Lecture 3 - DNA Damage and it's Repair Part I
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
How do we know that DNA is the critical target of radiation
theory
experimentation
what experiment was done to prove DNA is the critical target
selective irradiation of the nucleus or the cytoplasm shows that the nucleus is more sensitive than the cytoplasm
to kill a cell, the required dose to the nucleus is 100 times less than dose to cytoplasm
what experiment was done to prove that DNA is the critical target
Polonium rods (high LET) were put into both the cytoplasm and nucleus
250 Gy to cytoplasm had no effect on cell proliferation
10 Gzy to nucleus resulted in cell death
Radioisotopes incorporated into DNA kill cells …
more efficiently than radioisotopes in RNA or proteins
cells deficient in DNA repair enzymes are more …
radiosensitive
drugs that inhibit DNA repair are …
sensitizers
the bigger the genome, …
the greater the probability the radiation hits the nucleus
easier to shoot an elephant than a pigeon
what is more radioresistant, the human genome or yeast genome
the yeast genome
it is much smaller than the human genome, making it harder to hit the nucleus
human cells have roughly ___ base pairs, ___ protein coded genes, and ___ non-coding genes
6 billion, 20 000, 26 000
Structure of DNA
phosphate group
sugar (deoxyribose)
nitrogenous base
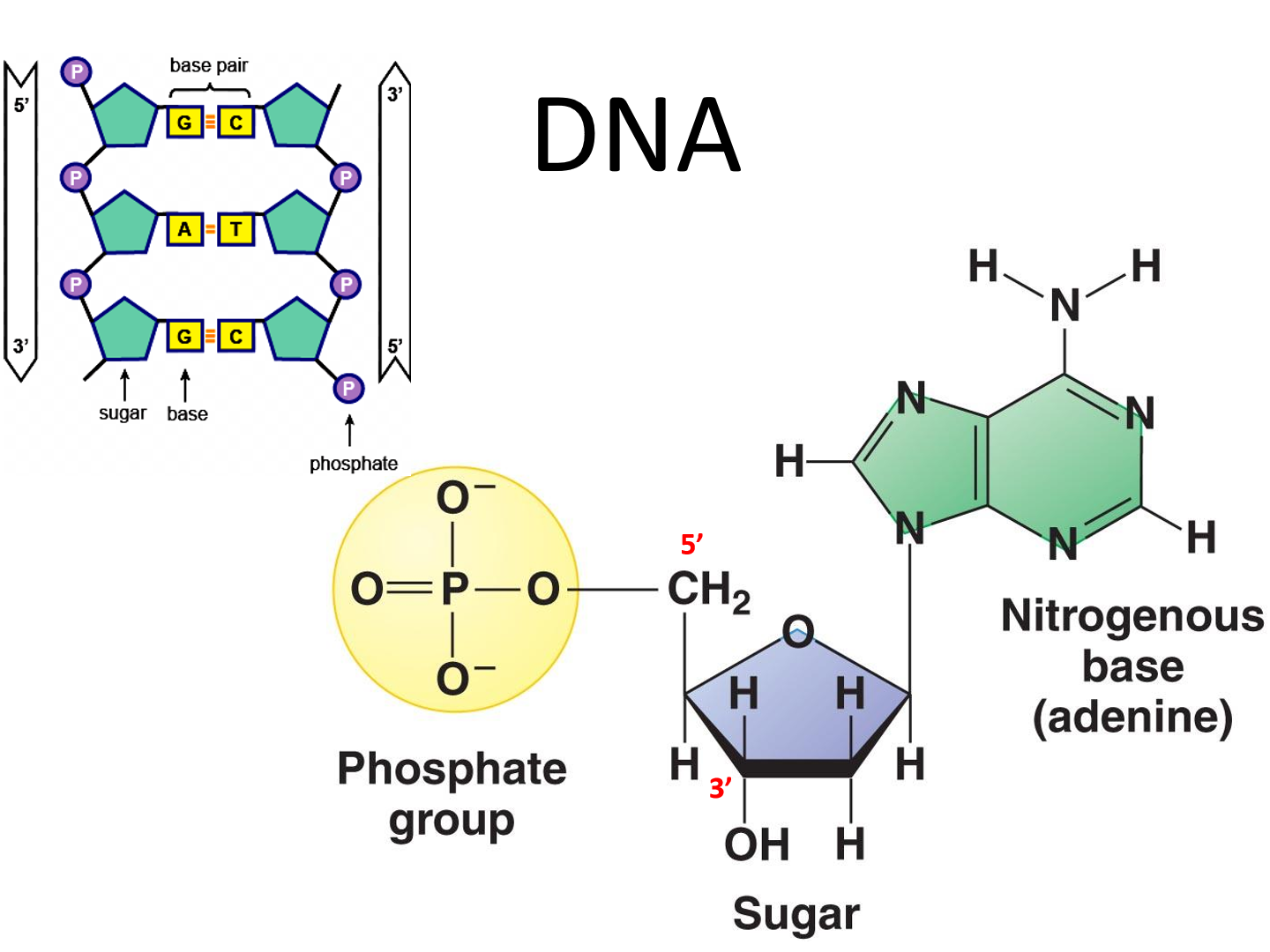
how is the bond between C-G different than between A-T
C-G bond is made up of 3 hydrogen bonds, A-T is made up of 2 hydrogen bonds
