Nephrons
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the functional unit of kidney?
Nephrons
Each nephrons is composed of?
Renal corpuscle
Proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubule
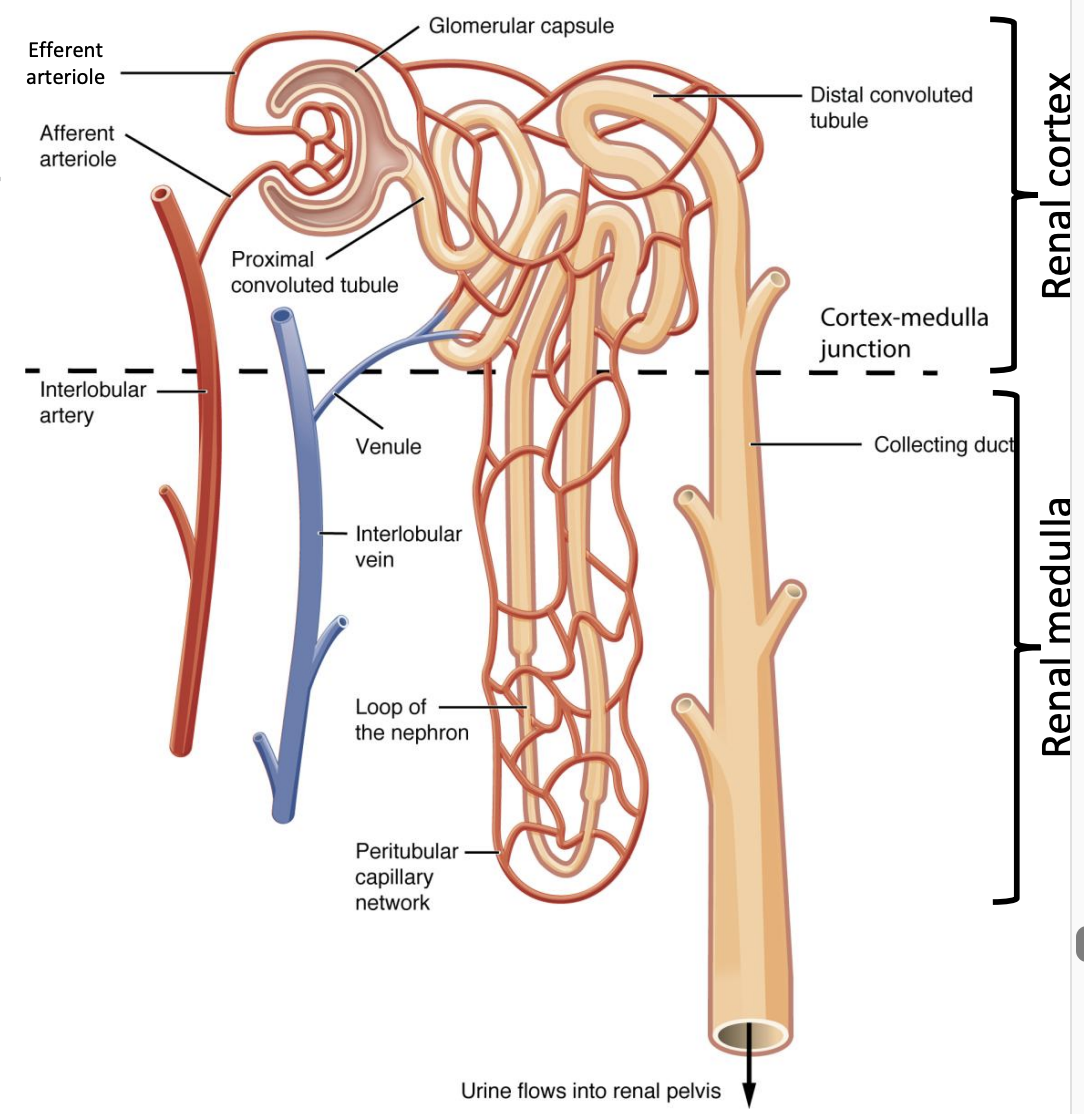
What are the 2 types of nephrons?
