31 ECG Interpretation
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Positive
Which electrode is ALWAYS the reference for an ECG?
INTRACELLULAR: Potassium
EXTRACELLULAR: Sodium
=this balance (thru ATP pump) creates chemical gradient and electrical charge
Describe the relationship of K and Na, which is intracellular? Extracellular?
1. Heart likes to normally sit around -80 mV
2. Stimuli depolarizes to threshold (maybe around 65-55 mV?) = QUICK depolarization as Na+ moves to intracellular. Hit +55mV and cell + charged
3. K+ must move extracellular as a result to make cell more negative
4. Ca+ slowly comes into cell to briefly plateau action potential
5. Once muscle has had time to rest, K+ moves out of the cell to reset the charge
6. Na/K ATP pump must correct remaining imbalance
Describe the process of propagating a cardiac action potential:
Cardiac myocytes have internal automaticity and other myocytes don't = if you cut out heart and throw it on a table, it will beat for a while
What is the difference between cardiac myocytes and other myocytes?
You need to give time for the muscle to actually contract aka give time for actin and myosin to bind and go thru process
Ca+ must slowly come into the cell at a similar rate to K+ moving extracellularly after an action potential. Why is leveling out this charge differentiation for a brief plateau important?
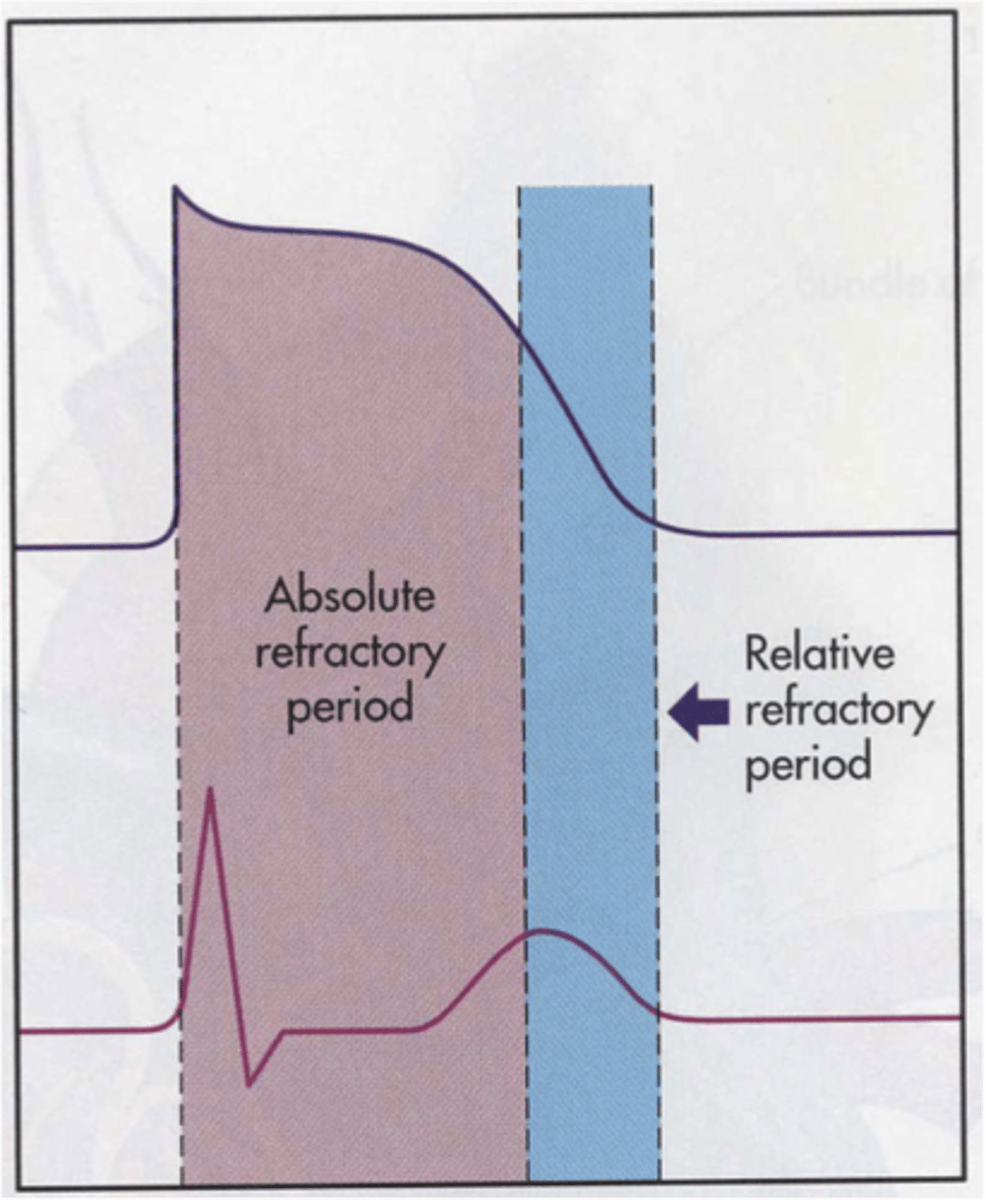
Absolute: NO RESPONSE EVER
Relative: if stimuli is large enough, something can happen BUT problem is, if it is stimulated during this time, may cause deadly arrhythmia
What is the difference between absolute and relative refractory period?
Upward deflection. Electrodes detect charge on the outside of the cell. Charge moves from the negative to positive electrode. So, if Na moves from outside to inside, the negative end will start to read more negative as sodium moves in, but the positive electrode will still read positive on the outside since not all of the cardiac cells have been affected yet. Since, negative is reading negative, and positive is reading positive, there is an upward deflection during depolarization.