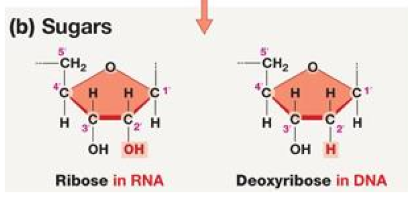
What is the difference between a ribose sugar and a deoxyribose sugar?
deoxyribose in DNA has a -H bonded to the 2’ carbon, while ribose in RNA has an -OH to the 2’ carbon
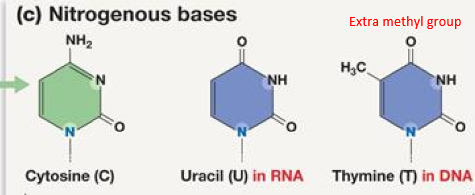
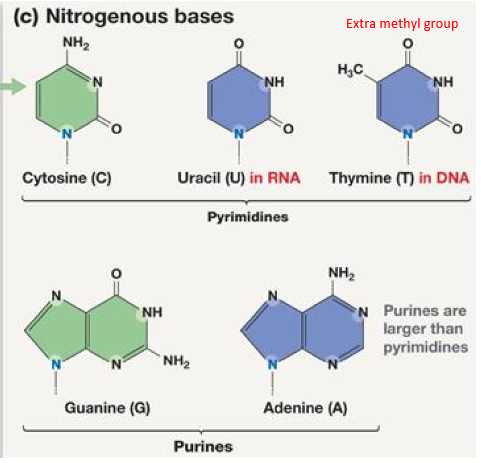
what is the structural difference between thymine and uracil
thymine has an extra methyl group
what are larger, pyrimidines or purines?
Purines (A and G)
DNA polymerase adds bases ____
5’ to 3’
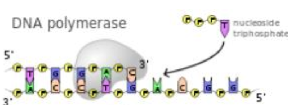
How can DNA polymerase check if it added the correct base pair
it can check how many hydrogen bonds are on the base pair
External Sources of DNA damage
UV light (non-ionizing), chemicals, radiation
internal sources of DNA damage
ROS and DNA replication errors
most common DNA replication error
DNA polymerase puts on a ribonucleotide instead of a deoxyribonucleotide
5 types of DNA damage
SSB
DSB
Base Modifications (addition of DNA adduct)
Interstrand crosslinks
Base mismatches, indels
What DNA repair pathway fixes SSBs
BER
What DNA repair pathways fixes DSBs
HR and NHEJ
What DNA repair pathways fixes base modifications
NER or direct reversal
What DNA repair pathway fixes inter-strand crosslinks
FANC
What DNA repair pathway fixes base mismatches and indels
MMR
What type of DNA damage can result of ionizing radiation
all 5 types: SSBs, DSBs, Base modifications, inter-strand crosslinks, base indels/mismatches
What is the DNA damage response?