Cortical nephron
Juxtamedullary nephron
Cortical vs Juxtamedullary Nephron #ff9500
Location
Loop of Henle
Function
Cortical:
Location: Outer cortex
Loop of Henle: Short (doesn’t dip into medulla)
Function: Filtration
Juxtamedullary:
Location: Boarder of cortex and medulla (corticomedullary junction)
Loop of Henle: Long (extends into medulla)
Function: Concentrates urine
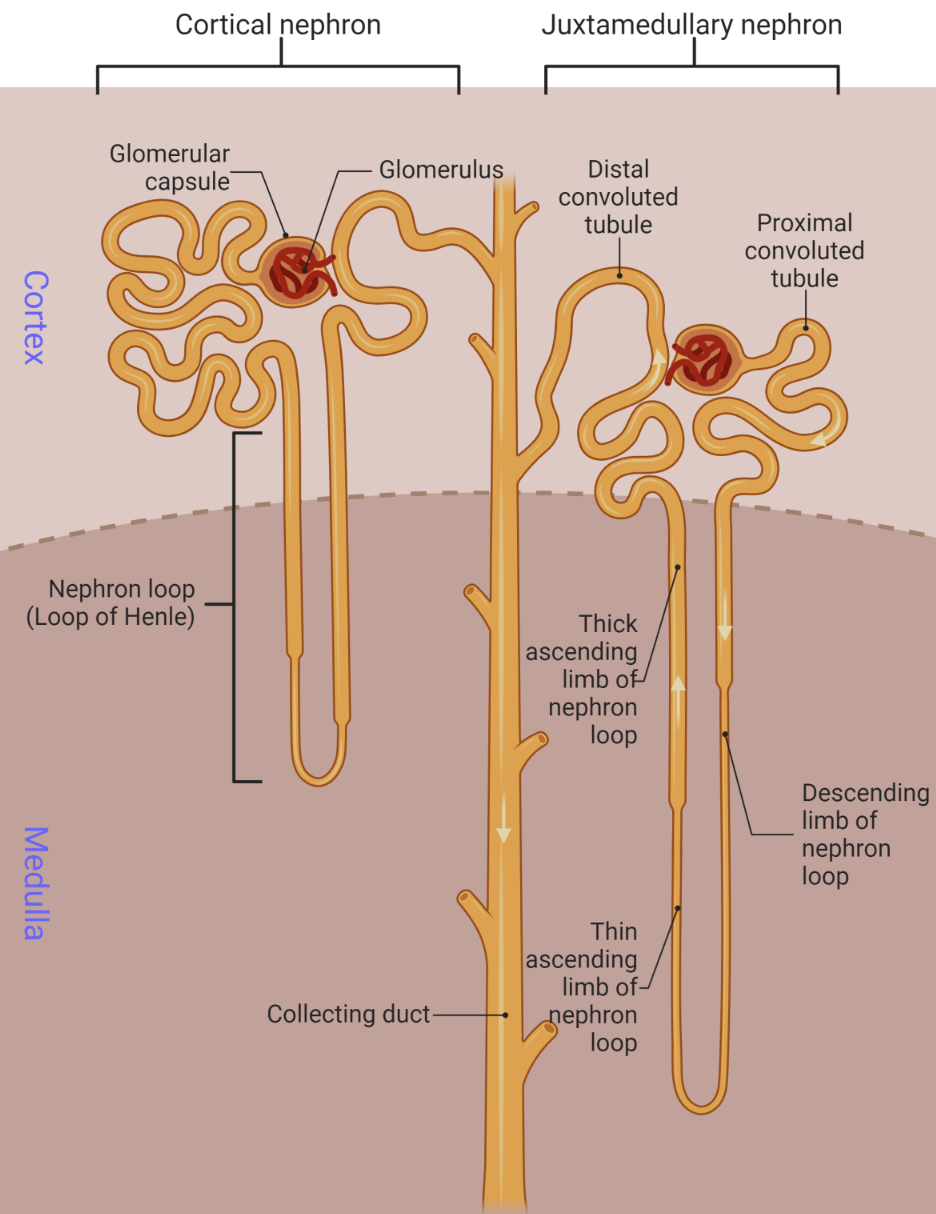
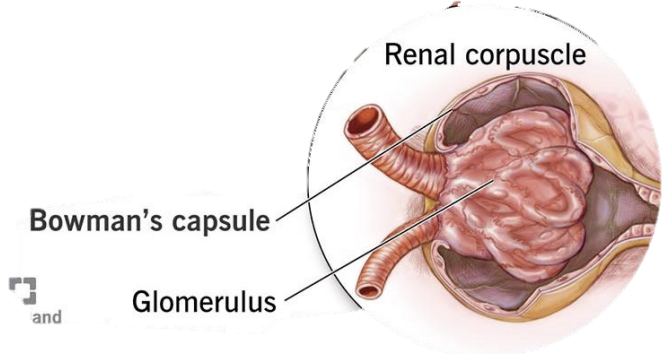