What will depolarization look like on ECG, why?
All charges are either reading positive or negative = both electrodes seen either positive or negative on the outside of the cell.
What does Isoelectric mean in an ECG?
Downward deflection. Electrodes detect charge out outside of cell. Charge moves from negative to positive electrodes. So, if K+ is moving from inside to outside the cell, the negative end will be reading a more positive outerspace, but since not all the cells have released K+ yet, the positive electrode will still be reading negative charge as the repolarization wave moves thru the heart.
What will repolarization look like on ECG, why?
1. SA (sinoatrial) node in top right of atrium
2. AV (atrioventricular) node
3. Bundle of HIS
4. Left bundle
5. Left bundle BRANCHES
6. anterior and posterior left bundle branches
7. Right bundle (branch)
8. Purkinje fibers
Name the pathway of electrical conduction of the heart
LEFT ONLY
Which bundle of the heart has brachES which then divide into anterior and posterior? left or right?
Class II
Which lead class do cats, humans, and dogs use?
Class I
Which lead class do horses and cattle use?
HORSES AND CATTLE
Why?: need many more "roads" than just cell to cell because we need to get a MASSIVE heart to contract at the same time
Which has more purkinje fibers, horses/cattle OR cats/dogs/humans? Why?
CLASS I (horses/cattle): signals move from epicardium to endocardium, downward deflection with depolarization
CLASS II (dog/cat/human): signals move from endocardium to epicardium, upward deflection with depolarization
Describe signals from the epicardium and endocardium between class I and class II ECG leads. Describe how this changes the deflection
50 mm/s
How fast does Lead II move?
-, +, grounding
What 3 different types of electrodes do you need?