DNA repair + all other things cell does when DNA damage occurs
increases energy, shut town transcription, stop cell cycle, etc
1 GY of x-ray ionizing radiaiton causes over ___ damaged bases, ___ SSBs, and ___ DSBs
1000, 1000, 30-40
What type of DNA damage is the least common but the biggest problem for the cell
double stranded breaks
Lethal damage - definition
irreverisble, irrepairible, damage leads to cell death
Sublethal damage - definition
repaired in hours, if a second dose is given, can interact with more damage to create lethal damage
potentially lethal damage - definition
can be modified by the post-irradiation environment to become lethal
what is the consequence of unrepaired DNA damage?
Chromosome damage
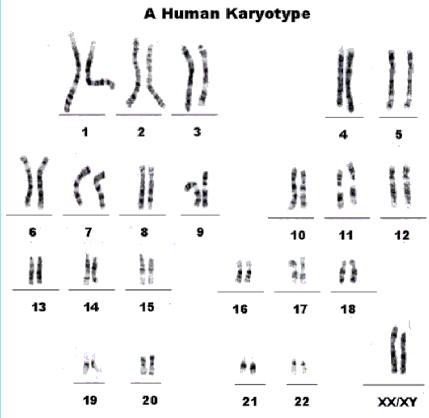
What are the three ways we can test for chromosome damage after irradiation?
Karyotyping
FISH
Micronuclei test
Karyotyping
look at chromosomes after staining them
under a microscope we may be able to see chromosome break or unrepaired damage
FISH
Fluorescent in-site hybridization
painting chromosomes to see if DNA chromosome fusions occur
micronuclei test
a third nucleus is formed during anaphase of mitosis after a chunk of the chromosome falls off after irradiation
chromosome fragments develop nuclear membranes and form a third nucleus
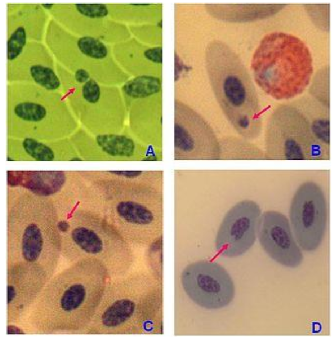
