Digestive anatomy & Physiology
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
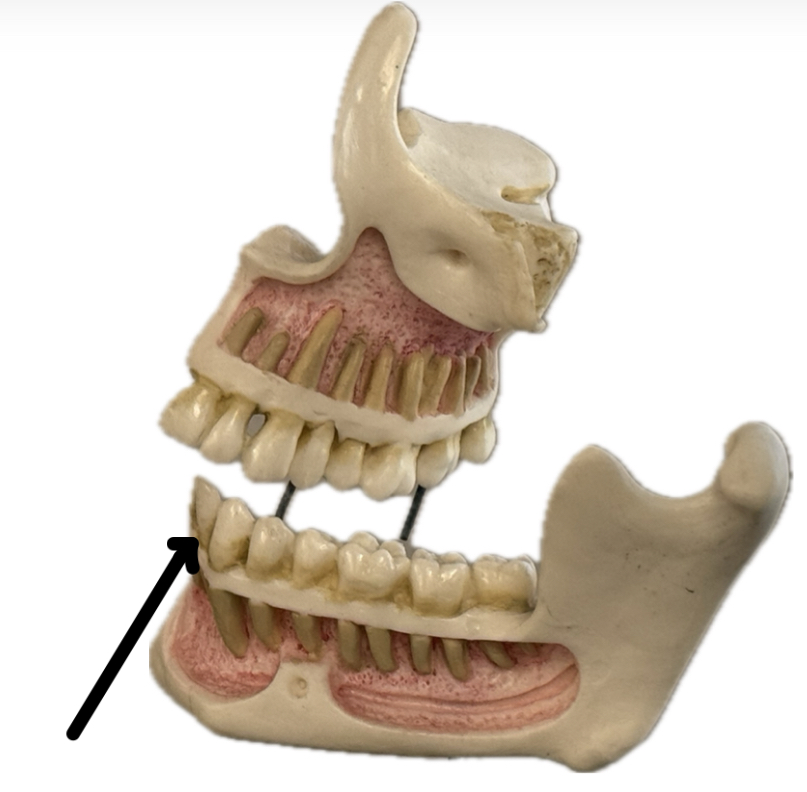
Incisor
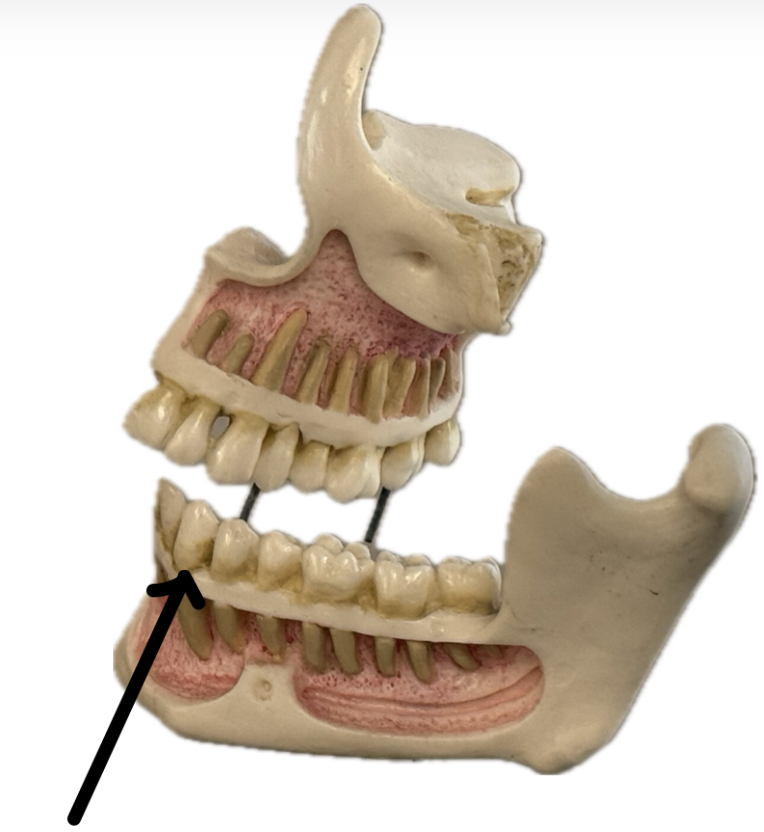
Canine (cuspid)
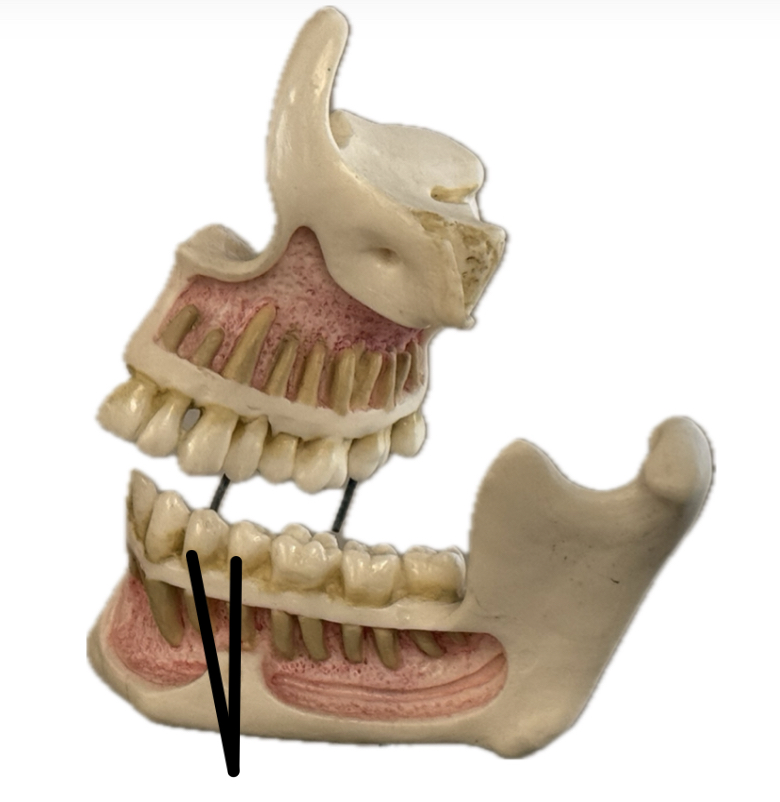
Premolar (bicuspid)
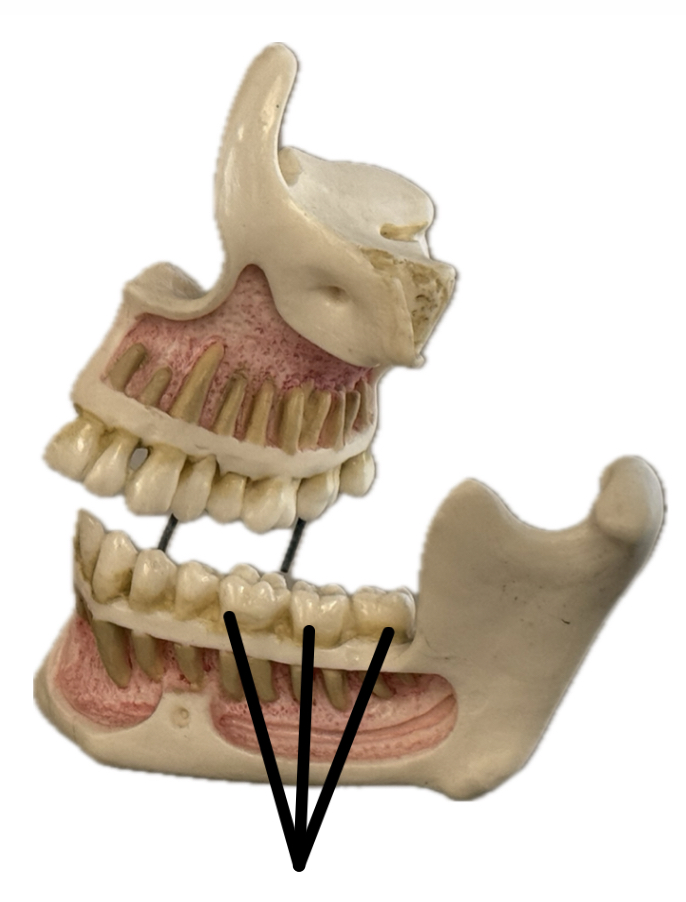
Molar (tricuspid)
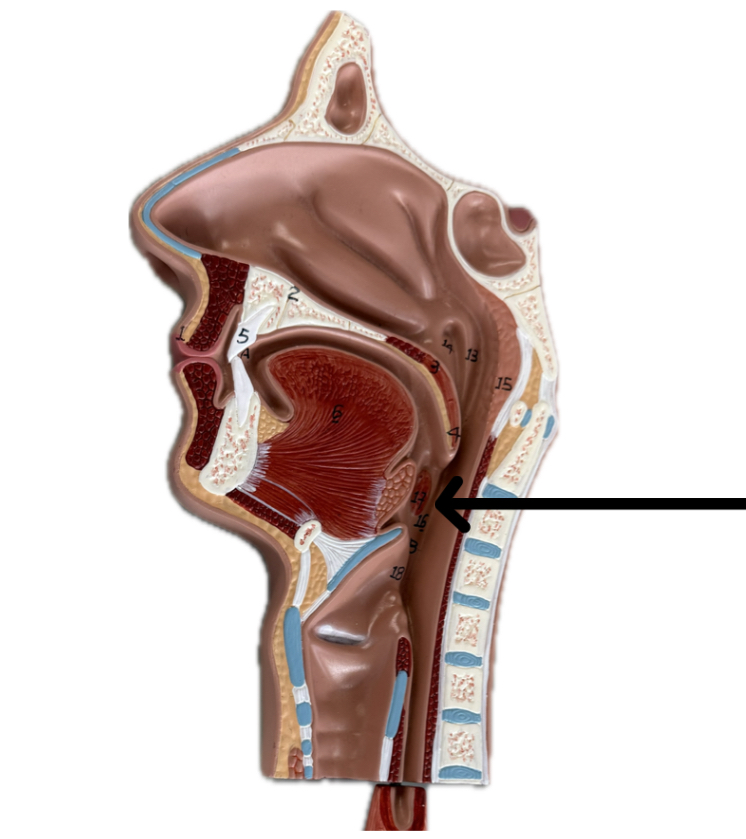
Oropharynx
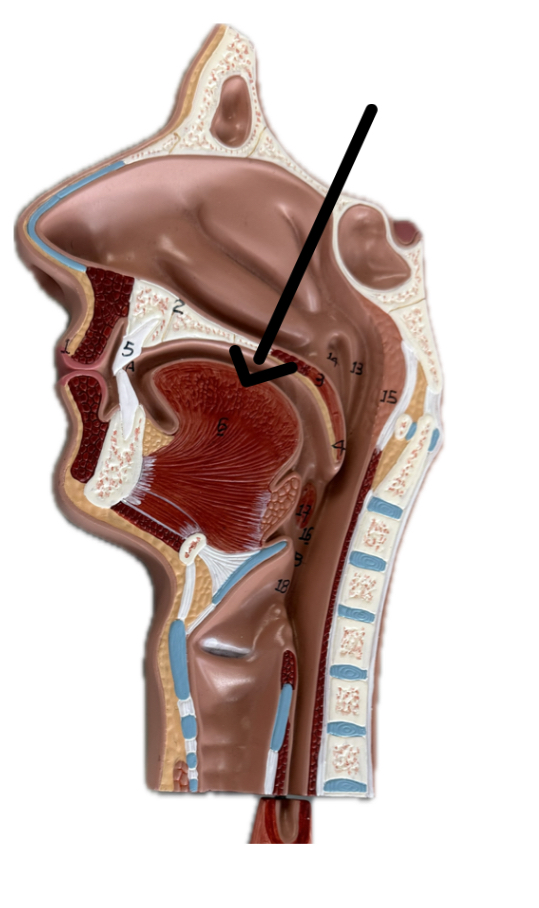
Tongue
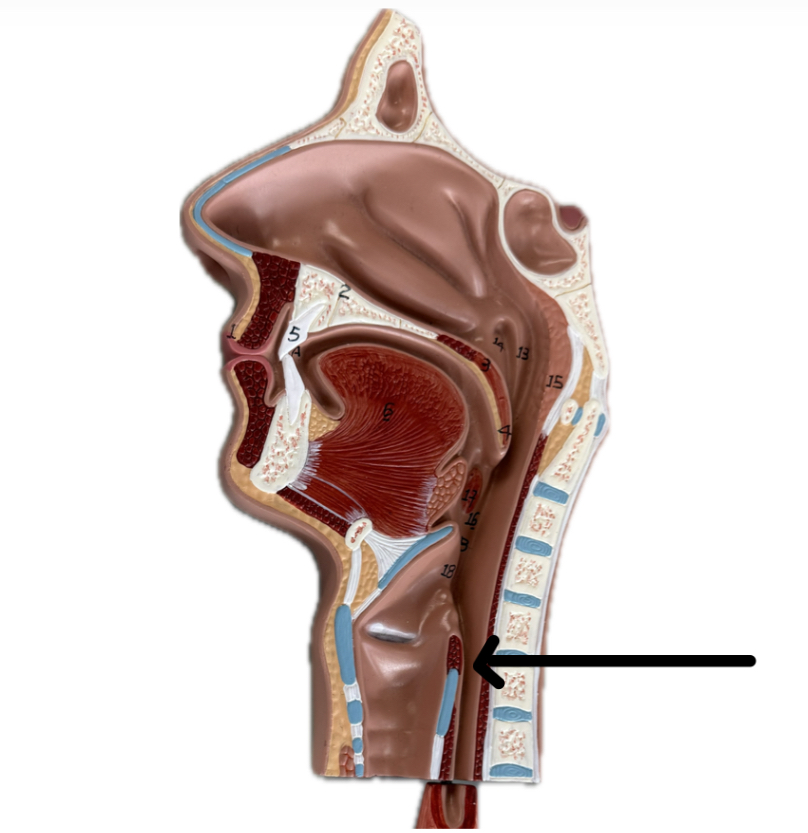
Esophagus
