KIN 336 Exam 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
neuron
basic component of nervous system
4-100 microns
receive, integrate, and send information throughout the entire nervous sytem
cell body
contains nucleus (regulars cellular homeostasis)
gray matter
dendrites
extensions from cell body (0 to 1000+ per neuron)
receive information from other neurons
axons
only one per neuron
most have many branches (collaterals)
white matter (myelin)
terminal
end of axons that allow chemical signals (neurotransmitters) to be passed between neurons
synapse
gap between axon and dendrites
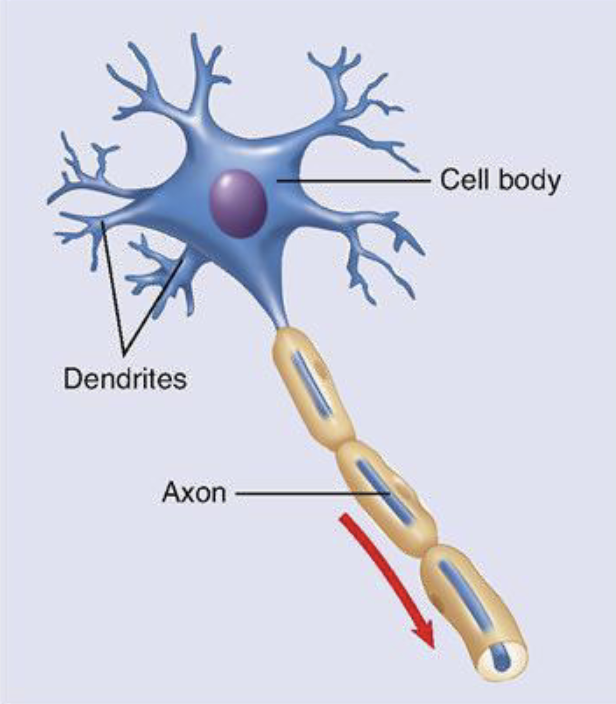
multipolar neuron (most common)
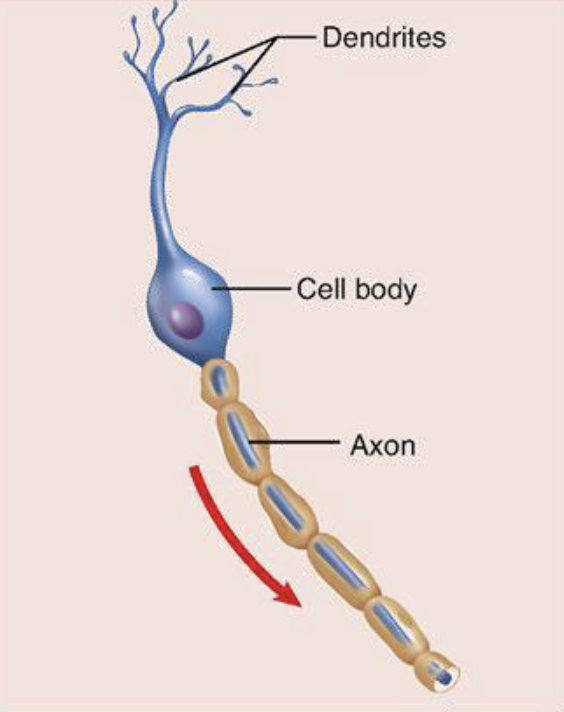
bipolar neuron
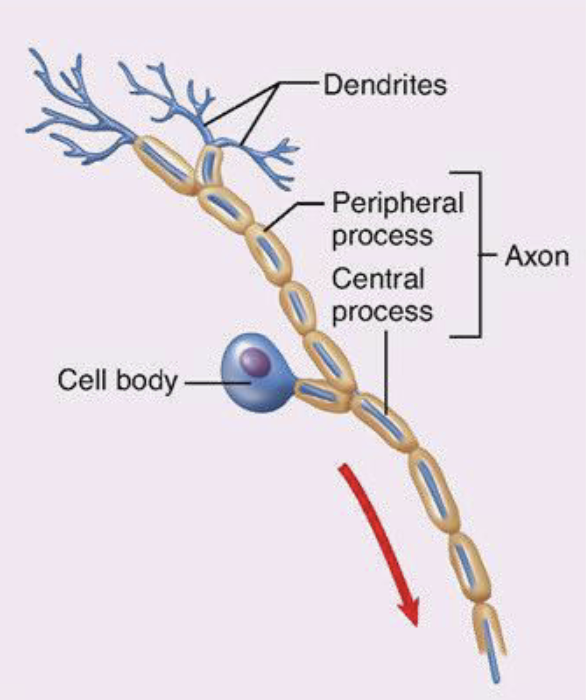
(pseudo)unipolar neuron (rare)
sensory (afferent) neurons
primary in PNS
transmit signals from sensory receptors to CNS
interneurons (connector neurons)
between neurons within CNS
motor (efferent) neurons
transmits signals from CNS to muscles
anterograde transport
from soma to axon
proteins, neurotransmitters, organelles
retrograde transport
from axon to soma
old mitochondria, pinocytotic vesicles from axon terminal (e.g., rabies virus)
pinocytosis
non-specific intake of liquids
phagocytosis
engulfing large particles (phagosomes, need trigger)
Amytrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Motor neuron degeneration
progressive degeneration of upper & lower motor neurons
disrupted axonal transport, glutamate excitotoxicity, oxidative stress
muscle weakness, atrophy, and eventual paralysis
properties of glial cells
maintain environment
no electric current passes through
more numerous than neurons
central nervous system (CNS) glial cells
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
peripheral nervous system (PNS) glial cells
satellite cells
Schwann cells
macrophages
astrocytes
In CNS
provide structural support
secretes growth factors to support neurons
act as intermediary between other cells
can modulate synaptic activity by releasing glutamate and D-serine
buffer pH and ionic environment in extracellular space