White on right elbow, green on right stifle (snow over grass), Black on left elbow, red on left stifle (smoke over fire)
Name the Lead II electrodes and where to place them
Monitors from lead on R arm to Left Leg
(II has 2 L's)
Where does lead II monitor? From what landmarks does it read?
Monitors from lead on Left arm to Left Leg
(III has 3 L's)
Where does lead III monitor, from what landmarks does it read?
Monitors from lead on Right arm to Left arm
(I has 1 L)
Where does lead I monitor, from what landmarks does it read?
40-100 degrees
not sure wtf this is i hate ecg
What is the normal angle between lead I and II on dogs?
0-160 degrees
i dont know wtf this means either but its bolded so just do it
What is the normal angle between lead I and II on cats?
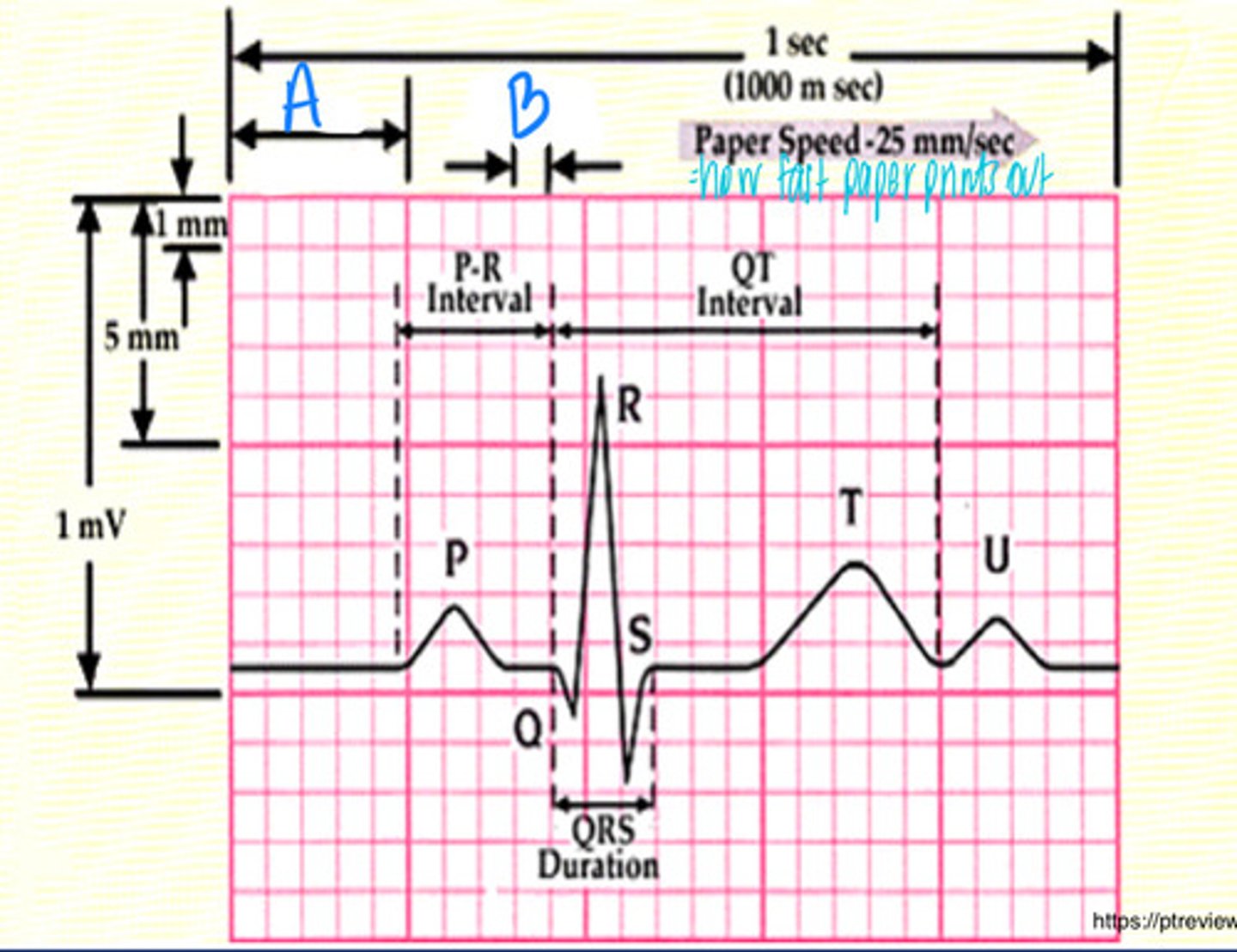
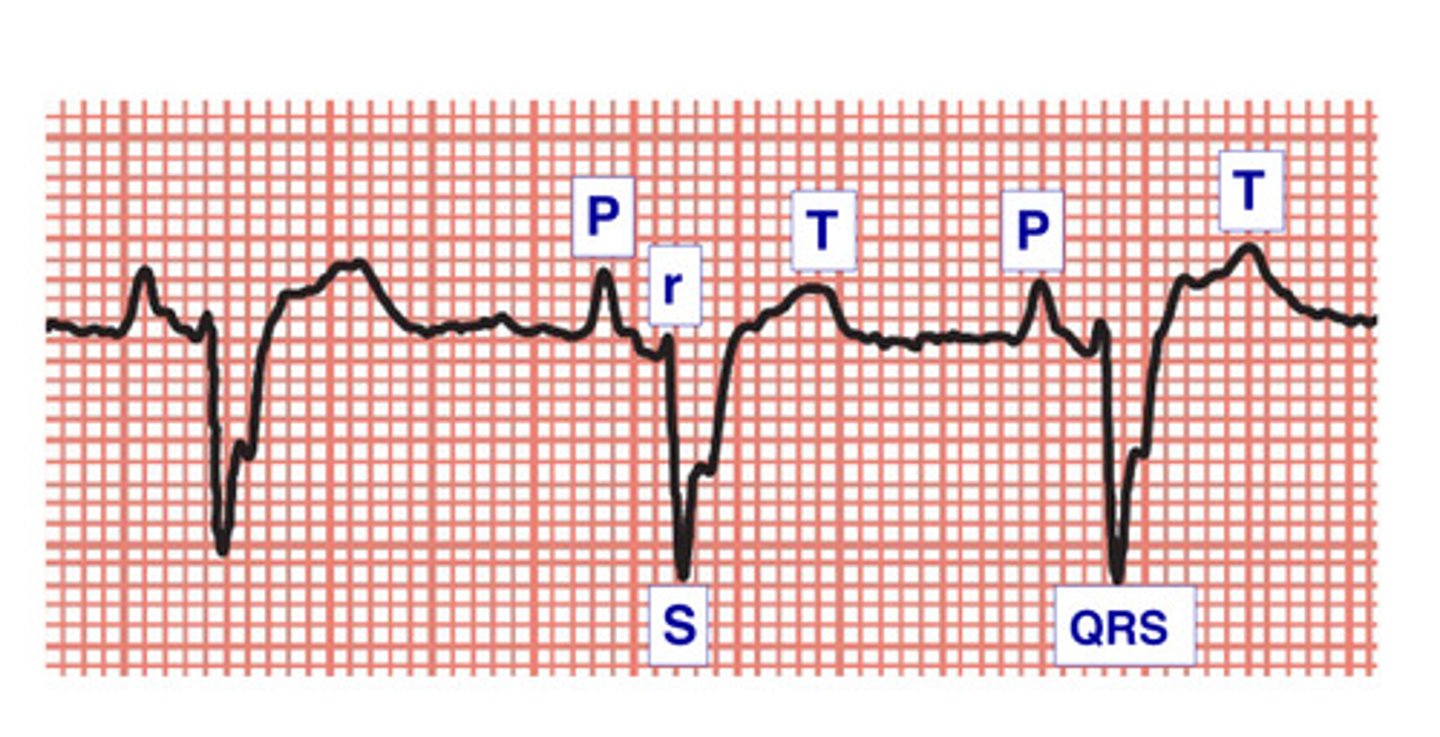
P wave. atrial depolarization (2 atria contract, SA node)
What is this and what happens here
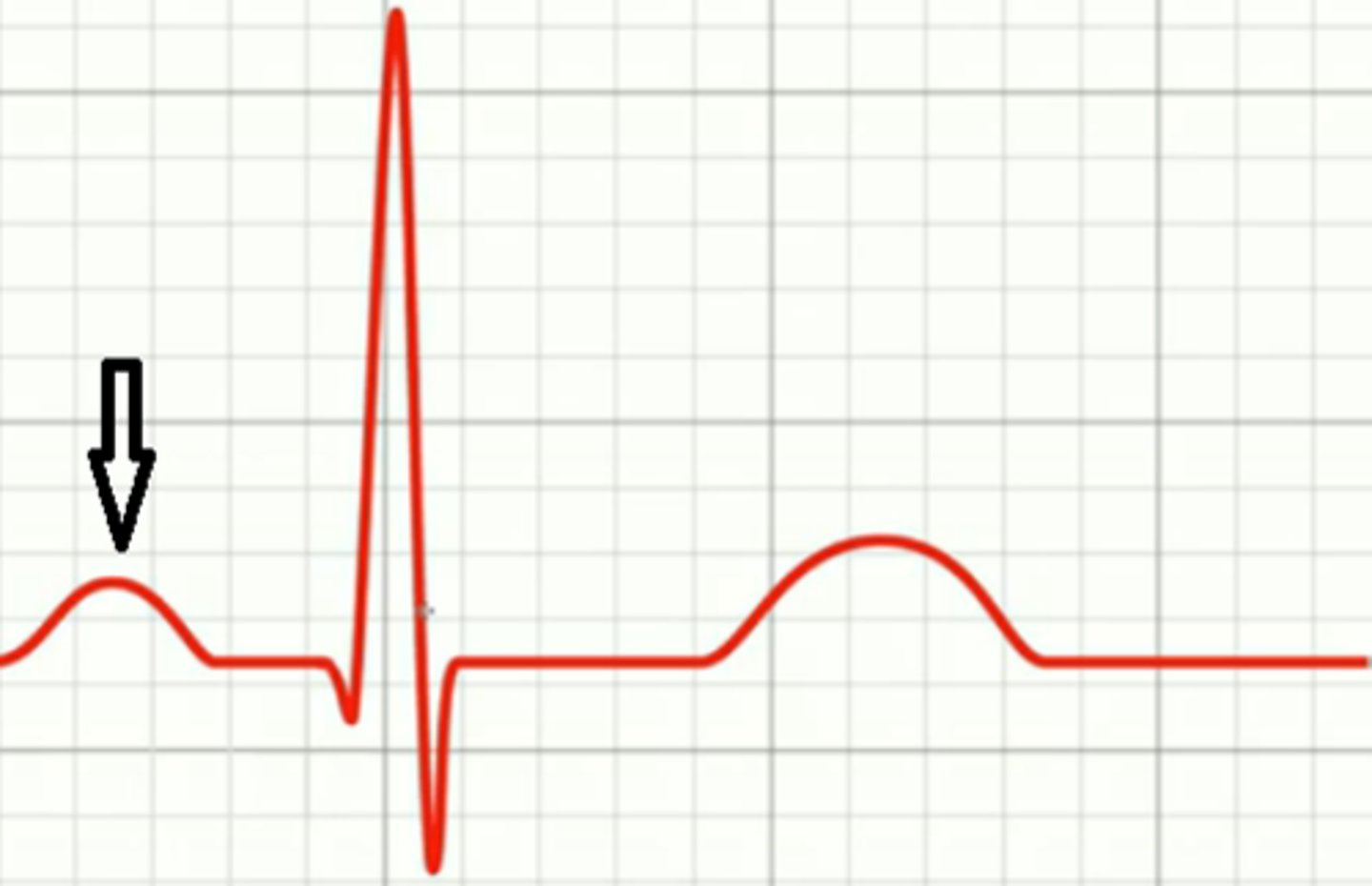
QRS complex. ventricular depolarization (2 ventricles contract, AV node/His/bundles/purkinje)
What is this and what happens here
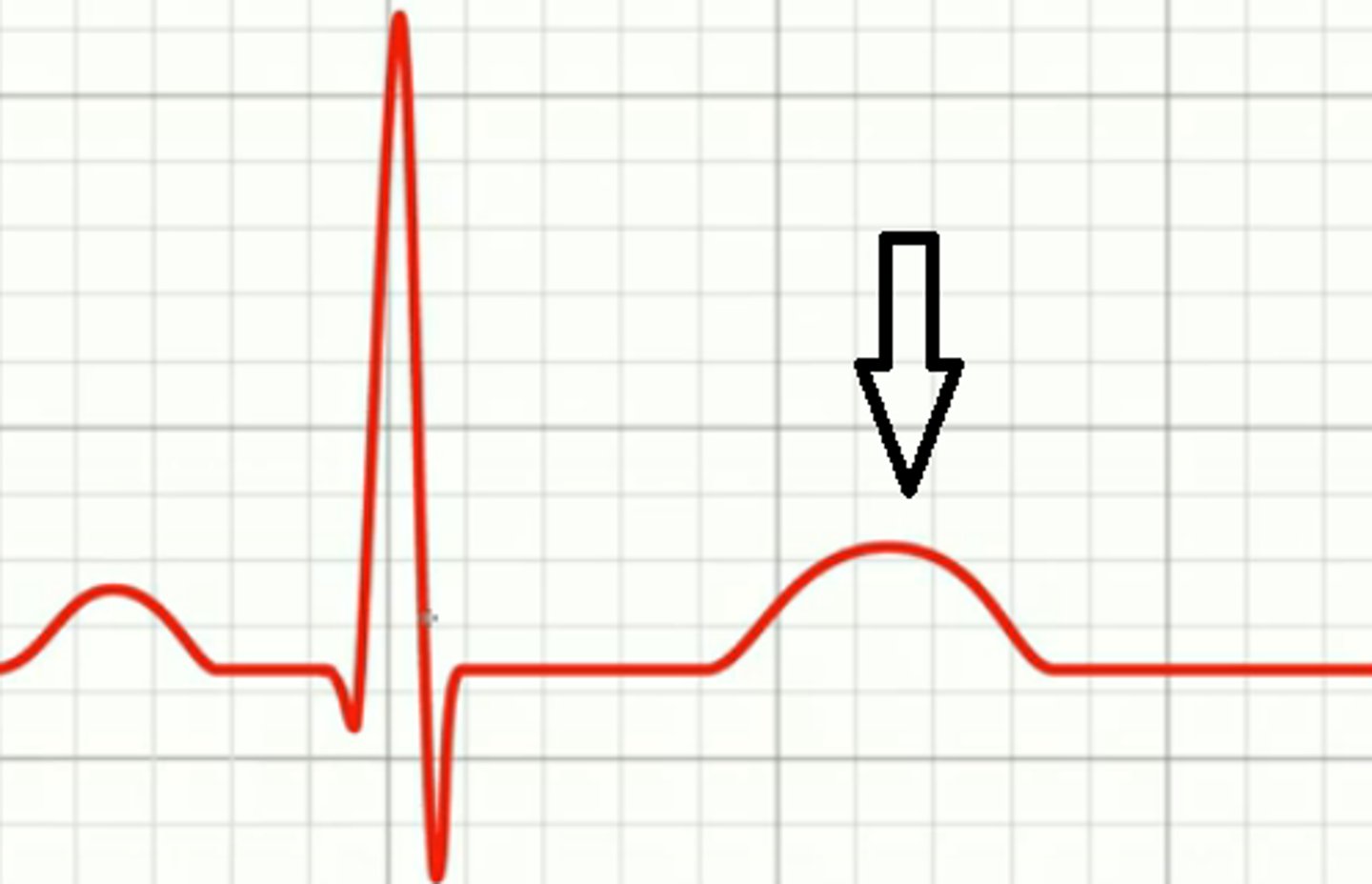
T wave. ventricular repolarization (2 ventricles relax)
What is this and what happens here
N/2
What is the sensitivity of this if I tell you 1/2 cm = 1 mV
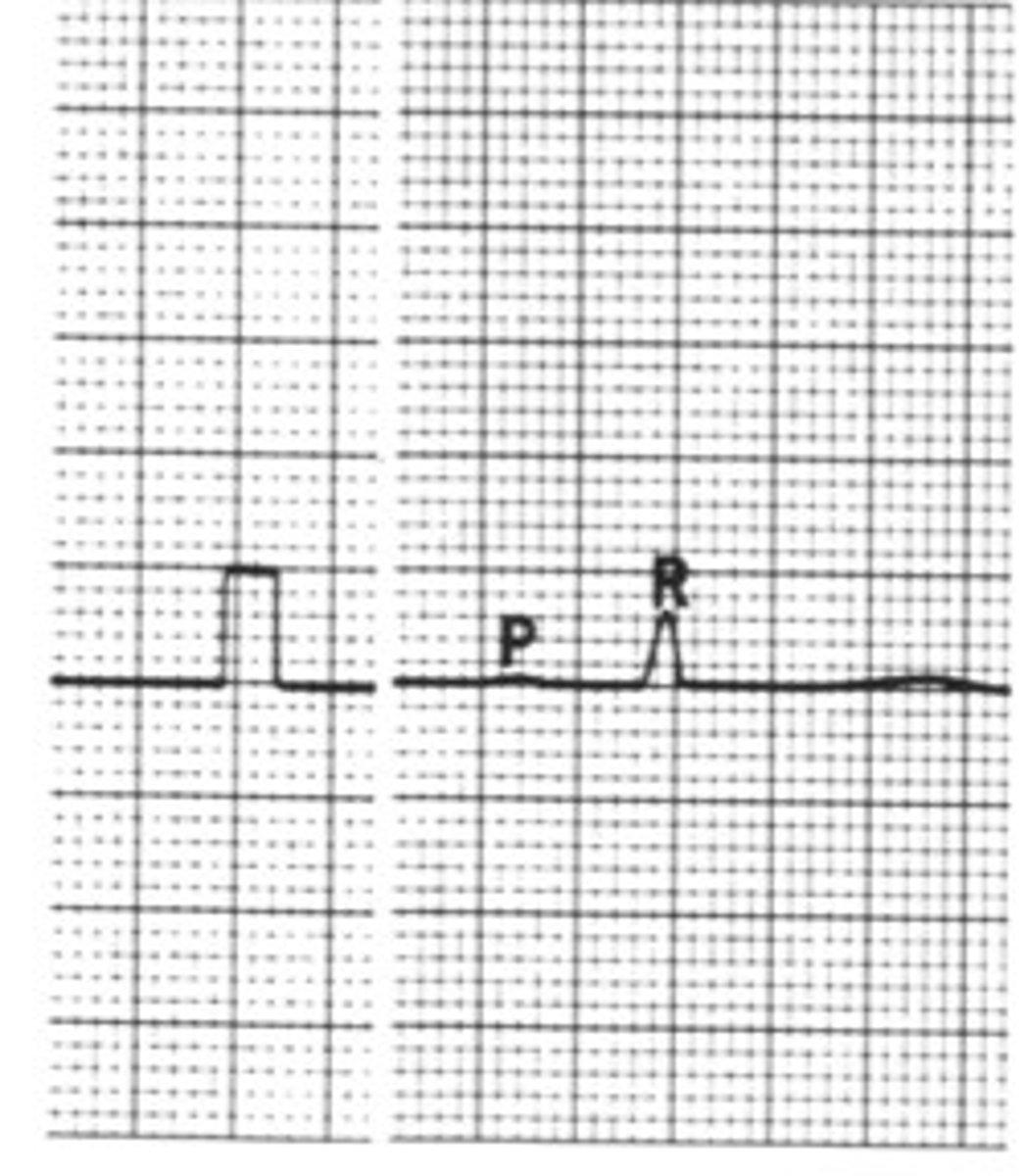
N
What is the sensitivity of this if I tell you 1 cm = 1 mV
2N
What is the sensitivity of this if I tell you 2 cm = 1 mV
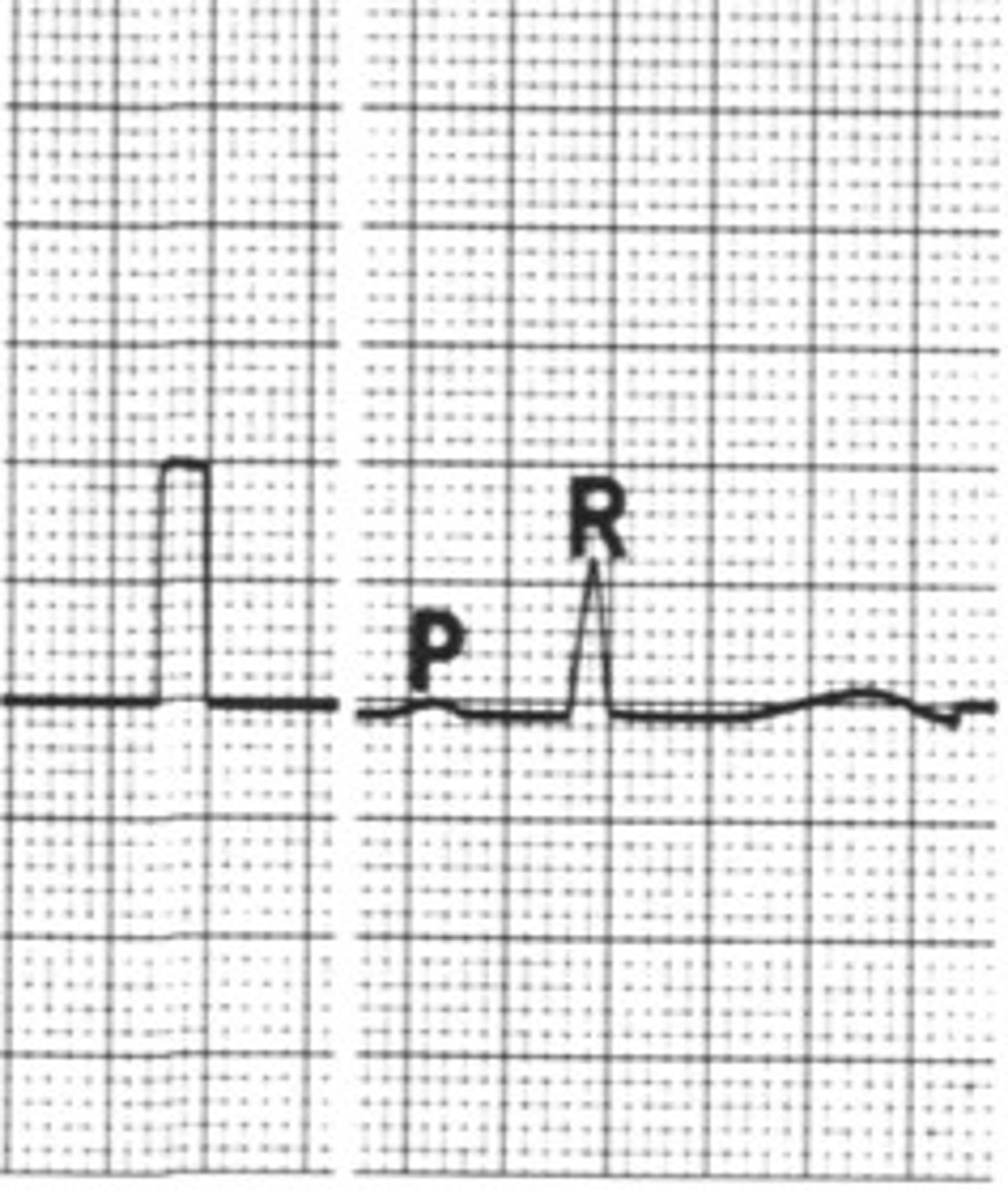
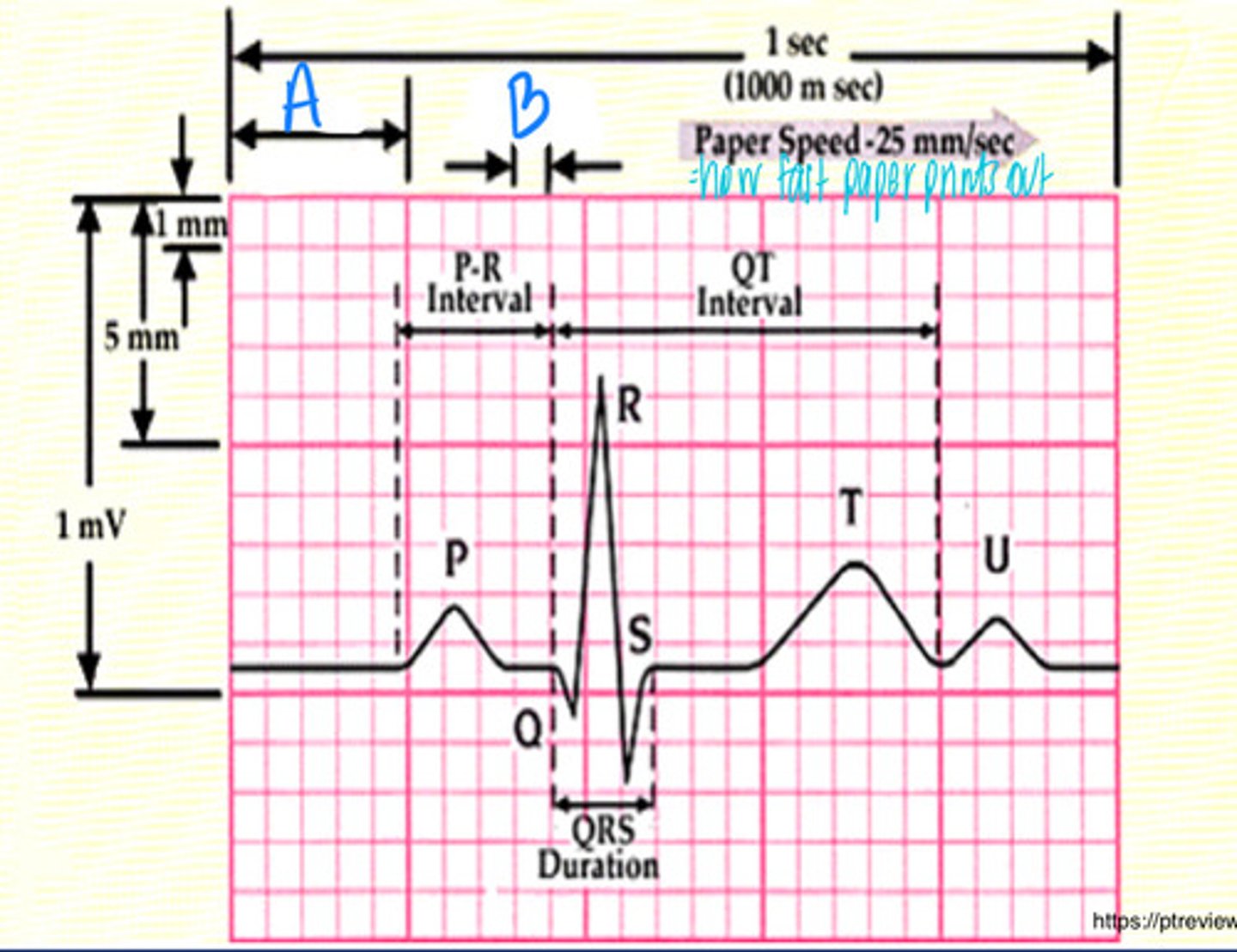
0.2 sec
What is A moving at the normal paper speed of 25 mm/s
0.04 sec
What is B moving at the normal paper speed of 25 mm/s
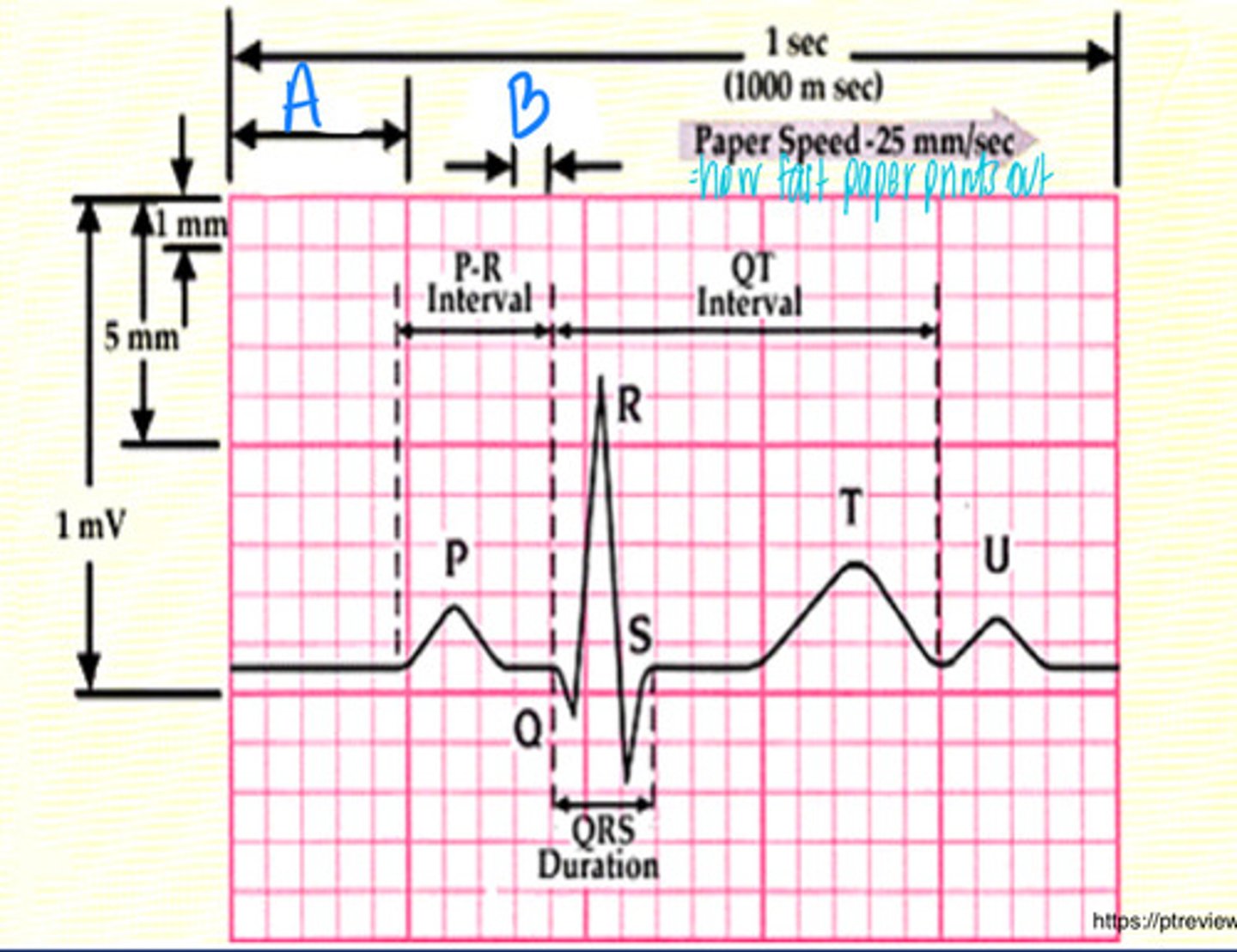
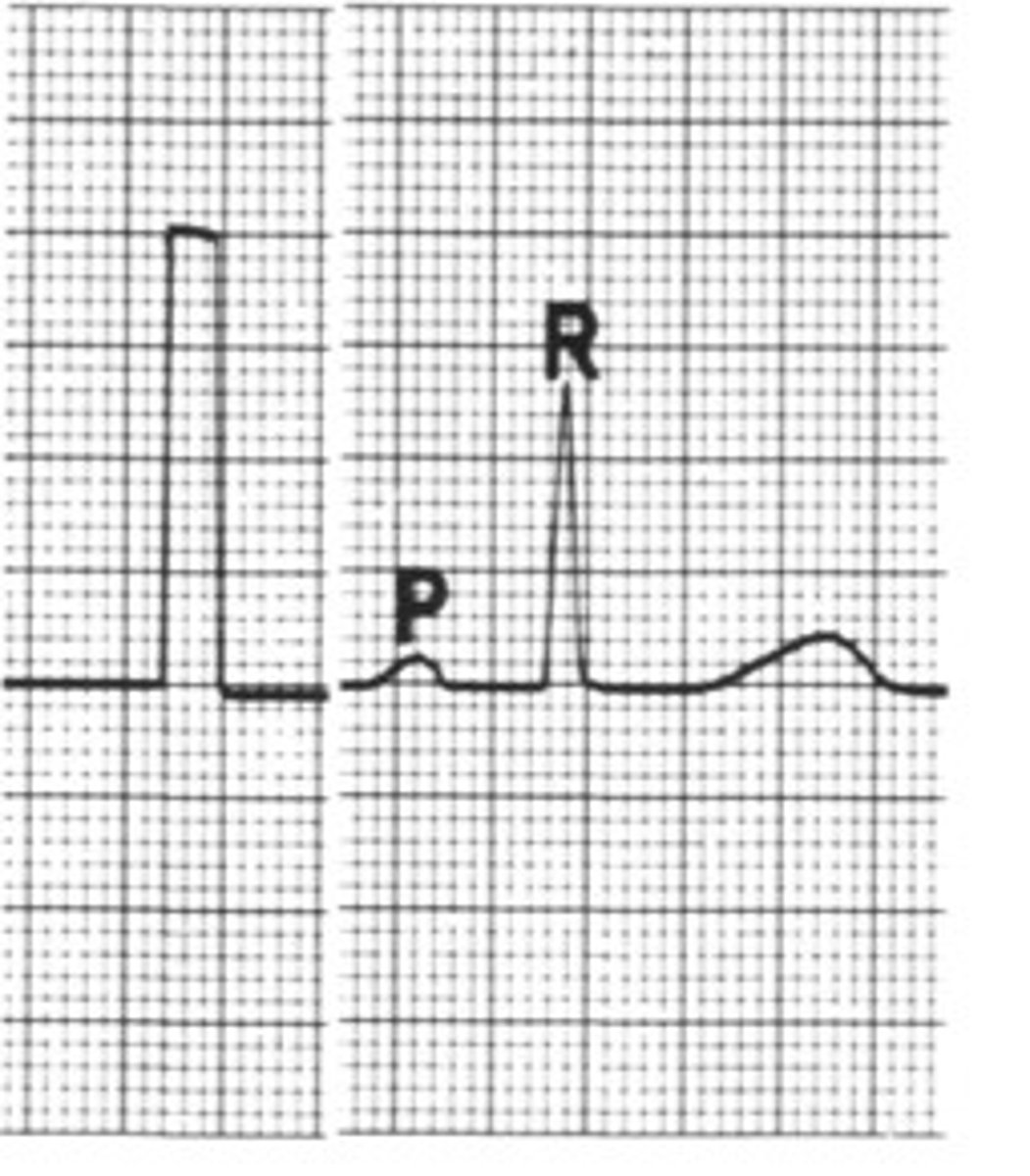
Instead of 0.04 sec --> NOW 0.02 sec (because the paper is moving at double the speed which halves the time)
If I were to tell you instead of the normal 25 mm/s, that this is instead moving at 50 mm/s, what does that change B to?
