Newton's laws of motion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Newton's 1st Law
An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force, and an object in motion will remain in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an external force. This law is often referred to as the law of inertia.
Newtons 2nd law
F=ma
Newtons 3rd law
For every action there is an equal/opposite reaction
Pitch
Related to the Frey of a sound wave
Young's modulus
measures a material's ability to withstand changes in length when compressed or stretched lengthwise. It's calculated by dividing the longitudinal stress by the strain.
Bulk modulus
material's ability to resist changes in volume when compressed from all sides.
Shear modulus
measures the amount of tangential force applied per unit area to the angular deformation in radians. It's calculated by dividing the shearing stress by the shearing strain
elastic modulus
general term for measuring a material's elasticity. It quantifies a material's resistance to non-permanent, or elastic, deformation
Scalar quantity
A physical quantity that has magnitude only, without direction, such as mass, temperature, or speed.
Bernoulli's principle
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure or potential energy.
Pascal’s principle
Fundamental unit
Unit independent of other units ex: m,s,k
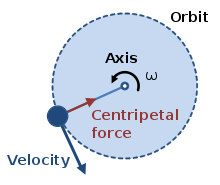
Centripetal force
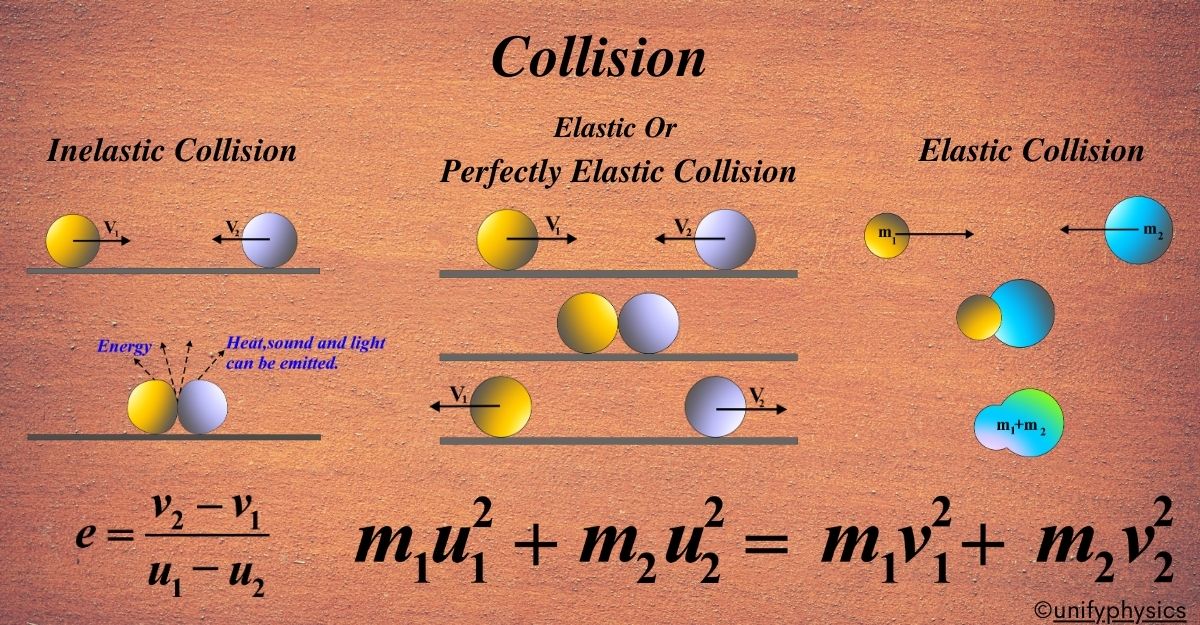
Elastic vs inelastic
Work energy there
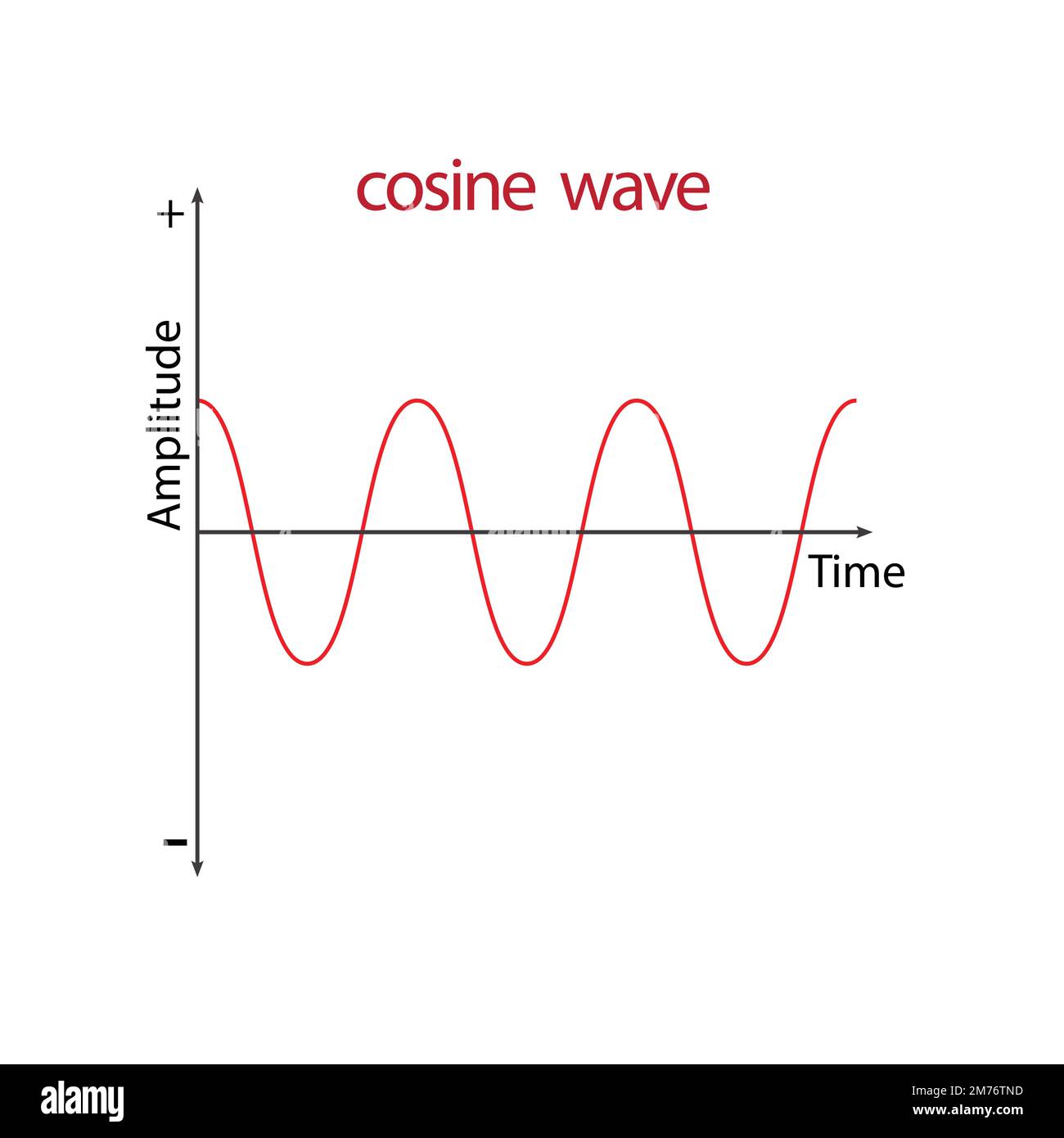
Cos wave
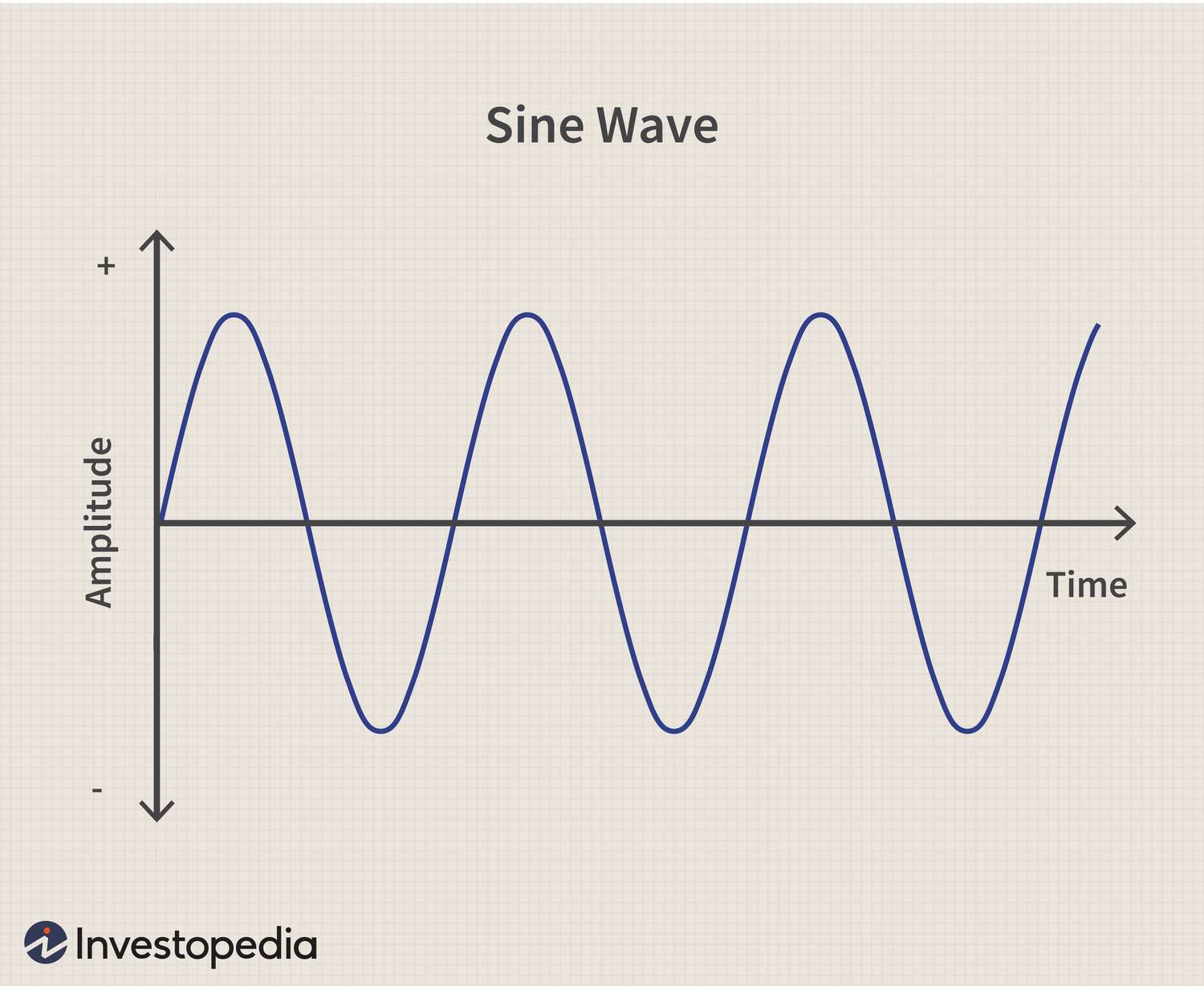
Sin wave
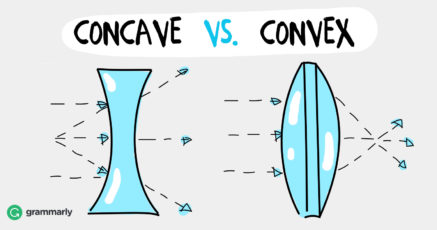
Convex vs concave
Pascals law

Alpha particle
4,2
Beta particle
O - l
Gamma
0/0
Scaler
No direction