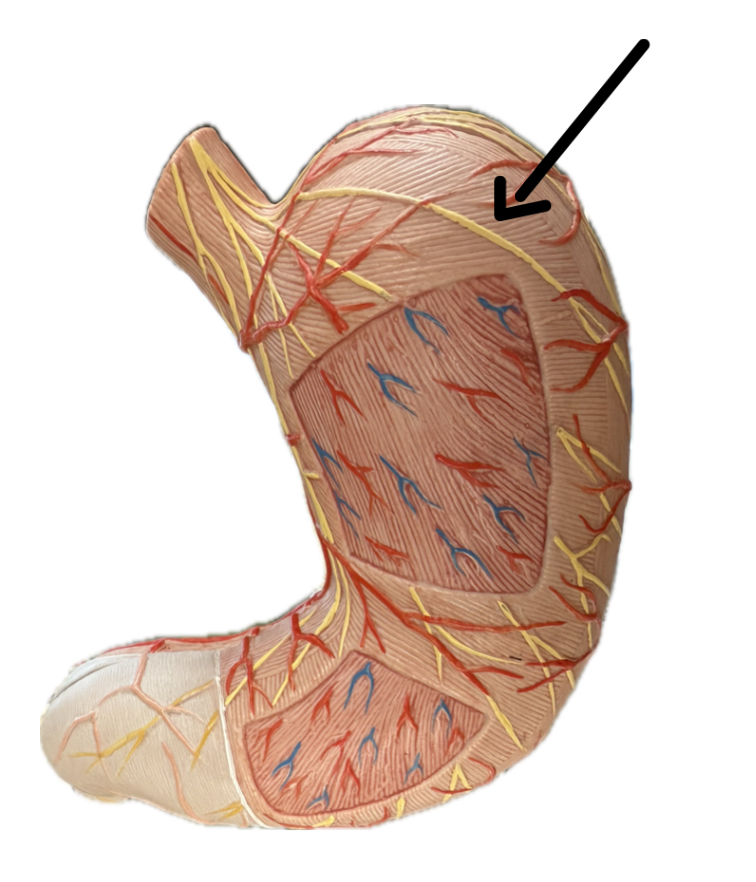
Circular Layer
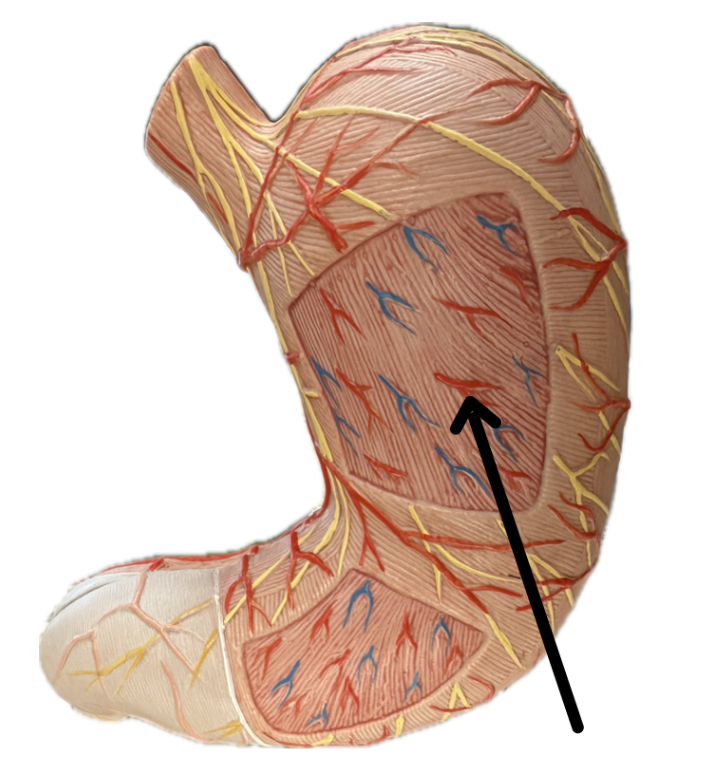
Oblique Layer
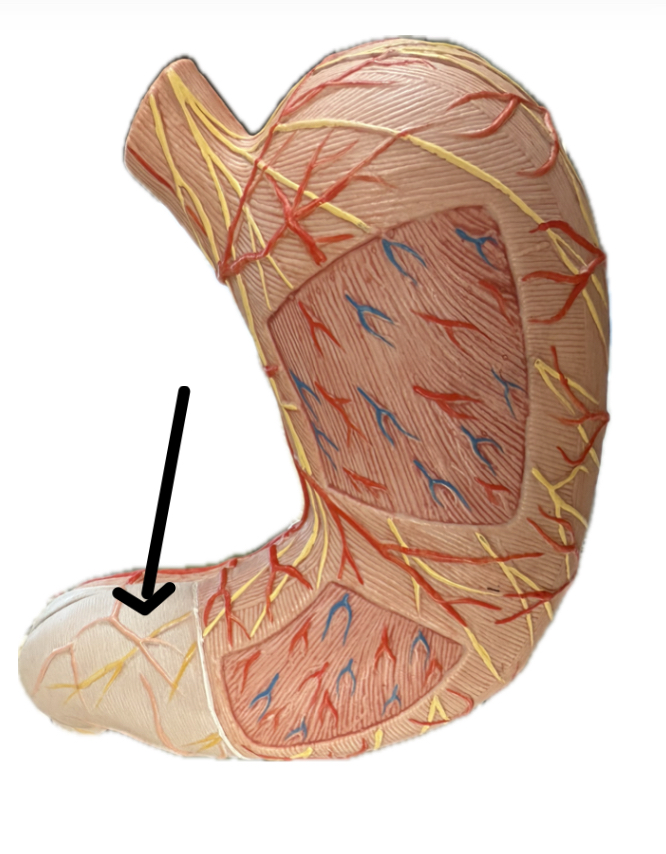
Longitudinal Layer
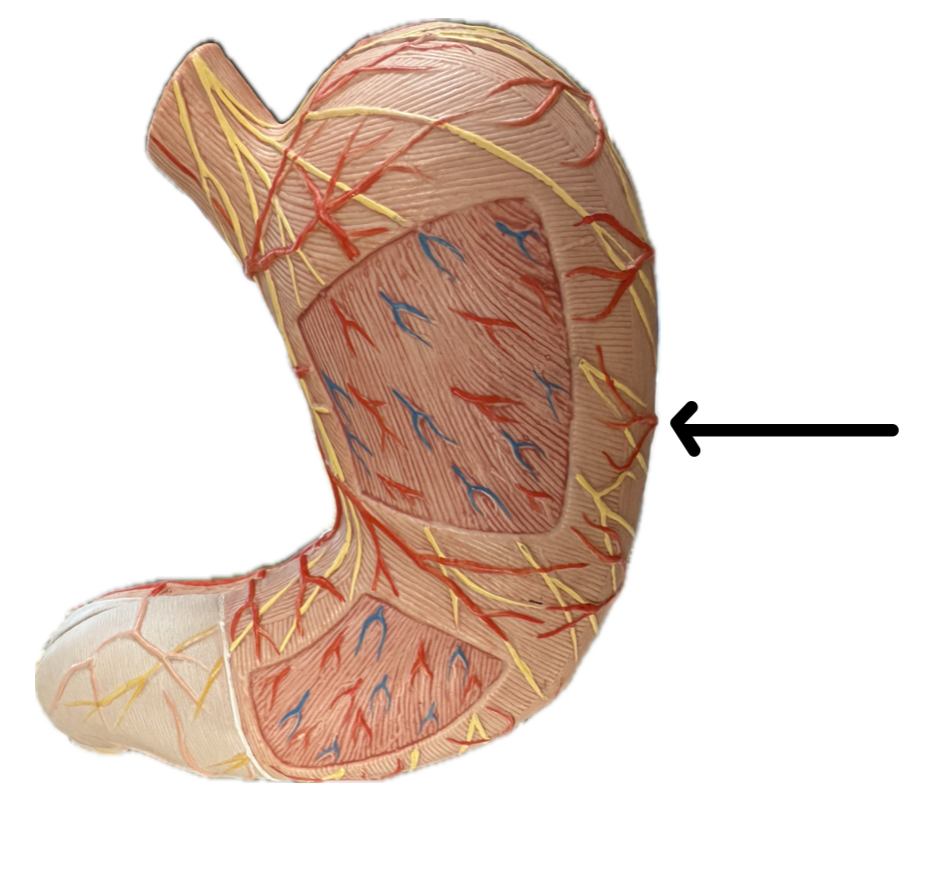
Greater curvature
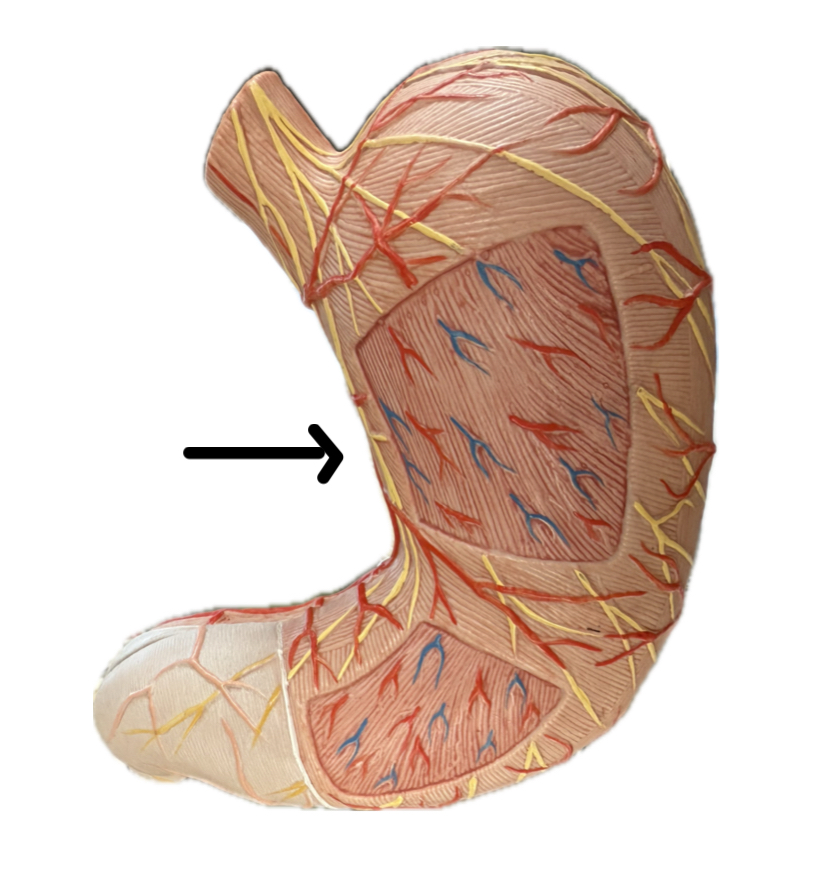
Lesser curvature
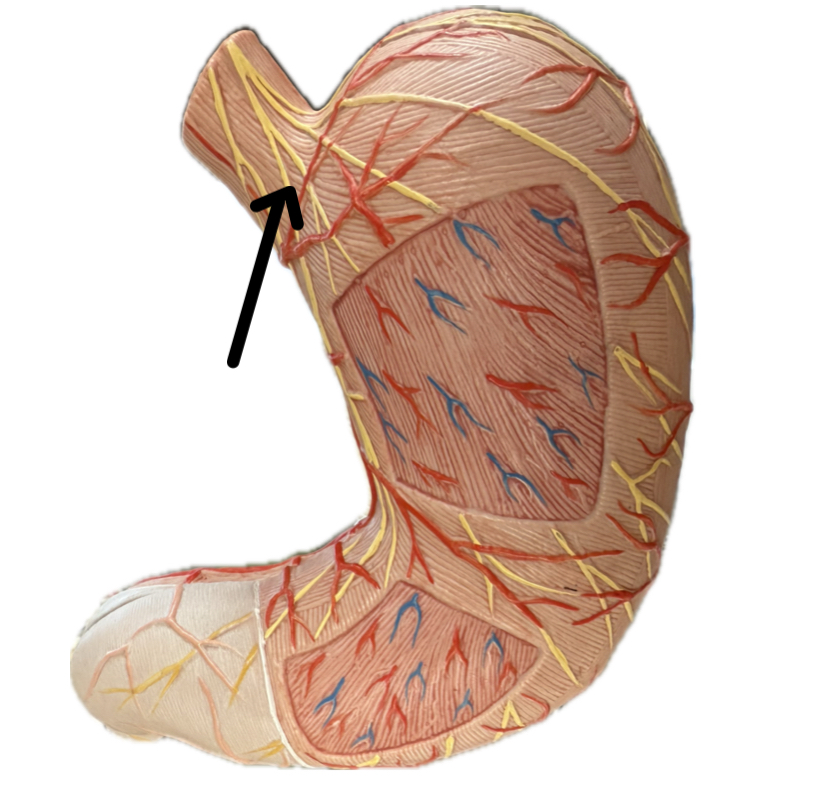
Cardia (gastric region)
Pyloric sphincter
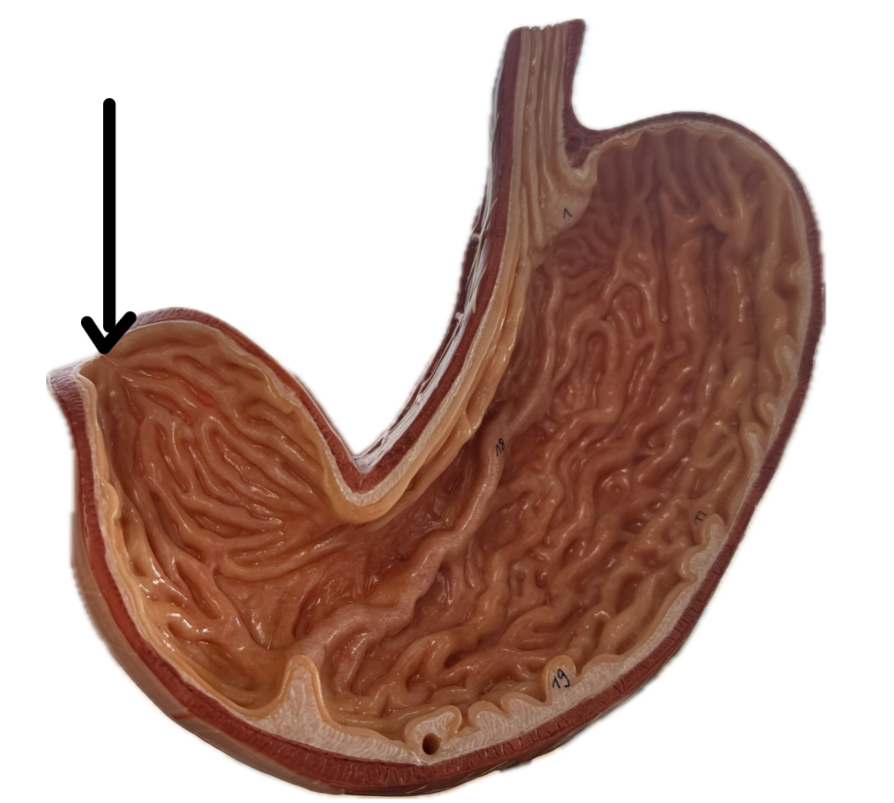
Rugae
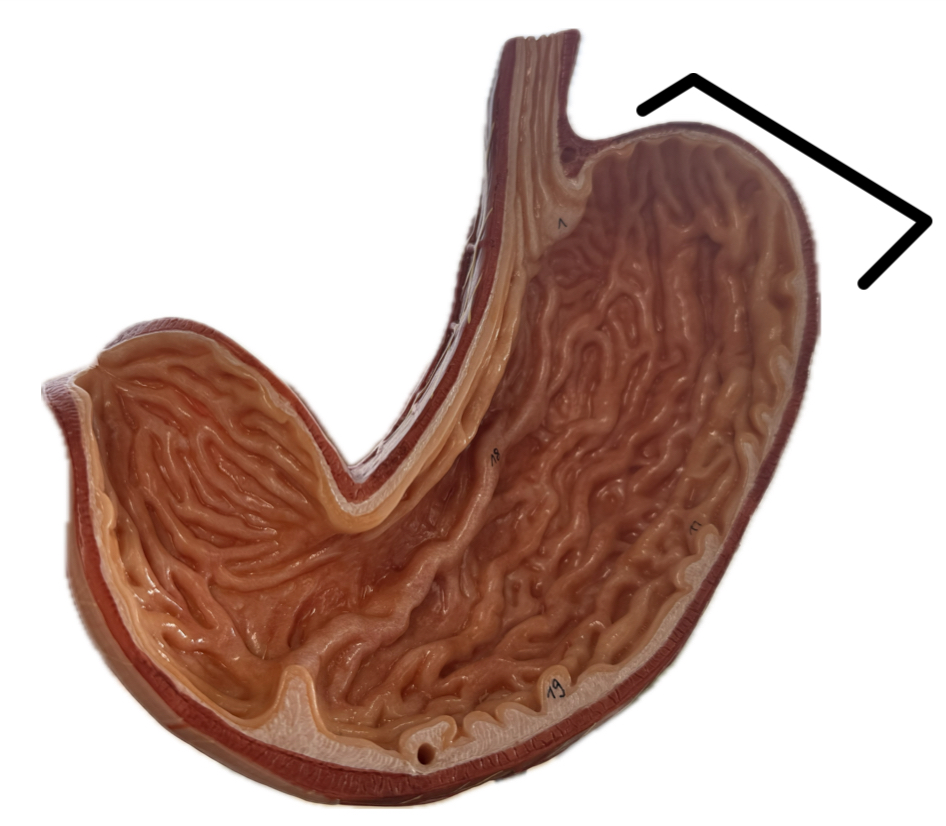