radiation ___ the amount of miconuclei
increases
how are micronuclei treated?
cytochalasin B: allows nuclear division, but stops cell division
Aberrant Chromosomes
broken ends of chromosomes rejoin with other broken ends to generate rings, dicentrics, and translocations
Dicentric Chromosome Aberrations
the joining of 2 broken chromatids in different chromosomes
can be used as marker for radiation exposure
when can dicentric chromosome aberrations be detected?
after replication
examples of lethal aberrant chromosome damage
ring chromosomes, dicentric chromosomes, anaphase bridge
rings and anaphase bridge cannot be pulled apart in mitosis
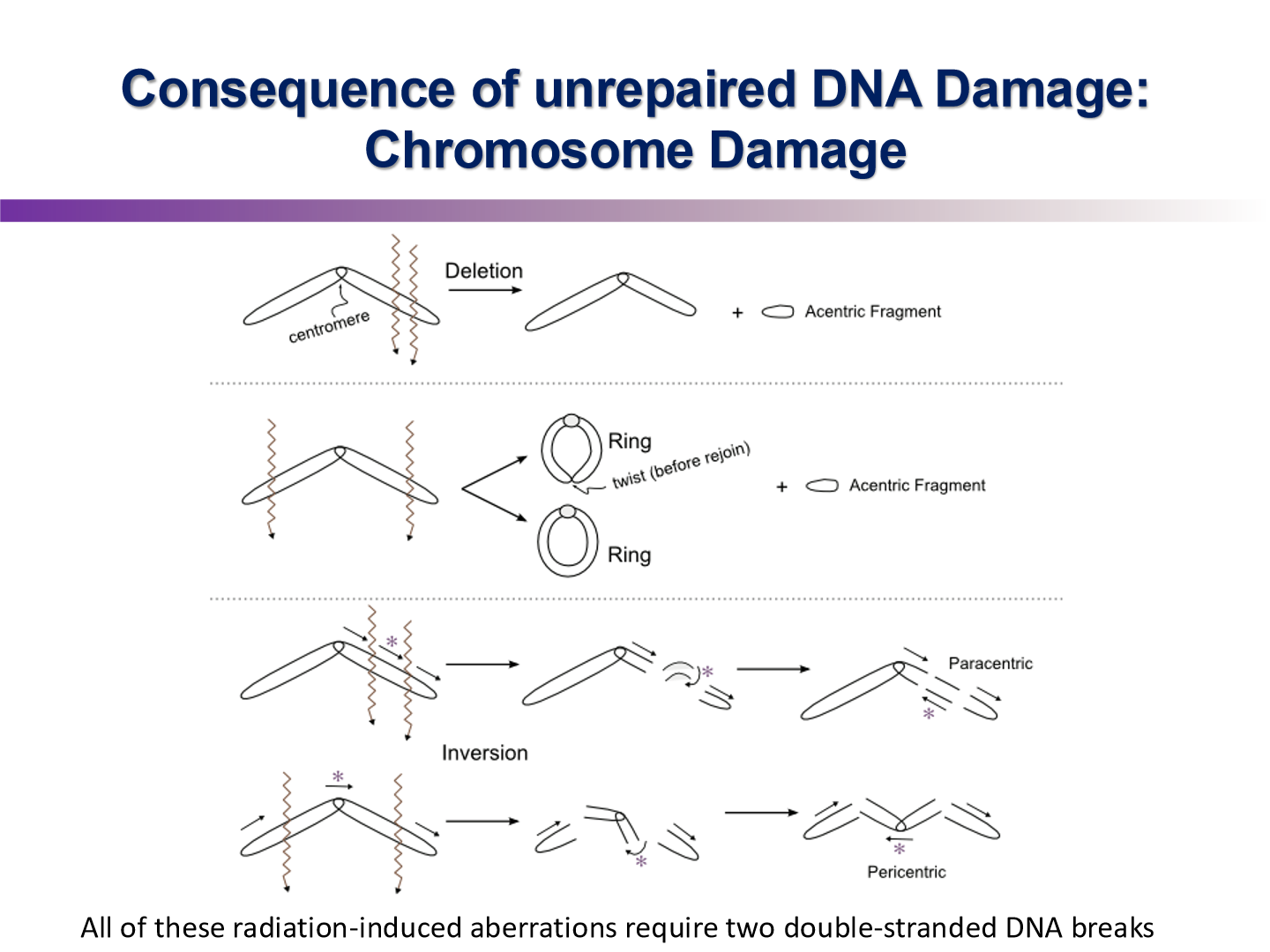
examples of non-lethal aberrations
small deletions
symmetric translocations
most chromosome aberrations lead to
cell death
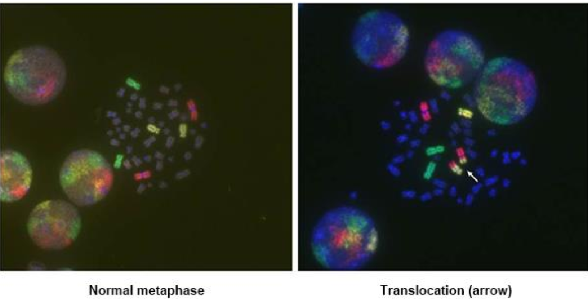
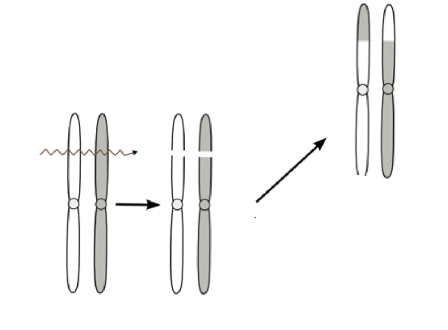
Translocation
reciprocal exchange of chromosmal fragments between two or more chromosomes
symmetric translocation
may be compatible with a normal phenotype
may have reproductive failures
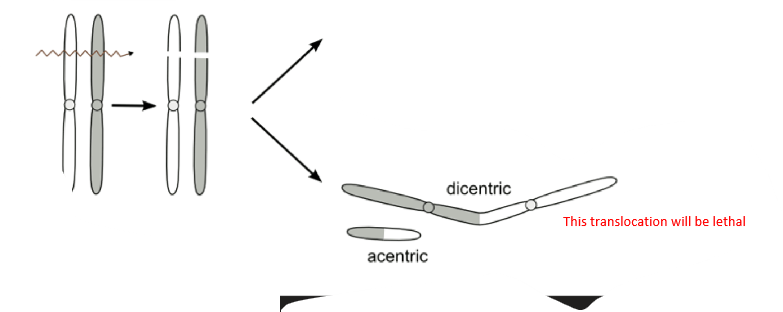
imbalanced translocation
offspring may receive only one of the rearranged chromosomes, becoming genomically incomplete
lead to miscarriage or impacted physical/mental development
What are the single stranded ends of DNA called?
