Orgo chapter 11 mcat
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Infrared spectroscopy/ IR spectroscopy
measures absorption of infrared light, which caused molecular vibration (stretching, bendingh, twising, folding)
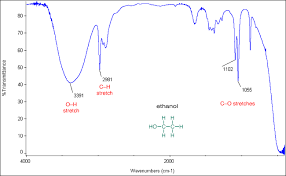
O H peak
broad peak between 3300 and 3000
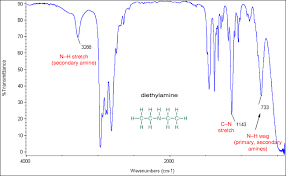
N H peak
sharp peak around 3300
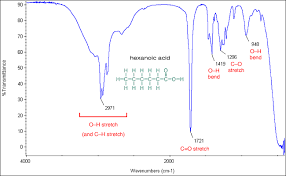
C=O peak
sharp peak at 1750
UV spectroscopy
most useful for studying compounds containing double bonds or heteroatoms with lone pairs that create conjugate system
proton NMR
best used for:
determining relative number og protons and their relative chemical environments
showing how many adjacent protons there are by splitting patterns
inferring certain functional groups
alkyl groups
0 to 3 ppm
alkynes
2-3 ppm
alkenes
4.6-6 ppm
aromatics
6-8.5 ppm
aldehydes
9-10 ppm
carboxylic acids
10.5-12 ppm
nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy/ NMR spectroscopy
measures alignment of nuclear spin with an applied magnetic field, which depends on the magnetic environment of the nucleus itself. It is useful for determining the structure (connectivity) of a compound, including functional groups
deshielding
occurs when EWG pull electron density away from the nucleus, allowing it to be more easily affected by the magnetic field, this moves peaks further downfield
left/downfield
higher chemical shifts are located where?
right/upfield
lower chemical shifts are located where?
linear
Bond angle: 180
Steric number: 2
trigonal planar
Bond angle: 120
Steric number: 3
tetrahedral
Bond angle: 109.5
Steric number: 4