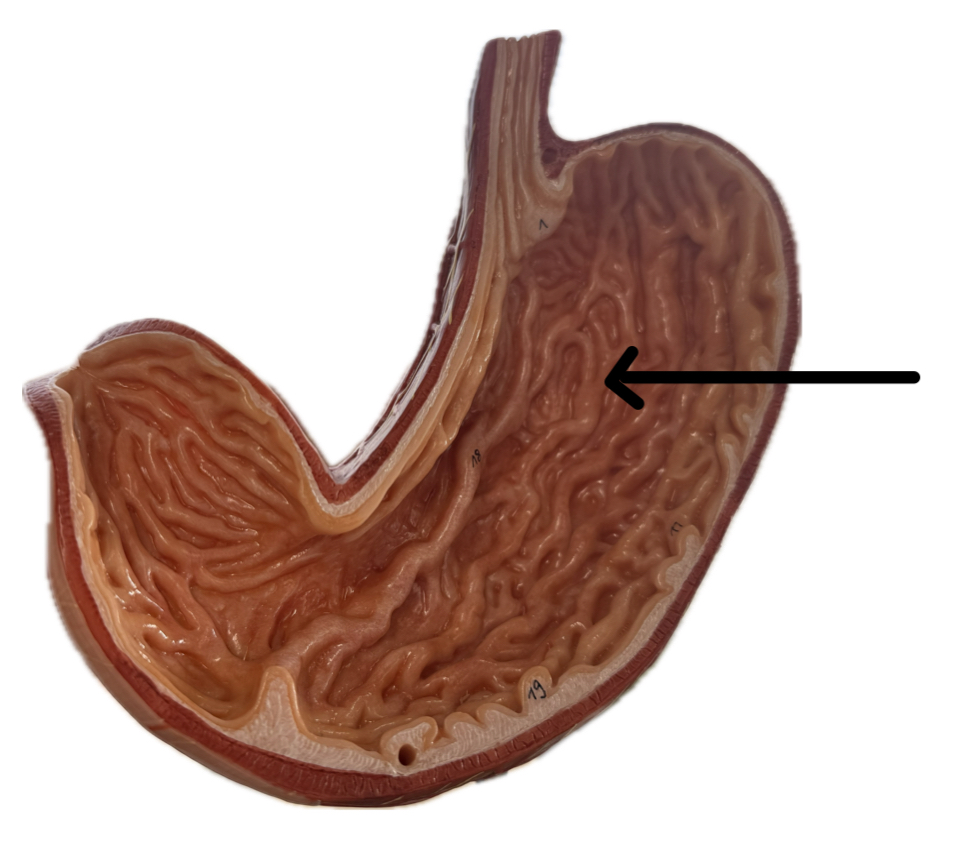
Fundus
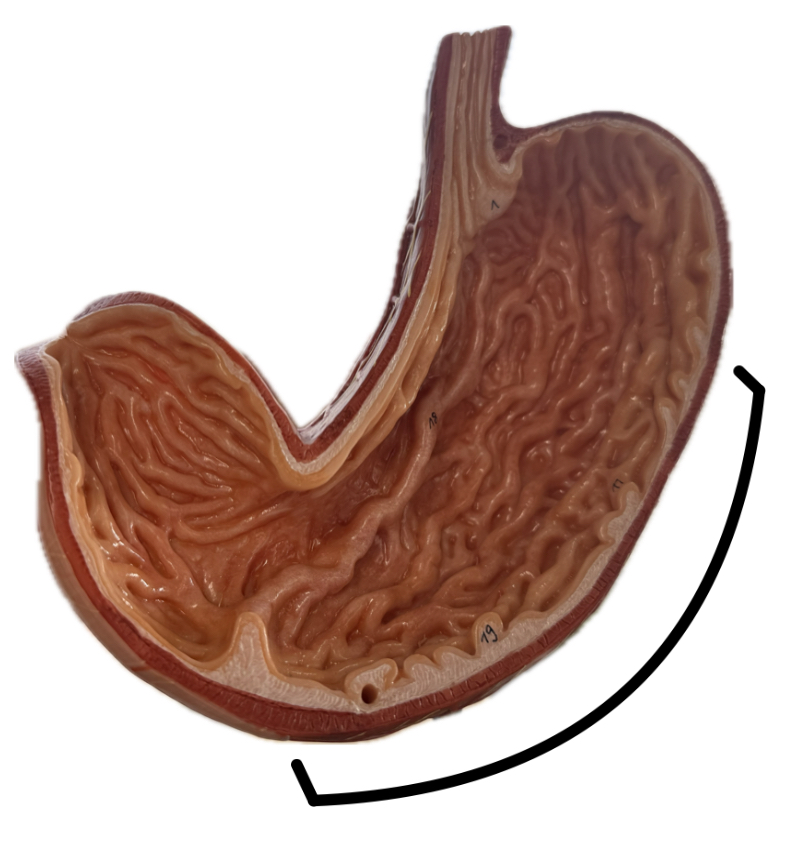
Body
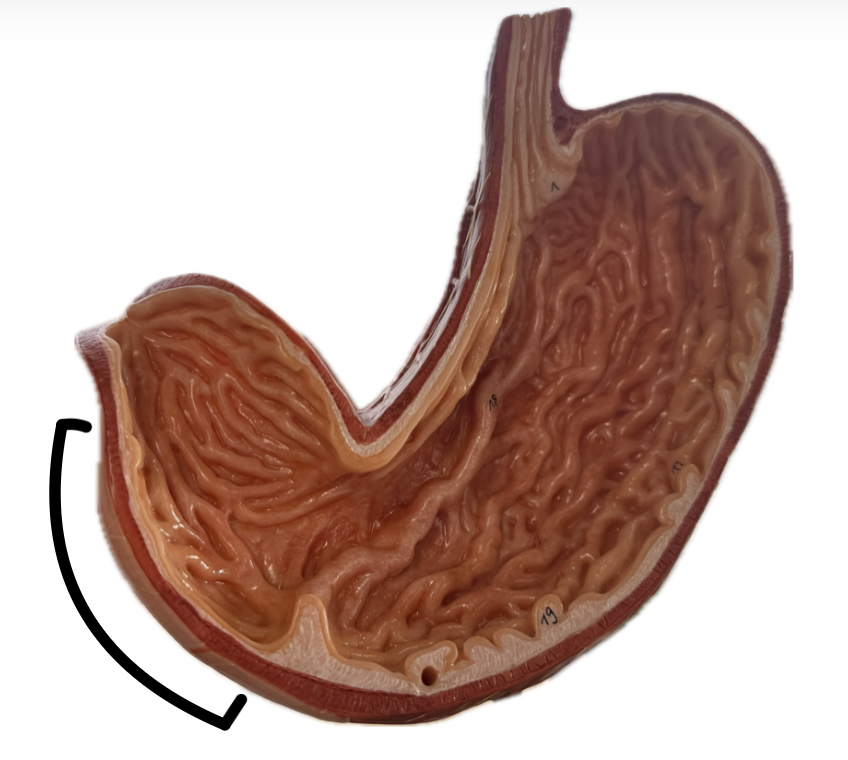
Pylorus
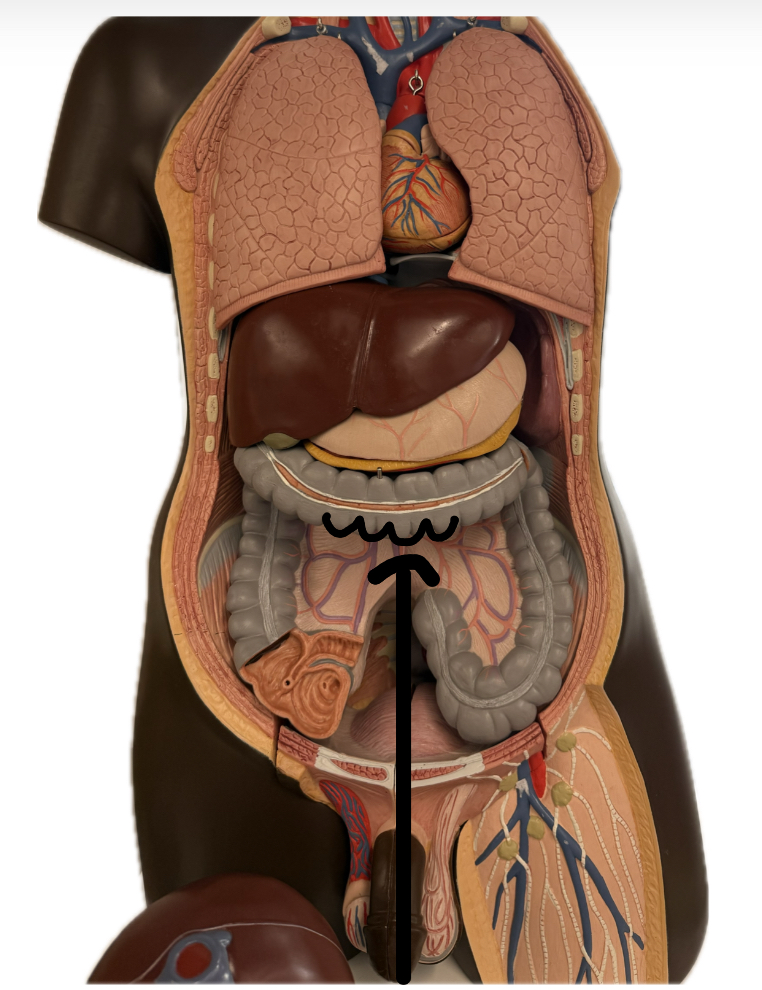
Haustra
Cecum
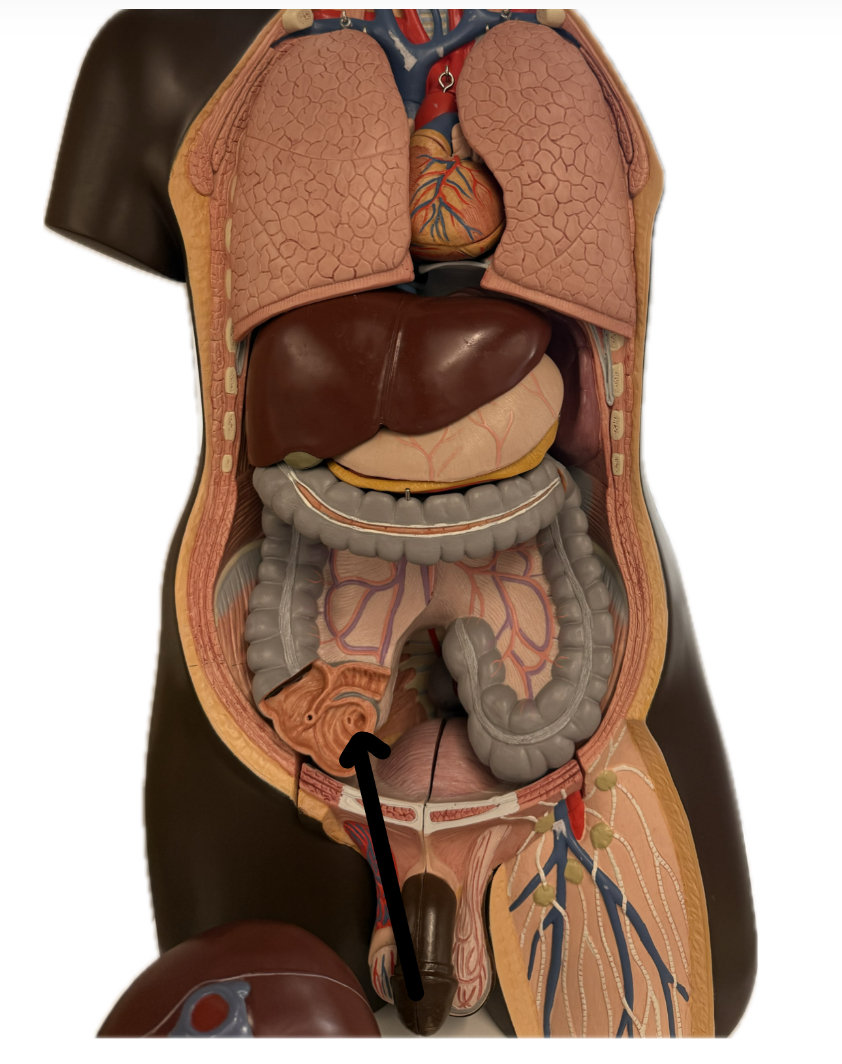
Ileocecal valve
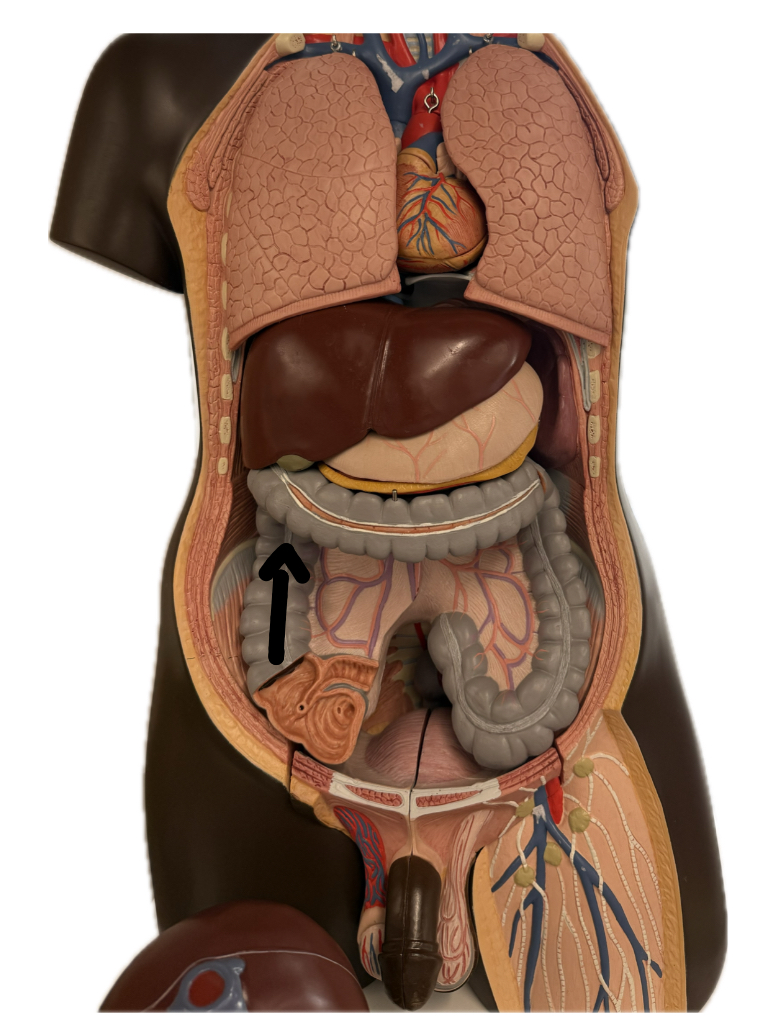
Ascending colon
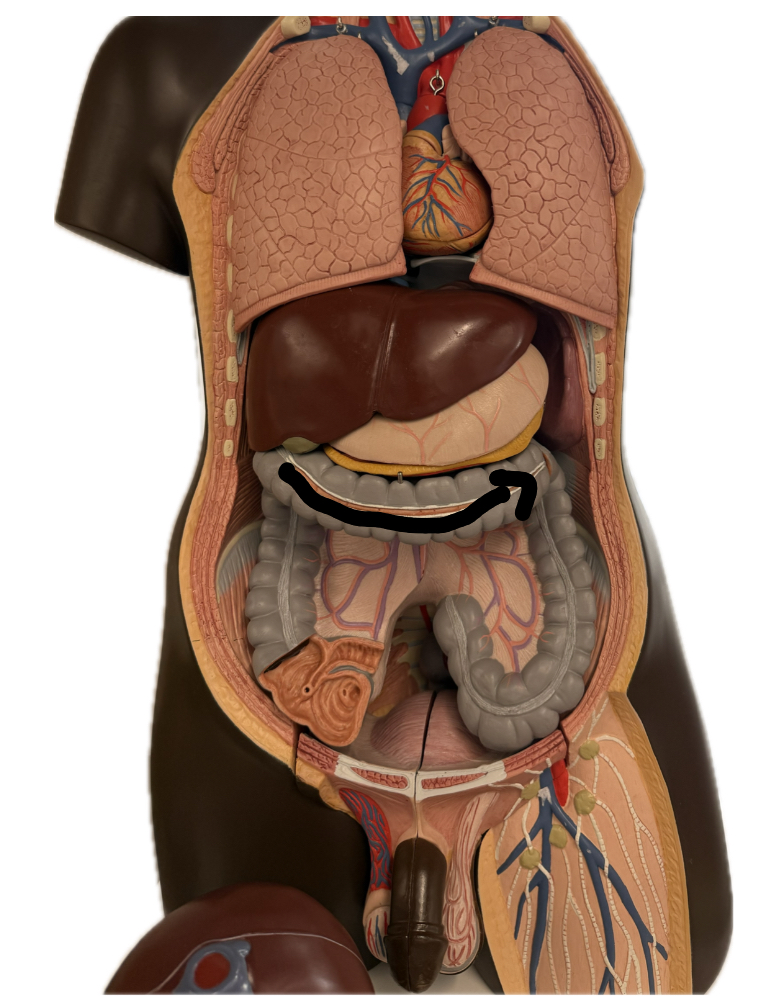
Transverse colon
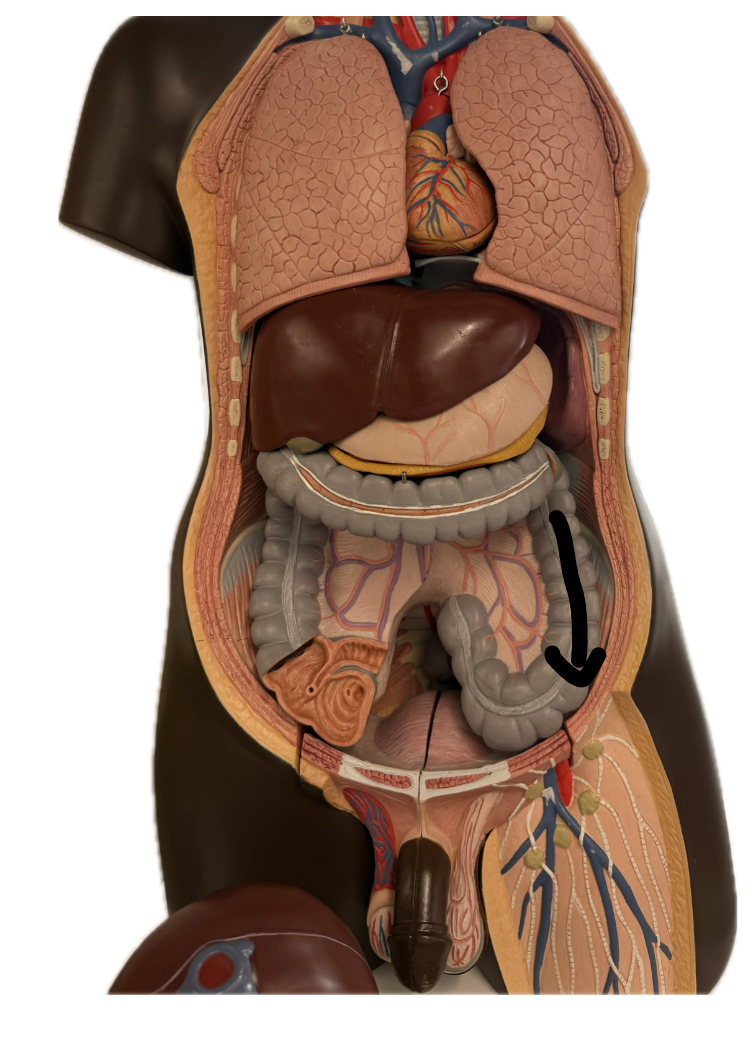
Descending colon
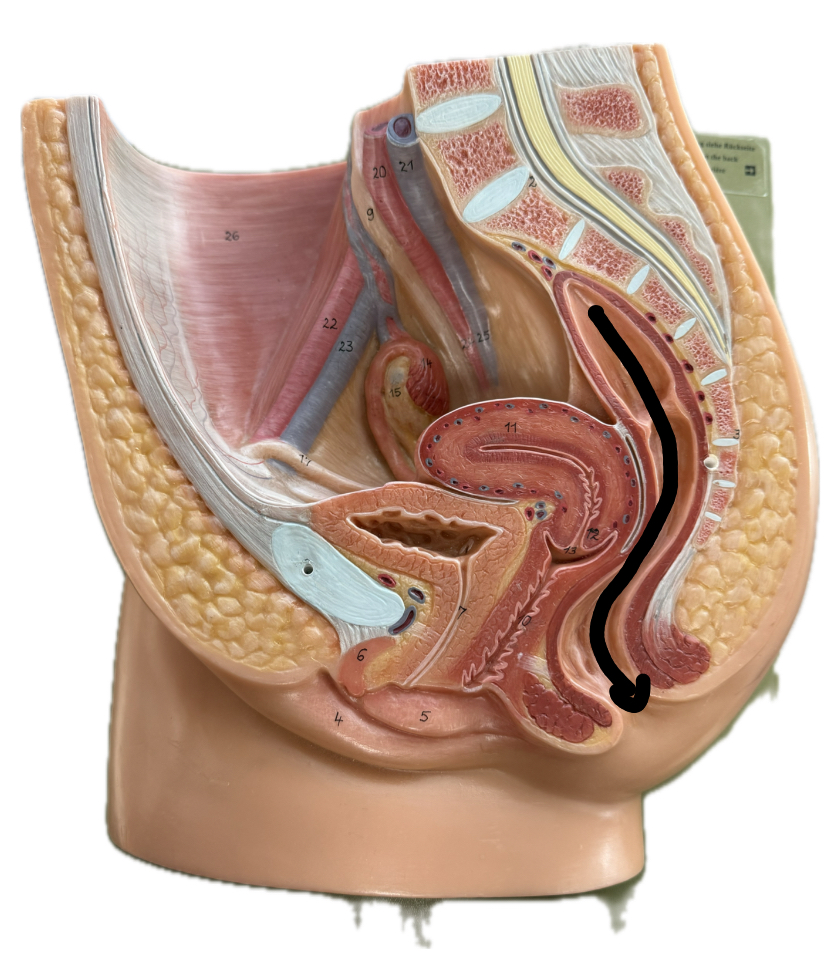
