M-mode and 2D Examples
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Constrictive pericarditis
What condition is seen in the following m-mode image?
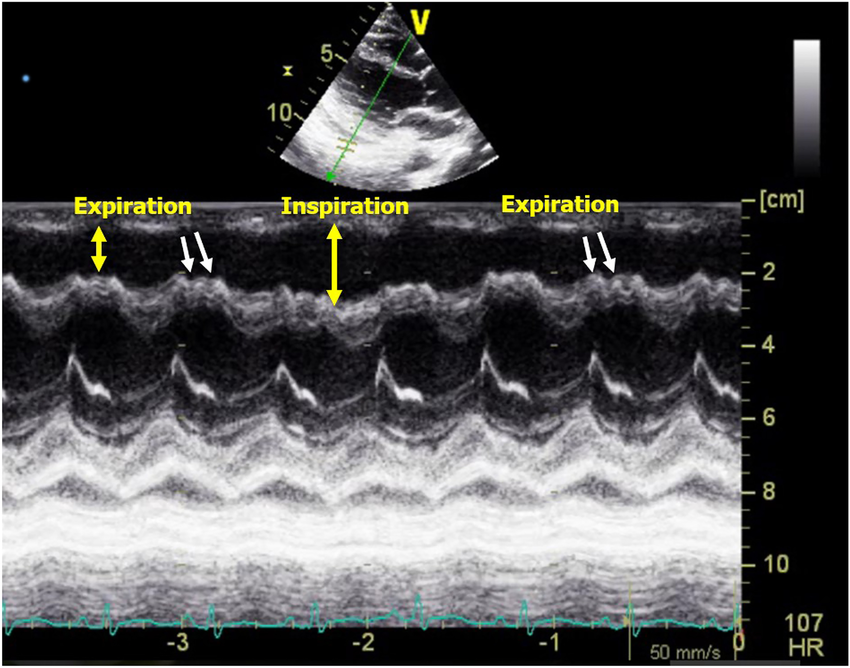
Cardiac tamponade
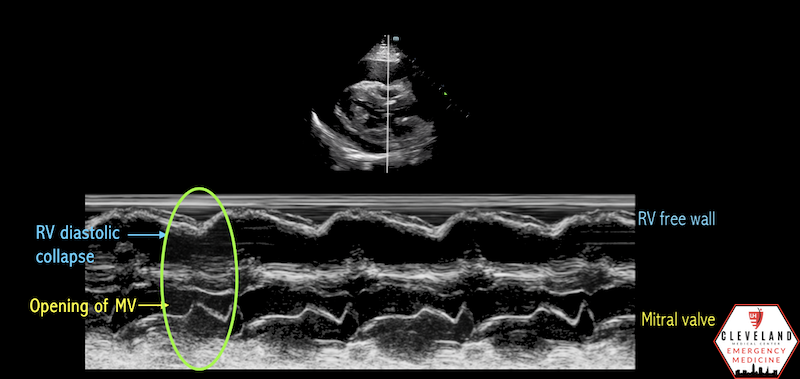
What condition is seen in the following m-mode image?
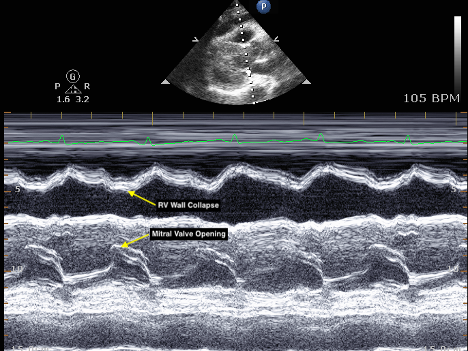
Cardiac tamponade
What condition is seen in the following m-mode image?
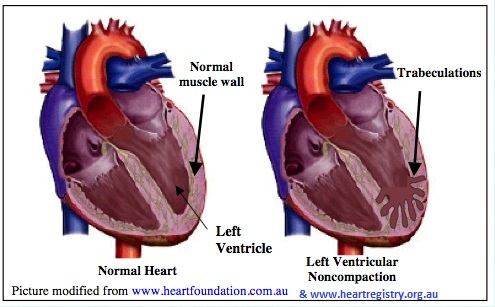
LV noncompaction CM
What is seen in this 2D image?
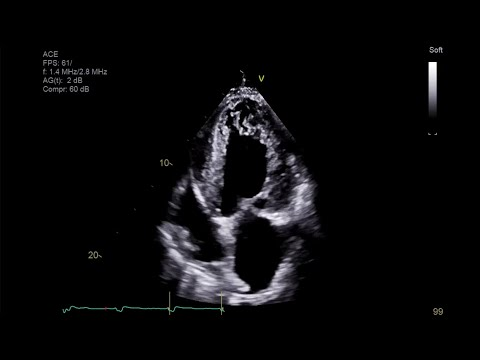
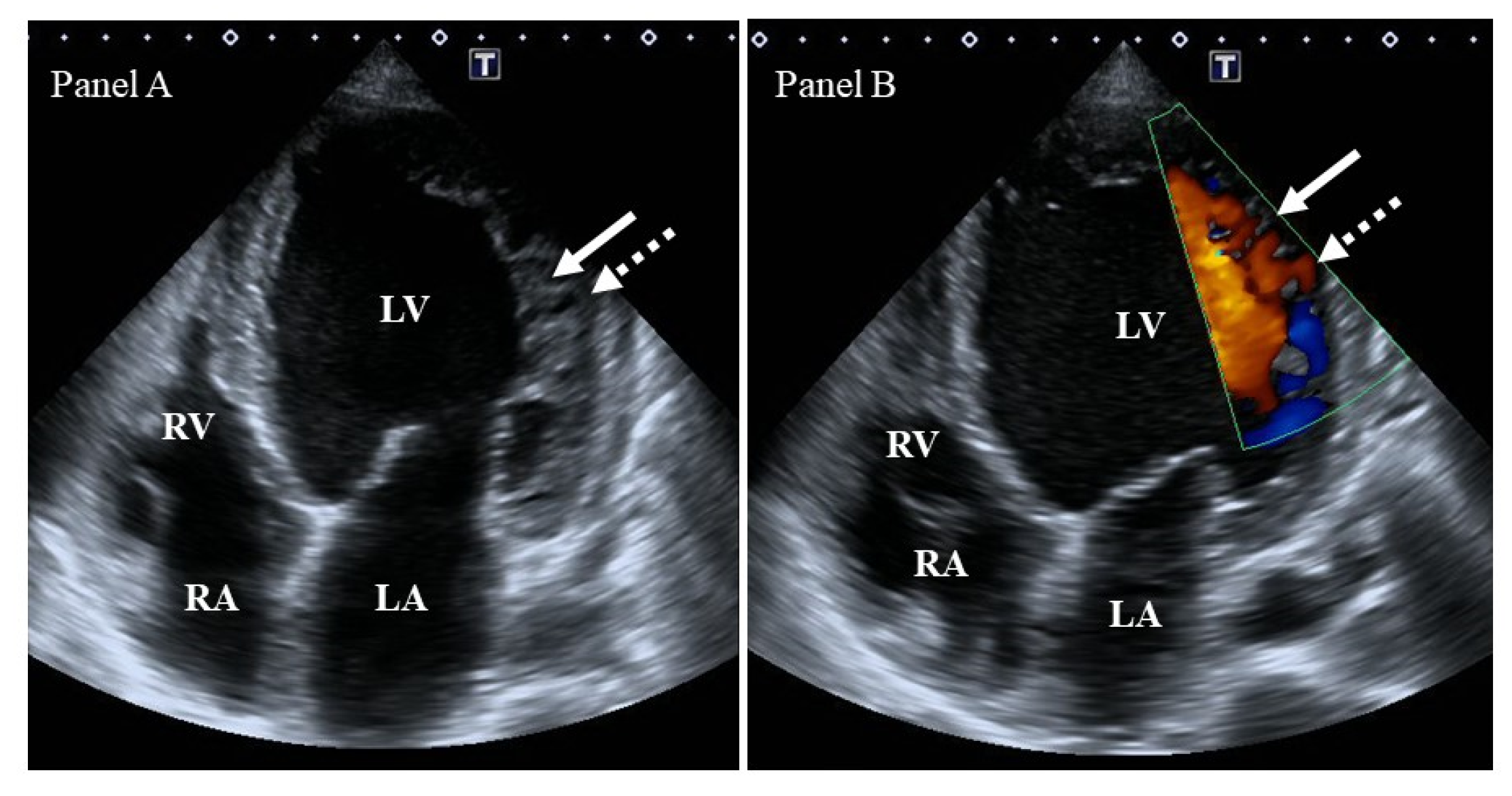
LV noncompaction CM
What is seen in this 2D image?
