarding extradiction
An individual can only be tried for the specific crime for which they were extradited
What does the Genocide Convention (1948) establish about state responsibility?
It establishes that states are responsible for preventing and punishing genocide. Article IX allows disputes about the Convention to be brought before the ICJ, addressing direct violations but not third-party state support.
What is the principle of complementarity under the ICC?
The ICC intervenes only when national jurisdictions are unwilling or unable to prosecute. It does not address the legal responsibility of third-party states.
What is jurisdition in IL?
Jurisdiction is the right to apply the law. It is primarily exercised by states, manifesting through territorial and personal jurisdiction.
What is territorial jurisdiction?
Territorial jurisdiction is the authority of a state to govern events, persons, and property within its borders, a fundamental aspect of state sovereignty.
What is personal jurisdiction?
Personal jurisdiction allows states to govern their nationals even when they are outside the state's territory.
What is protective jurisdiction?
Protective jurisdiction allows a state to claim jurisdiction over crimes threatening its security, regardless of where the crime occurred or the nationality of the accused.
What is extraterritorial jurisdiction?
Extraterritorial jurisdiction is a state's ability to apply its laws outside its borders, often involving nationals overseas or activities outside its territory that have domestic effects
What are key limitations on jurisdiction?
State immunity: restricts national courts from exercising jurisdiction over foreign states, their property, or representatives.
Functional immunity: for official acts of state representatives.
Personal immunity: for high-ranking officials while in office.
How do political dimensions influence jurisdiction?
States may use legal arguments on jurisdiction to advance strategic goals (interpreting international law in ways favorable to their positions)
What does ratifying a treaty mean for sovereignty?
Ratification can impose obligations that may limit certain sovereign actions.
What case highlights limitations on functional immunity for state officials?
The Pinochet Case (UK House of Lords, 1999) ruled that former heads of state could not claim functional immunity (ratione materiae) for acts of torture committed during their time in office, as these acts violated international law and did not constitute legitimate sovereign acts.
What case famously discusses extraterritorial jurisdiction?
Lotus case: Remembered for asserting that jurisdiction doesn’t stop at borders if international law permits, coining the idea of a “permissive view” of state power.
What was the impact of the "Nicaragua v. United States" case on the interpretation of the prohibition on the use of force?
The ICJ ruled that U.S. actions—supporting the Contra rebels in Nicaragua—violated the prohibition on the use of force articulated in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter. The case clarified that indirect uses of force, such as providing financial and military support to armed groups, can breach international law. This reinforced the principle that states can be held responsible for indirect violations of force
Is Sovereignty Absolute?
Sovereignty is not absolute. Modern trends suggest it may be gaining or losing strength in different regions and contexts. (R2P as example)
How does external intervention complicate the principle of sovereignty?
The principle of non-intervention is a cornerstone of state sovereignty; however, humanitarian crises often prompt debates about the legitimacy of external intervention. The Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine suggests that sovereignty entails a duty to protect populations from mass atrocities, which may justify intervention when states fail to uphold these responsibilities
Lotus principle?
It states that, in the absence of a prohibitive rule, states are free to act as they wish, meaning that what is not explicitly forbidden by international law is permitted. This principle emphasizes state sovereignty and restricts the presumption of illegality unless a specific rule prohibits a given action.

Extra-Territorial Jurisdiction
The ability of a state to exercise its laws beyond its territorial boundaries.
Extra-territorial jurisdiction example
UK's broad jurisdiction related to terrorism and financial crimes.
where is State Immunity affirmed (sources)
Governed by customary international law, supplemented by the European Convention on State Immunity (2018) and the 2004 UN Convention (not yet in force, but reflecting customary law).
State Representatives and Immunity
Personal Immunity: Heads of state enjoy absolute immunity due to the positions they hold. This includes protection from foreign prosecution and civil suits.
Functional Immunity: Immunity applies to actions taken in their official capacity, not personal conduct.
Diplomatic Immunity
Diplomatic Immunity: Foreign diplomats and diplomatic premises enjoy widespread immunity and protection under international law, ensuring they are free from the jurisdiction of host countries.
Why did Israel argue that the ICC lacks territorial jurisdiction over Palestine?
Israel argued that the ICC lacks jurisdiction because Palestine is not recognized as a state under international law and does not have effective control over the disputed territories.
What are the three primary forms of jurisdiction in international law?
The three primary forms of jurisdiction in international law are prescriptive jurisdiction (the power to make laws), enforcement jurisdiction (the power to enforce laws), and adjudicative jurisdiction (the power to resolve legal disputes).
How does the principle of non-intervention relate to state sovereignty?
The principle of non-intervention is closely tied to state sovereignty, asserting that no state should intervene in the internal affairs of another state, upholding the respect for territorial integrity and political independence.
What is the difference between prescriptive, enforcement, and adjudicative jurisdiction?
Prescriptive jurisdiction refers to a state’s authority to create and enforce laws, enforcement jurisdiction is the power to ensure compliance with laws, and adjudicative jurisdiction allows a state or international body to settle disputes through legal rulings.
What is the principle of sovereign equality of states in international law?
The principle of sovereign equality of states means that all states have the same legal rights and obligations under international law, regardless of size or power.
How does international law address territorial disputes between states?
International law addresses territorial disputes through negotiation, arbitration, and adjudication by various international bodies, including the International Court of Justice (ICJ), based on established legal norms and principles.
What is the significance of the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties?
The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties provides the foundational rules and procedures for interpreting and enforcing international treaties.
What is the Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine in international law?
The Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine asserts that the international community has a duty to intervene when a state fails to protect its population from mass atrocities. This challenges traditional notions of state sovereignty, /particularly in the context of human rights obligations (Reus-Smit, 2001; Deng, 1995).)
What is the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP)?
The UNDRIP is a non-legally binding document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2007, which sets out the individual and collective rights of indigenous peoples.
Why is the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples not considered a legally binding convention?
Because it was adopted as a declaration, not a treaty, meaning it does not carry the same binding legal obligations as international conventions.
When did Bolivia incorporate the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples into its national law?
Bolivia incorporated the UNDRIP into its national law through the 2009 Constitution, recognizing indigenous peoples’ rights and autonomy.
What significant impact did the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples have on Bolivia?
The UNDRIP significantly influenced Bolivia by empowering indigenous peoples through constitutional protections, political representation, and recognition of their cultural and territorial rights.
What has been the international community's response to the Western Sahara conflict?
non-binding resolution for refforrundum, not accepting Moroccosterritorial claim
What did draft conclusion on identification of customary international law mean for state practise
Expanded the forms of state practice that can count as evidence, including diplomatic acts, official statements, and inaction.