Sigmoid colon
Rectum
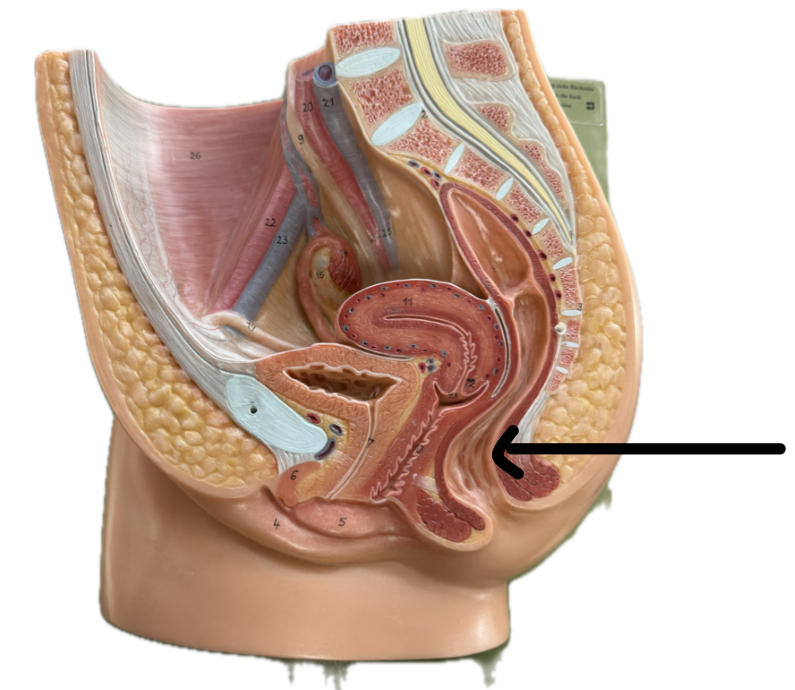
Anus
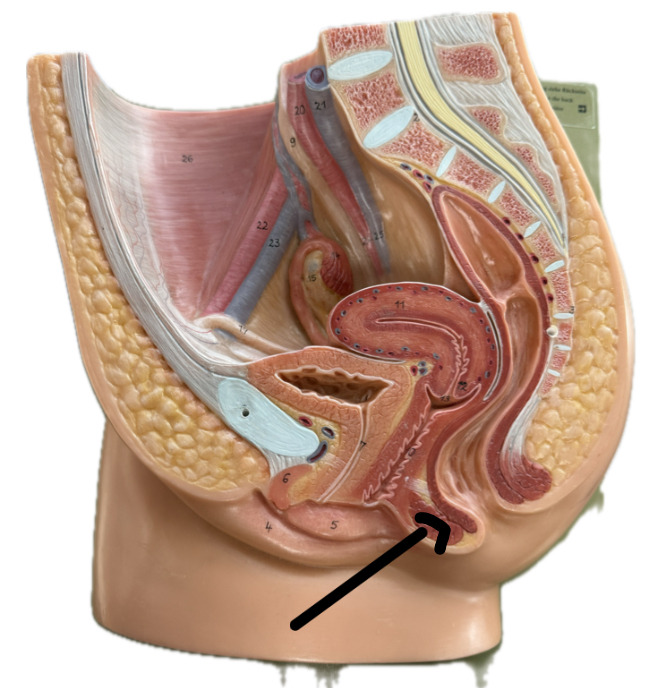
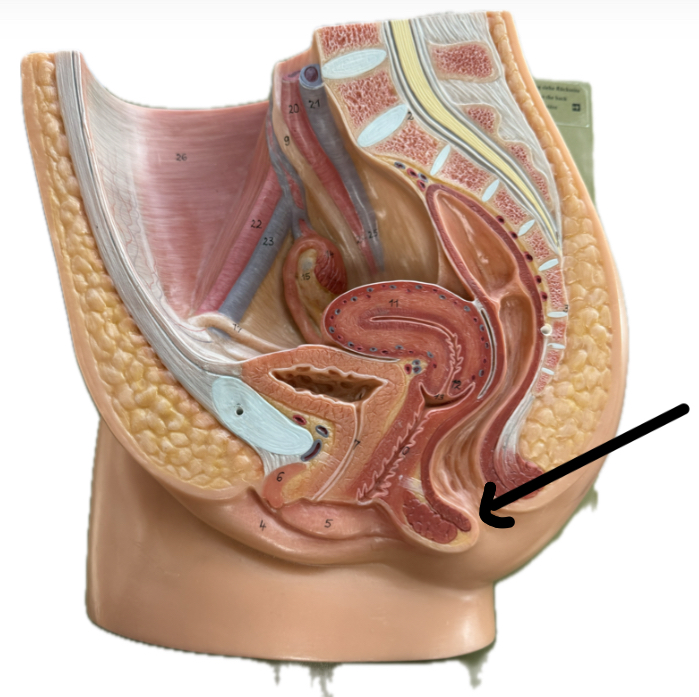
Anal sphincter
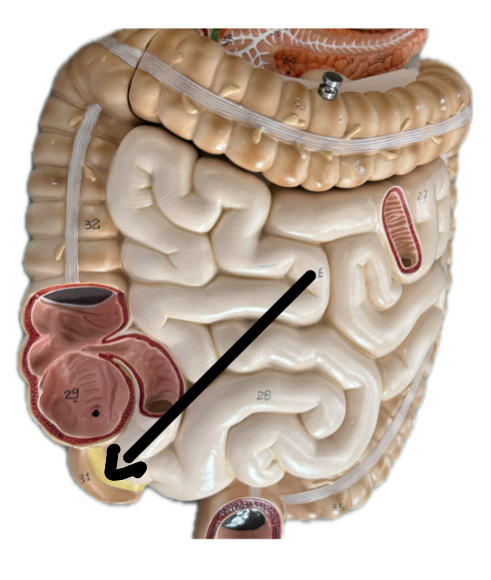
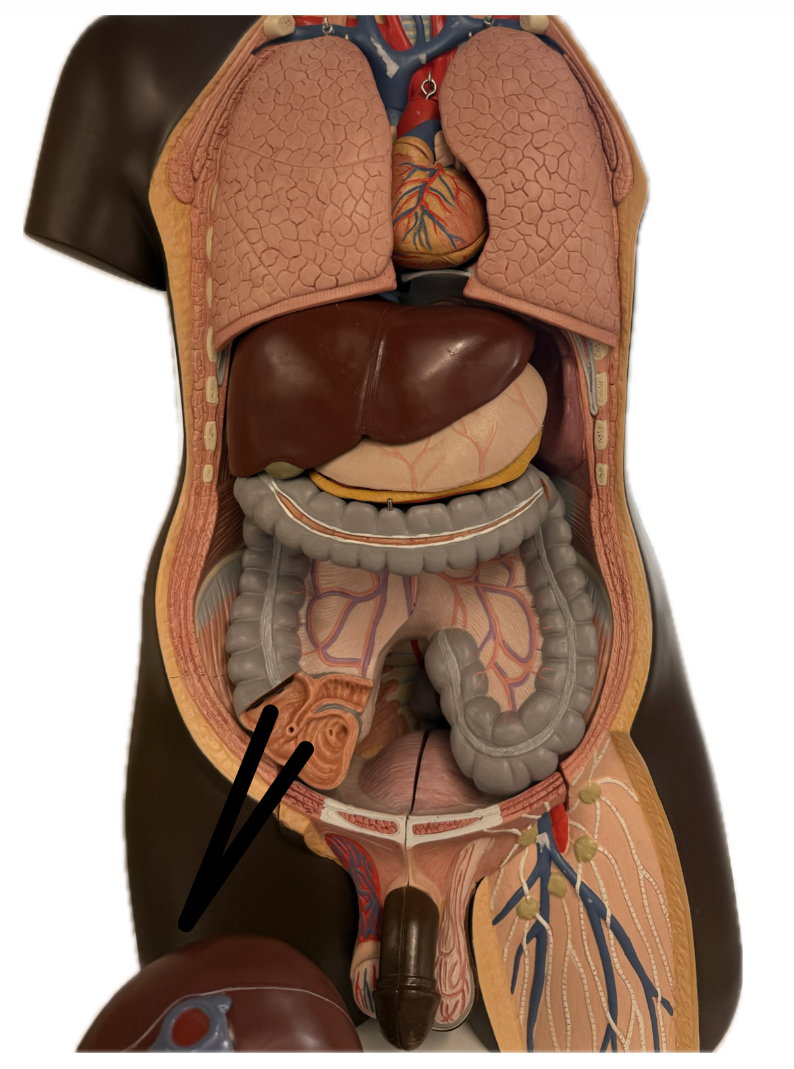
Appendix
Cystic duct
Hepatic duct
Gallbladder & Liver
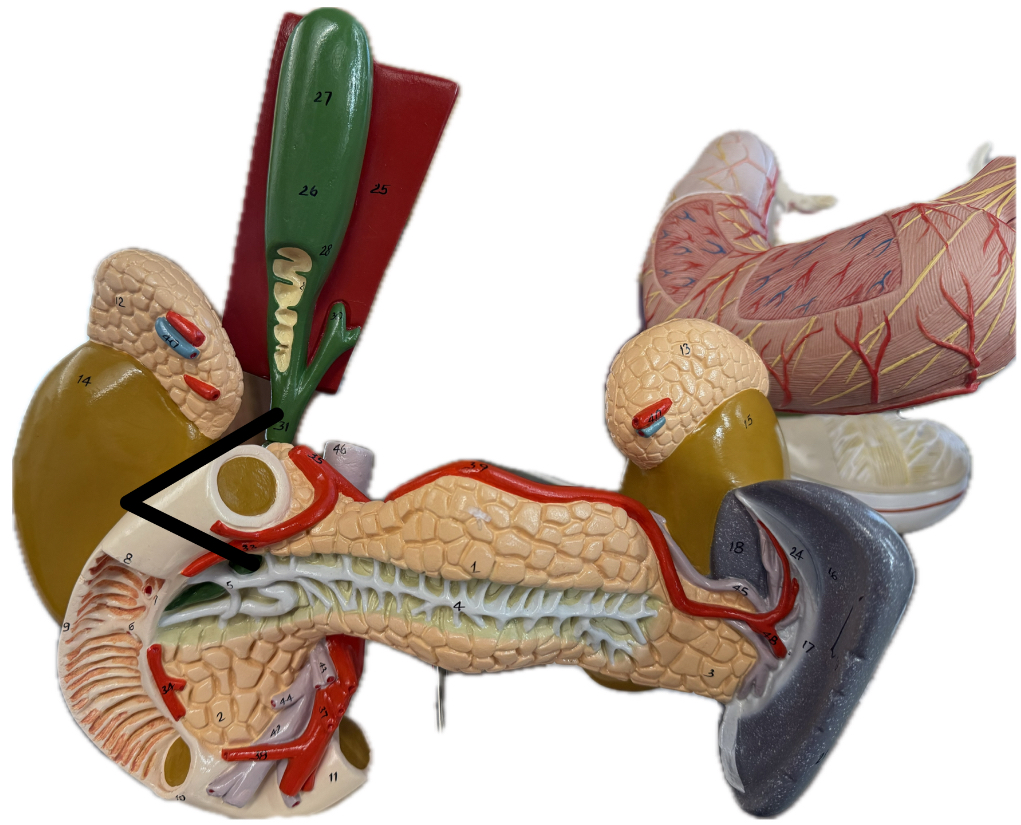
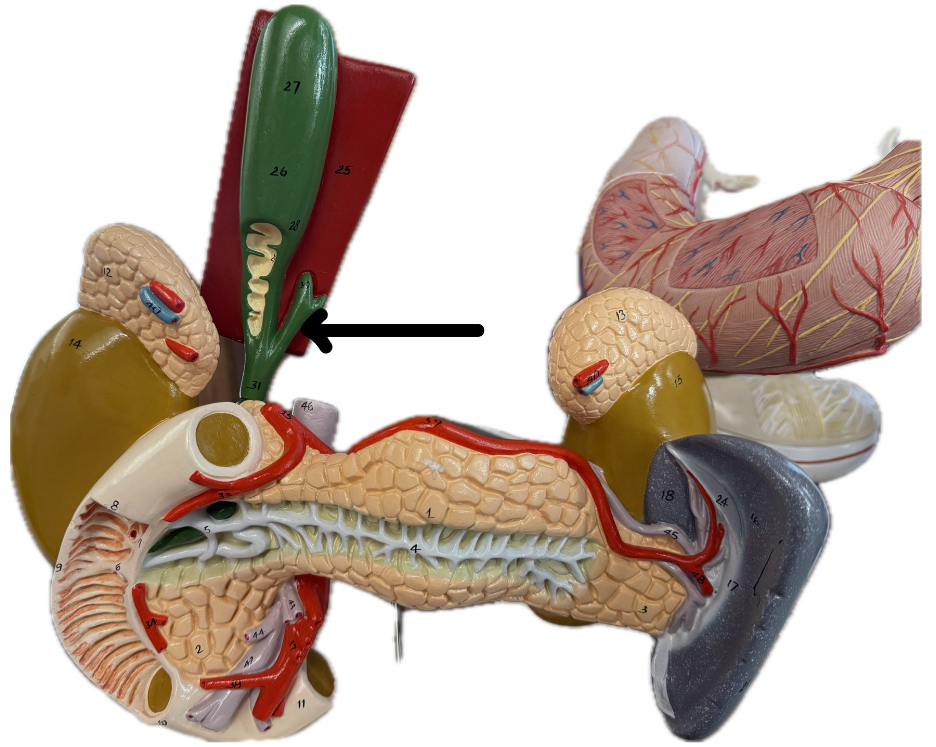
Common bile duct
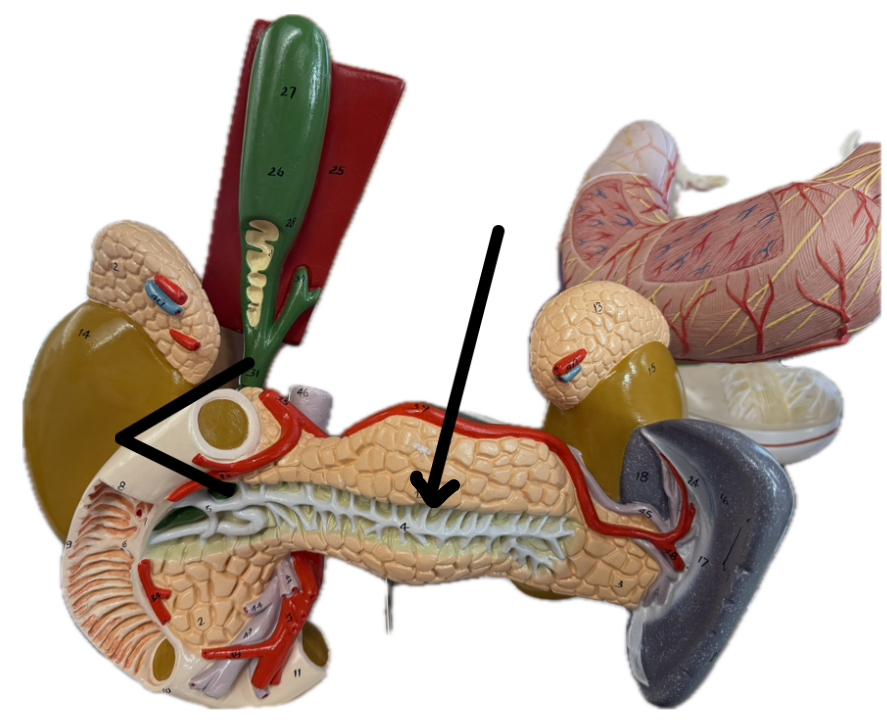