Nephrons: Renal Corpuscle #ff00d8
Function
Location
Consist of
Function: Filter blood (first stage urine production)
Location: Cortex of kidney
Consist of:
Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries)
Bowman’s capsule (double walled capsule that surrounds glomerulus)
Nephron: Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) #e6ca00
What
Location
Function
What: Longest part of tubular system of nephron
Location: Continuation of capsular space of Bowman’s capsule
Function: Reabsorption and secretion (to balance pH)
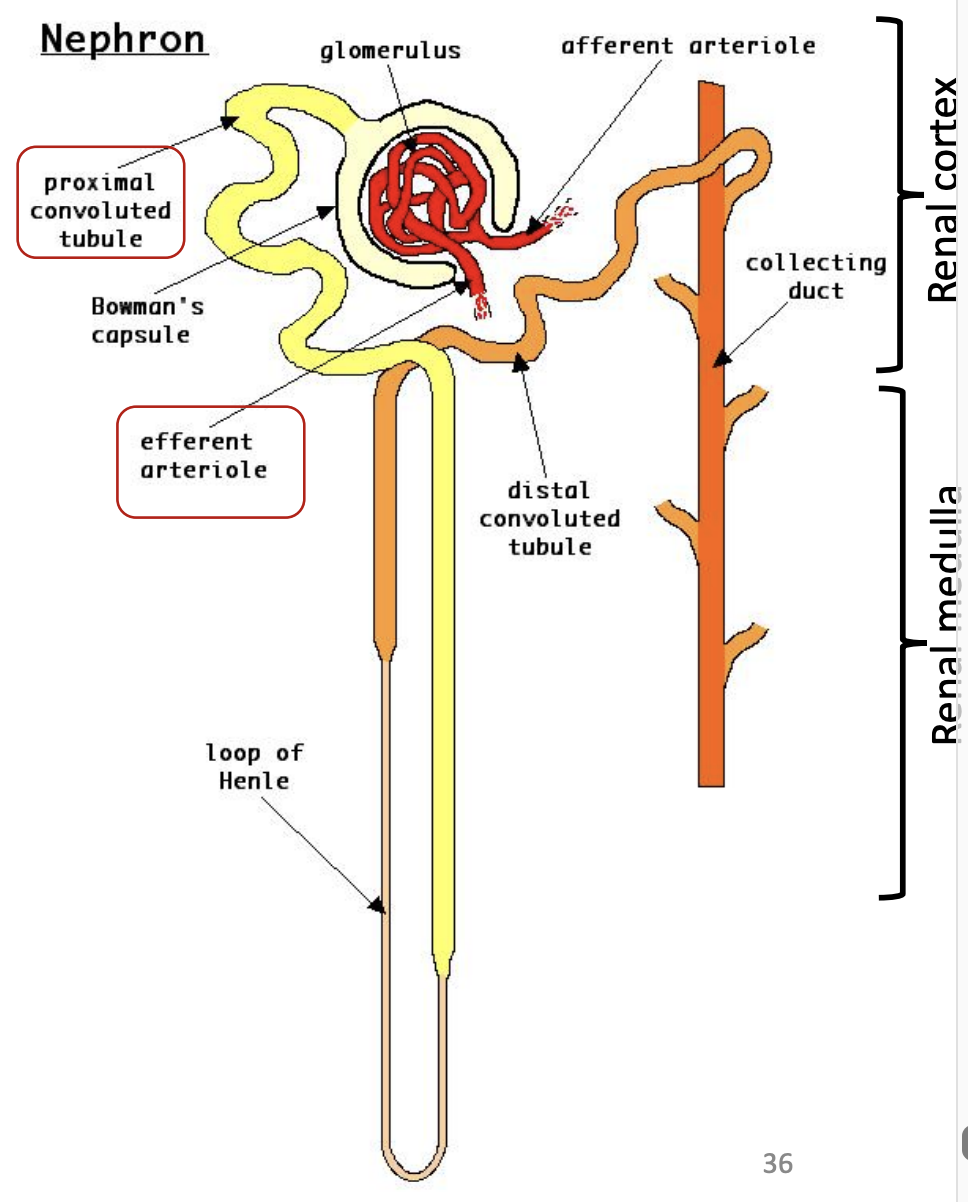
Nephron: Loop of Henle
Continues from
Location
Function of descending limb
Function of ascending limb
Continues from: PCT
Location: Descend into medulla of kidney, makes U-turn and heads back up into cortex
Function of descending limb: H2O reabsorption