telomeres
how does the cell know that a telomere is normal and not a DSB?
The cell's telomeres has a long set of repeats, and if they are flipped over on themselves, they can complement the other strand
So technically the DNA ends can pair with it's own strand, so it doesn't look like a DSB
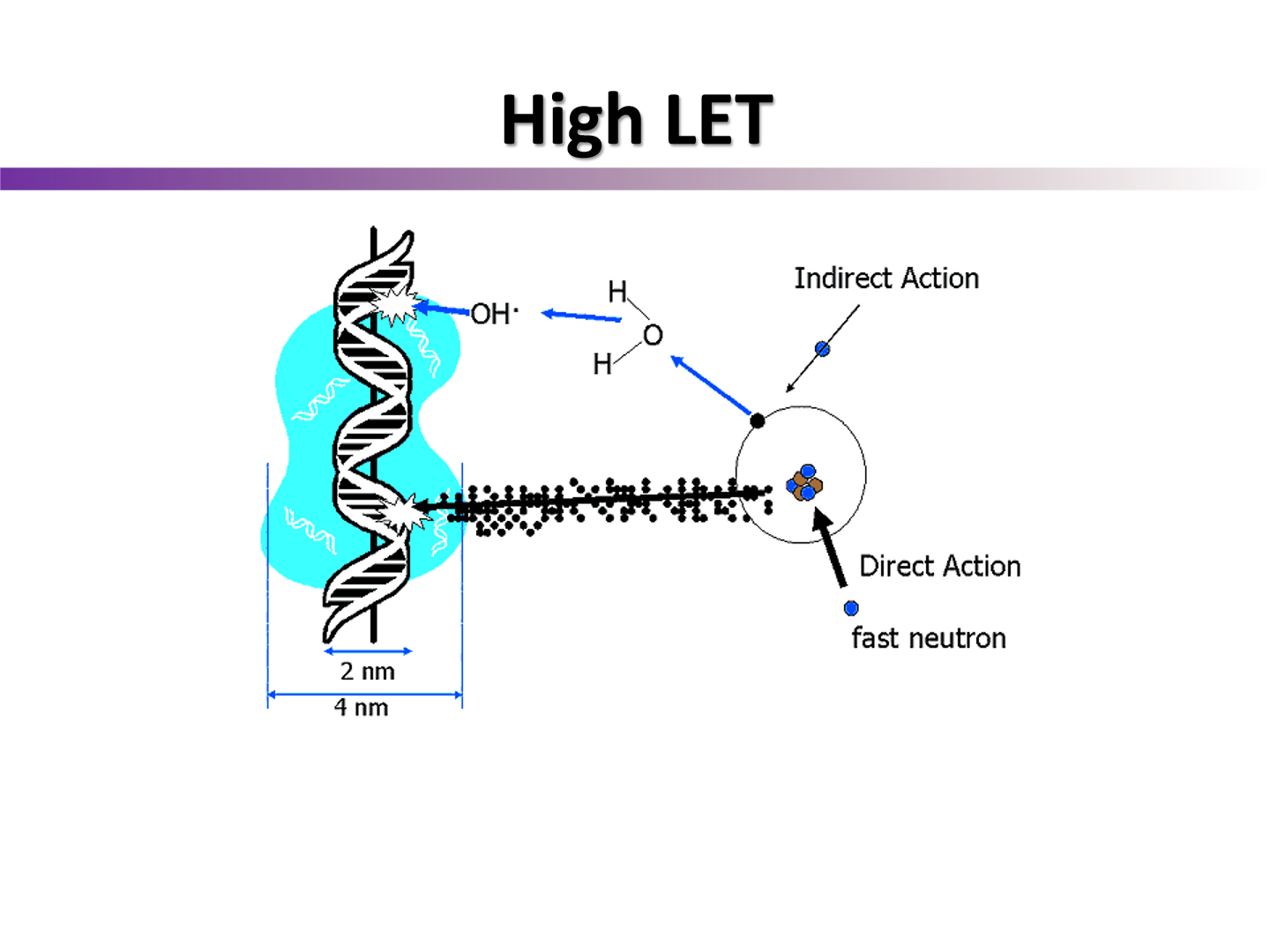
with high LET, do we get direct or indirect ionization actions?
direct action; electron damages the DNA strand directly if it lies in the direction of the electron track
with low LET, do we get direct or indirect ionization actions?
indirect ionization
electron hits radical species first, then species damages DNA
