Systems Path Section 5- The heart pg 26-50
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
left ventricle overworked by increased HTN
systemic hypertensive heart disease
complications associated with systemic hypertensive heart disease
CHF, arrhythmia, stroke, renal failure
how does systemic hypertensive heart disease occur?
hypertrophy of left ventricle not accompanied by increased blood supply
who gets systemic hypertensive heart disease?
those with history of HTN (African Americans)
possible causes of systemic hypertensive heart disease
stress, high sodium, low physical activity, atherosclerosis
right sided heart disease due to a lung pathology causing right ventricular hypertrophy
pulmonary hypertensive heart disease
acute pulmonary hypertensive heart disease is associated with what?
large PE (saddle embolism) which obstructs pulmonary a.
chronic pulmonary hypertensive heart disease is associated with what?
prolonged lung pathology
what accounts for 30% of all birth defects ranging from mild to severe/lethal?
congenital heart disease
risks associated with congenital heart disease
prematurity, trisomies, teratogens, material diabetes, fetal infection
left-to-right shunts
VSD, ASD, PDA
right-to-left shunts
tetralogy of fallout, transposition of great arteries
examples of obstructed flow causing CHD
valve stenosis, aortic coarctation
MC congenital heart defect (left-to-right shunt in ventricles)
ventricular septal defect
how does VSD occur?
increased pressure on R side of heart and pulmonary circulation
2nd MC congenital heart defect (left to right shunt in atria)
atrial septal defect
congenital malformation involving four distinct heart defects (right to left shunt)
tetralogy of fallot
the defects associated with tetralogy of fallot
VSD, pulmonary valve stenosis, overriding aorta, R ventricular hypertrophy
tetralogy of fallot is the MC congenital heart disease to cause ________
cyanosis
tetralogy of fallot is characterized by a ______ - shaped heart
boot
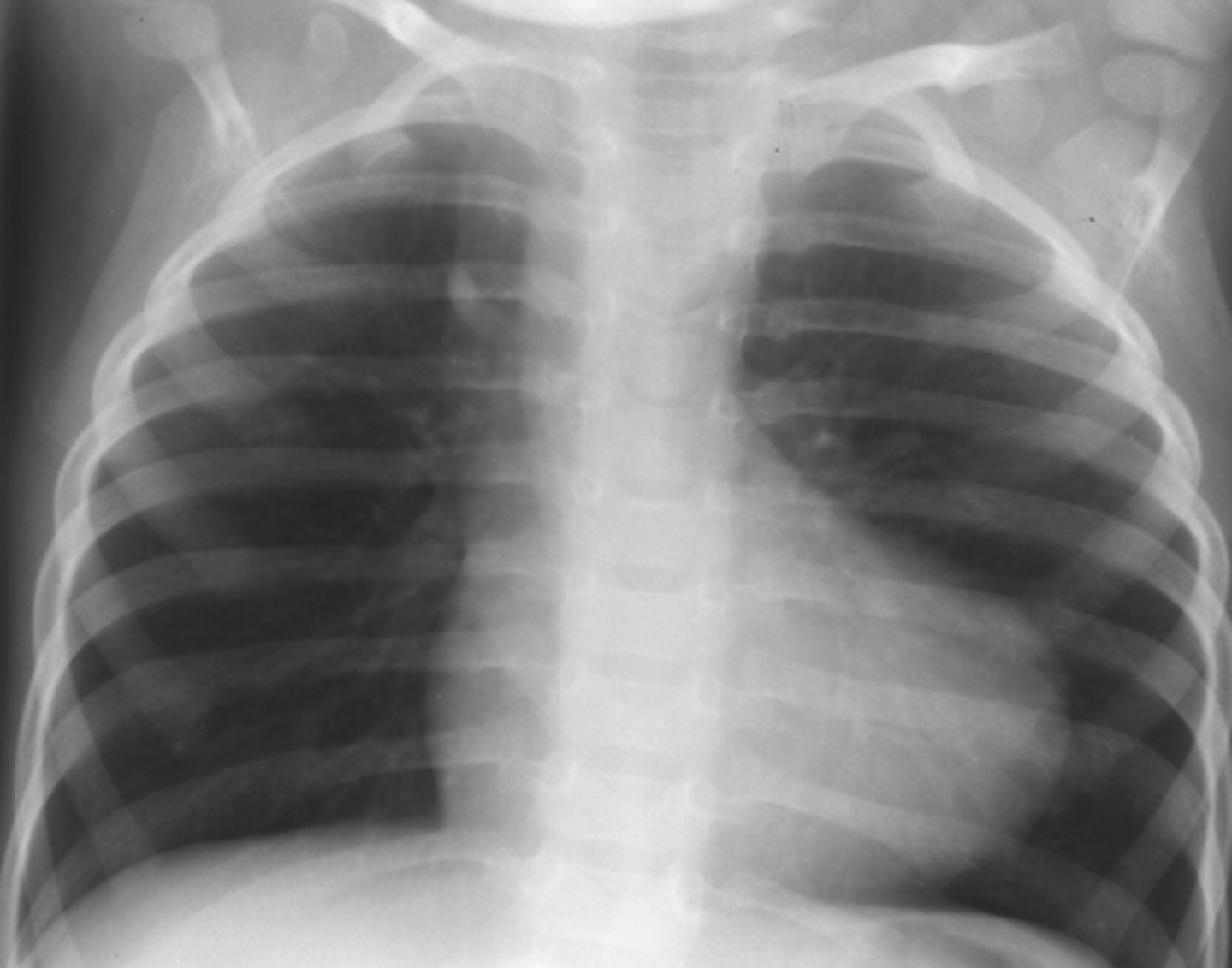
how does tetralogy of fallot occur?
4 malformations -> deoxygenated blood to be pumped into circulation -> cyanosis
swapped aorta and pulmonary trunk which is "incompatible with postnatal life" if no intervention is done = cyanosis + death
transposition of the great arteries
with transposition of the great arteries, the right ventricle is connected ->
aorta
with transposition of the great arteries, left ventricle is connected ->
pulmonary artery
how does transposition of the great arteries occur?
R ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into systemic circulation