The Digestive System
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on some slides on the digestive system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Fistulated cow
A cow with a passageway connecting the cow’s stomach to the outside for observation and measurement

Scurvy
A disease caused by a lack of vitamin C where the body is unable to replenish the protein collagen in the skin; can cause bleeding gums, swelling, wounds, bruising
Often experienced by the sea-bound without fruits or vegetables
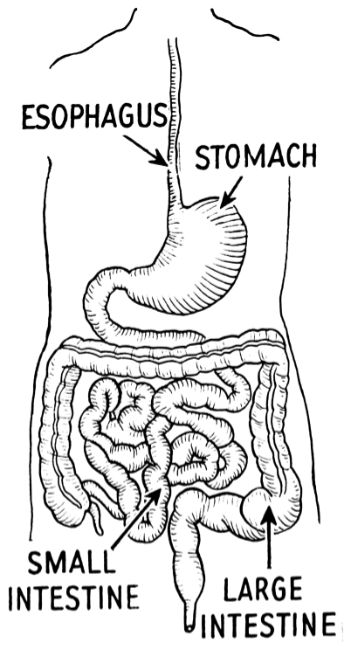
Digestive system
System formed for the absorption of nutrients through the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food; consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs
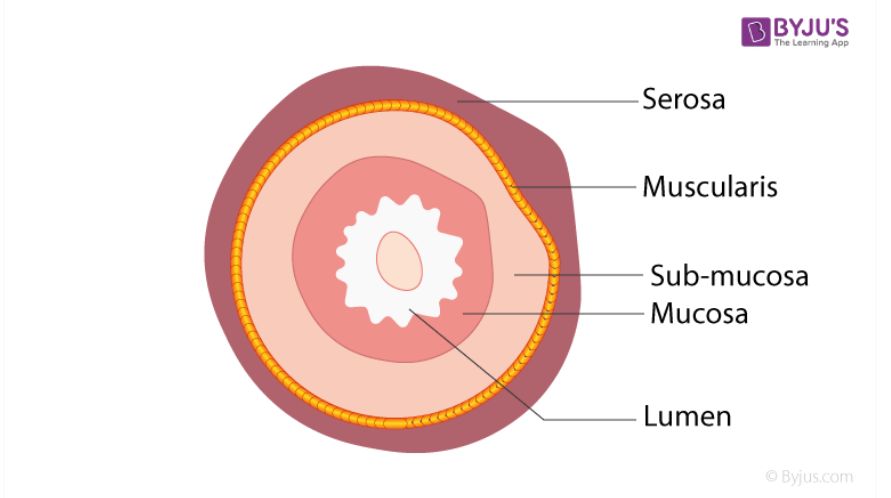
Mucosa
The innermost layer of the alimentary canal that protects tissues and aids absorption
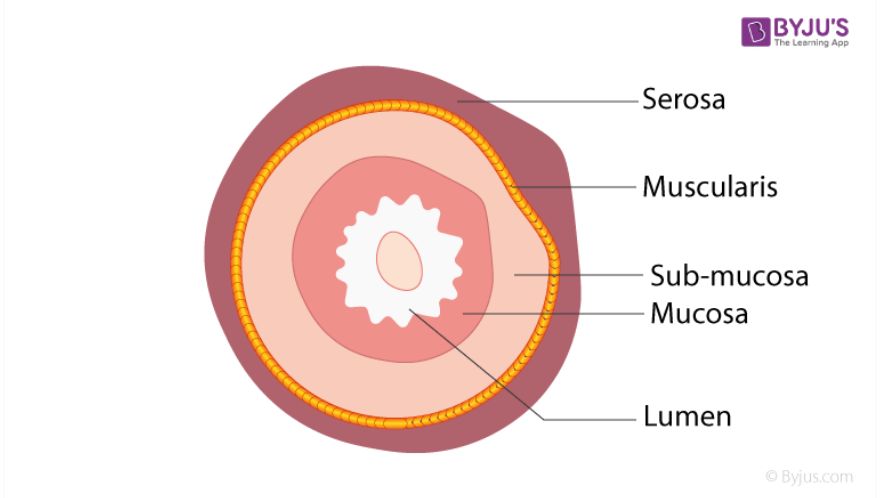
Submucosa
The layer outside of the mucosa that holds glands, blood vessels, and nerves
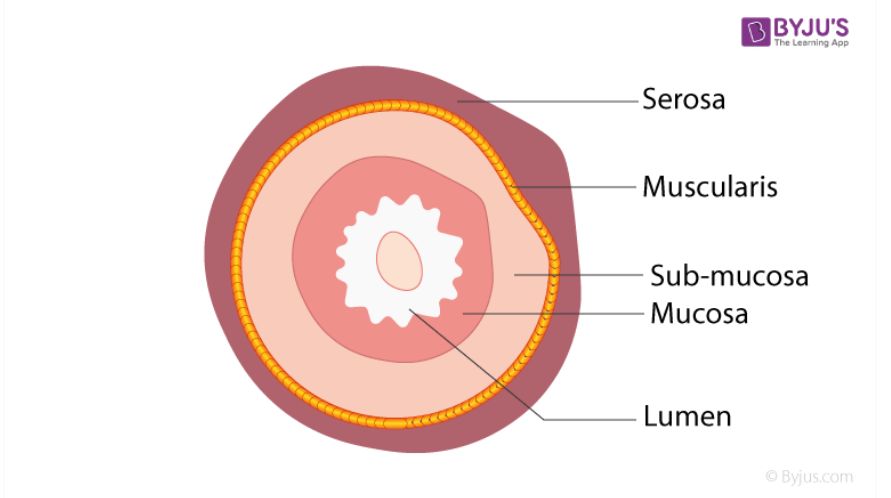
Muscular layer
The smooth muscle of the alimentary canal that pushes food through
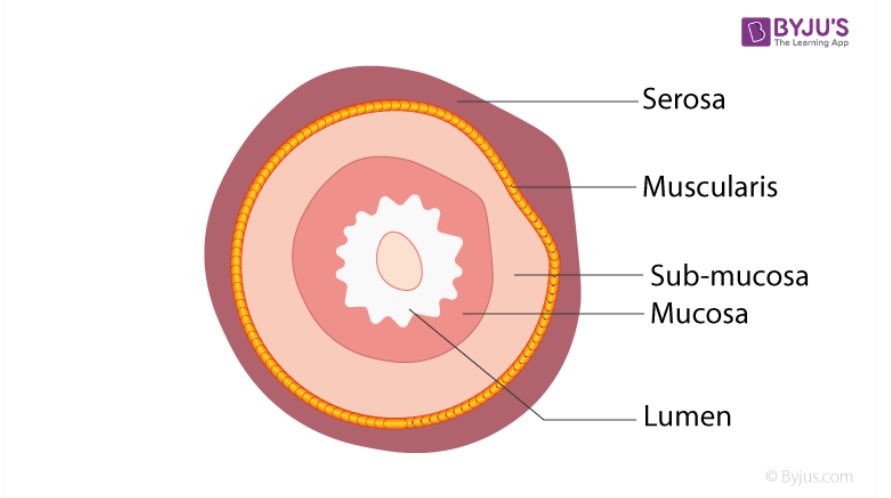
