alkene reactants/ reactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what side of the molecule does the H+ add on to
the least substituted side (less amount of carbons)
hydrohalogenation: HCL, HBr, HI result in what product?
additional if both h and the halogen x; h in less substituted and x in most subst.; markovnikov rule
acid catalyzed hydration: H2SO4, H2SO4/H2O, H3O+
adding H and OH; h added to less substituted side oh added to more substituted mark.
oxymercuration-demercuration: (1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O/ (2) NaBh4
adding an H and OH (mark); H adds to less substituted side
1) HgOAc adds to both carbons (on double bond)
water attacks sp3 carbon (most bonded (3 single bonds)); oxygen attaches
add second water molecule to deprotenate (turn the h2o into oh)
2) NaBH4 just adds a hydrogen in replacement of HgOAc
hydroboration- oxidation: BH3, THF/ H2O2, NaOH
adds an h and oh; ANTI MARK
1) B attaches to LESS substituted side; a hydrogen breaks off the b as well and goes to the other side of bond
= end up with bh2
transition state: draw potentials (dotted lines) for the double bond and connection of h and bh2
2) after having bh2, create b attached to 3 separate propyl groups (photo attached)
replace them all with oh’s using h2o2, naoh reactants
acid catalyzed alcohol addition: H2SO4/CH3OH
adding an h and an OR group ( or is oxygen and methyl)
same steps as acid catalyzed hydration
end product = OCH3 instead of a plain OH
alkoxymercuration-demercuration: (1) Hg(OAc)2, CH3OH/ (2) NaBH4
adding H and OR; MARK; sane mechanism as oxymercuration
catalytic hydrogenation: H2/Pd
adding 2 h’s
halogenation: X2/CCl4 or CH2Cl2
adding both halogens to both sides if the double bond
halohydrin formation: X2/H2O or ROH
adding halogen and oh molecule; MARK (halogen on LESS substituted side)
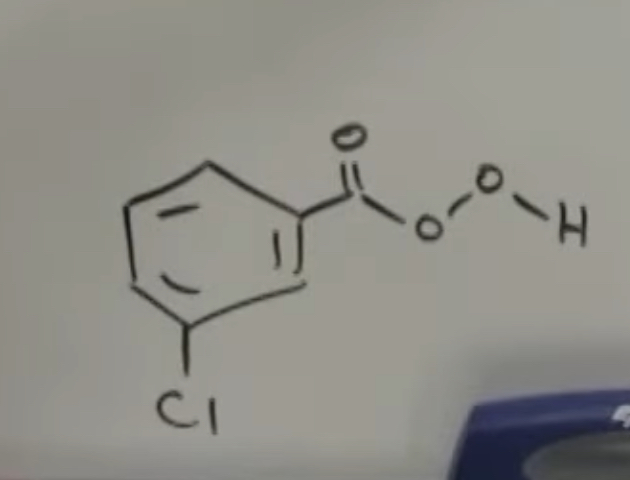
epoxidation & antidihydroxylation: (1) mcpba/ (2) H3O
(mcpba photo attached)
epoxide= hexane ring with o attached to 2 carbons
dihyd. = two oh molecules on OPPOSITE SIDES OF EACH OTHER
syn-dihydroxylation: (1) OsO4/ (2) NaHSO3 and KMnO4/NaOH
adding 2 oh molecules on the SAME SIDE