15) Lymph node
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
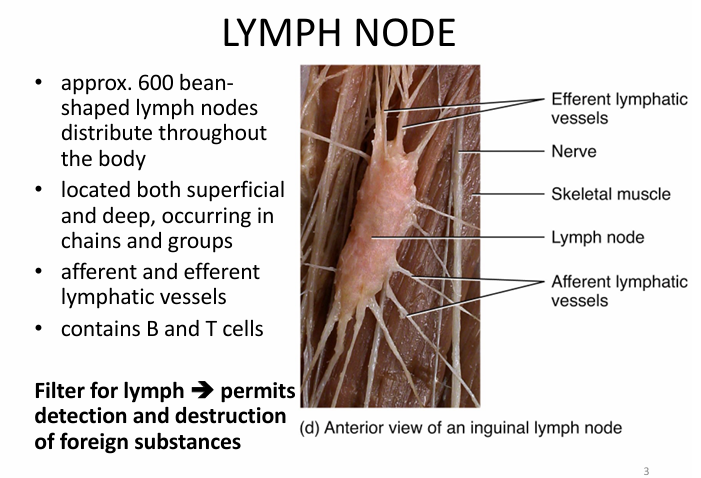
What is the lymph node?
Filters lymph
→ permits detection & destruction of foreign substances
contains B cell/Tcell
afferent/efferent lymphatic vessels
small bean shape
(LO1)
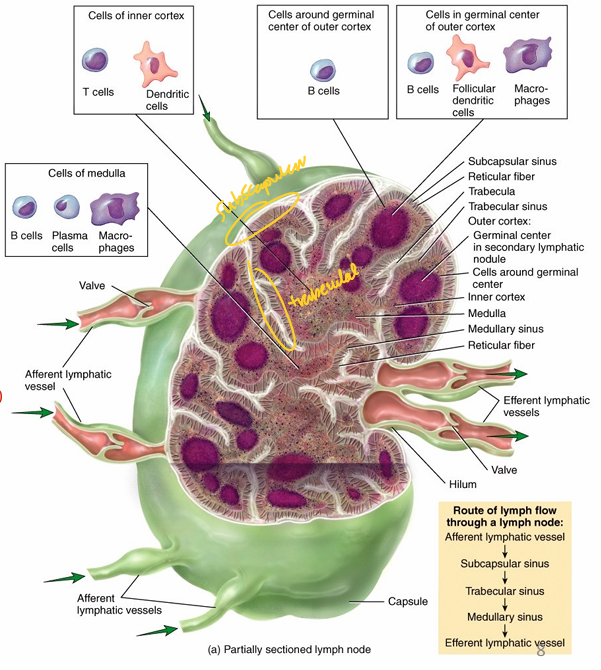
Describe the histological architecture of the lymph node.
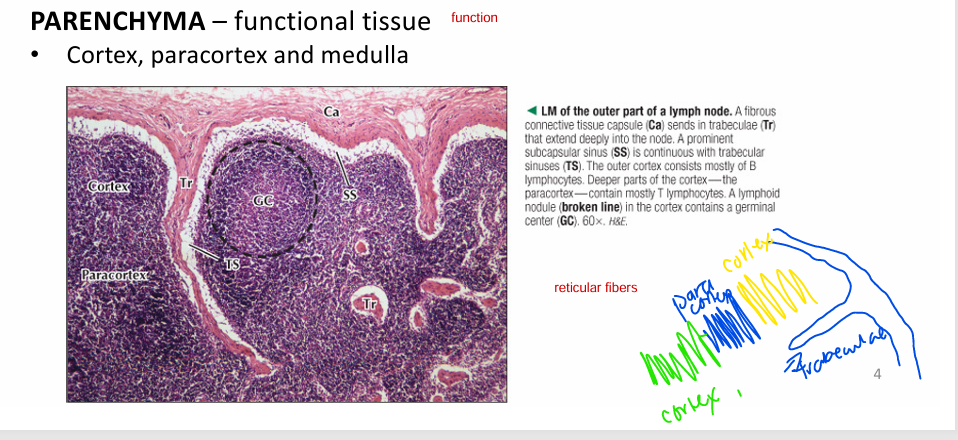
1) Stroma = structural tissue (overall architecture)
- capsule of dense irregular CT
- trabeculae penetrates into lymph node
- reticular fiber mesh (via fibroblastic reticular tissue)
2) Parenchyma = functional tissue (function)
- cortex, paracortex, medulla
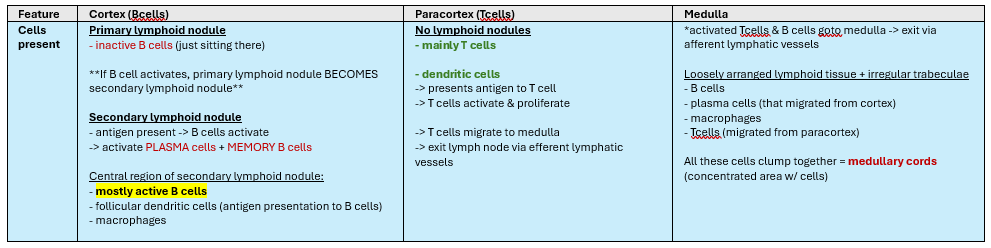
(LO2) Describe the different layers of the lymph node & population of cells found in each layer
central region = germinal centre
Describe the process of ONE-WAY FLOW of lymph through the lymph node
1) IN via Afferent lymphatic vessels
(w/ valves; one way flow)
2) Lymph enters sinus of lymph node
- subscapular sinus
→ trabecular sinus
→ medullary sinus
3) OUT via efferent lymphatic vessels
- secretes:
- AB
- activated T cells
Why are there less efferent lymphatic vessels than afferent lymphatic?
aka why less OUT than IN
-slows flow of filtrate
Describe the significance of the hilum in the lymph node.
Area for exit of efferent lymphatic vessels
- carries AB & activated T cells
- site for blood vessel access to LN
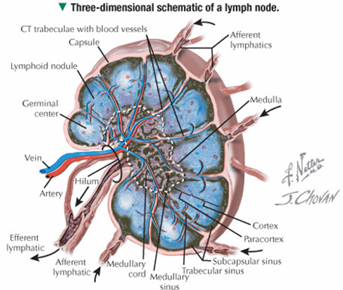
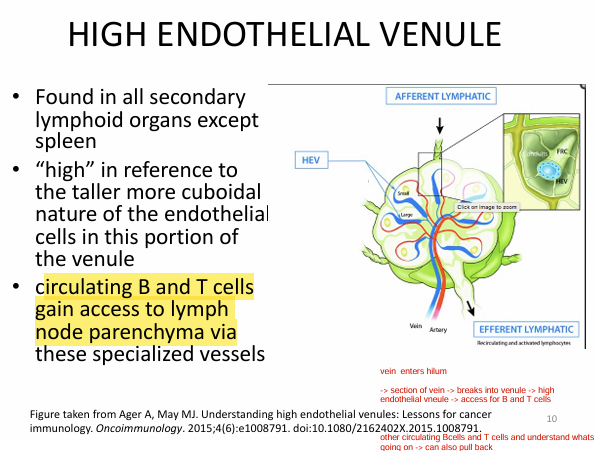
What is the HIGH ENDOTHELIAL VENULE?
found in ALL secondary lymphoid organs (except spleen; aka just LN?..)
- circulating B & T cells gain access to lymph node parenchyma via these specialized vessels
TLDR: circulating T/Bcells can help out in these LN → and then go away when not needed