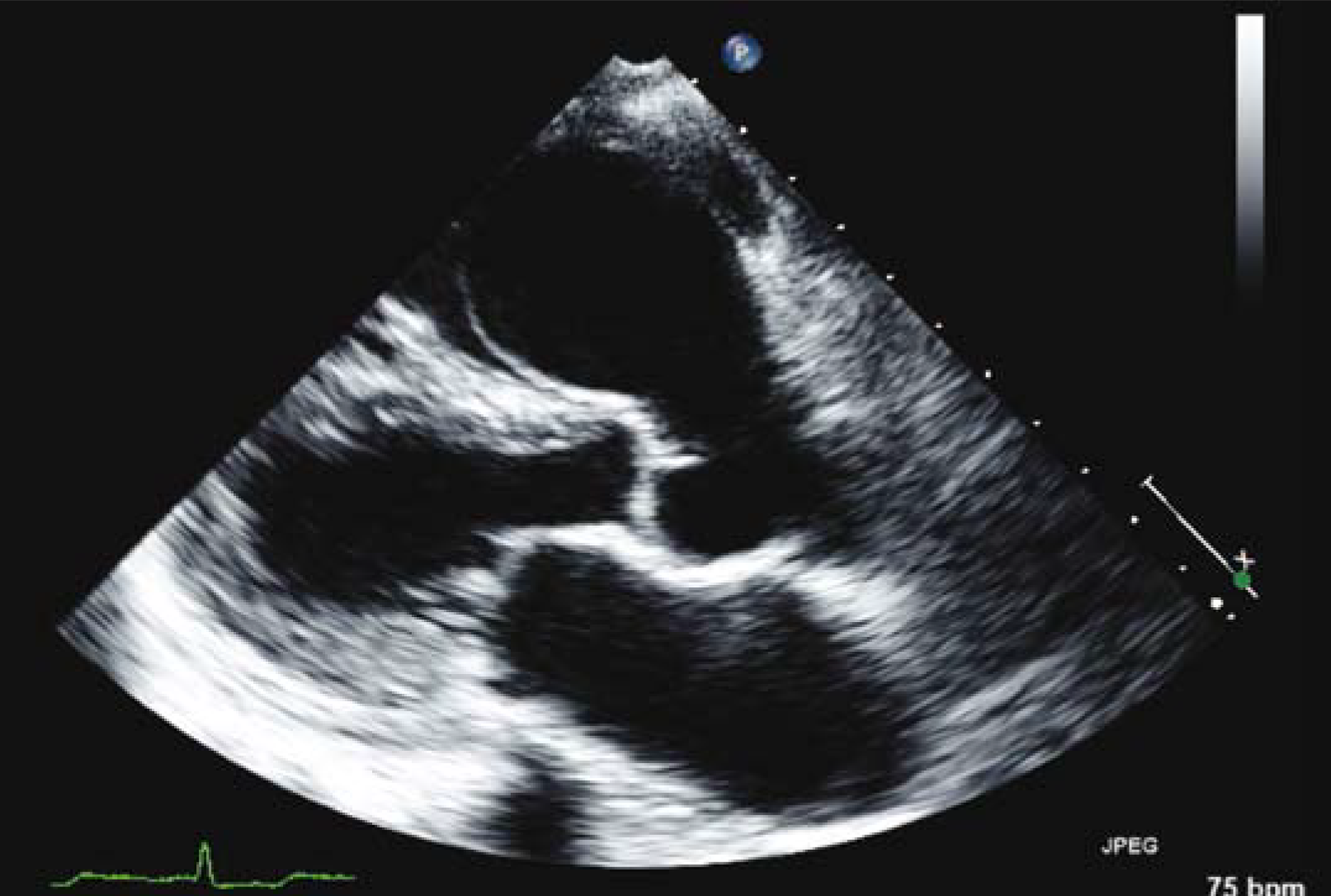
True aneurysm
Localized, full-thickness bulge of the heart wall that is still intact, but weakened.
Surrounded by myocardial tissue.
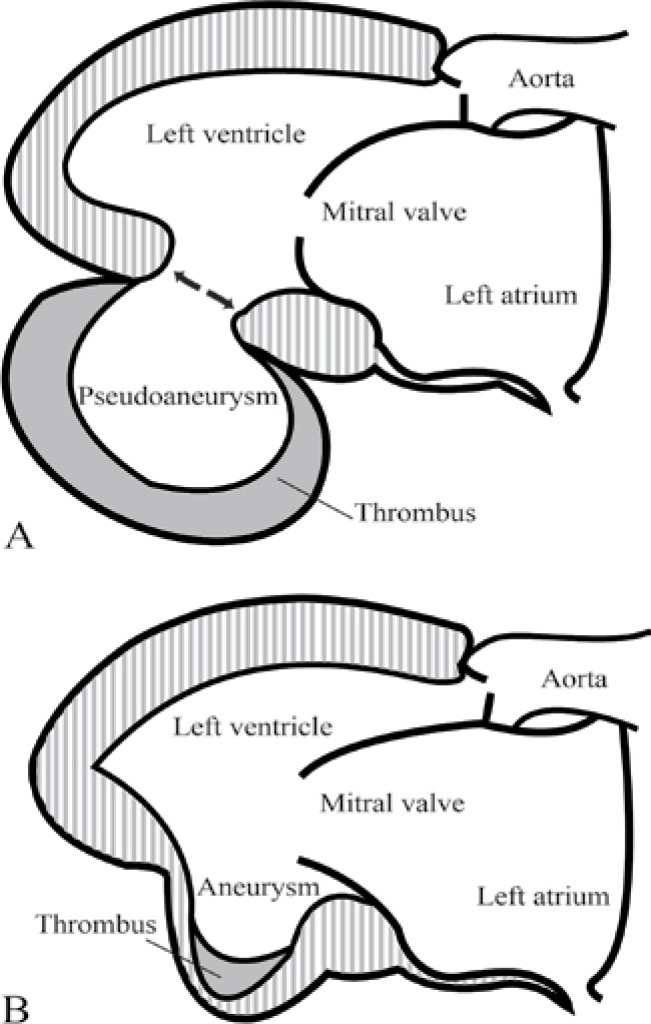
Pseudoaneurysm
A saccular outpouching with a narrow neck originating from a discontinuity in the heart wall.