Serosa
Layer of the alimentary canal that lubricates surfaces
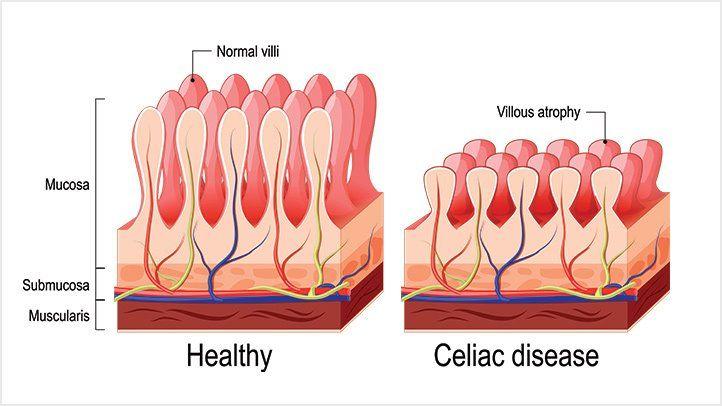
Villi
Structures in the small intestine that increase surface area for nutrient absorption
Celiac disease
Disease that damages the villi and reduces nutrient absorption capacity; gluten triggers villi immune destruction
Mixing movements
Movements that mix food with digestive juices in the digestive system
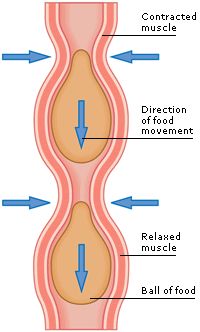
Peristalsis
Movements that push food down the esophagus
Saliva
Liquid in the mouth that begins digestion through chewing and mixing
Frenulum
Tissue that connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth
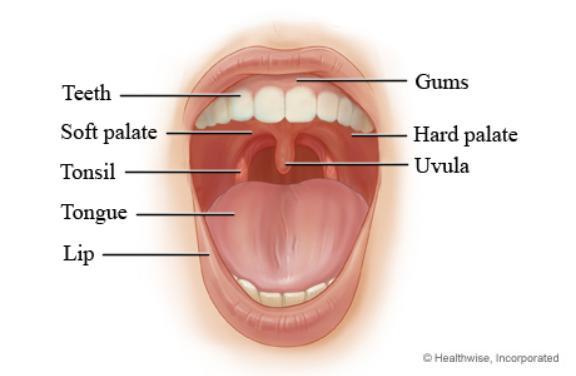
Tongue
Structure in the mouth that moves food
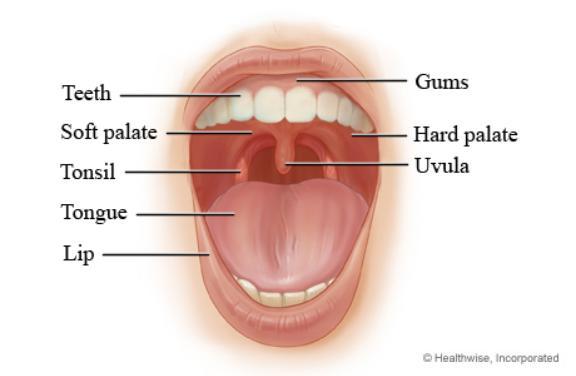
Palate
The roof of the oral cavity with hard and soft parts
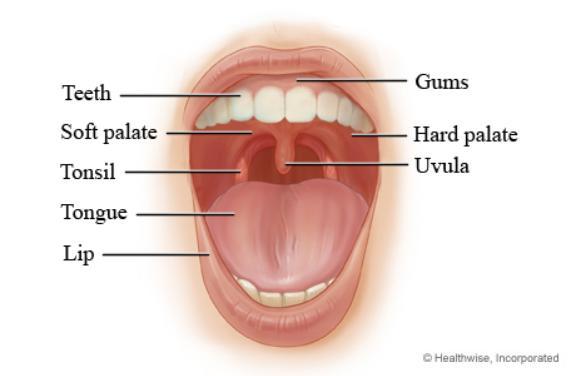
Uvula
The back bulbous structure in the mouth
Palatine tonsils
Structures in the back of the mouth that are part of the immune system; can be inflamed and require removal
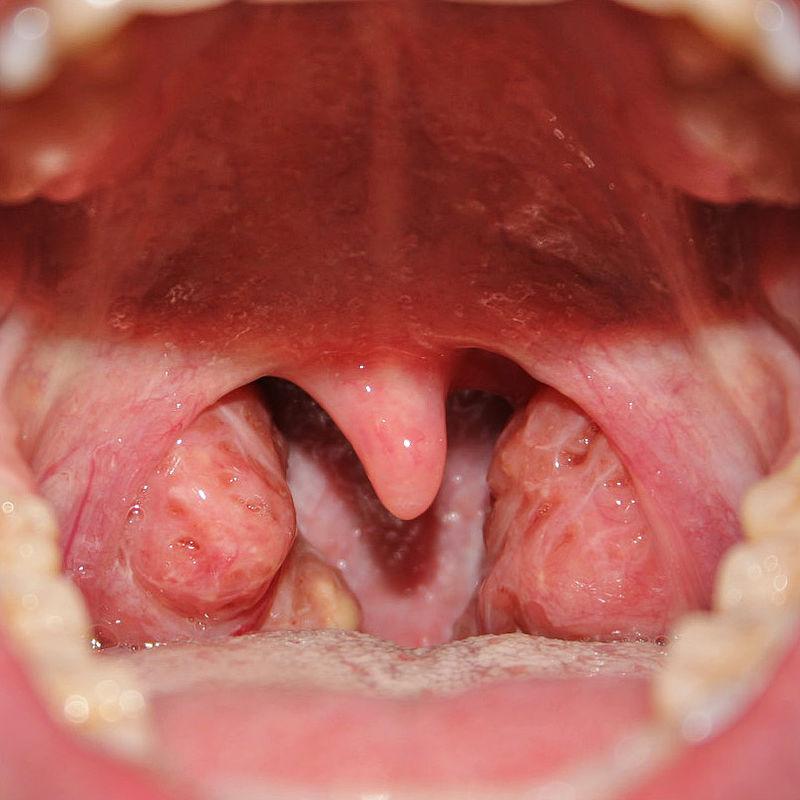
Tonsillitis