1. fast or slow rate?
2. regular or irregular?
3. wide or narrow QRS?
4. is there a P for every Q?
5. is there a Q for every P?
(because there may be a Q with no P or a P with no Q)
Name the 5 questions you ask yourself when reading an ECG
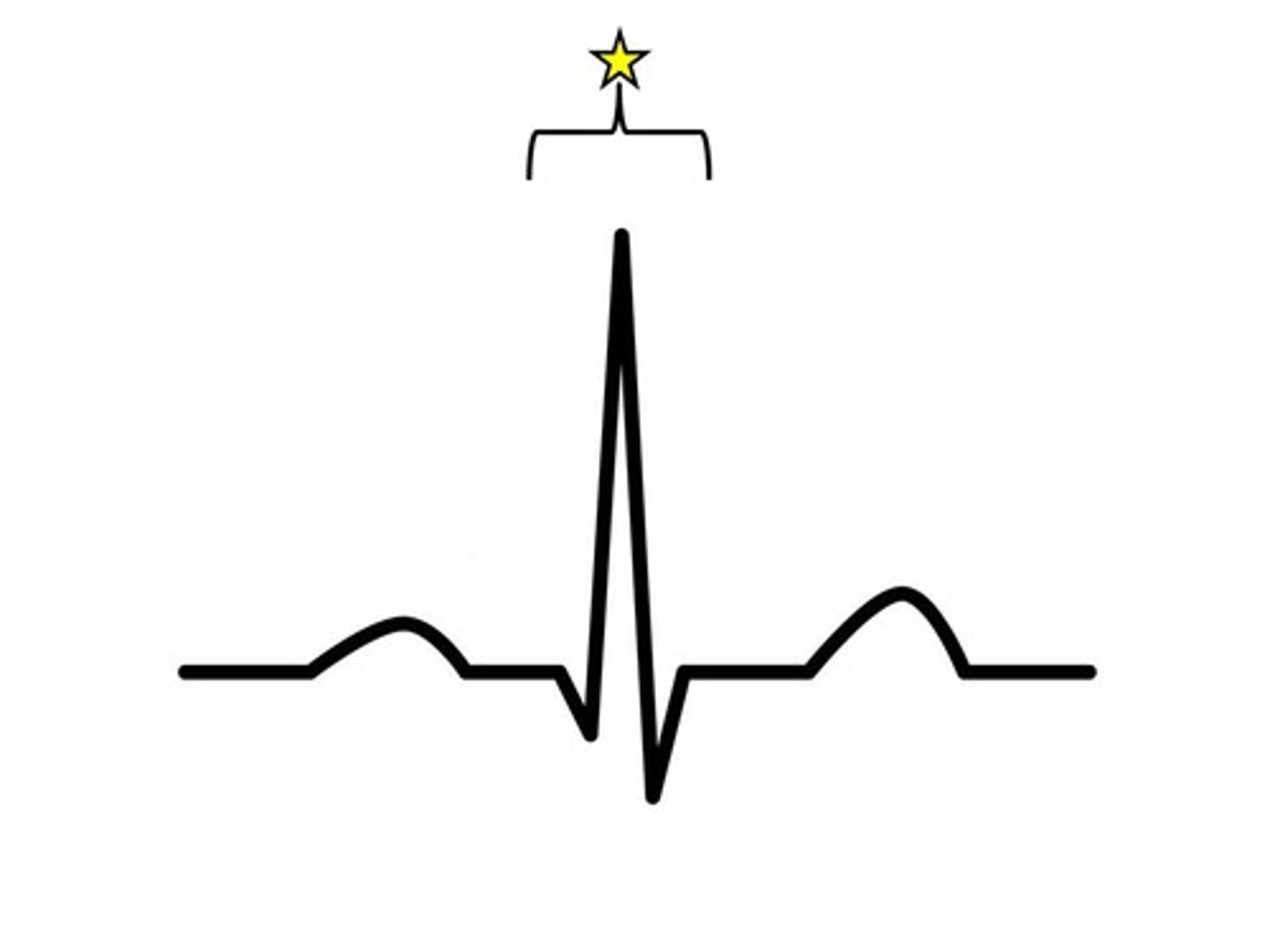
QRS
Which is the biggest wave on an ECG?
10 mm
How long are the blocks represented by the letter "A"?
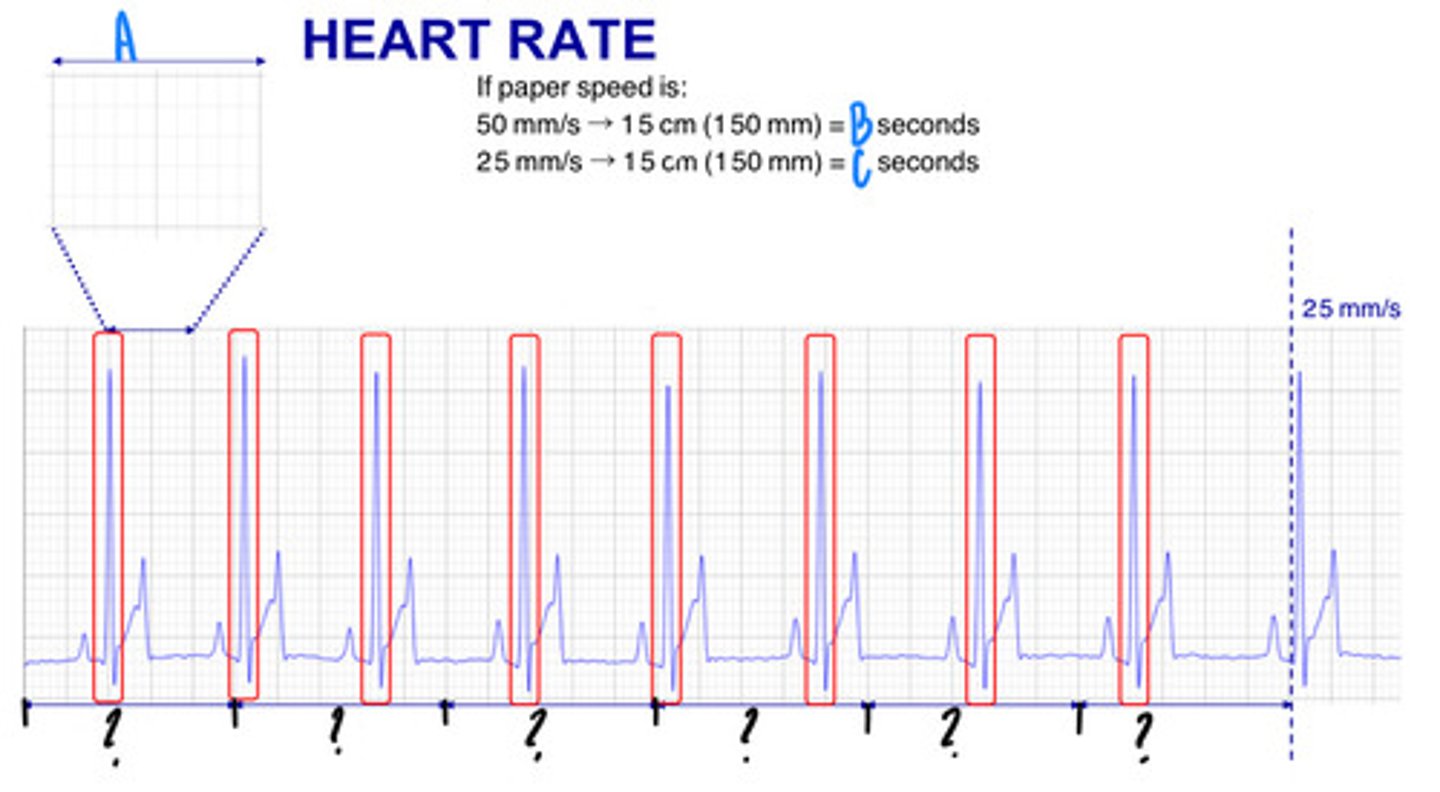
3 seconds
What is B?
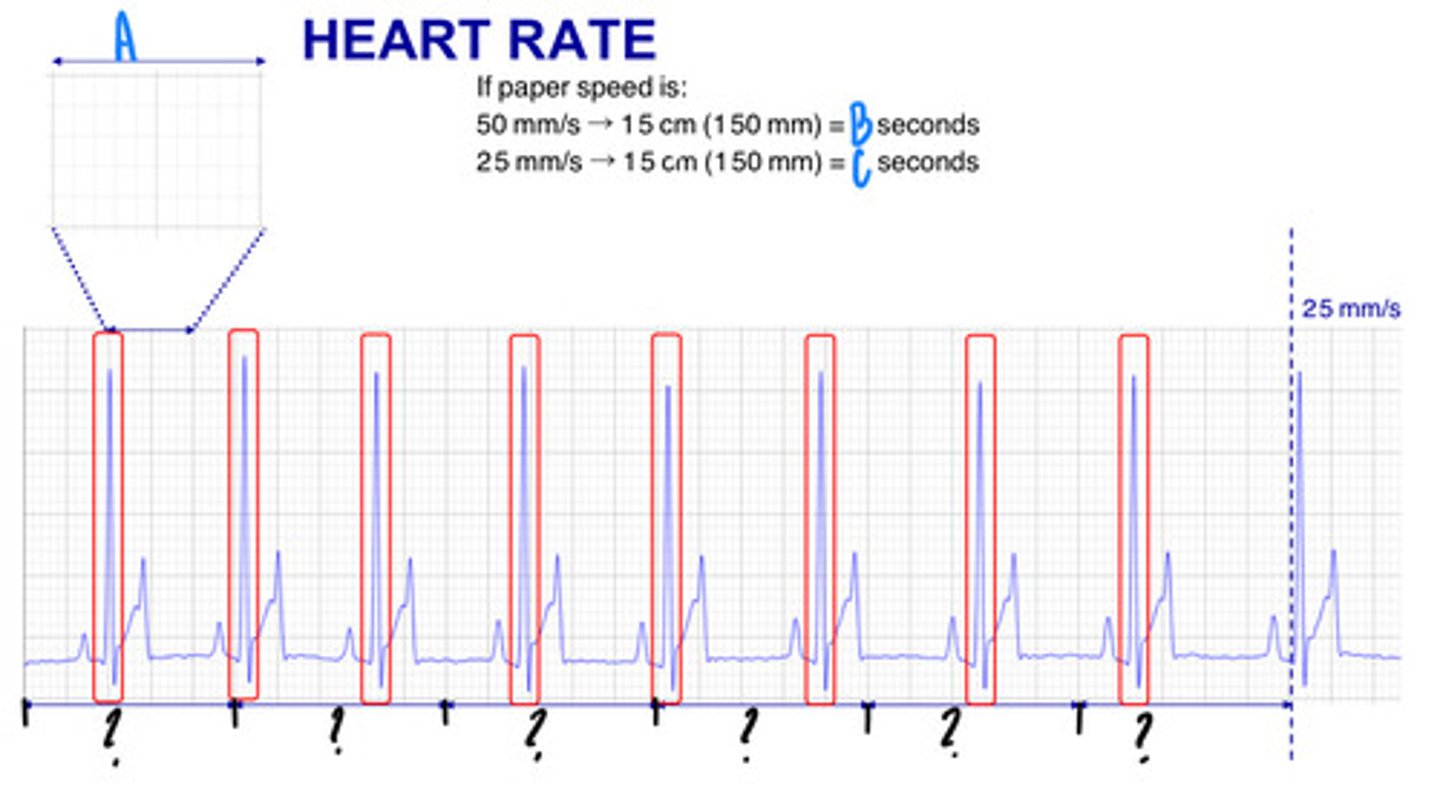
6 seconds
What is C?