Narrow neck and lack myocardial or endocardial tissue.
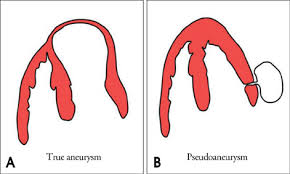
True cardiac aneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
True cardiac aneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
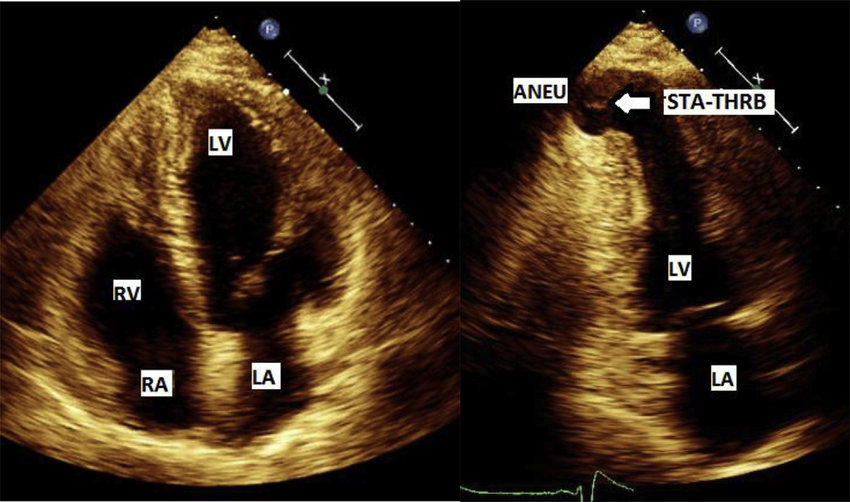
Pseudoaneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
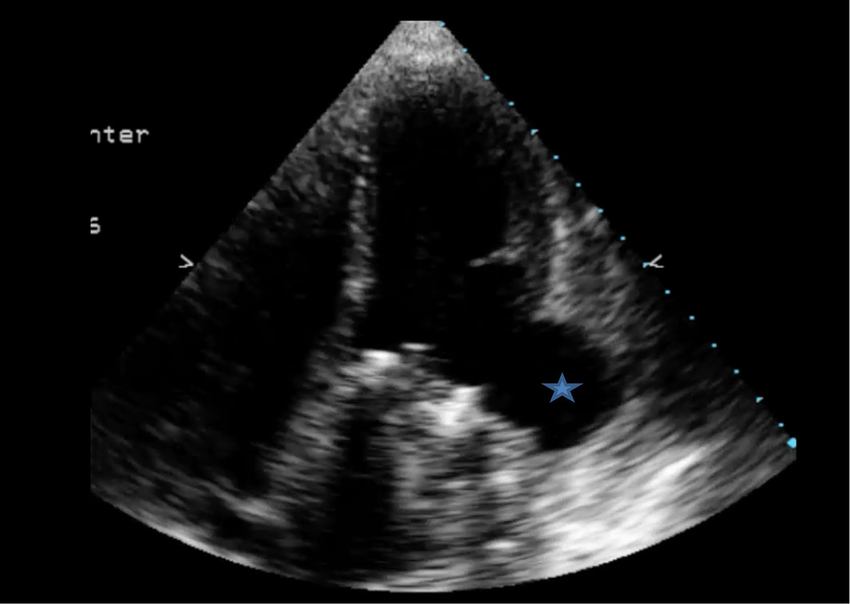
Pseudoaneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
Dilated CM w/ MS
What does this m-mode image show?

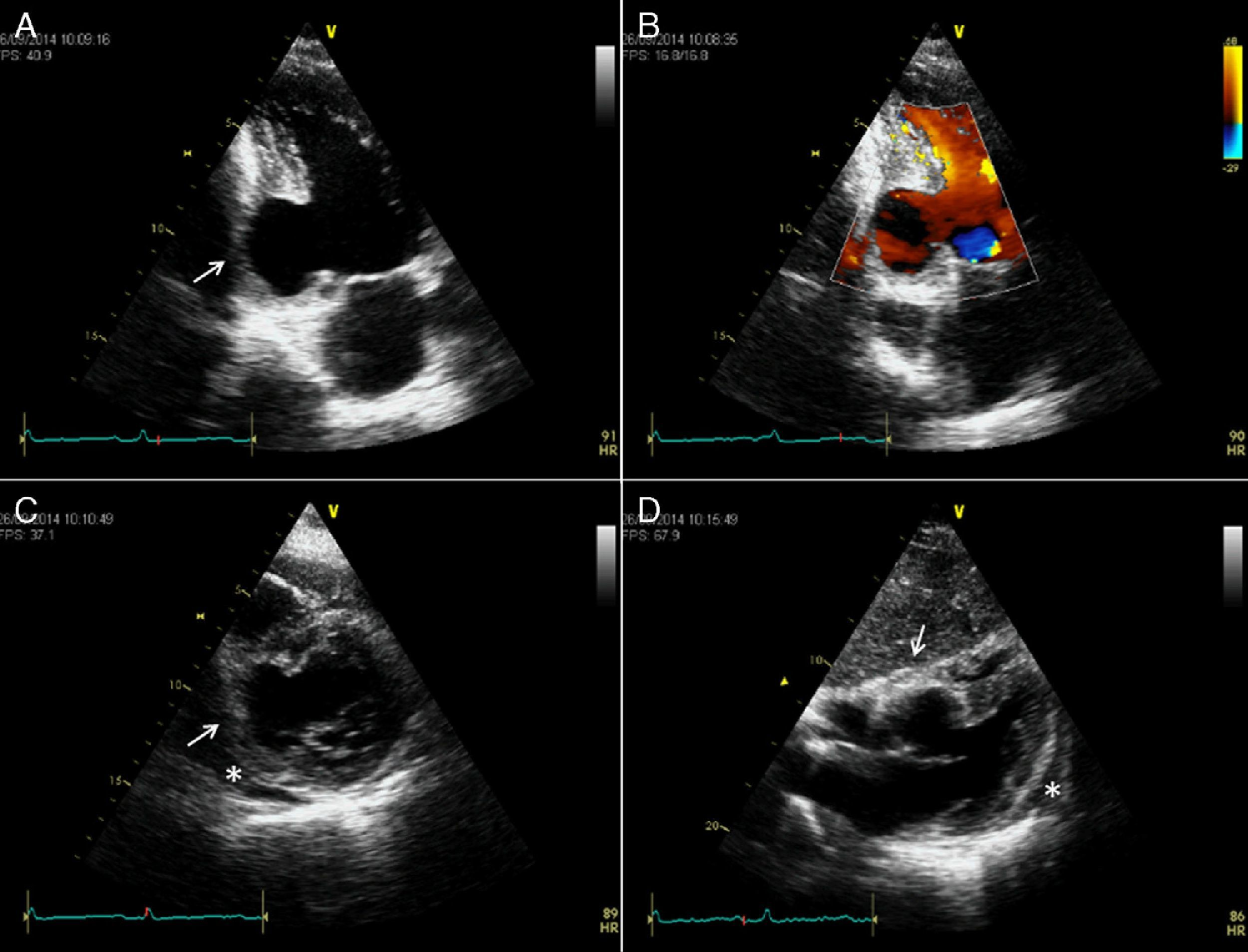
Sinuses of valsalva aneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
Sinuses of valsalva aneurysm
What is seen in the 2D image?