Inflammation of the tonsils that can cause a sore throat and fever; a tonsillectomy (tonsil removal) may be required
Primary teeth (baby teeth)
Teeth that first appear in children, then fall out with growth
Secondary teeth
Teeth that replace primary (baby) teeth and remain permanently
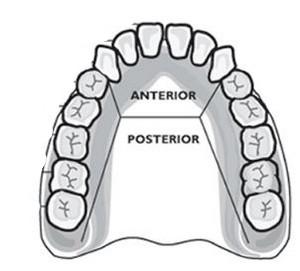
Incisors
The frontmost teeth in on the jaw
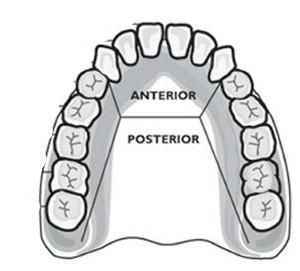
Cuspids (canines)
The teeth behind the incisors; one layer
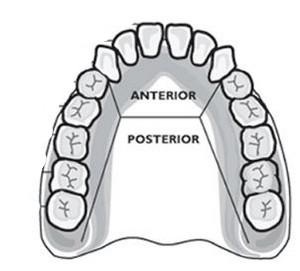
Bicuspids
Teeth behind the cuspids
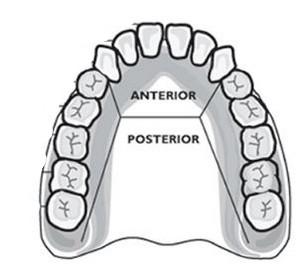
Molars
Teeth in the very back of the jaw
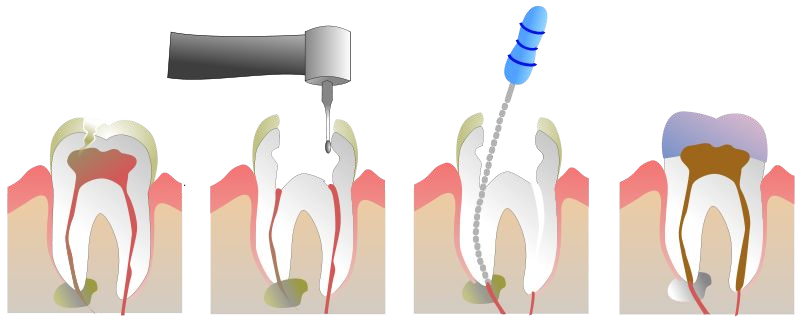
Root canal procedure
The repair of a badly damaged or infected tooth to avoid removal with a new cap; the name is derived from the cleaning of a tooth’s root
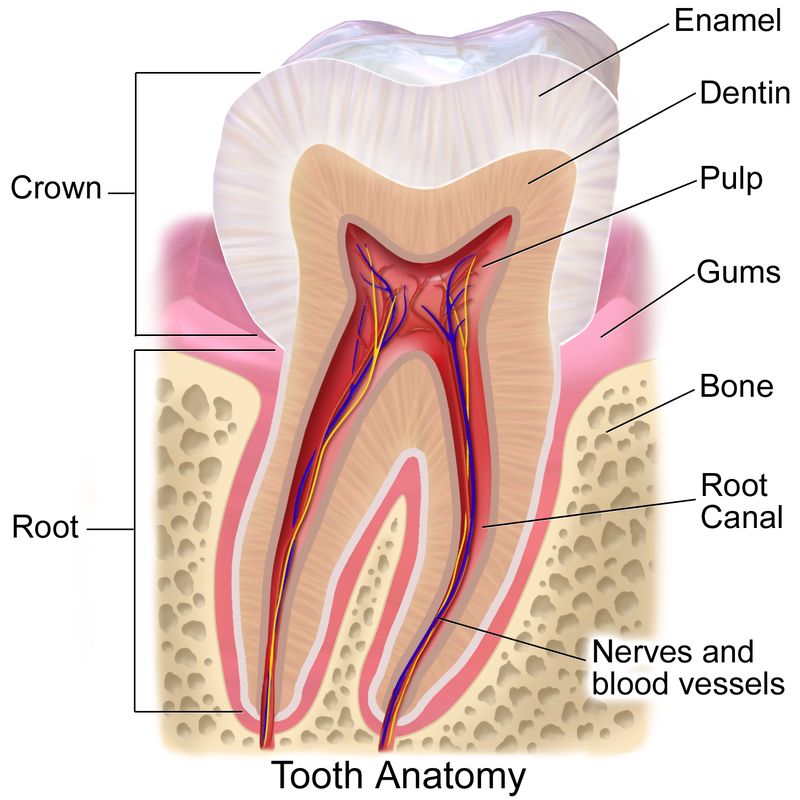
Crown
The top exposed part of the tooth with the enamel, dentin, and pulp cavity
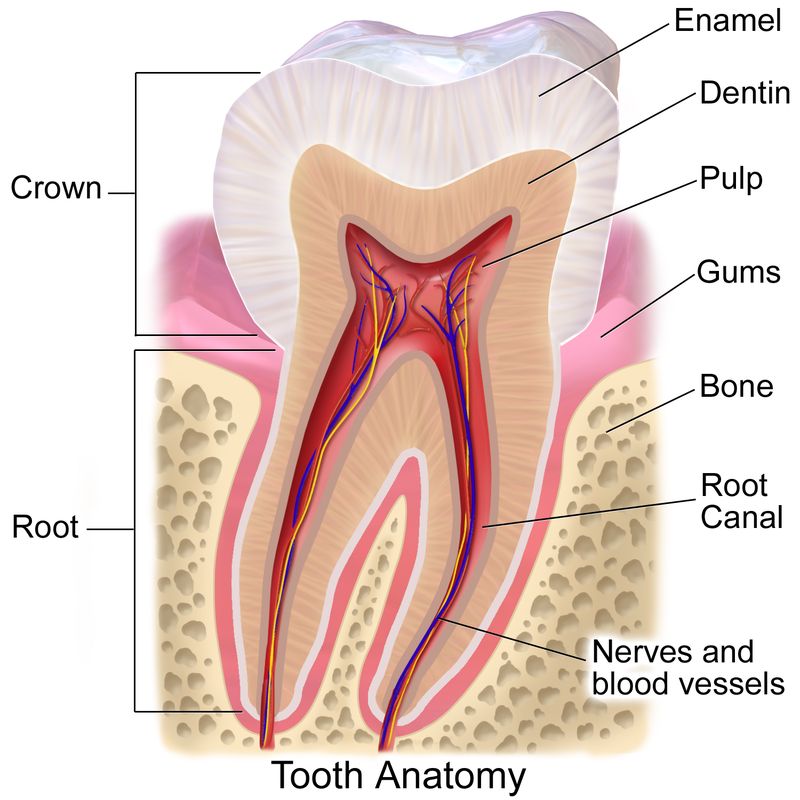
Root
The part of the tooth covered by the gums surrounded by bone with a root canal that carries nerves and blood vessels
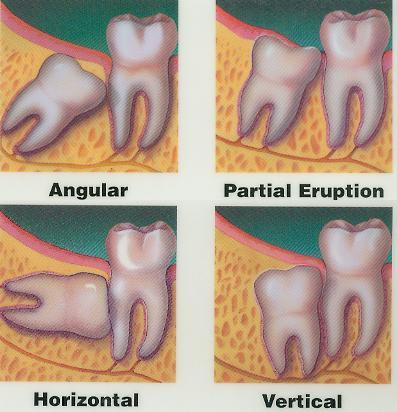
Wisdom teeth (third molars)