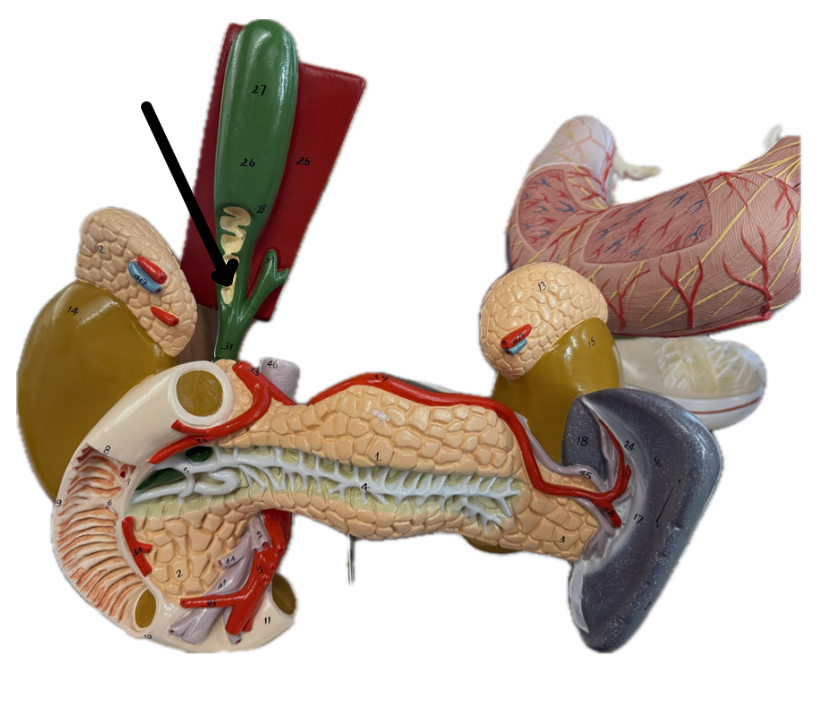
Pancreatic duct
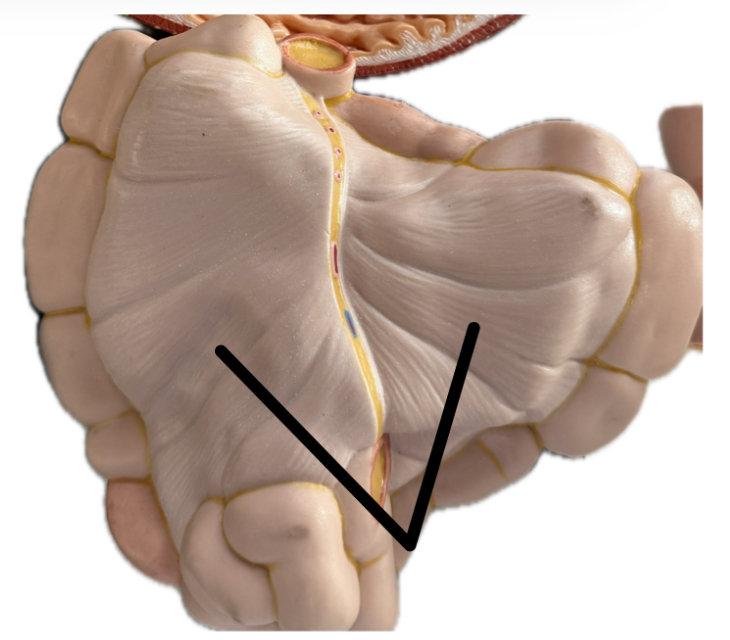
Mesentery
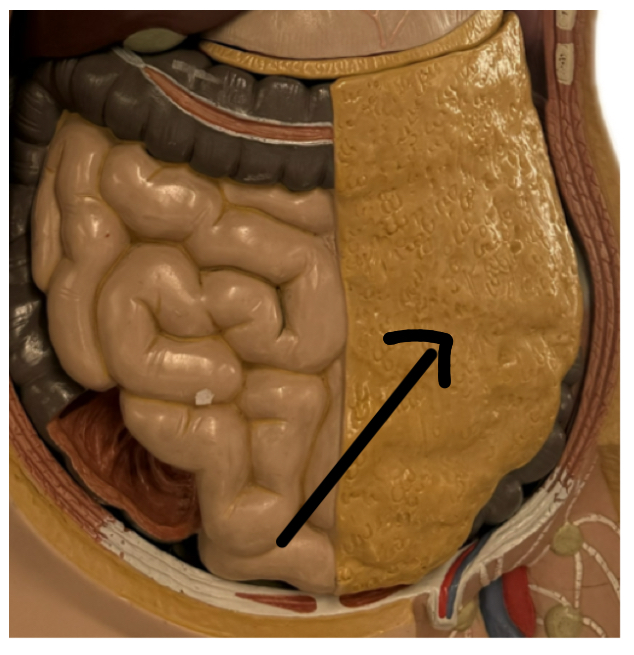
Greater omentum
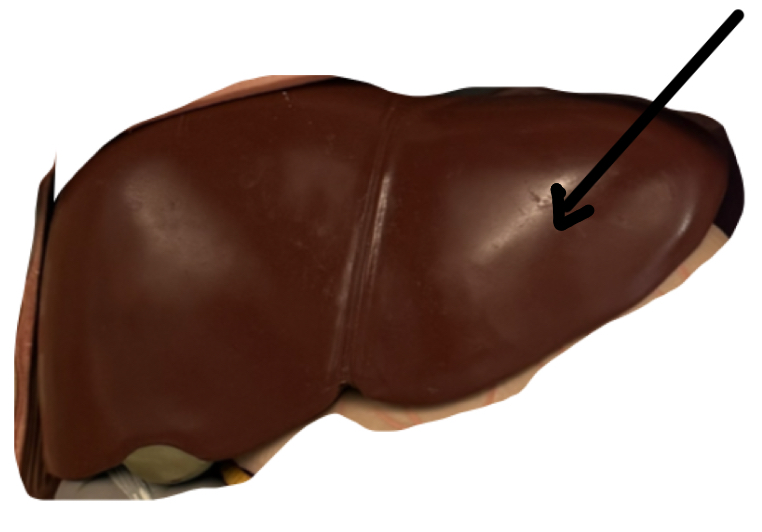
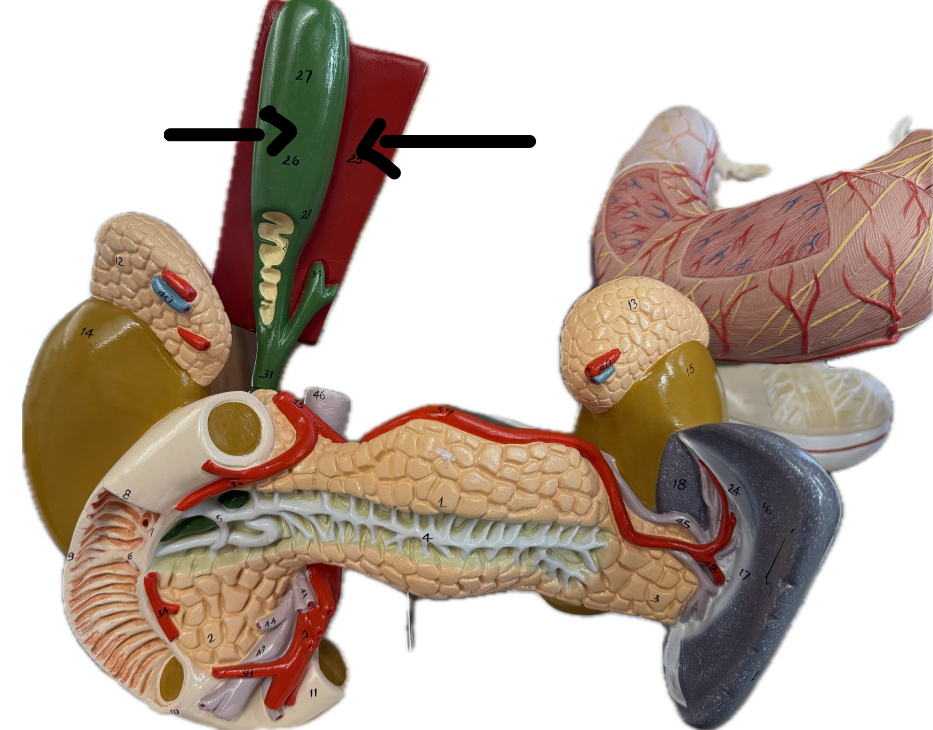
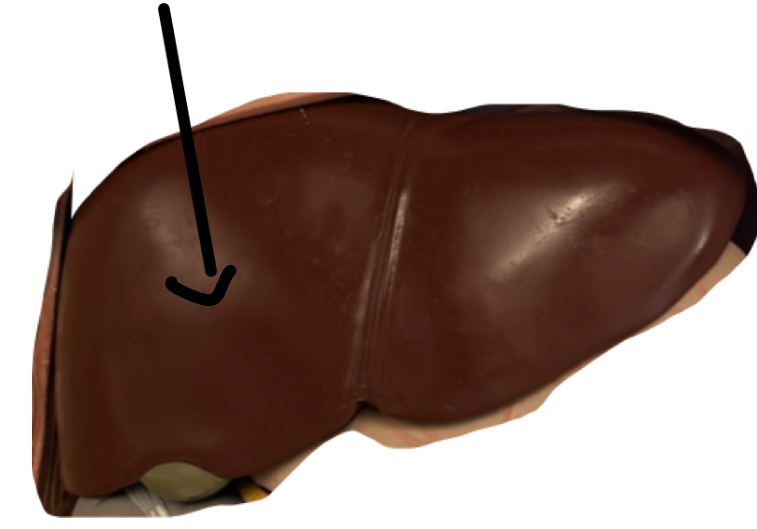
Left Lobe
Right Lobe
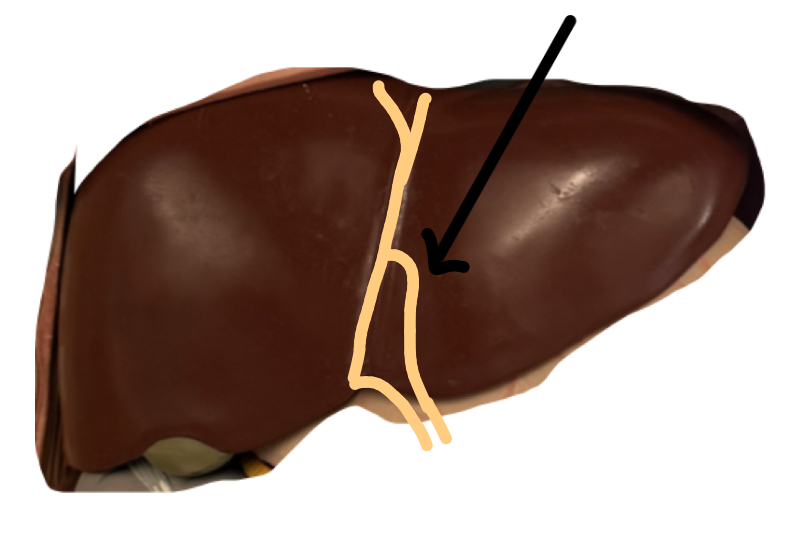
Falciform ligament
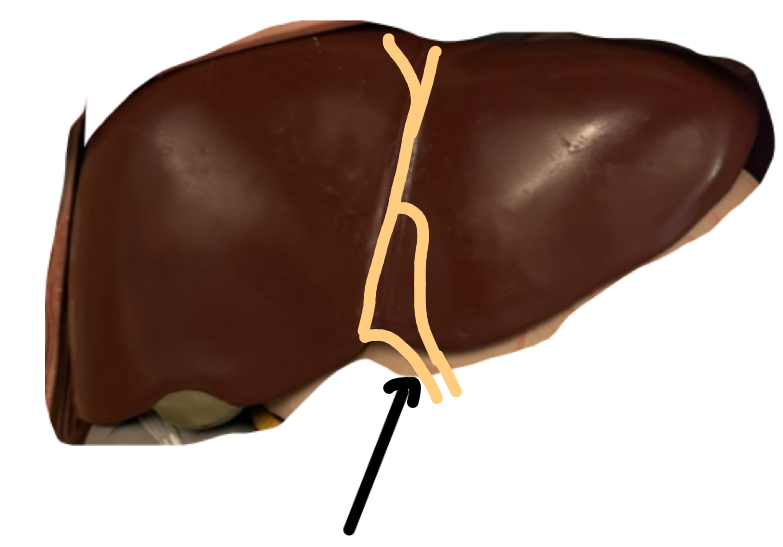
Round ligament
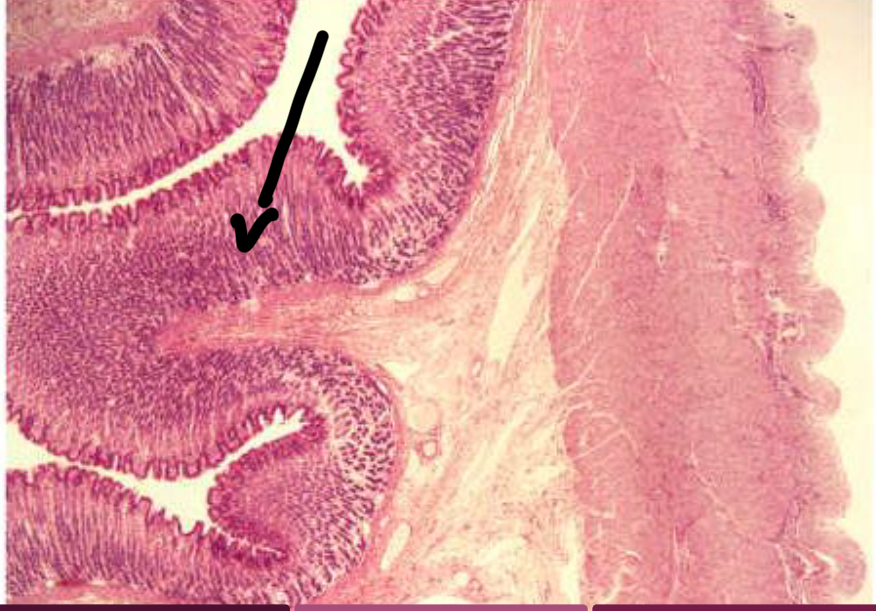
Mucosa
