Dental Radiology (might need adjustments)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
All forms of energy are measured by?
Wavelength
Who invented X-rays in what year?
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895
Wavelengths are measured from…
Crest to crest and trough to trough
Electromagnetic energy travels at the speed of
Light, which is 186,000 miles per second
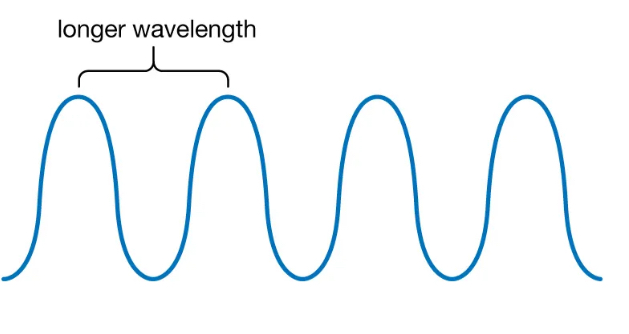
Long wavelengths are…
Soft Radiation (Lower energy, lower frequency, less penetrating power)
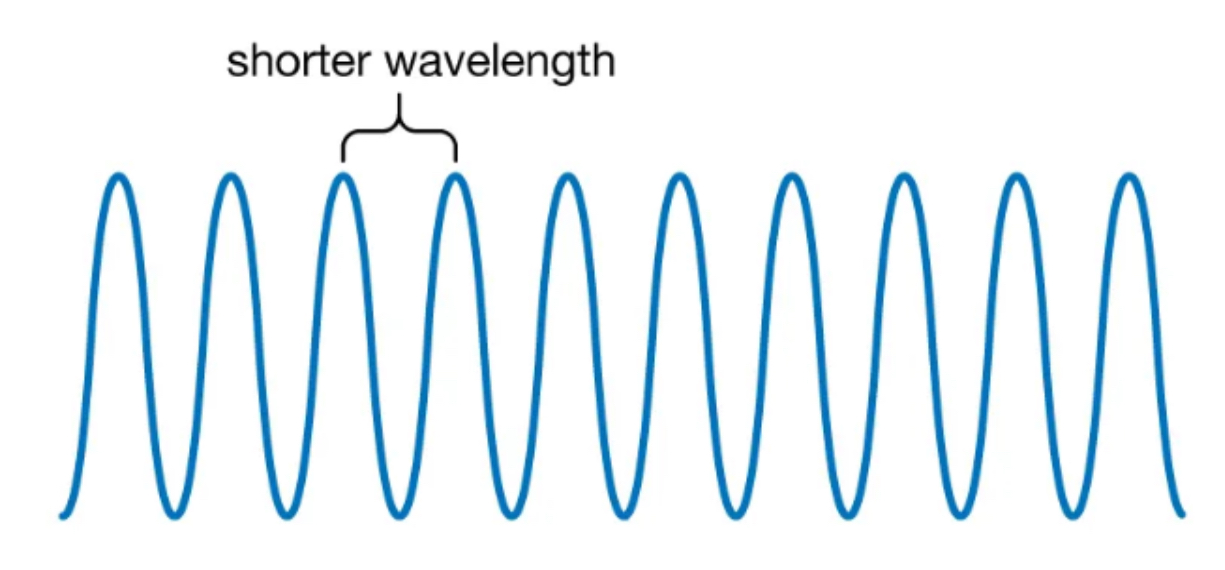
Short wavelengths are…
Hard Radiation (High frequency, high energy, high penetrating power)
Primary Radiation
Central beam from X-Ray Tube, high energy which exposes the film
Secondary Radiation
Reflects off of primary beam when it strikes matter
Scatter Radiation
Type of Secondary Radiation which is either deflected from or absorbed into the patients face
Leakage Radiation
Radiation leaking from the machine which escapes in all directions
What are the two types of X-rays?
Intra Oral Films and Extra Oral Films
What are the two types of cells in the body
Genetic and Somatic
Genetic Cells
Reproductive cells, sensitive to radiation, effects are passed on to future generations
Somatic Cells
All cells besides reproductive, effects stay with individual, examples such as cancer and cataracts
ALARA stands for
As low as reasonably achievable
REM stands for
Roentgen Equivalent Man, unit of radiation exposure
MPD
Maximum Permissible Dose
Sievert (Sv)
Unit of radiation exposure
Occupational exposure limit?