Molars that come in during adolescence that are often removed due to their position
Amylase
The enzyme within the saliva that breaks down starch into sugars
Mucus
Substance produced by mucous cells for lubrication during swallowing
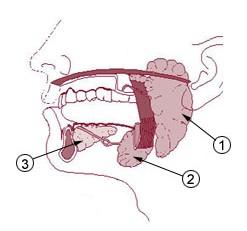
Salivary glands
Parotid gland (most anterior gland, back of mouth)
Submandibular gland (salivary gland behind tongue)
Sublingual gland (salivary gland below tongue)
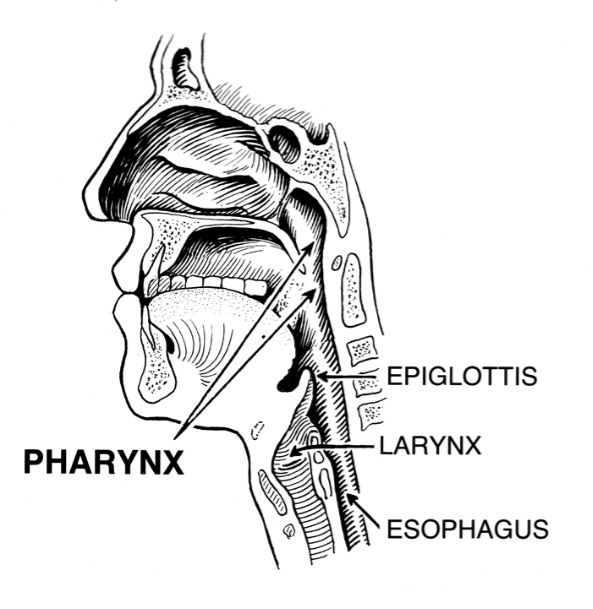
Pharynx
Passageway leading to the throat that consists of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx that are located near the nose, mouth, and larynx respectively
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing
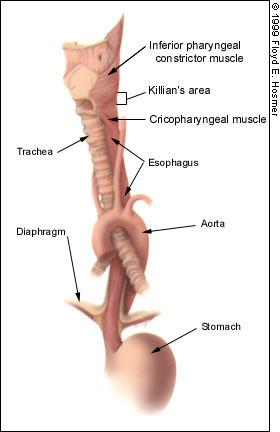
Esophagus
The passageway that moves food to the stomach
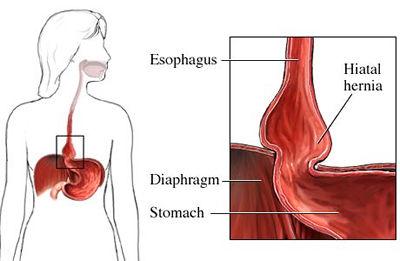
Esophageal hiatus
Where the esophagus penetrates the diaphragm of the stomach
Longitudinal muscles
Muscles with an upward structure on the stomach
Circular muscles
Muscles with a structure going around the stomach
Oblique muscles
Muscles with a diagonal structure around the stomach
Pepsin
Digestive enzyme for breaking down food