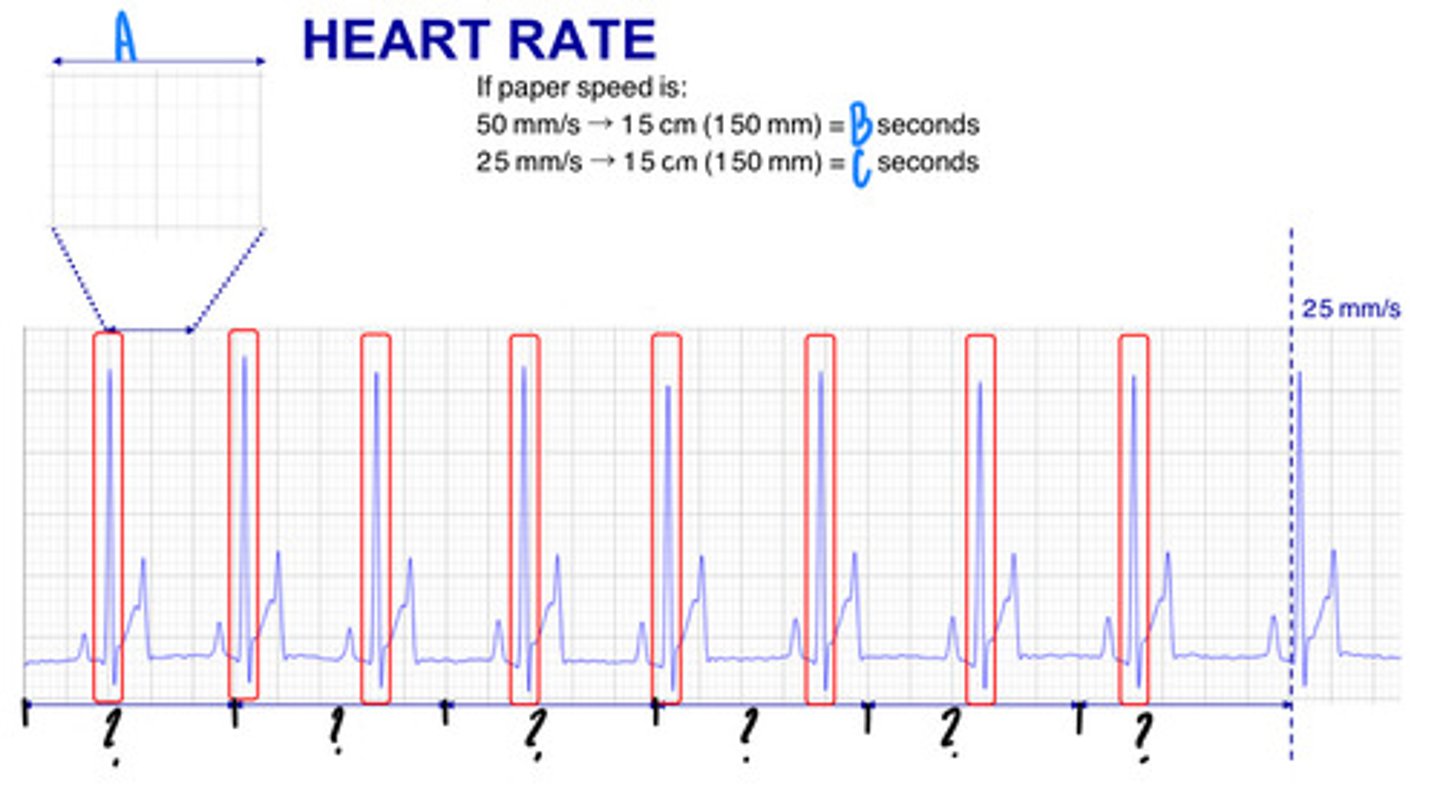
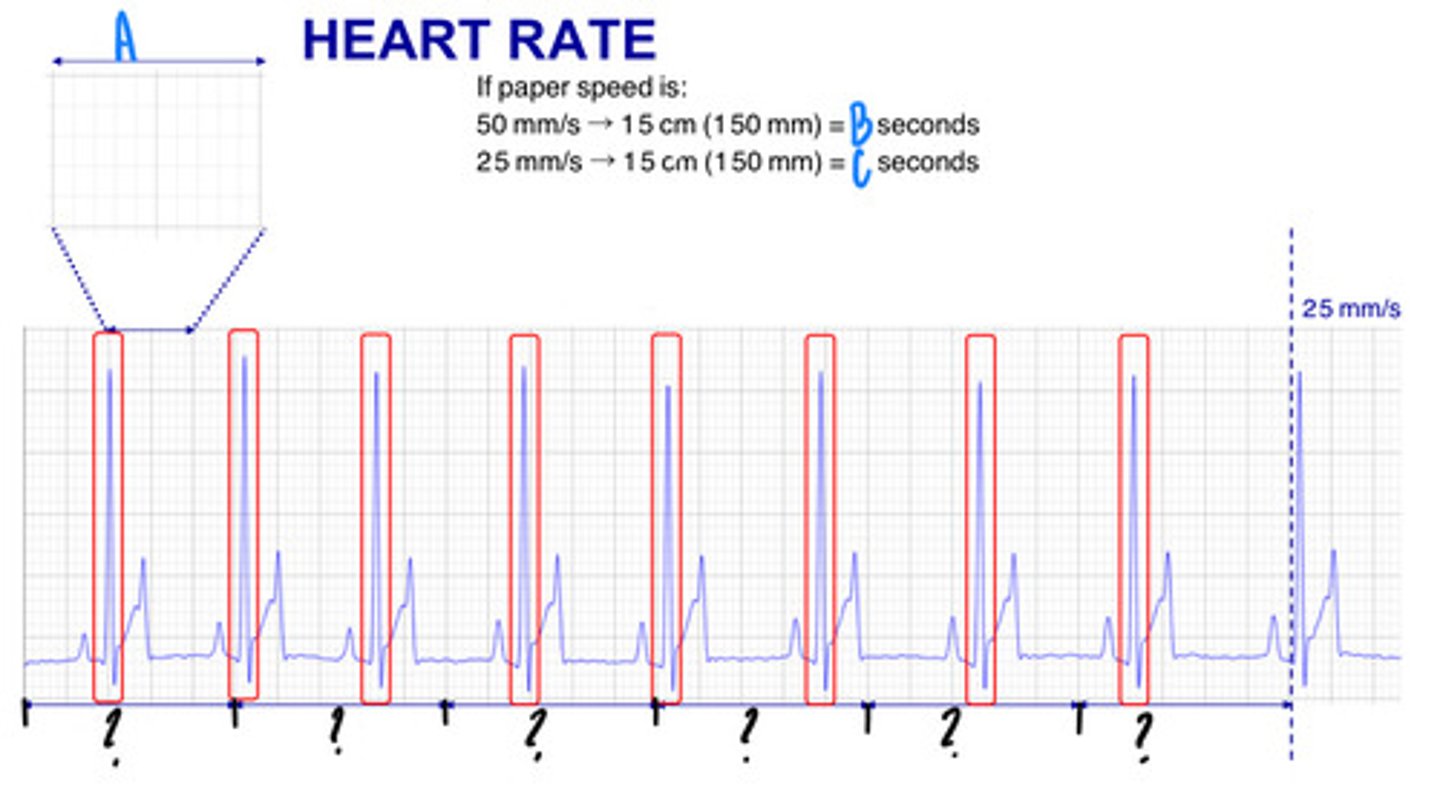
25 mm covered in 1 second
What are the lengths and times represented by the "?" (they are all the same number and length)
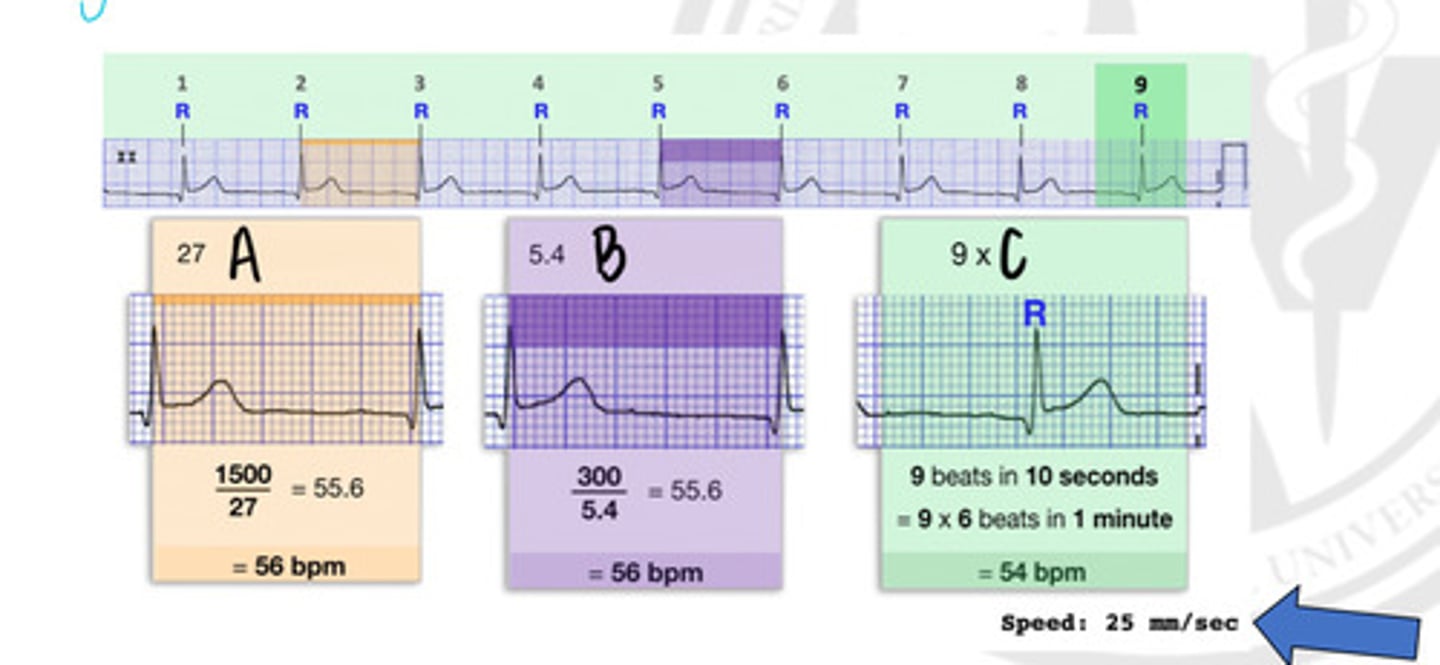
27 small squares
In what way can you get a heart rate, represented by "A"?