Function of ascending limb: Solute (Na+, K+, Cl-) reabsorption
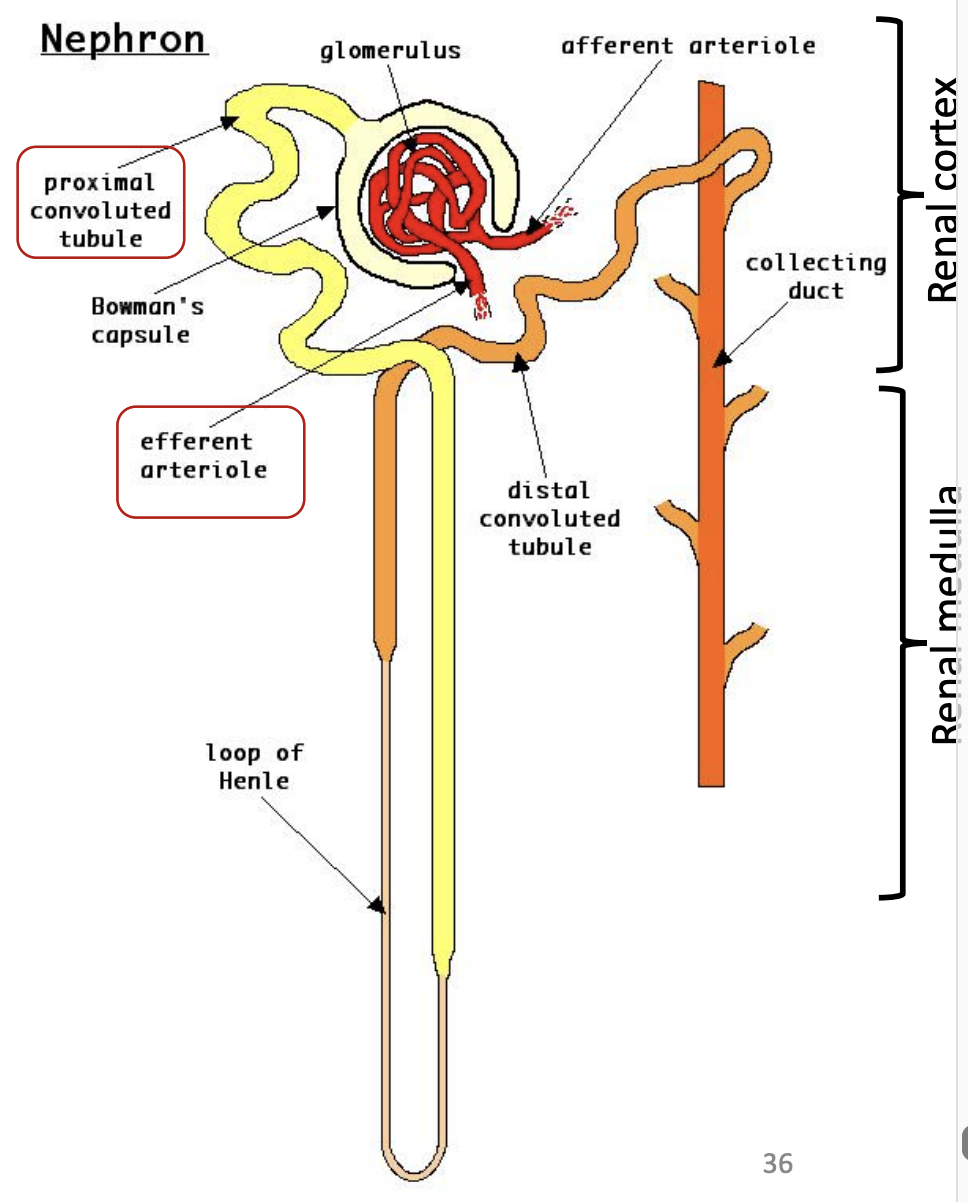
Nephrons: Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Location
Drain into
Then what occurs
Location: Continuation of ascending part of LoH
Drain into: Collecting duct
Then what occurs: Collecting duct collects renal filtrate and transport it to calyx or renal pelvis directly
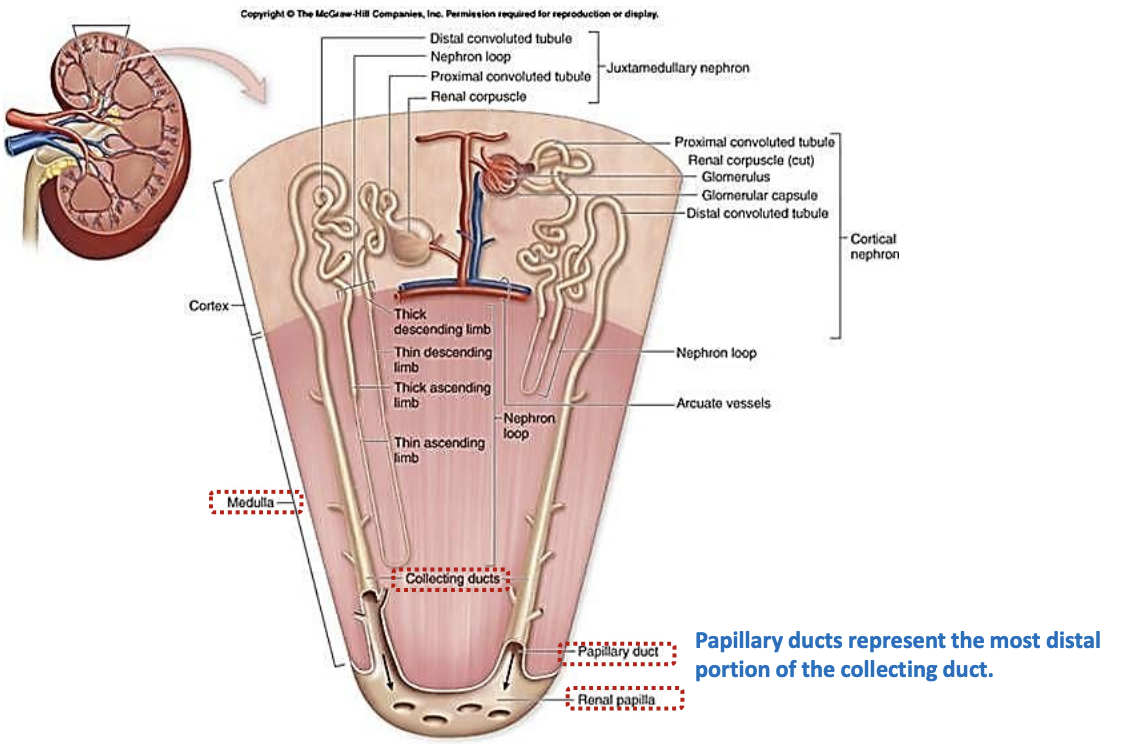
What is the pathway of collecting ducts?