Chyme
Paste released into the duodenum from the stomach
Rugae
Wrinkles within the lining of the stomach
Acid reflux
Condition that occurs when stomach acid splashes back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation (heartburn)
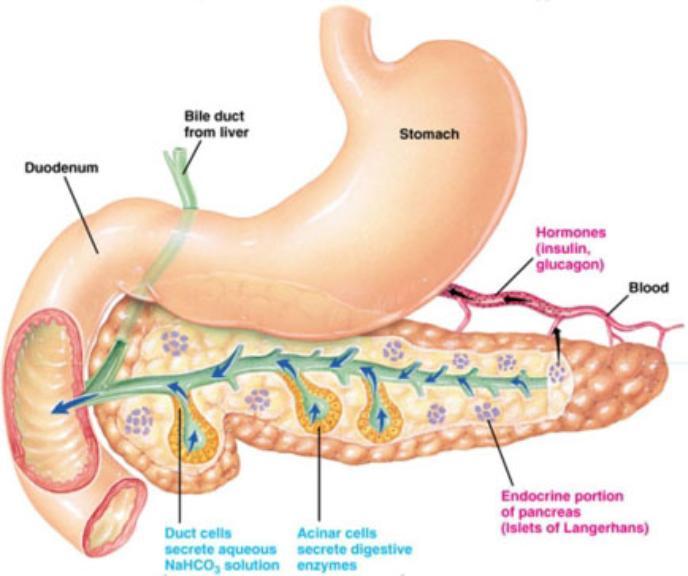
Pancreas
Organ that secretes insulin which breaks down sugars and pancreatic juice that breaks down fat; empties into the duodenum
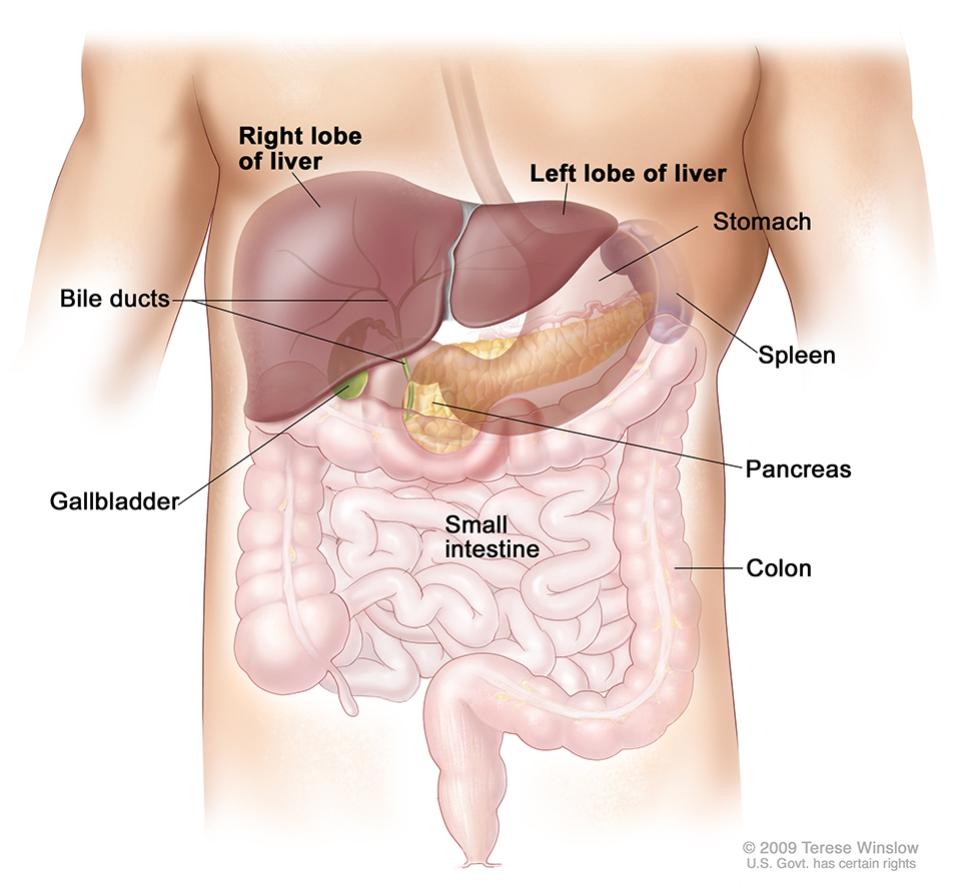
Liver
Organ that functions to create bile and proteins alongside storing glycogen and vitamins; also aids blood clotting, clears bilirubin, and has detoxification functions
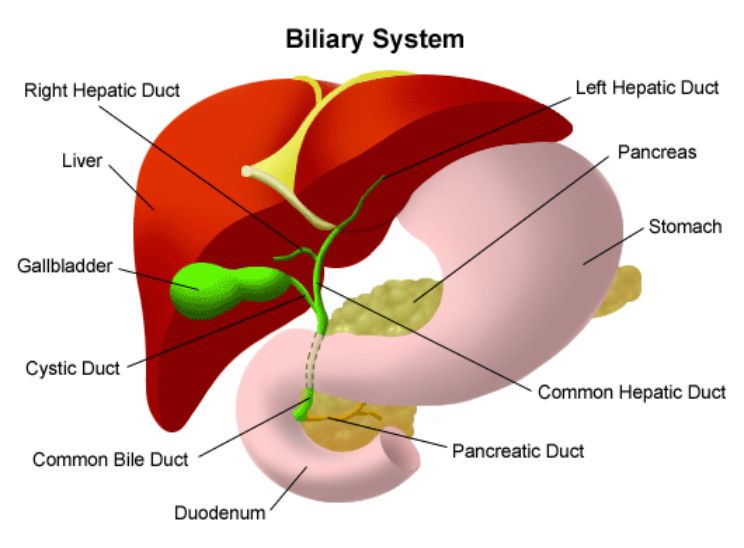
Cystic duct
Duct that carries bile from the gallbladder
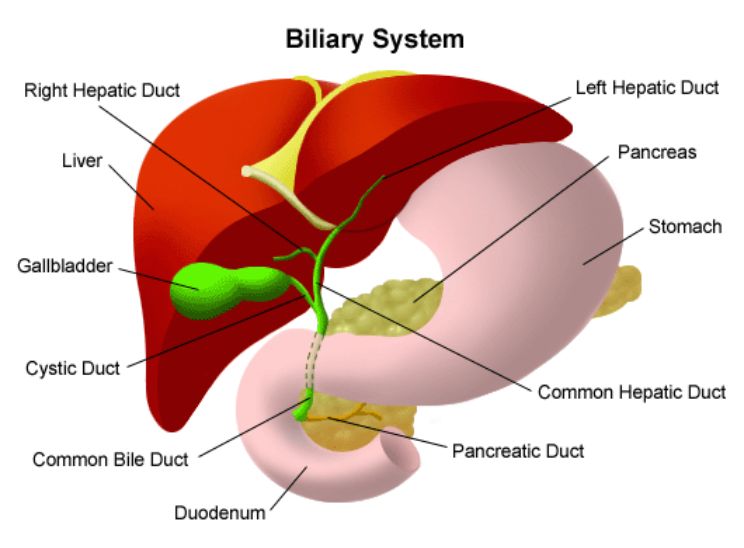
Hepatic duct
Duct that comes from the liver
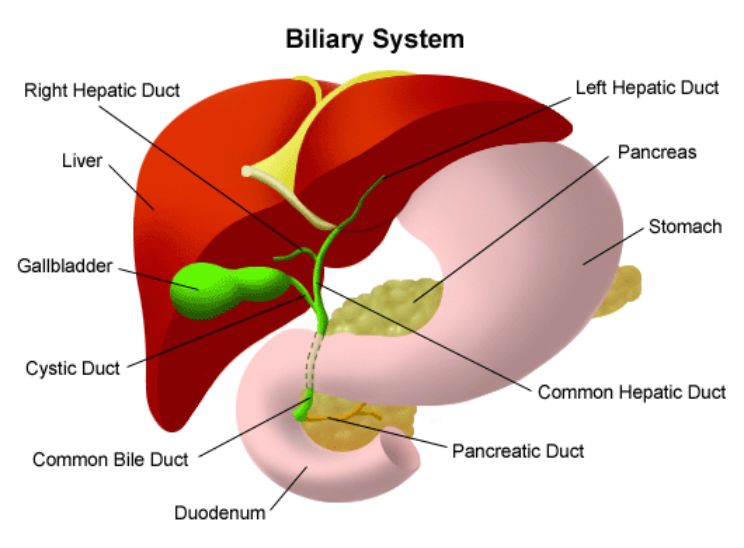
Common bile duct
Duct that forms as a convergence of the cystic and hepatic ducts, emptying into the duodenum
Bile
A yellowish-green liquid that aids in digestion and the breakdown of fat
Bilirubin
Substance produced when blood cells are broken down
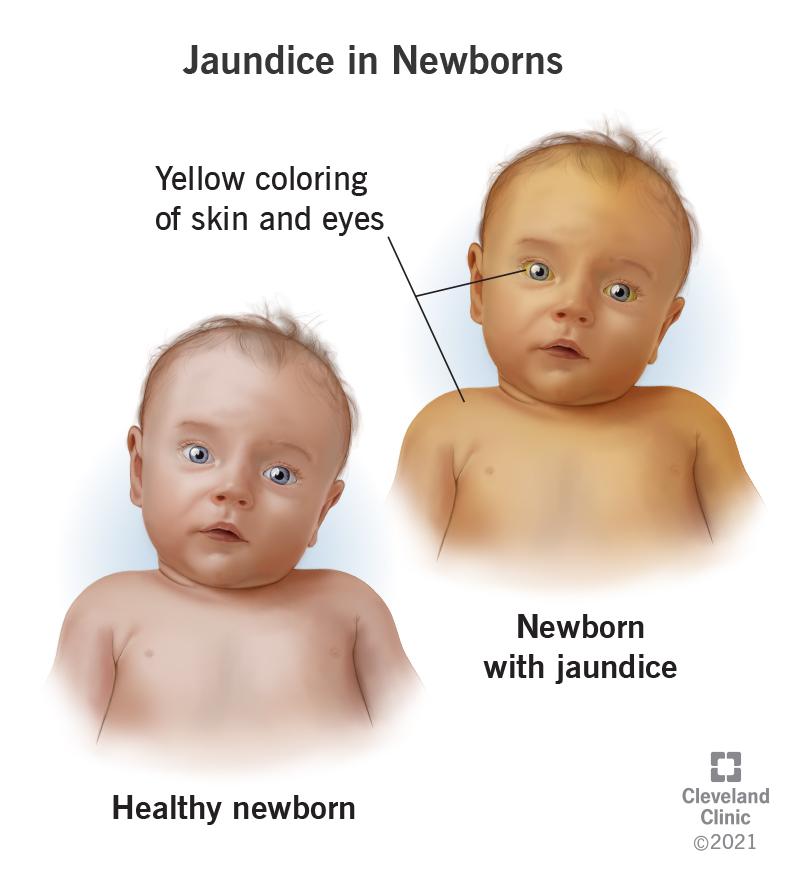
Jaundice