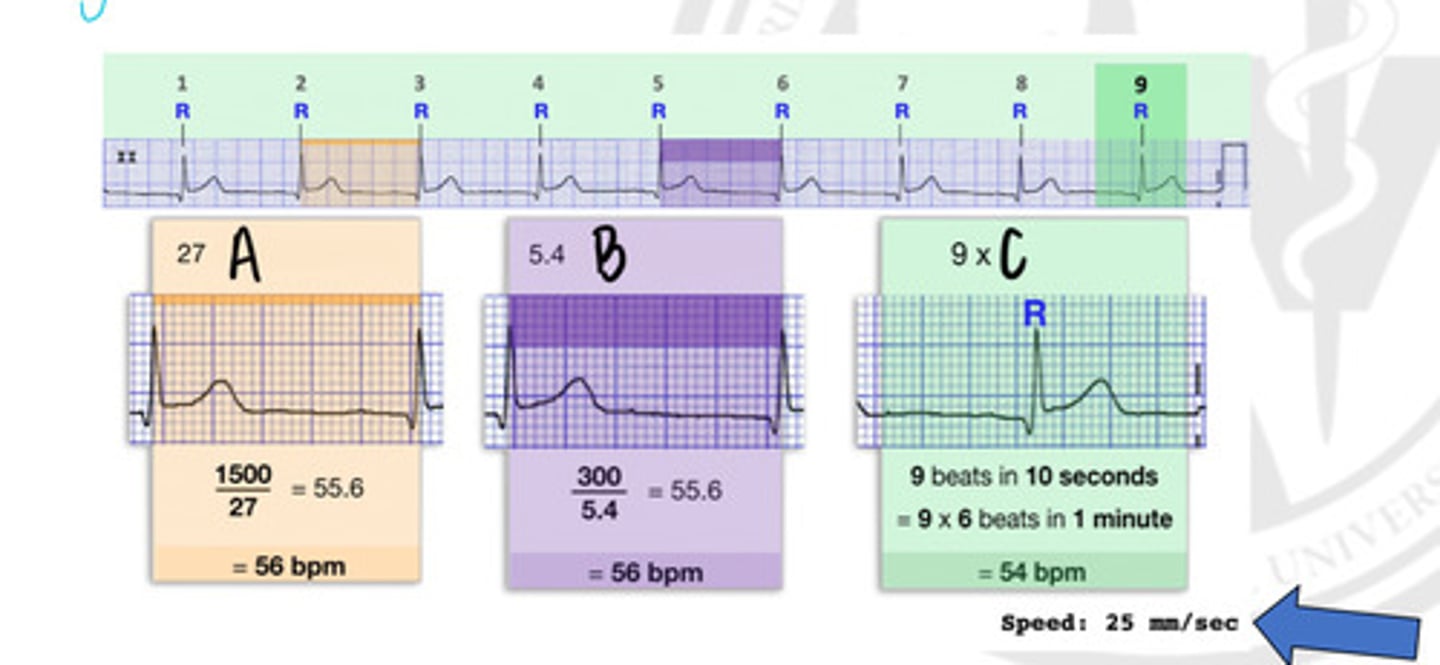
5.4 Large squares
In what way can you get a heart rate, represented by "B"?
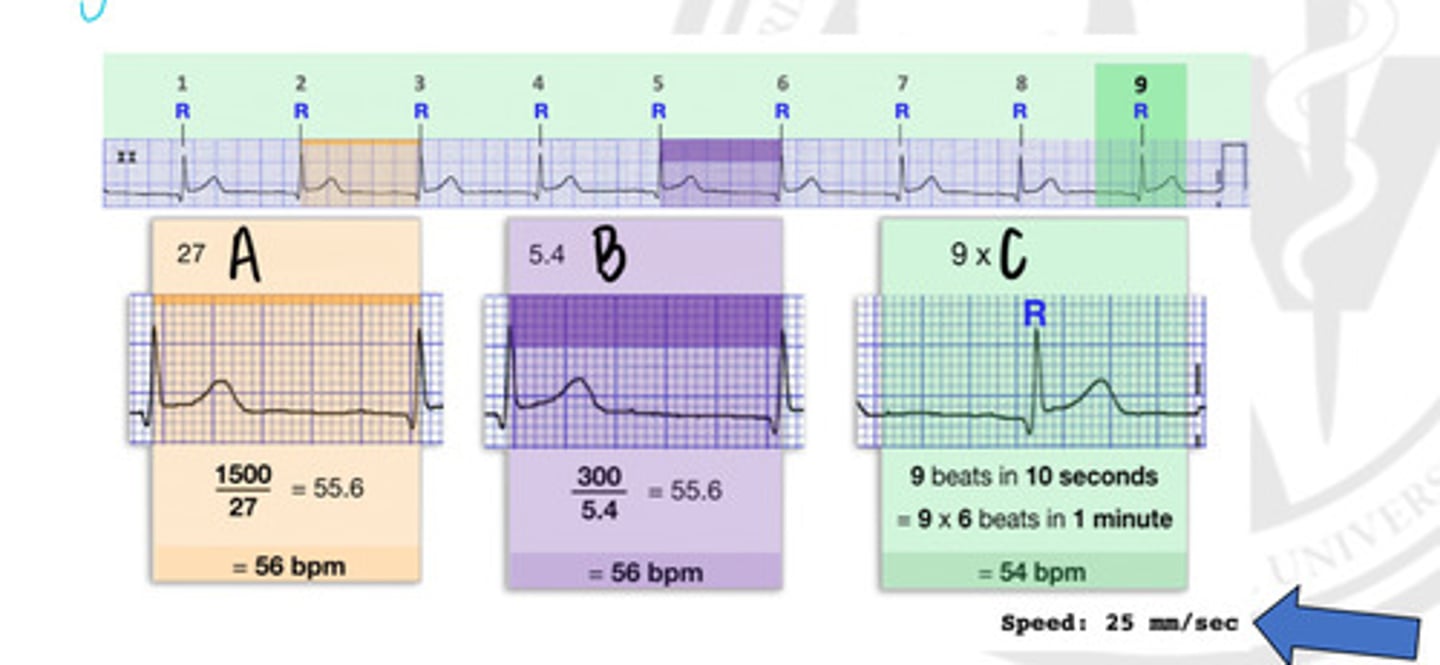
9 x R waves
In what way can you get a heart rate, represented by "C"?
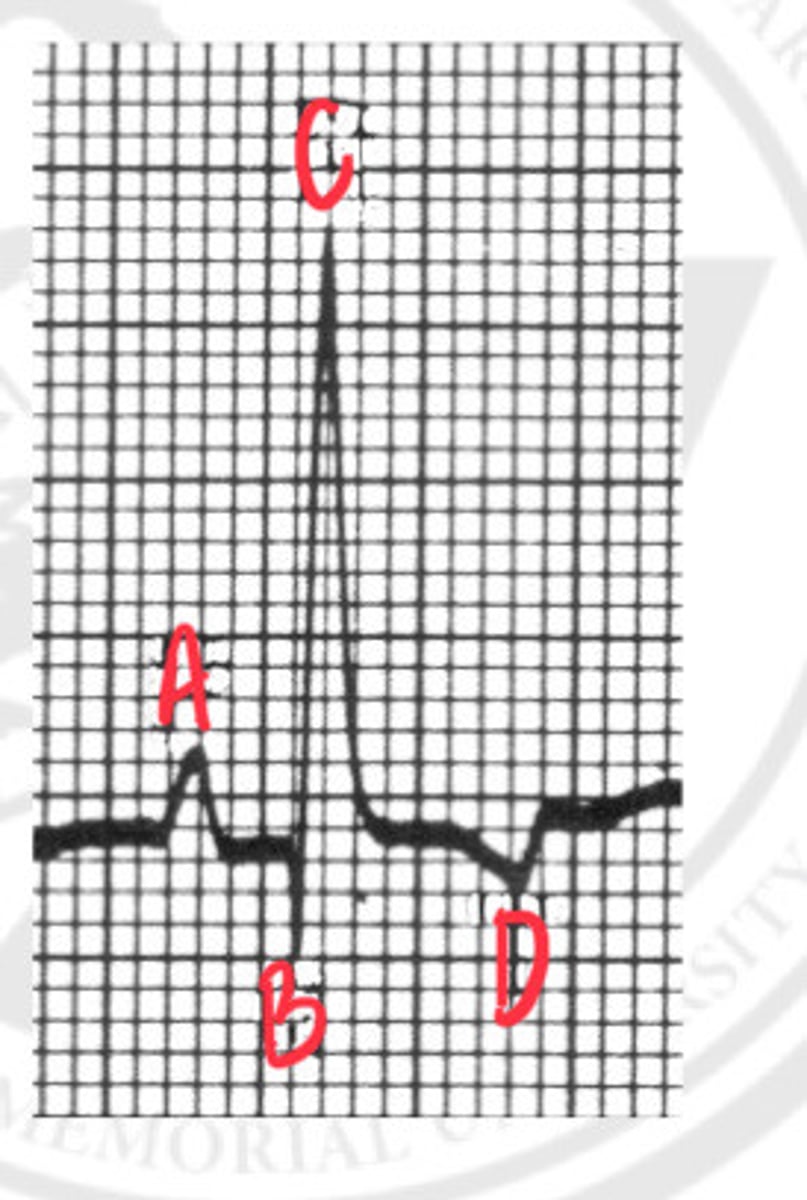
P wave
What is A?
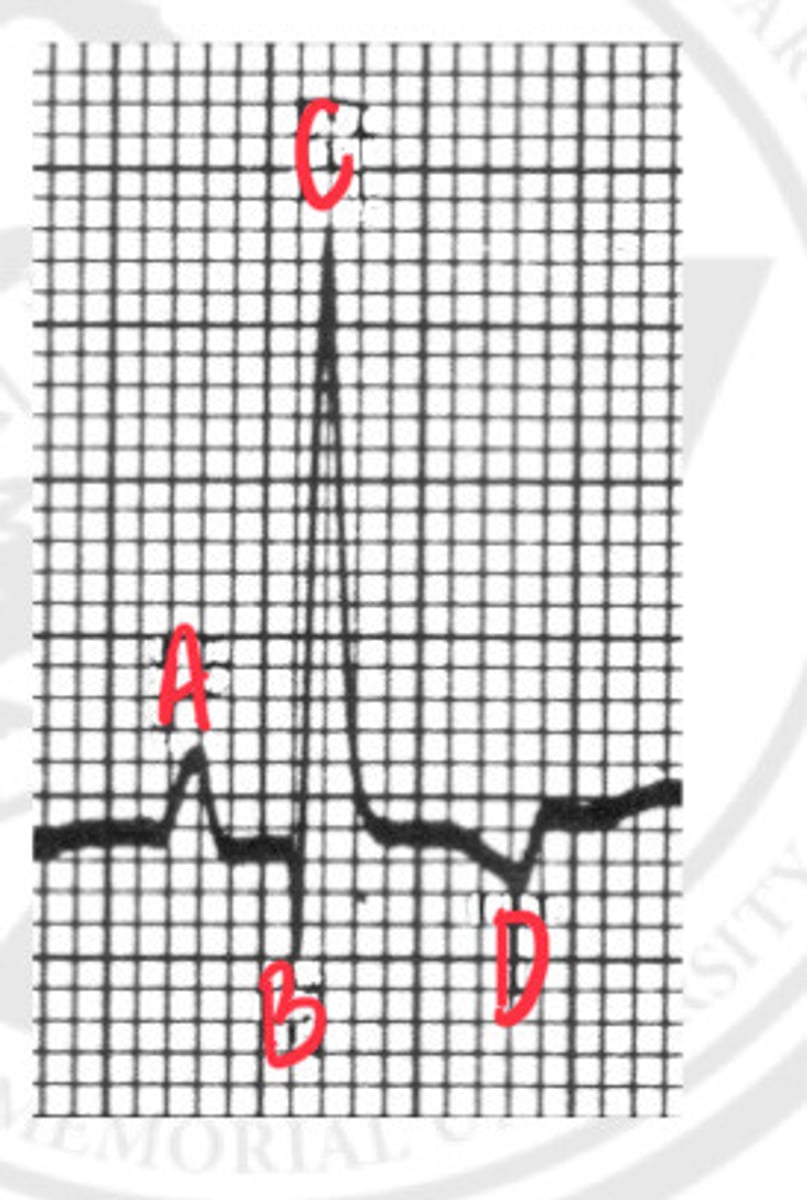
Q wave
What is B?
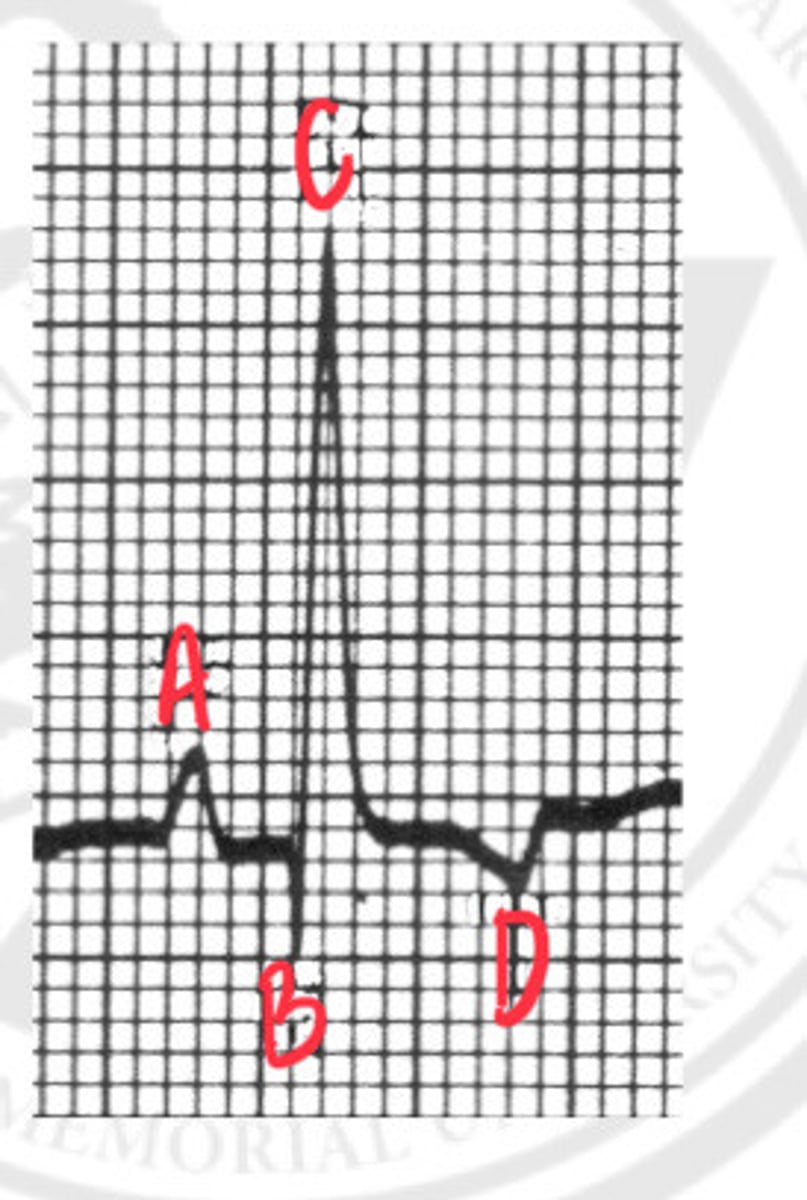
R wave
What is C?
