Alcohols
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Oxidation
Heat
KMnO4/H+ → purple to colorless
K2Cr2O7/H+ → orange to green
Esterification
alcohol + carboxylic acid + h2so4
Test for Alcohols
ethanoic acid, conc Sulfuric, warm NaHCO3
+PCl5
anhydrous
Lucas Test
Lucas Reagent → conc. HCL and ZnCl2
1 → white cloudiness only on heating
2 → white cloudiness after 5-10 mins
3 → white cloudiness immediately
Hydrogen Halides (Hbr)
conc of hydrogen halide, reflux and heat
Dehydration - Preparation of Alkene
cH2So4, 180
Dehydration to form an ether
c H2So4, 140*C
Iodoform
→ vicinal Ch3 to Oh
→ NaOH
Preparation of Alcohols - Hydration of Alkenes
conc Sulfuric acid
reflux with warm H30
Preparation of Alcohols - Reduction of Aldehydes/Ketones and Carboxylic acids
LiAlH4 in dry ether → reduces all groups
NaBH4 → NOT CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Preparation of Alcohols - Alkaline Hydrolysis of Haloalkanes
Heat, reflux NaOH
Industrial Preparation of Ethanol - Fermentation of Sugars
Yeast provides - zymase
no air → prevent oxidation of ethanol
yeast is killed at 15%
35 degrees allowing the enzyme to work
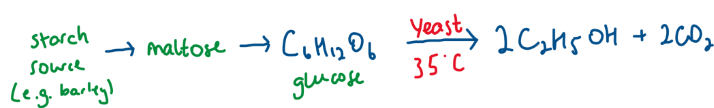
Industrial Preparation of Ethanol - Steam Hydration of Ethene
300 degrees, 60-70atm, H3Po4
LOW TEMP AND HIGHER PRESSURES → BETTER YIELD
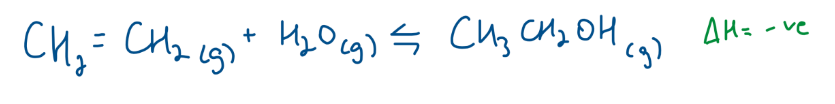
Characteristics of Polyhydric Alcohols
better solubility
more viscous
ALL BCS OF HYDROGEN BONDING!!
Physical Properties of Alcohols
b.p and m.p increase with the mass of alchol → more id-id
branching reduces it bcs poorer packing
Longer chain alcohols are not soluble in water as the surface area of id-id increases but the surface are of the h-bond doesnt