Condition that occurs when the liver fails to clear bilirubin, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes
Bili lights
A therapeutic procedure for infants to reduce elevated bilirubin levels and jaundice symptoms
Gallbladder
An organ that stores bile from the liver and connects to the duodenum via the bile duct; stored bile can form gallstones
Small intestine
Part of the intestine with the main function of absorbing nutrients; split into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Mesentery
Supports the coils of the small intestine and contains blood vessels
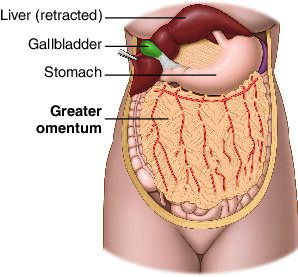
Greater omentum
Membrane that covers the intestines and stores fat
Duodenum
The first part of the small intestine
Jejunum
The second part of the small intestine, about 2.2 meters long
Ileum
The third part of the small intestine, about 3.3 meters long
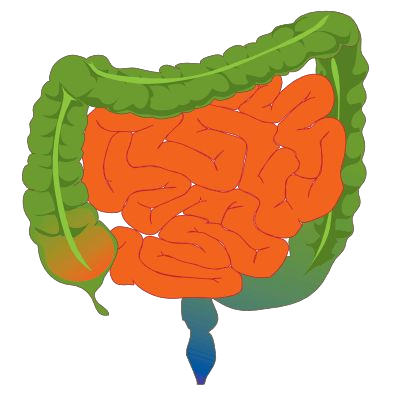
Large intestine
The part of the intestine that starts at the cecum after the small intestine and ends at the rectum to secrete mucus, reabsorb water, and compact with contained bacteria
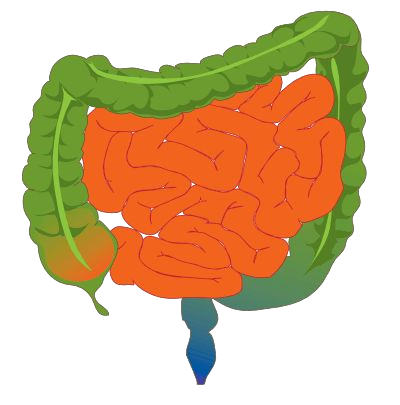
Cecum