Right heart - RA or RV
Where do sinus of valsalva aneurysms most often rupture into?
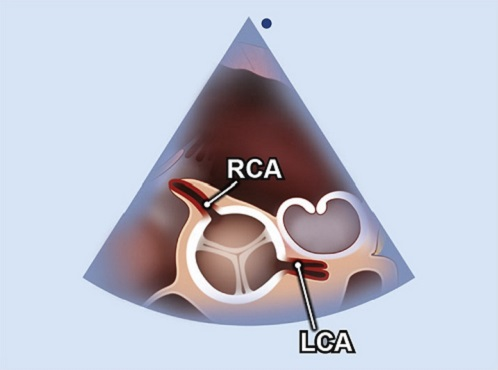
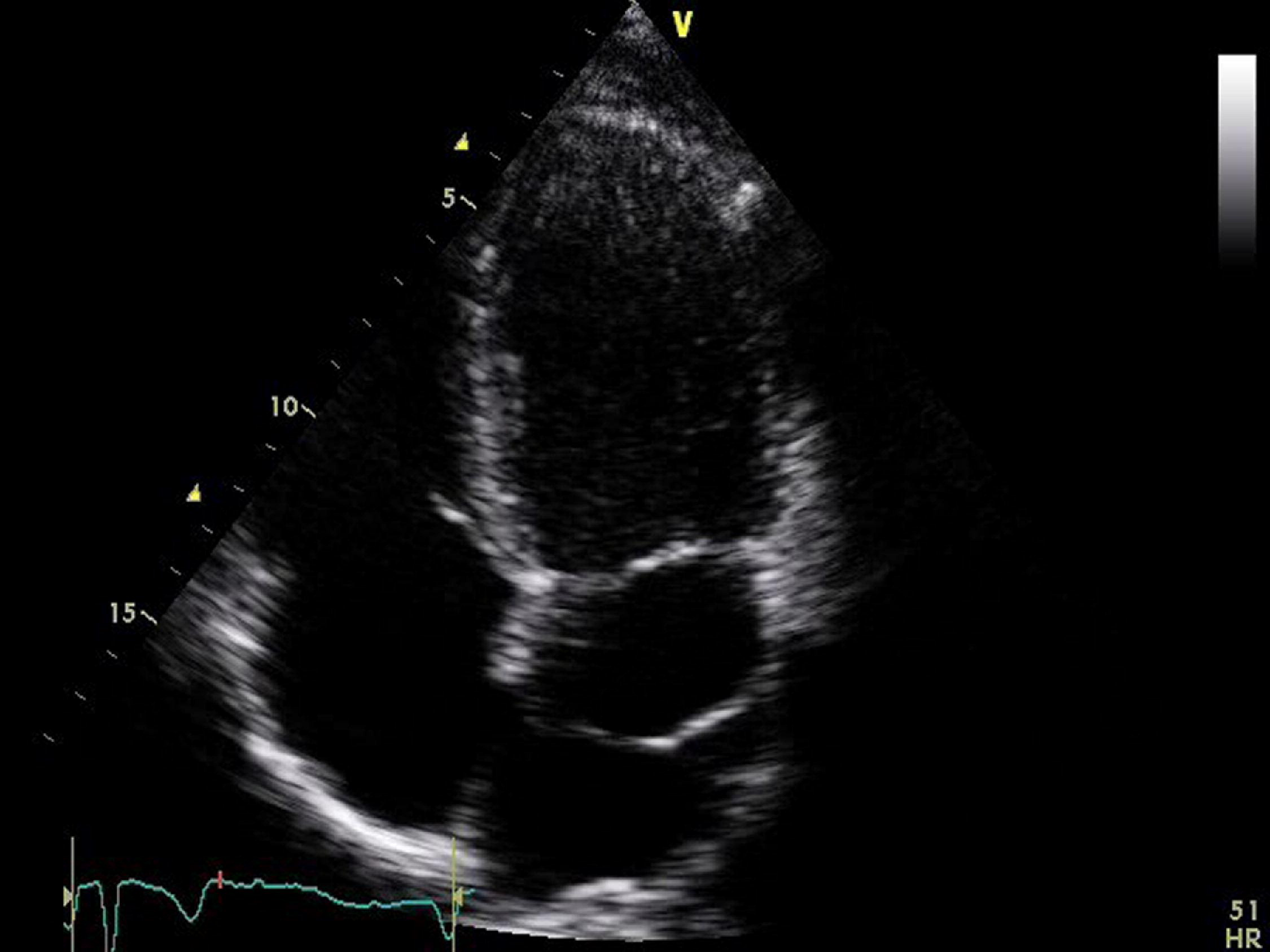
Left main coronary artery
What artery is seen in this image?
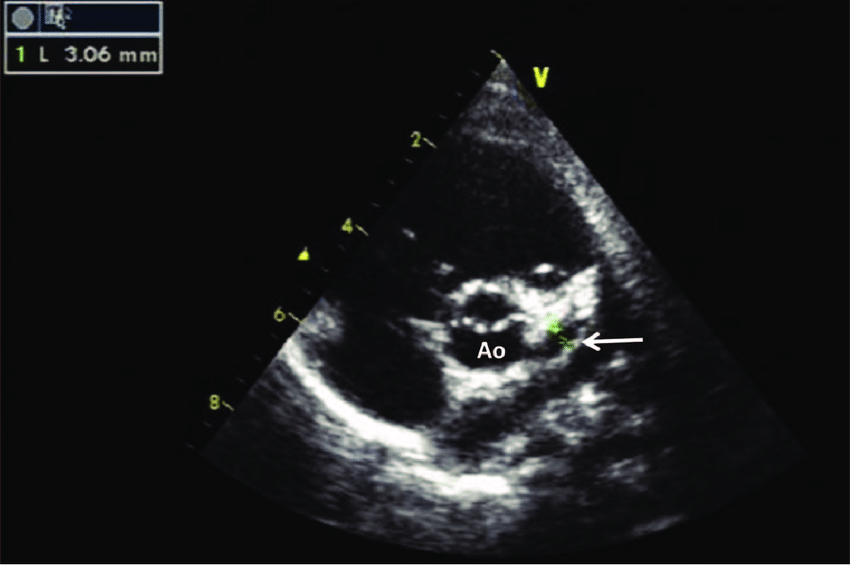
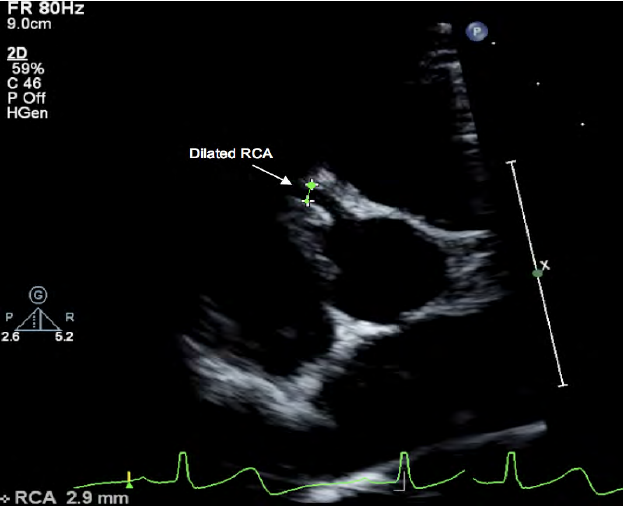
Right main coronary artery
What artery is seen in this image?