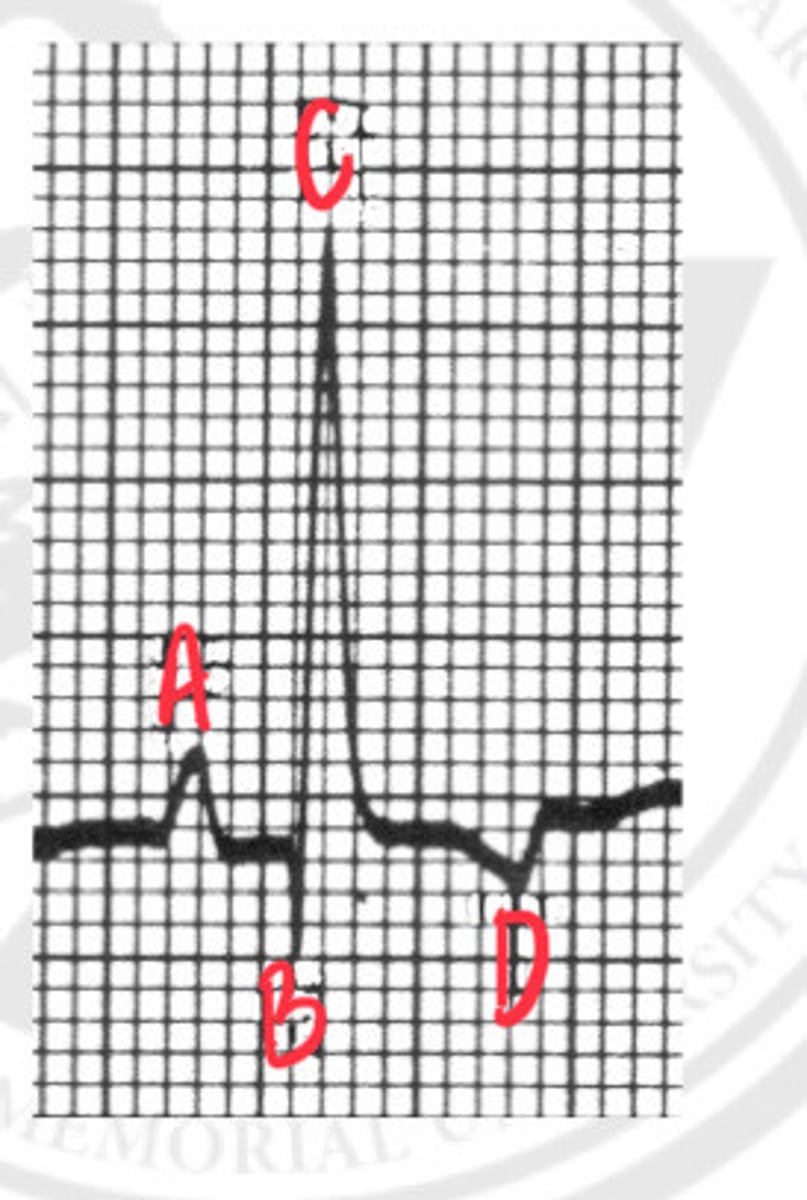
T wave
What is D?
"Tin man" ECG
What is the broad lehman term when you see an ECG like this?
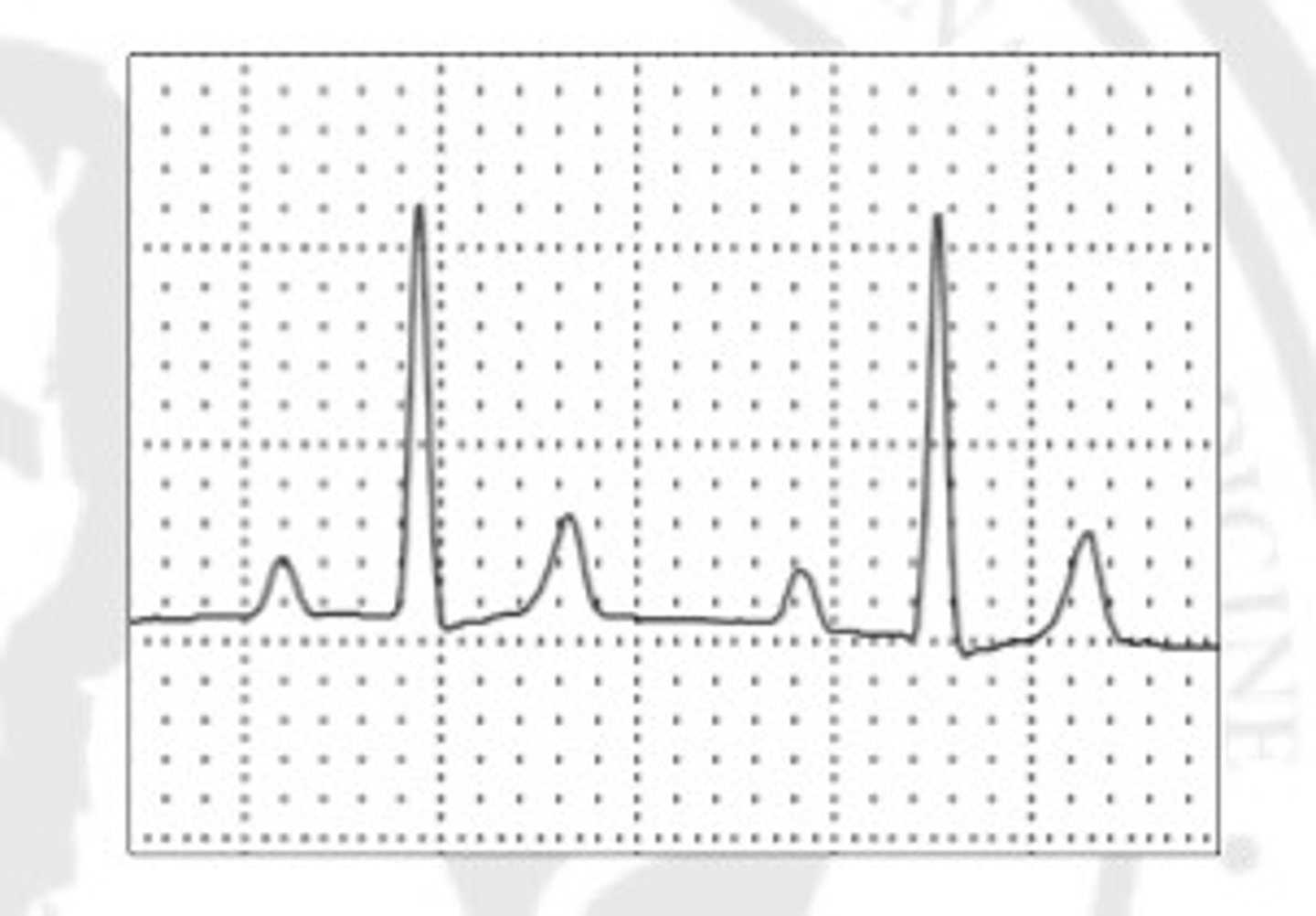
Supraventricular
What is the origin of this ECG?
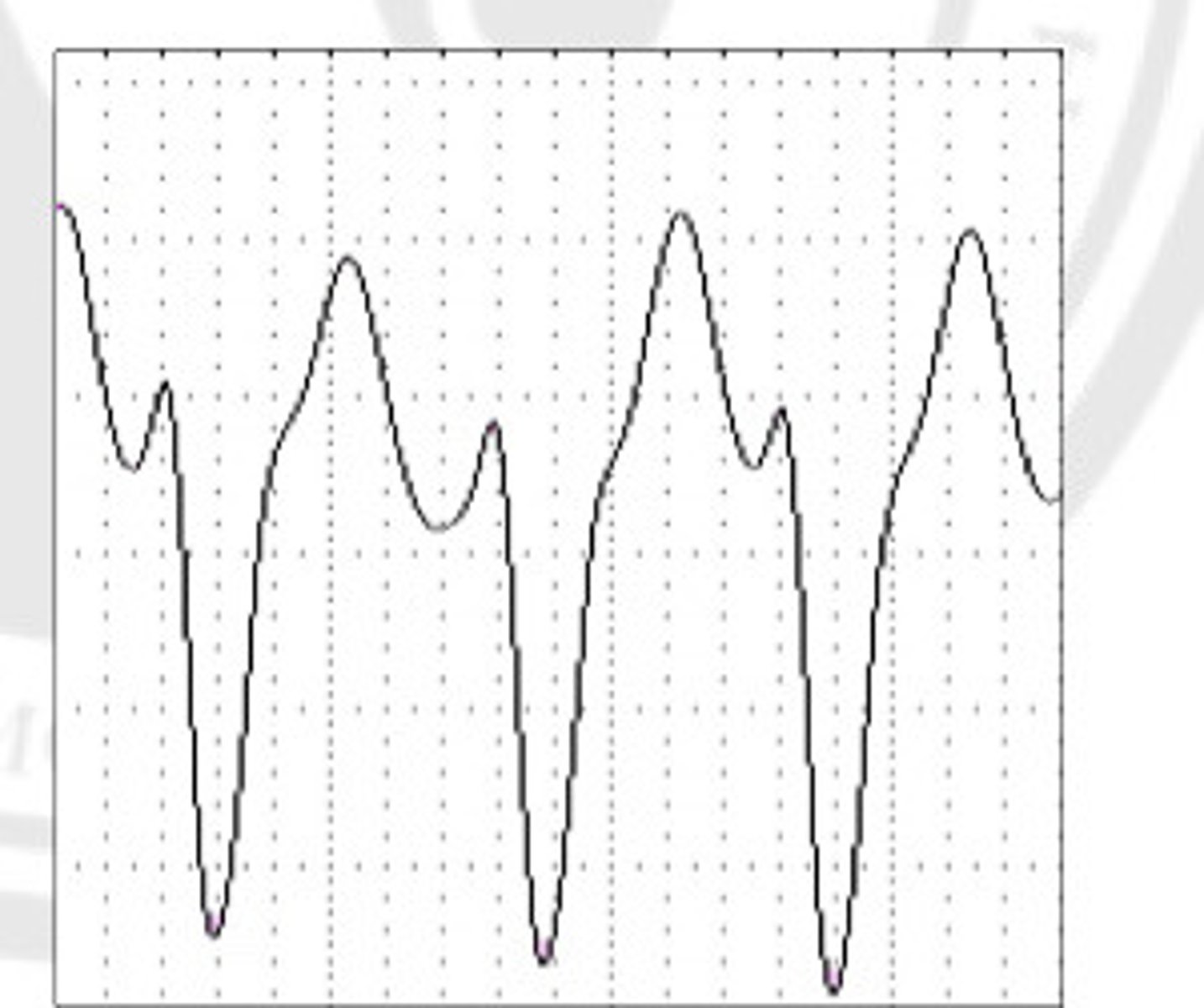
Ventricular
What is the origin of this ECG?
ventricular
What is the origin of this ECG?