The start of the large intestine with an attached appendix
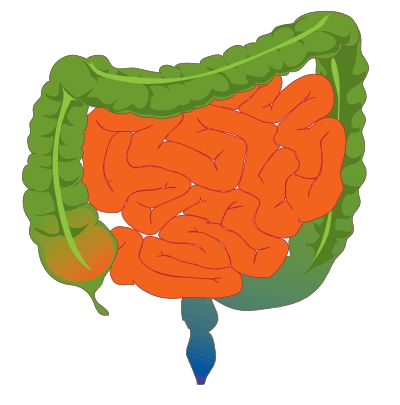
Ileocecal valve
Valve between the small intestine and cecum
Colon
Part of the large intestine with four sections: ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid
Rectum
Part of the large intestine that stores waste before it is expelled from the body
Anus
Muscular sphincter which controls the exit of waste
Appendix
Small, finger-shaped organ attached to the large intestine that stores good bacteria after illness
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix that may necessitate removal
Mass movements (defecation)
Movements of the large intestine that remove undigested food
Bristol Stool Chart
Chart that analyzes the consistency of feces
Gastroenterologist
A physician with dedicated training in the management of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver
Colonoscopy
A test used to detect cancer in the colon via an inserted camera
Gastroenteritis
A generic name used to describe vomiting and diarrhea

Cholera
A bacterial disease transmitted through unclean water and food that causes diarrhea, leading to a massive loss of water that can be fatal