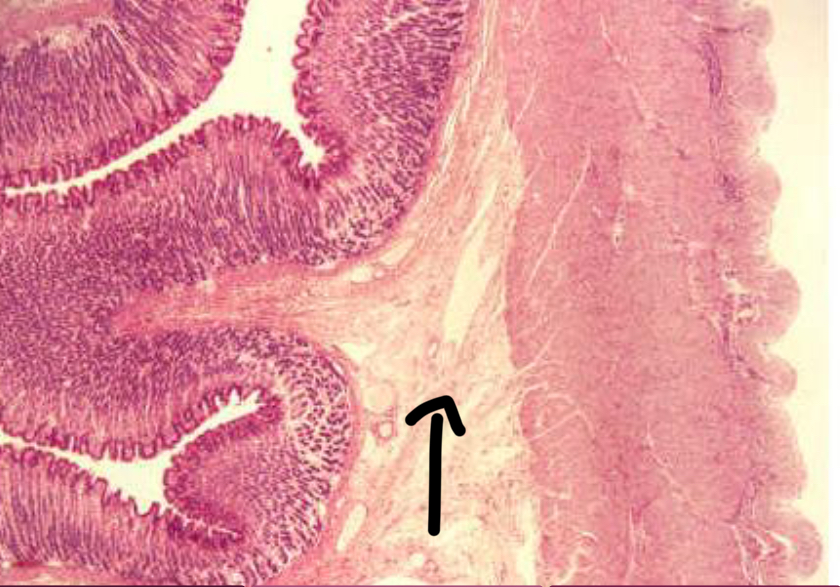
Submucosa
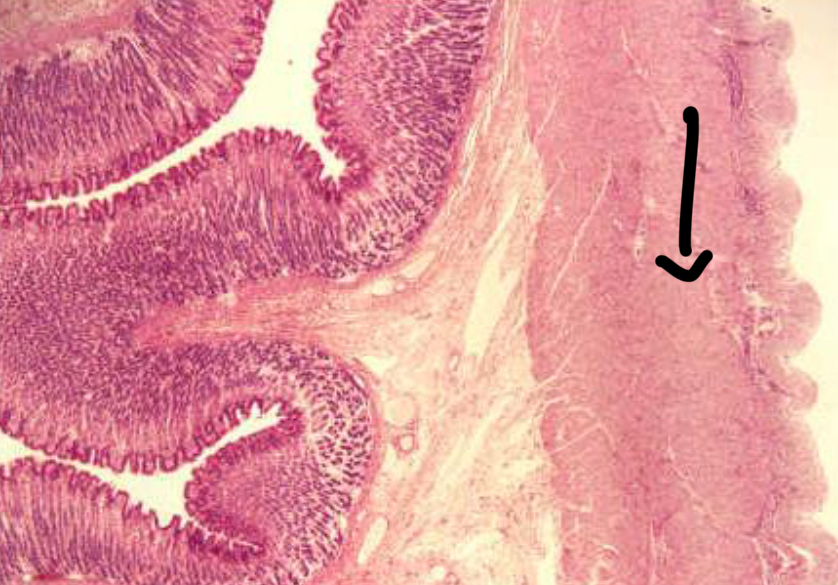
Muscularis Externa
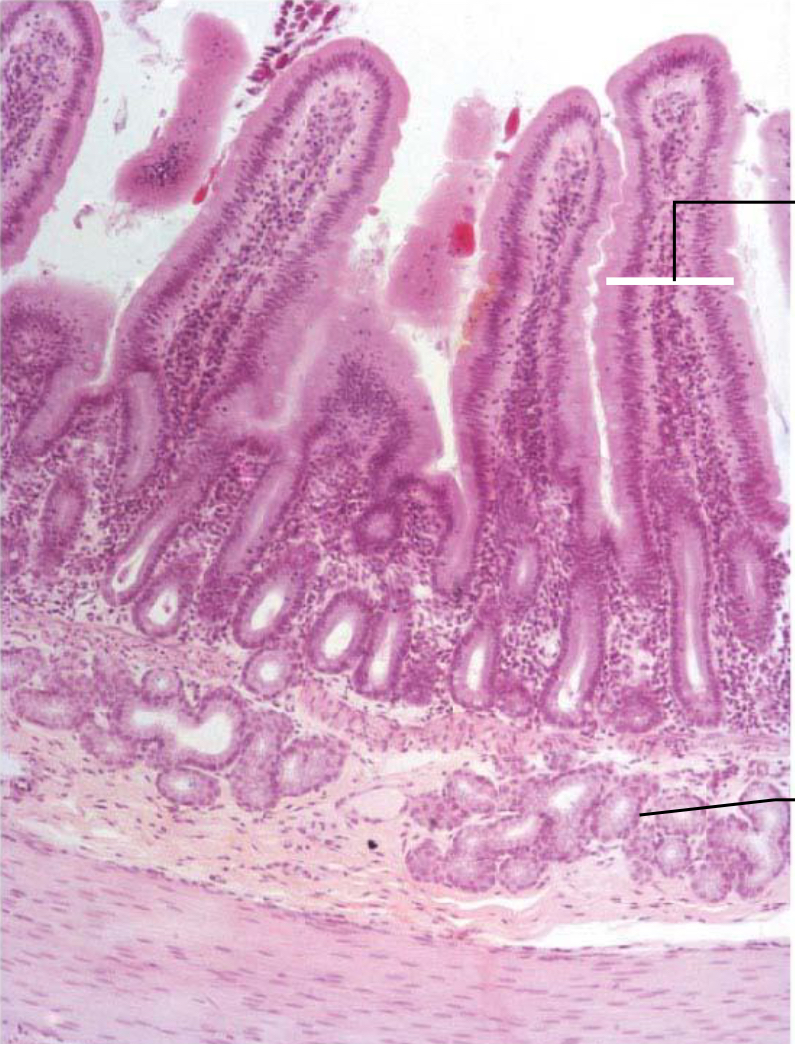
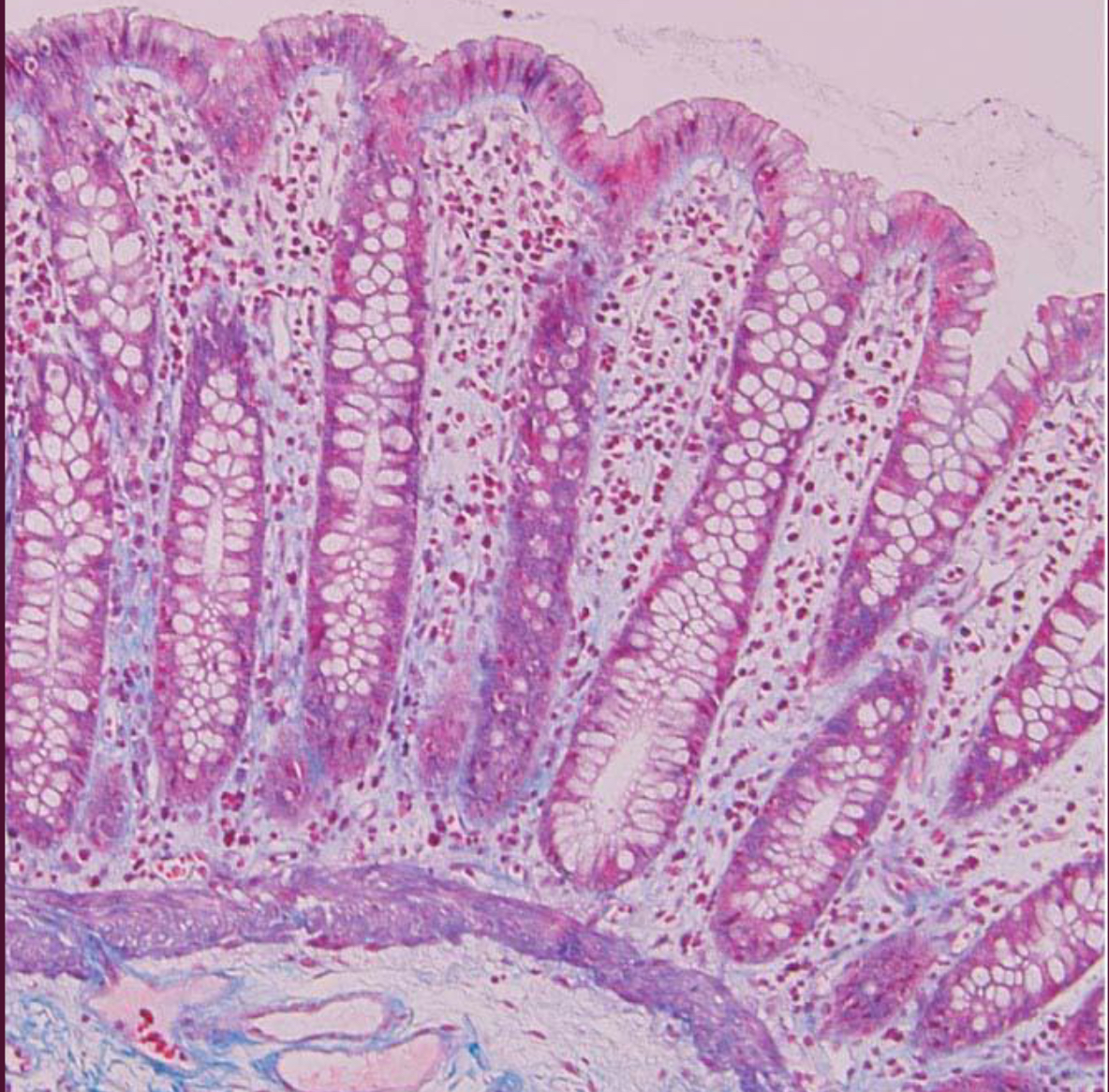
Duodenum
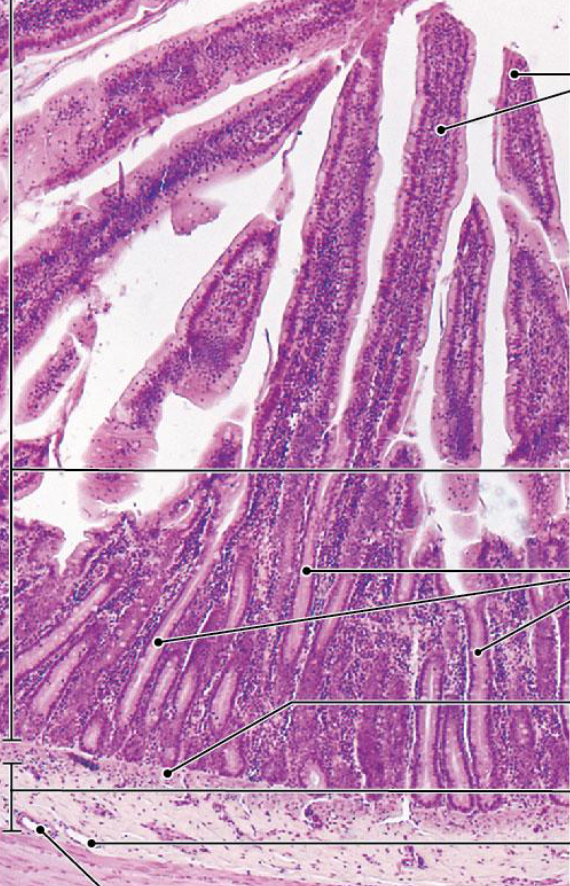
Jejunum
Ileum
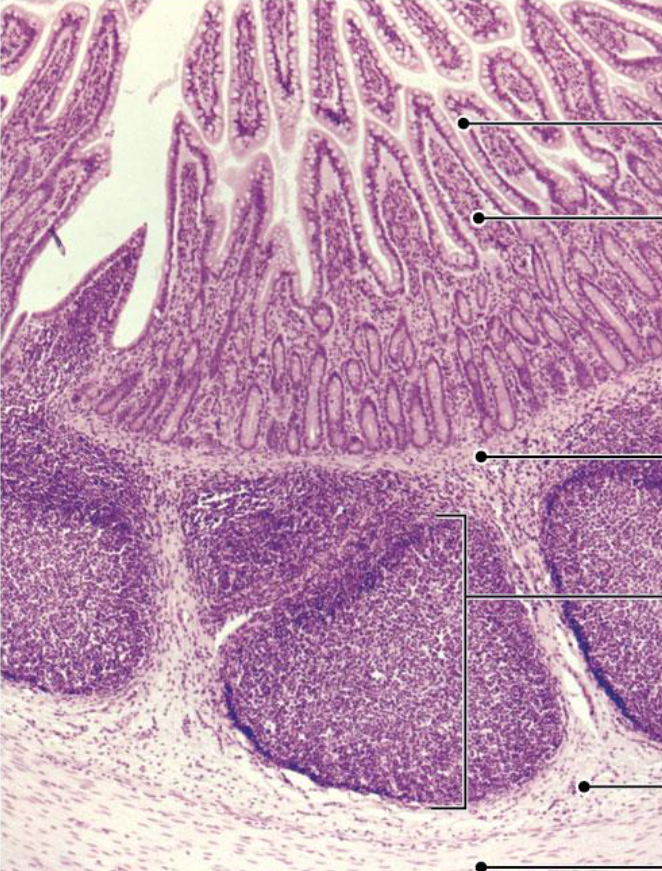
Large Intestine
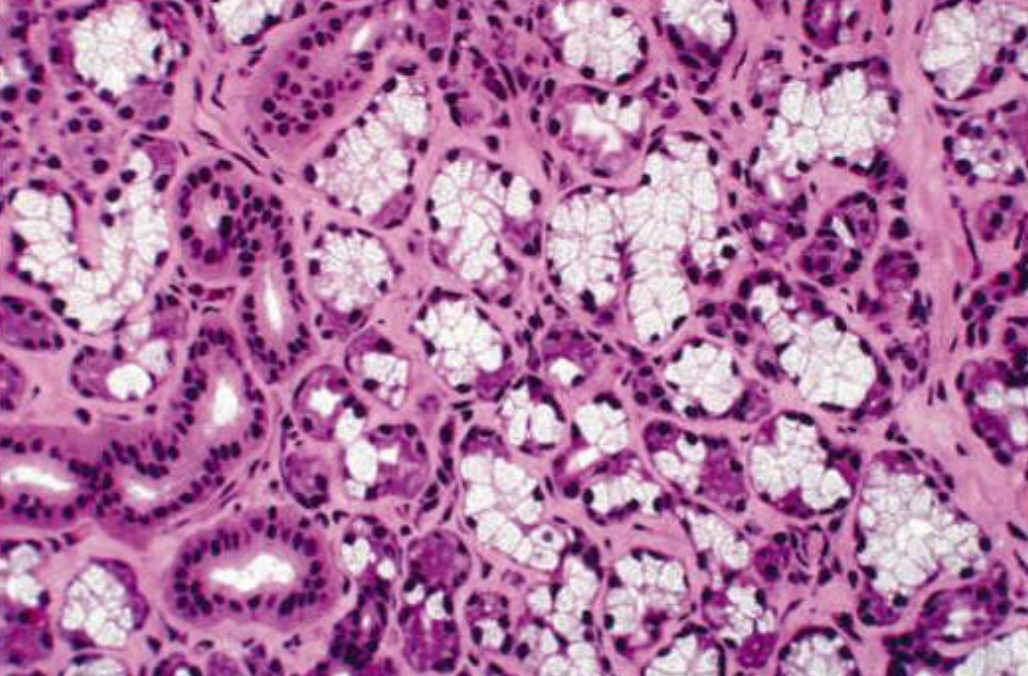
Submandibular gland
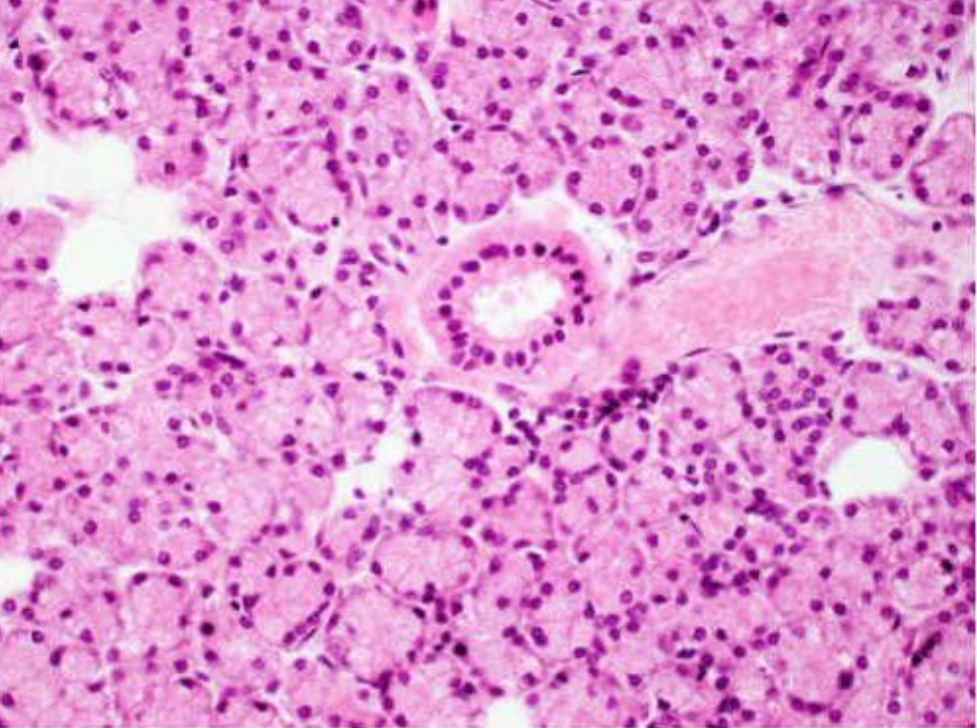
Parotid Gland
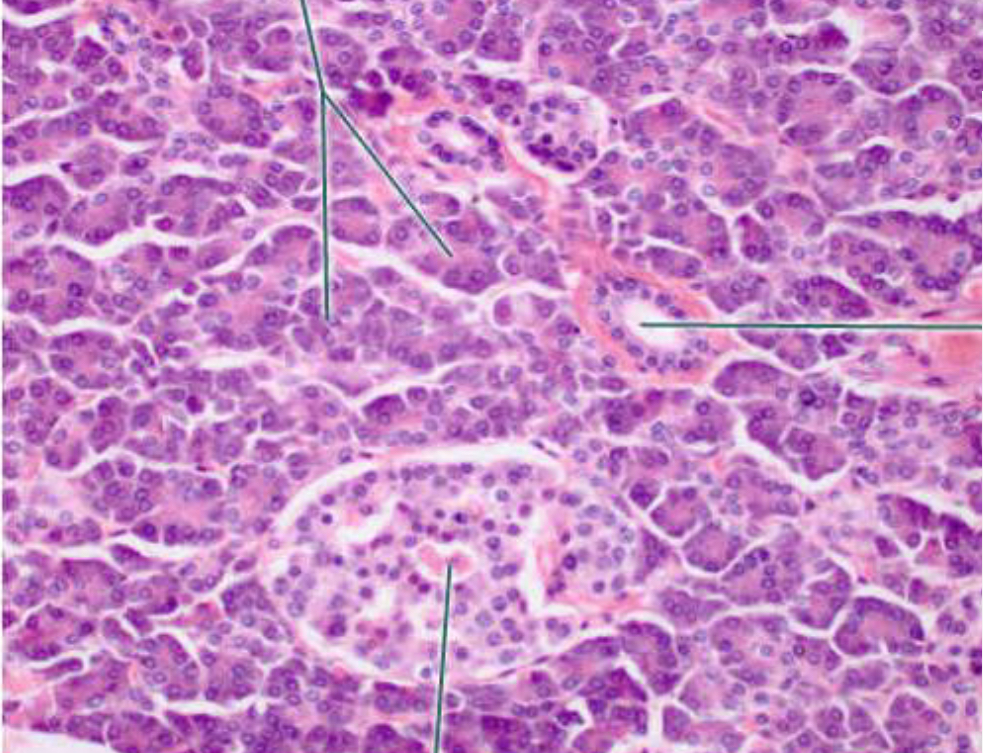