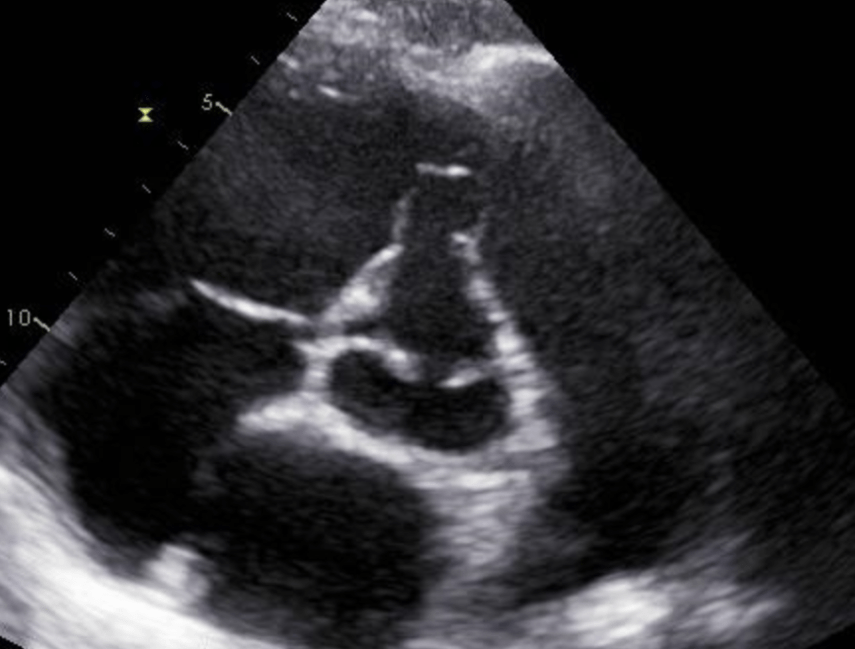
Cor triatrium
What is seen in the 2D image?
Eustachian valve
What is seen in the 2D image?
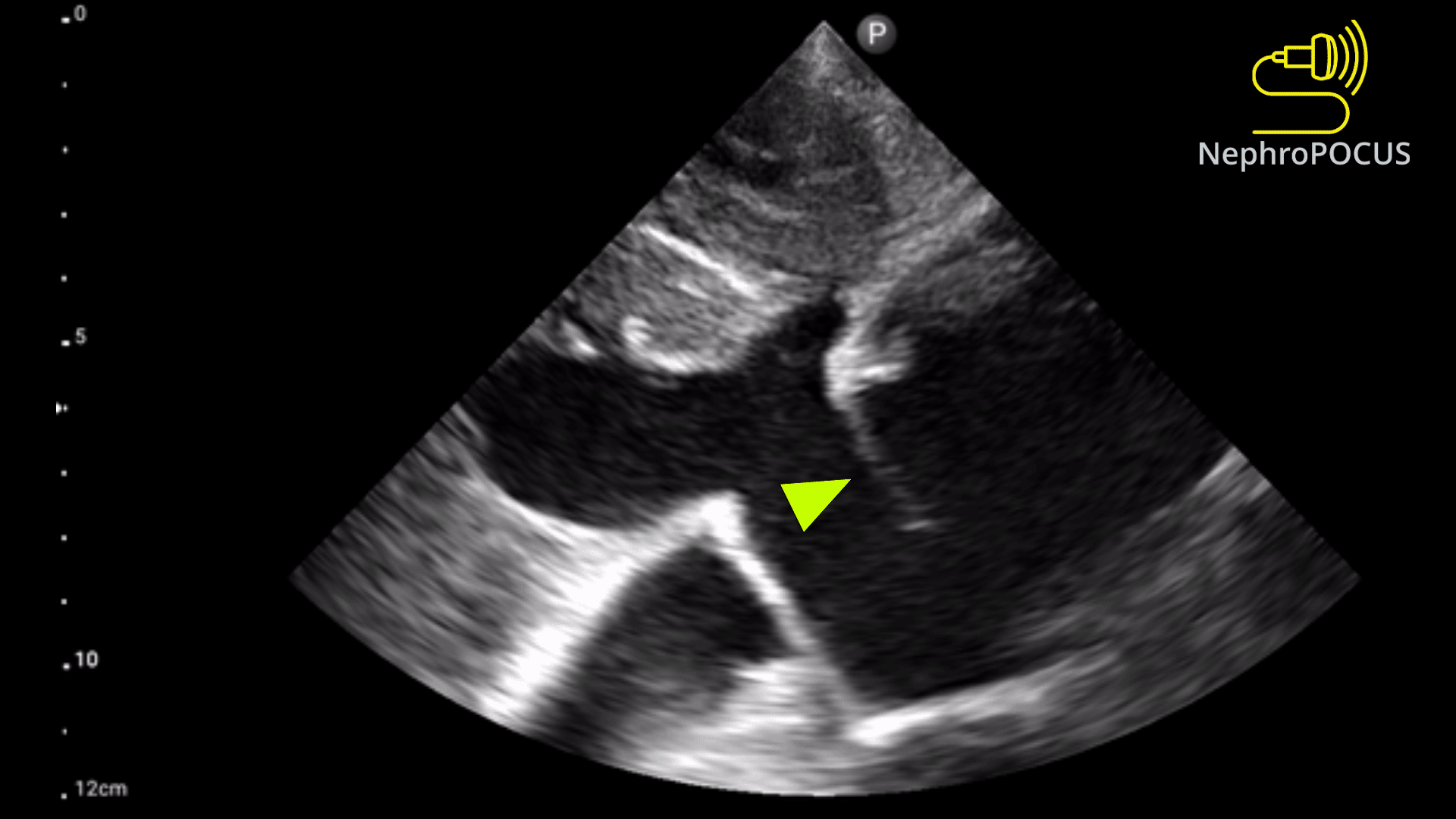
SSN
High basal PSAX
What views can a PDA be seen from (2)?
Patent ductus arteriosus
What is seen in this 2D image?
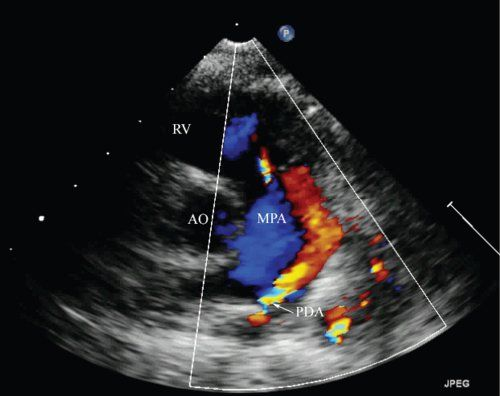
Patent ductus arteriosus
What is seen in this 2D image?