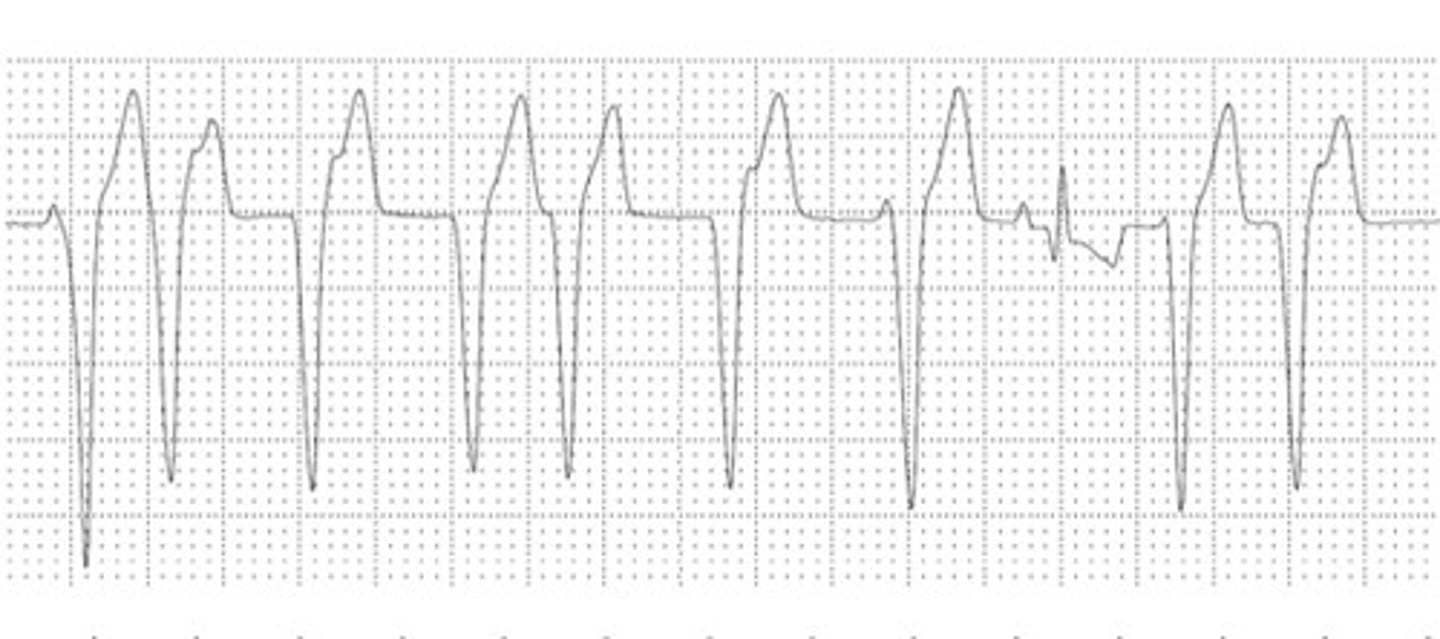
Ventricular origin
What is the origin of this ECG?
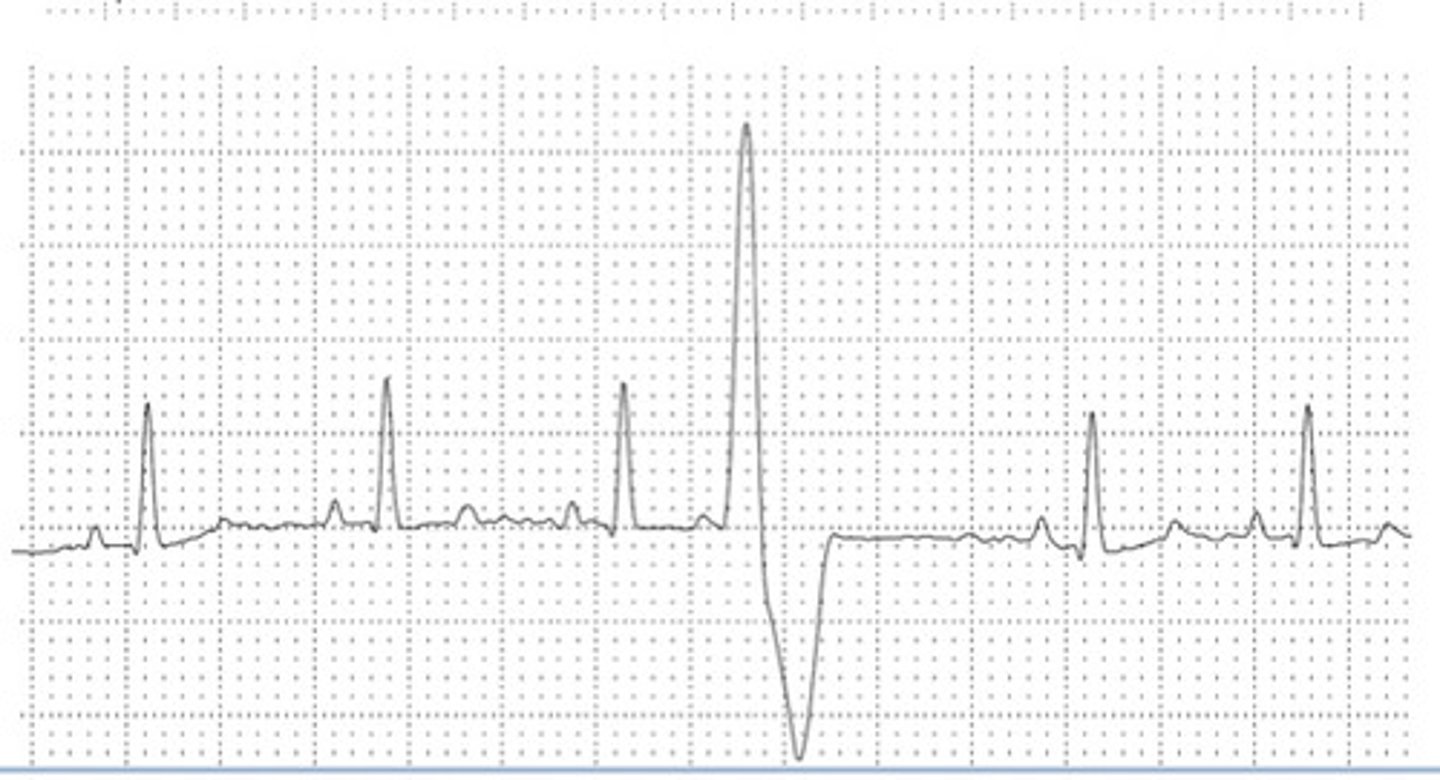
ventricular origin
What is the origin of this ECG?
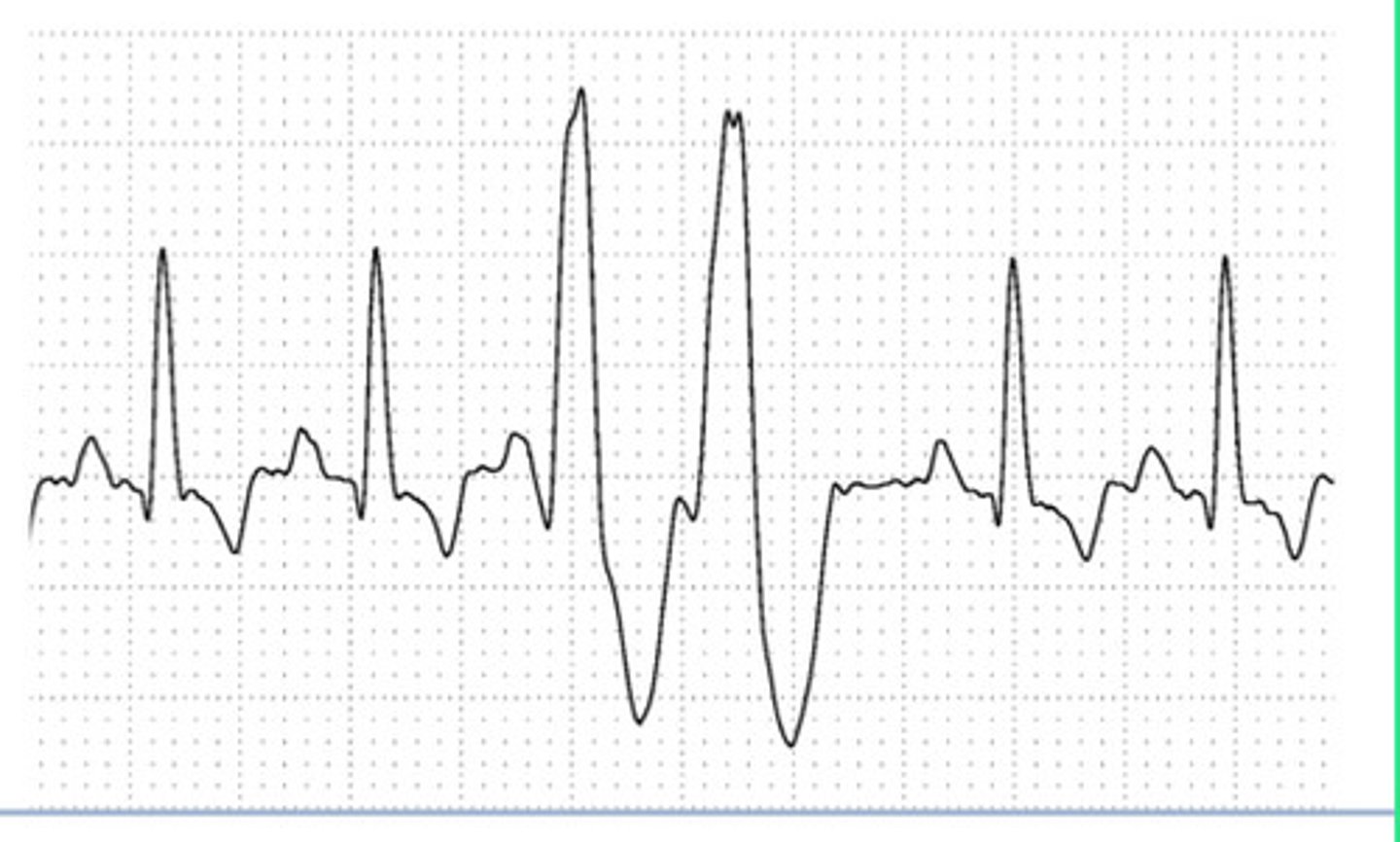
Ventricular Origin
What is the origin of this ECG?
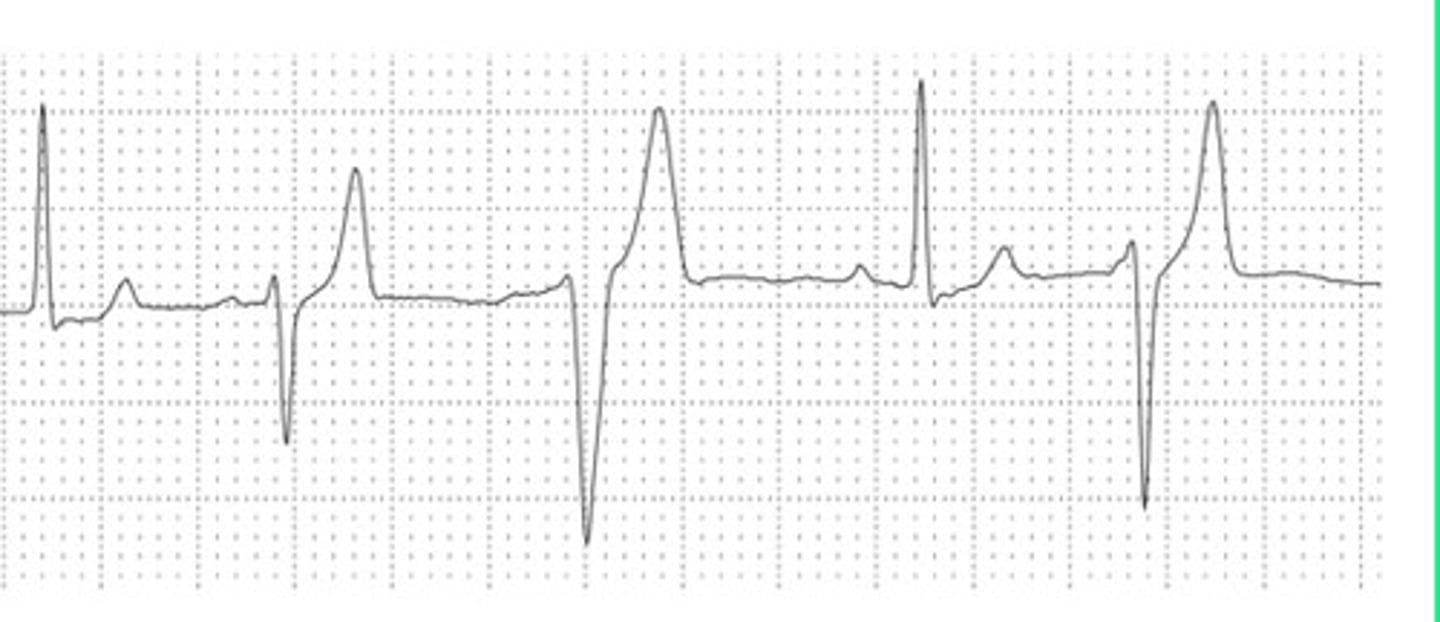
Count small squares, large squares, or by R waves
What 3 ways can you get a heart rate on ECG?
Irregular rhythm = cannot draw out pattern over next 6 seconds
How do you define an irregular rhythm? Over what period of time?
Sinus arrhythmia
What is a "regularly irregular" pattern called, where you can consistently identify positive P waves on a lead II ECG?
SUPRAVENTRICULAR: normal QRS complex
VENTRICULAR: bizarre and wide WRS complexes
How can you tell if a wave has supraventricular or ventricular origin on an ECG?