Pancreas
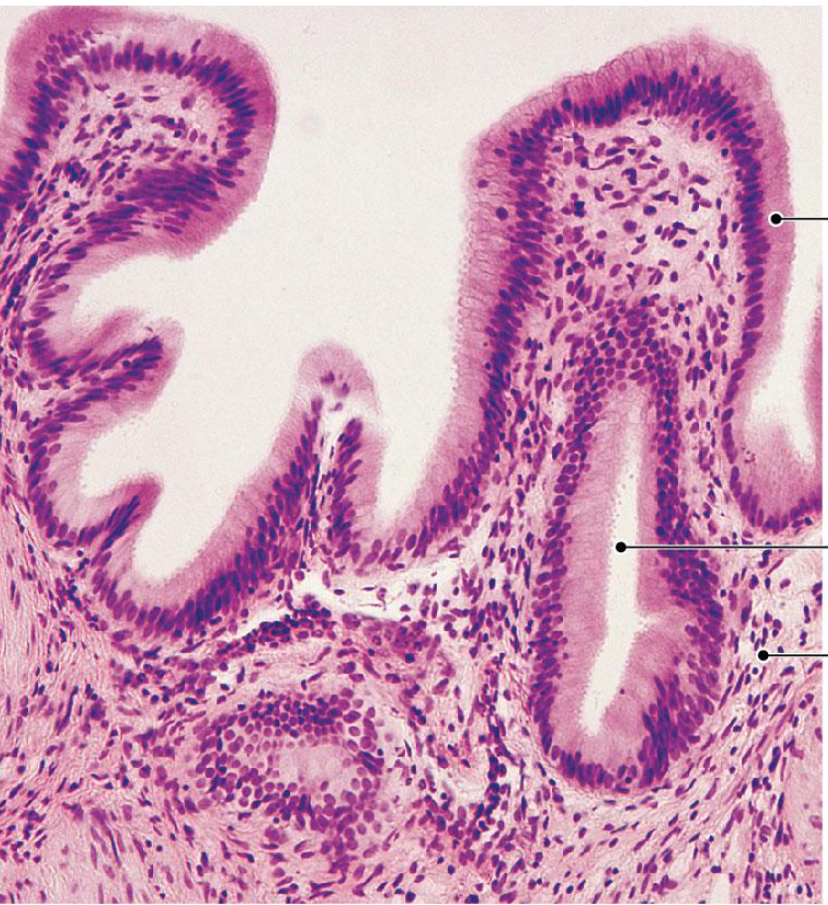
Gallbladder
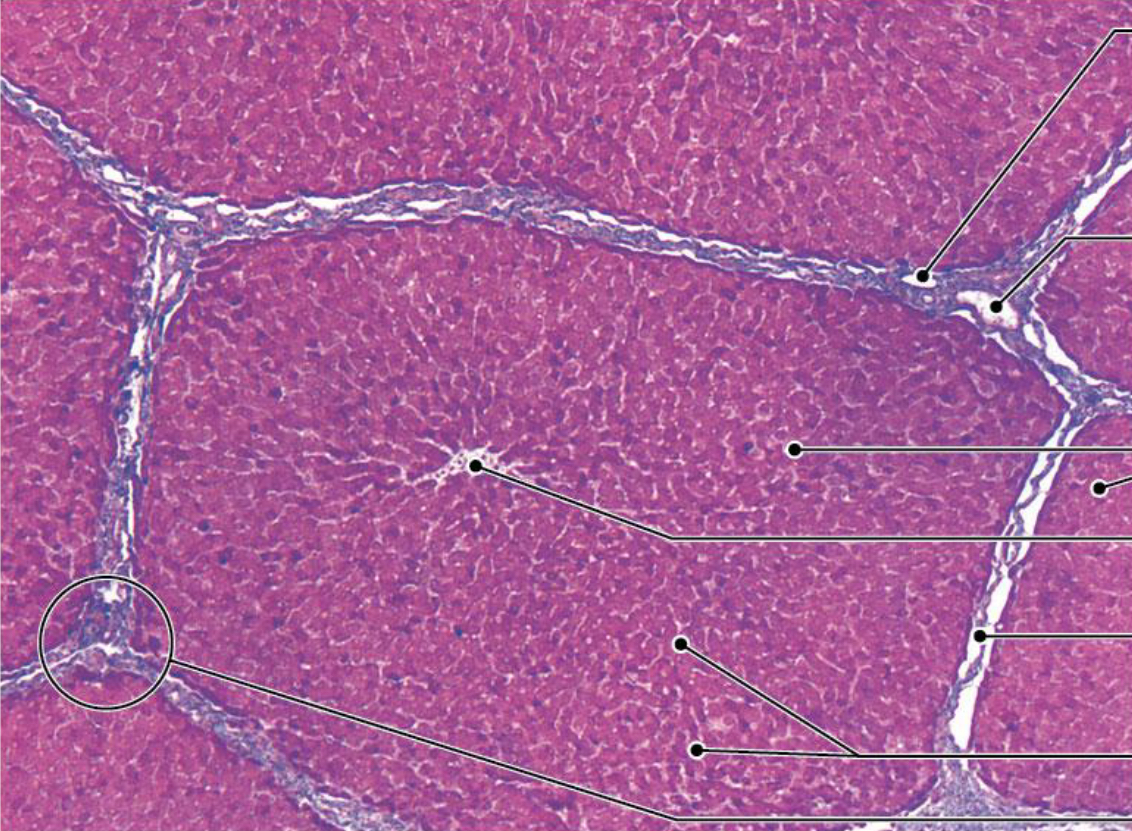
Liver
Mechanical digestion
food is broken down physically into smaller particles
Chemical digestion:
food particles are chemically altered by digestive enzymes
Environmental conditions
A factor that affects enzyme activity rate, if these conditions are not optimal, the enzyme will not work
carbohydrases
they are classified as amylase and they produce simple sugars
Salivary amylase:
they are able to begin starch digestion
Pancreatic amylase:
they are AbIe to further digest starches
Sucrease, lactase, Maltese:
able to finish sugar digestion
Proteases:
also known as protein, and produce amino acids, small peptides
Pepsin:
begins to cleave proteins into Amino acids
Trypsinogen
an digestive enzyme from the pancreas to help digest protein
Lipases
A type of enzyme class produced fatty acids and glycerol