Microbiome
The microorganisms within the digestive tract that aid digestion; imbalance can cause sickness and uncontrolled bacterial growth
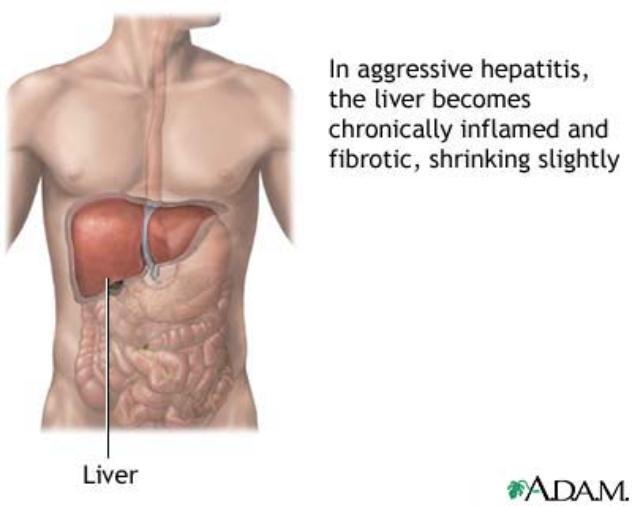
Hepatitis A
Liver inflammation caused by a virus transmitted through food or water
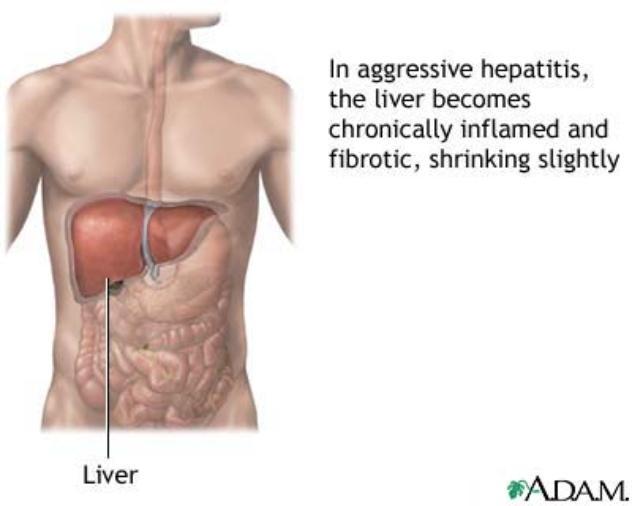
Hepatitis B and C
Liver inflammation caused by a virus transmitted through STIs; can lead to chronic disease and liver failure

Constipation
Difficulty in emptying the bowels, usually associated with hardened feces
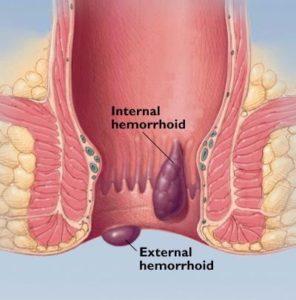
Hemorrhoids
Swollen veins within the anus and rectum; may result from straining or pressure from pregnancy with pain, itching, and minor bleeding during bowel movements

Lactose intolerance
The inability to digest milk that can cause stomach upset
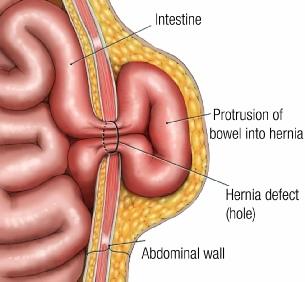
Hernia
Condition where the intestines poke through the abdominal muscles
Malnutrition
The lack of proper nutrition or nutrients; can cause diseases like scurvy (lack of vitamin C) or rickets (lack of vitamin D)
Essential nutrients
Nutrients required for normal body functioning that cannot be synthesized by the body