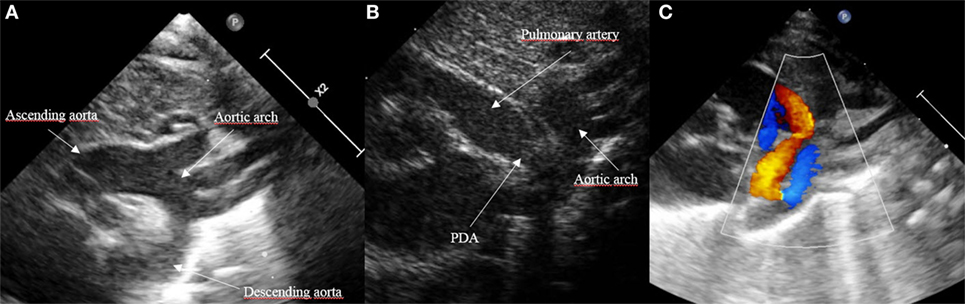
Severe pulmonary hypertension
What is the “flying w” sign on echo associated with?
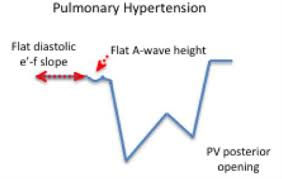
Flying w sign
What is seen in the m-mode image?
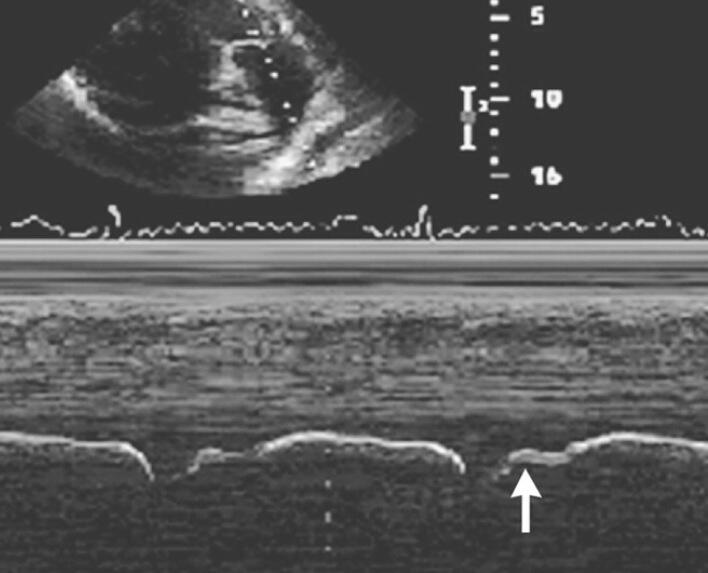
Pulmonary HTN
Flying w sign
What diagnosis is consistent with this spectral Doppler?
What sign is seen?
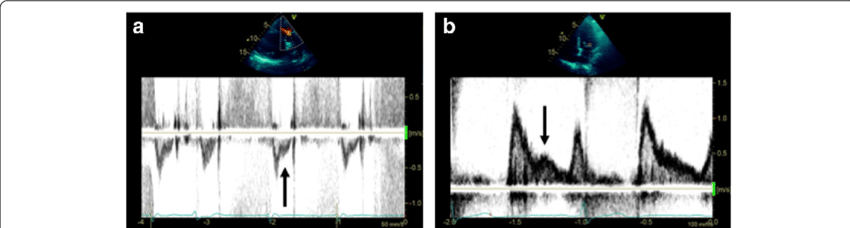
Acute PE
McConnell’s sign is associated with what finding?

McConnell’s Sign
Acute PE
What is seen in this 2D image?
What does it indicate?
Dressler’s syndrome
Secondary form of pericarditis that occurs in the setting of injury to the heart or pericardium.
Acute MI
What can cause Dressler’s syndrome?
Acute MI
Chronic HTN and diffuse ST elevation indicate ___.
ST
Elevation
Myocardial
Infarction
STEMI stands for ___?
Aortic dissection
Sudden back pain and SOB indicate ___.
Life-threatening condition.
Perimembraneous VSD
What is seen in this 2D image?

Outlet VSD (supracristal)
What is seen in this 2D image?
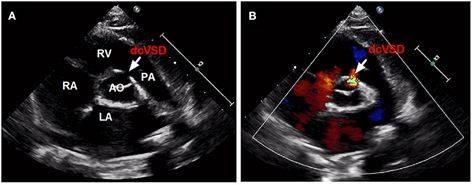
Outlet VSD
Located below the aortic and pulmonary valves in the outlet of the septum of the right ventricle.
ASD
What is most commonly seen with Ebstein’s anomaly?
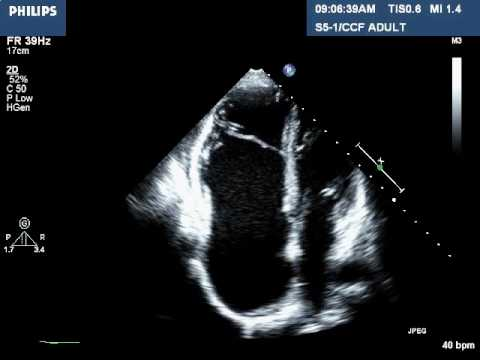
Ebstein’s anomaly
What condition is seen in the 2D image?
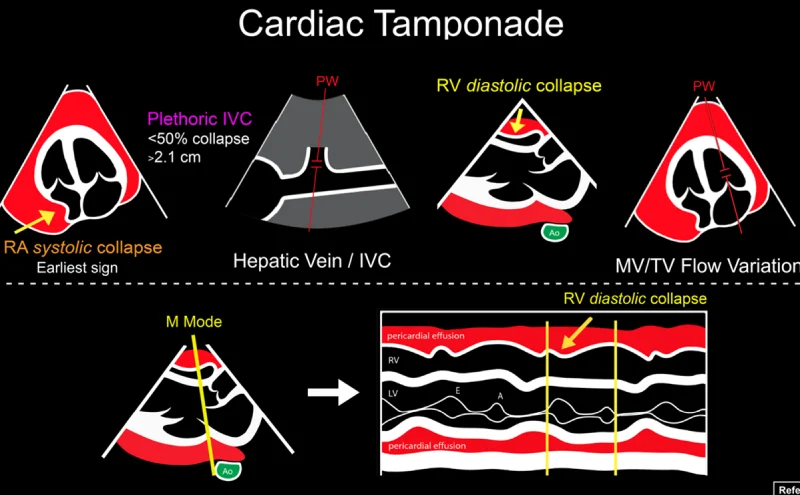
Cardiac tamponade
What condition is seen in this 2D image?

Mid systolic closure of aortic valve
Stress CM (Takotsubo)
What condition is seen in this 2D image?
What condition is it seen in?
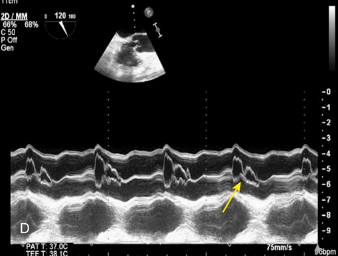
Mid-systolic closure of aortic valve
HOCM
What condition is seen in this 2D image?