Collecting duct runs through medulla before opening into papillary duct which opens at the renal papilla into renal calyx/pelvis
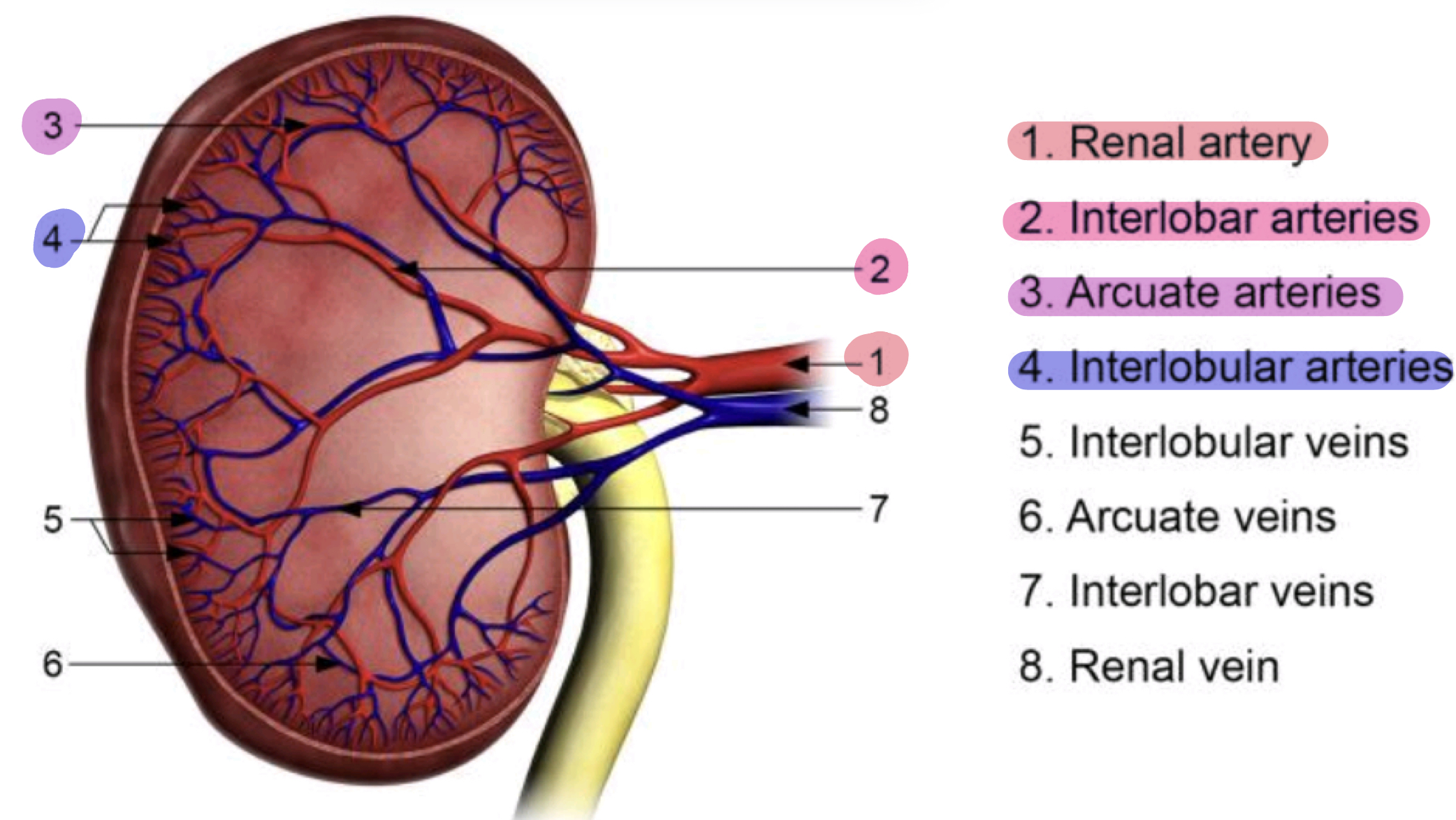
Renal Circulation
Kidneys are supplied by
Renal arteries branch to form
Interlobular arteries branch to form
Arcuate arteries branch to form
Kidneys are supplied by: Renal arteries
Renal arteries branch to form: Interlobar arteries which extend between medullary pyramids
Interlobular arteries branch to form: Arcuate arteries in meullary cortical boundary
Arcuate arteries branch to form: Interlobular arteries where they divide into afferent arteries —> arterioles supplying glomerular capillaries
Aorta → main artery of the body
Renal artery → supplies each kidney
Interlobar artery → runs between pyramids in the renal columns
Arcuate artery → arches over base of renal pyramids
Interlobular artery → enters the cortex
Afferent arteriole → supplies each nephron’s glomerulus
Glomerular capillaries → where filtration occurs
Efferent arteriole → exits the glomerulus and splits
Blood picks up waste and enters the kidney how?
Renal artery —>
Interlobar artery —>
Arcuate artery —>
Afferent arteriole —>
Glomerular capillaries
What molecules can enter Bowman’s capsule?
Only small molecules (urea, minerals), excess water and waste products while larger (protein, blood cells) stay in blood vessels
What are the 3 important processes
Filtration
Reabsorption
Urine excretion
How does the filtered deoxygenated blood leave the kidney?
Peritubular capillaries (cortical) OR Vasa recta (juxtamedullary) —>
Interlobular vein —>
Arcuate vein —>
Interlobar vein —>
Renal vein —>
Caudal vena cava —>
Heart