removes extracellular K+ from action potentials and transports it to perivascular spaces
absorbs nutrients from blood supply and passes it to neuron
microglial cells
In CNS
immune cells of brain
phagocytic scavengers (like macrophages in PNS)
secretes neurotoxic substances (e.g, cytokines)
oligodendrocytes
In CNS
Cover CNS cell axons in myelin
myelin: raises conduction speed of neural transmission
loss of oligodendroytes → demyelinating diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis)
Selma Blair Multiple Sclerosis (MS) diagnosis
Demyelination of CNS axons
loss of oligodendrocytes → impaired myelin sheath formation
slowed or blocked action potential conduction
leads to muscle weakness, fatigue, impaired coordination, impaired speech
satellite cells (PNS)
surround neuronal cell bodies in ganglia; regulate microenvironment
Schwann cells (PNS)
myelinate one axon per cell; critical for PNS axon regeneration
macrophages (PNS)
immune cells that clear debris and aid recovery after injury
Oligodendrocytes vs Schwann Cells
Oligodendrocytes
wrapping: cell body projections
only in CNS
Schwann cells
wrapping: pancake
only in PNS
general neuropathic pain
maladaptive glial & synaptic activity
overactive microglia release proinflammatory cytokines
enhanced excitatory transmission, reduced inhibition in spinal circuits
leads to chronic pain syndromes
Excitable cell membrane
electrical potential changes in response to a stimulus
each neuron receives stimuli from many neurons at dendrites
excitatory potential
increases electrical potential of cell membrane (+)
brings neuron closer to threshold
inhibitory potential
decreases electrical potential of cell membrane (-)
takes neuron father from threshold
If net effect of all + and - stimuli on a neuron maintains membrane potential below threshold level,
Neuron does not generate an action potential (AP)
If net effect of all + and - stimuli on a neuron increases membrane potential above threshold level,
Neuron depolarizes and AP is generated
propagates down axon to terminal endings to stimulate
sensory neuron: other dendrites
motor neuron: muscle fibers