What condition is it seen in?
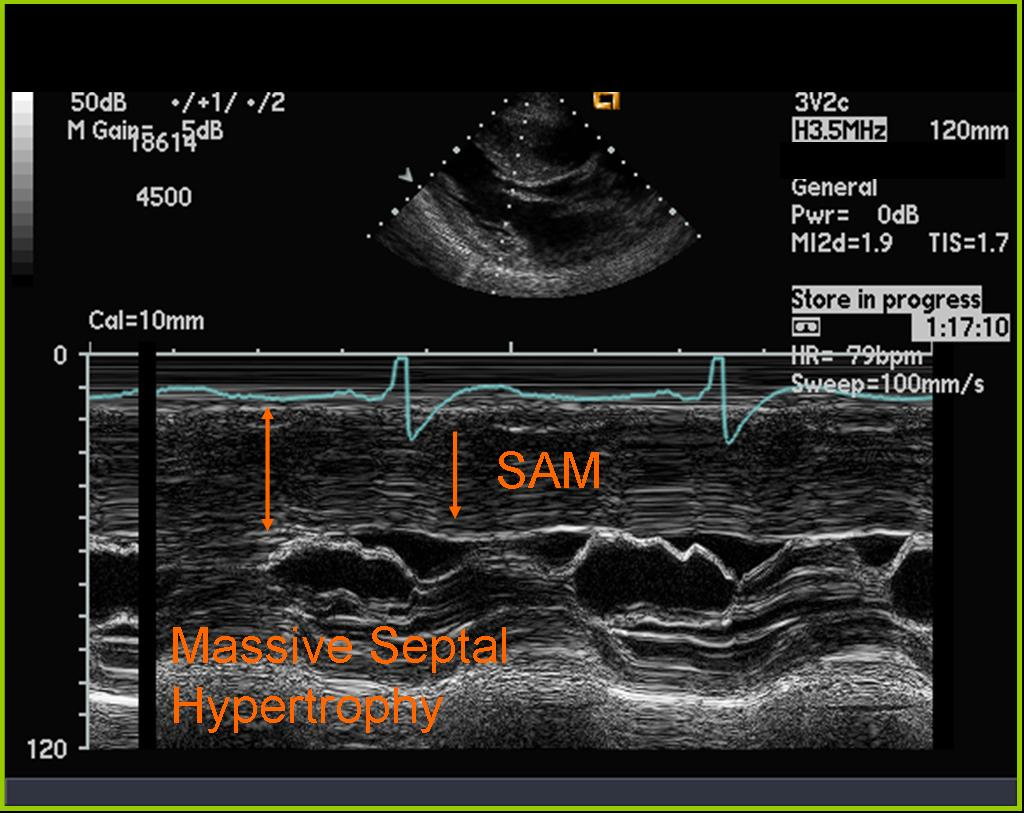
Systolic anterior motion of MV
HOCM
What is seen in this 2D image?
What condition is it seen in?
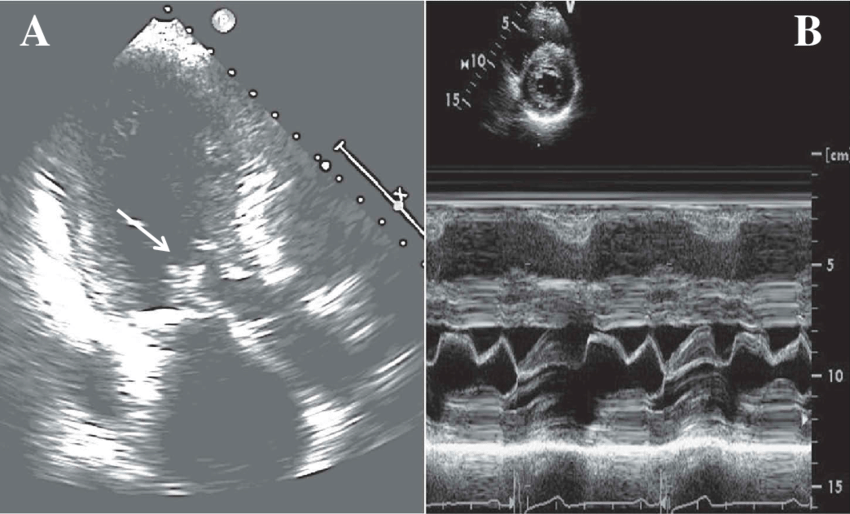
Pericardial “rind” or thickening of the visceral pericardium
Secondary to inflammation related to acute pericarditis.
Best seen adjacent to the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
What are the arrows pointing to?

Epicardial fat
What is being pointed to in this image?
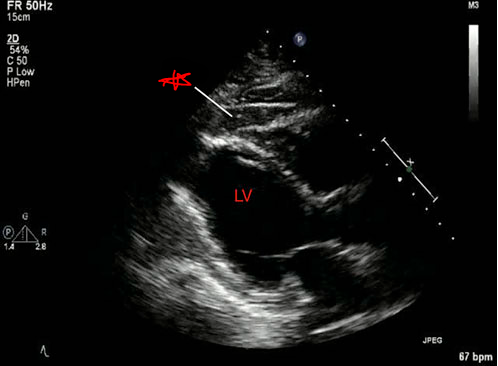
Early systolic beak
Left bundle branch block
What is the arrow pointing to?
What condition is this finding demonstrated in?
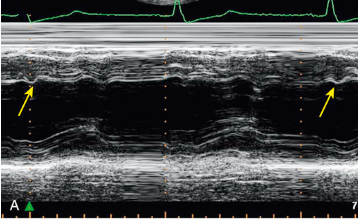
Oscillatory changes of the IVS
Constrictive pericarditis
What is the arrow pointing to?
What condition is this finding demonstrated in?
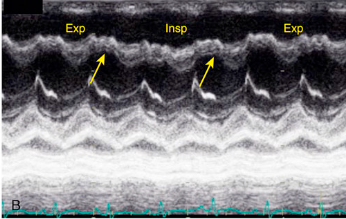
Septal compression toward LV (systole and diastole)
Right ventricular pressure overload
What is the arrow pointing to?
What condition is this finding demonstrated in?
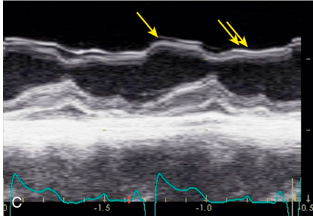
Septal compression toward LV during diastole (normal systole)
Right ventricular volume overload
What is the arrow pointing to?
What condition is this finding demonstrated in?
Bicuspid aortic valve
Aortic dissection or aneurysm
Coarctation of the aorta
Aortic dilatation
Valvular aortic stenosis - from BAV
What echo findings are associated with Turner’s syndrome?
Type A aortic dissection
What is seen in the TEE image?

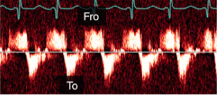
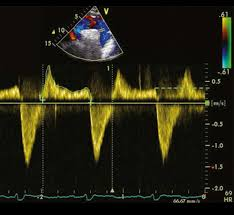
To-and-fro pattern
Secondary communication points
What is this spectral Doppler pattern called?