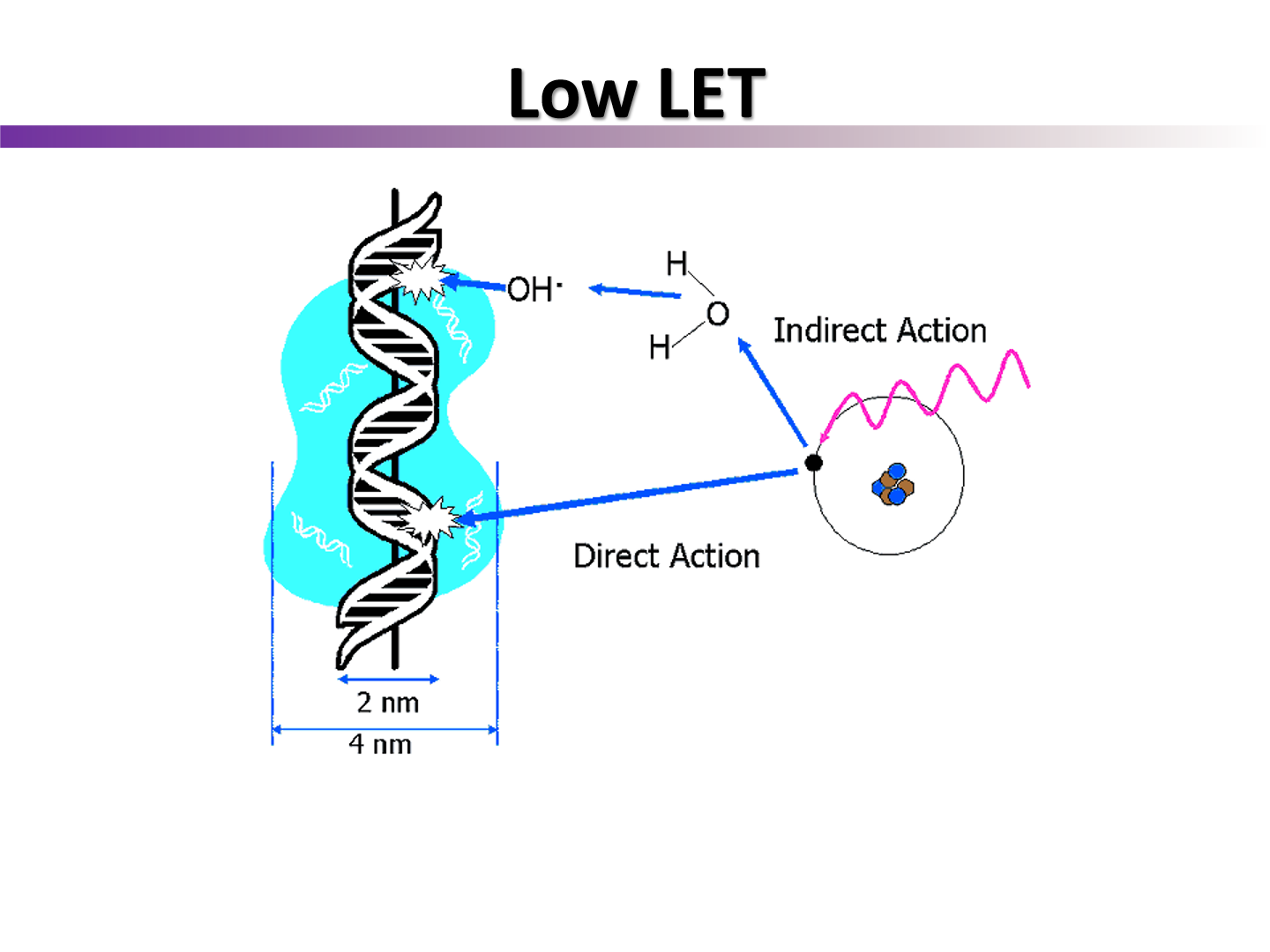
In low LET indirect ionization, electrons hit secondary molecules, leading to
clouds or pockets of ionizations on DNA molecules
two types of ionization clouds
Blobs and spurs
blobs larger than spurs
What damage products on DNA are a result of UV damage
Thymine Dimers (T-T) or photoproducts
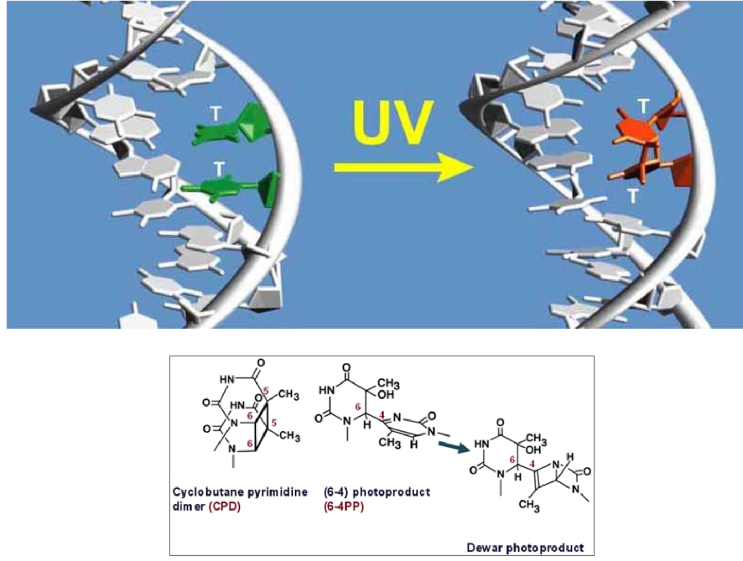
is UV damage easy for the cell to recognize?
yes, because the T-T dimers will kink the strand
What are the four general steps of DNA repair
recognize DNA damage
remove damaged nucleotides
fill the gap with DNA synthesis
polymerase needed
Seal the gap
ligase needed
What DNA repair mechanism is used to repair UV radiation damage
NER
NER - Step 1
DNA damage is recognized by XPC
NER - Step 2
excision of damaged DNA base pairs by XPF and ERCC1
NER - Step 3
New DNA is synthesized and filled into gap by polymerase beta
NER - Step 4
DNA gap is selaed with Ligase I
Mutations in the XP genes cause?
xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne syndrome
why is BER DNA damage more difficult to recognize?
it is harder to see a single nucleotide that was damage
BER - Step 1
DNA damaged recognized by DNA glycosylase
BER - Step 2
Damaged DNA is removed by APE1
BER - Step 3
DNA gap is filled with DNA polymerase beta
BER - Step 4
Gap is sealed with Ligase III and XRCC1