Where is it found in regards to aortic dissection?
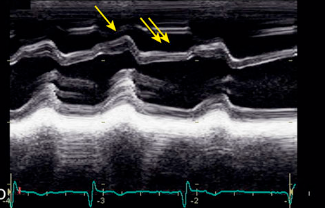
Incomplete separation in aortic dissection
What are the arrows pointing towards?
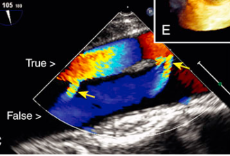
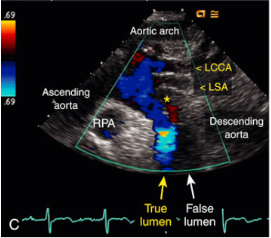
Aortic dissection
What is seen in this 2D image at the SSN?
Severe, sudden-onset chest or back pain
Pulse deficit
Intimal flap on TTE
Hypotension
What are the signs and symptoms of aortic dissection?
Pulse deficit
A significant difference in blood pressure between the arms.
Seen in aortic dissection.
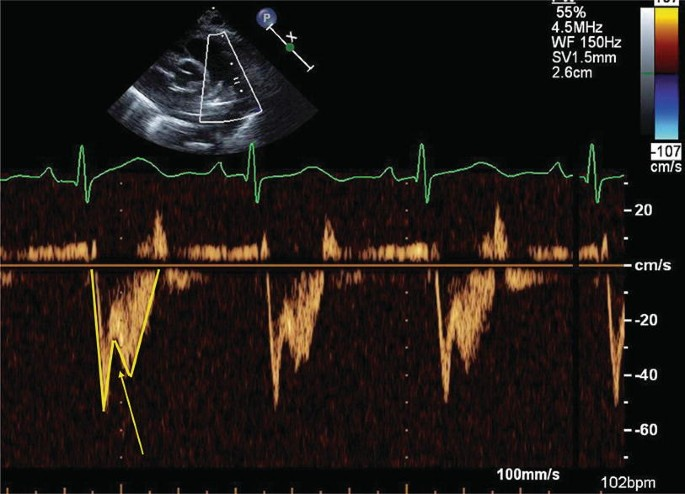
Holodiastolic flow reversal
Above the baseline
Severe aortic regurgitation
What is seen in this image?
Where is it located?
What condition is it seen in?
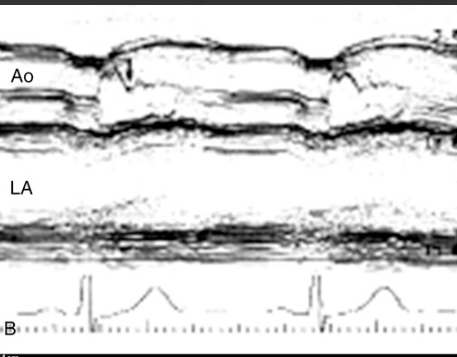
Delayed mitral valve closure due to elevated EDP
Dilated cardiomyopathy
What does the b-bump represent on m-mode?
What condition is it seen in?
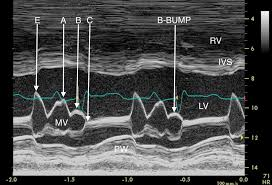
Increased e point septal separation
What m-mode finding is seen on both aortic insufficiency and DCM?
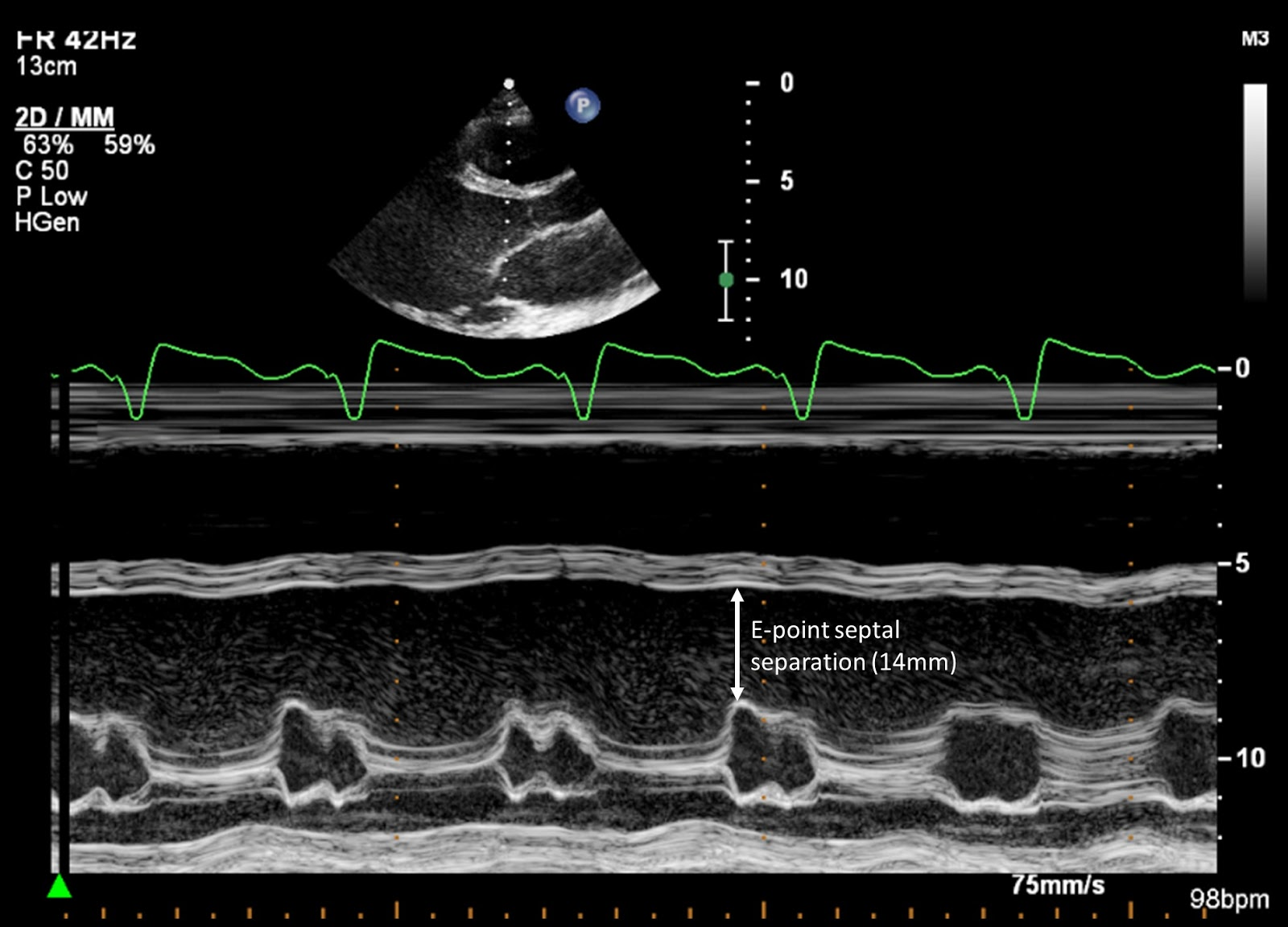
Aortic regurgitation
An absence aortic dicrotic notch on pressure-volume curve most likely indicates ___.