.05 Sv or 5 Rems
Dosimeter
Film Badge which records the amount of radiation exposure
55% of your daily radiation exposure comes from
Natural Sources, such as the earth, sun, atmosphere, radon
45% of your daily radiation exposure comes from
Artificial Sources, such as X-rays, TV, tobacco, and airline travel
Latent Image is…
the image on film after exposure before processing
Latent period refers to…
the period of time between radiation exposure and symptoms of damage
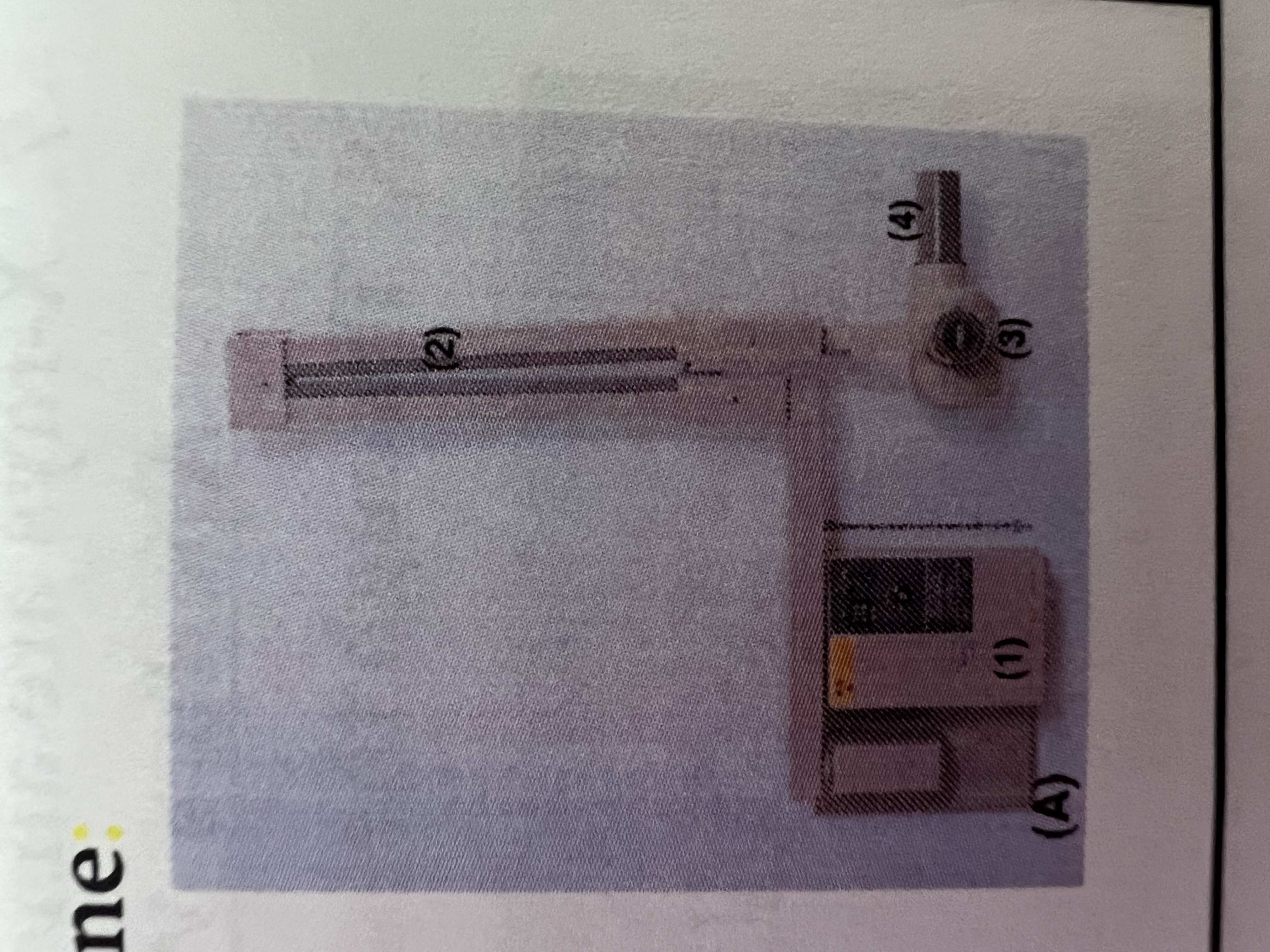
#1 is the
Control Panel
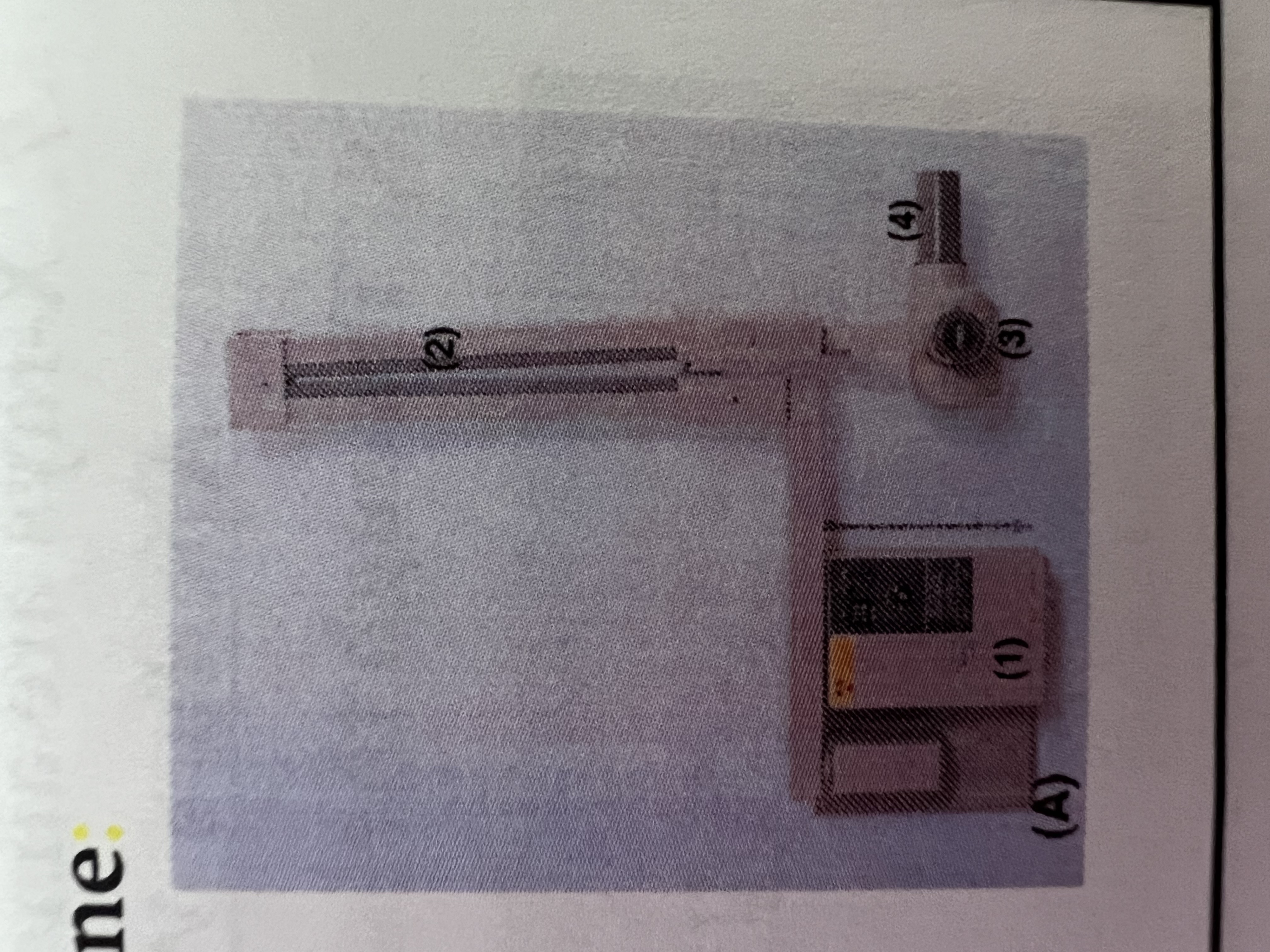
#2 is the
Extension Arm
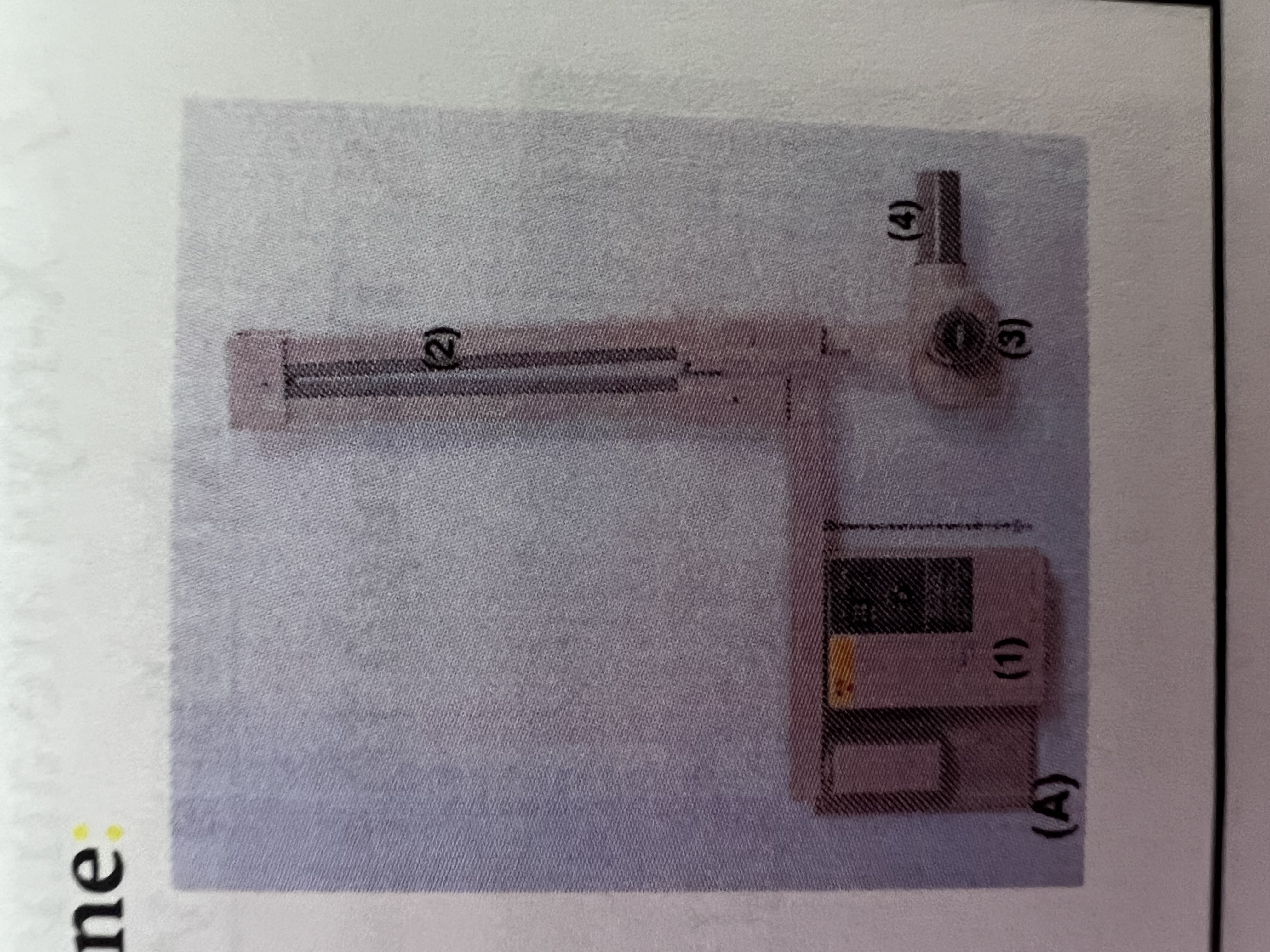
#3 is the
Tube Head
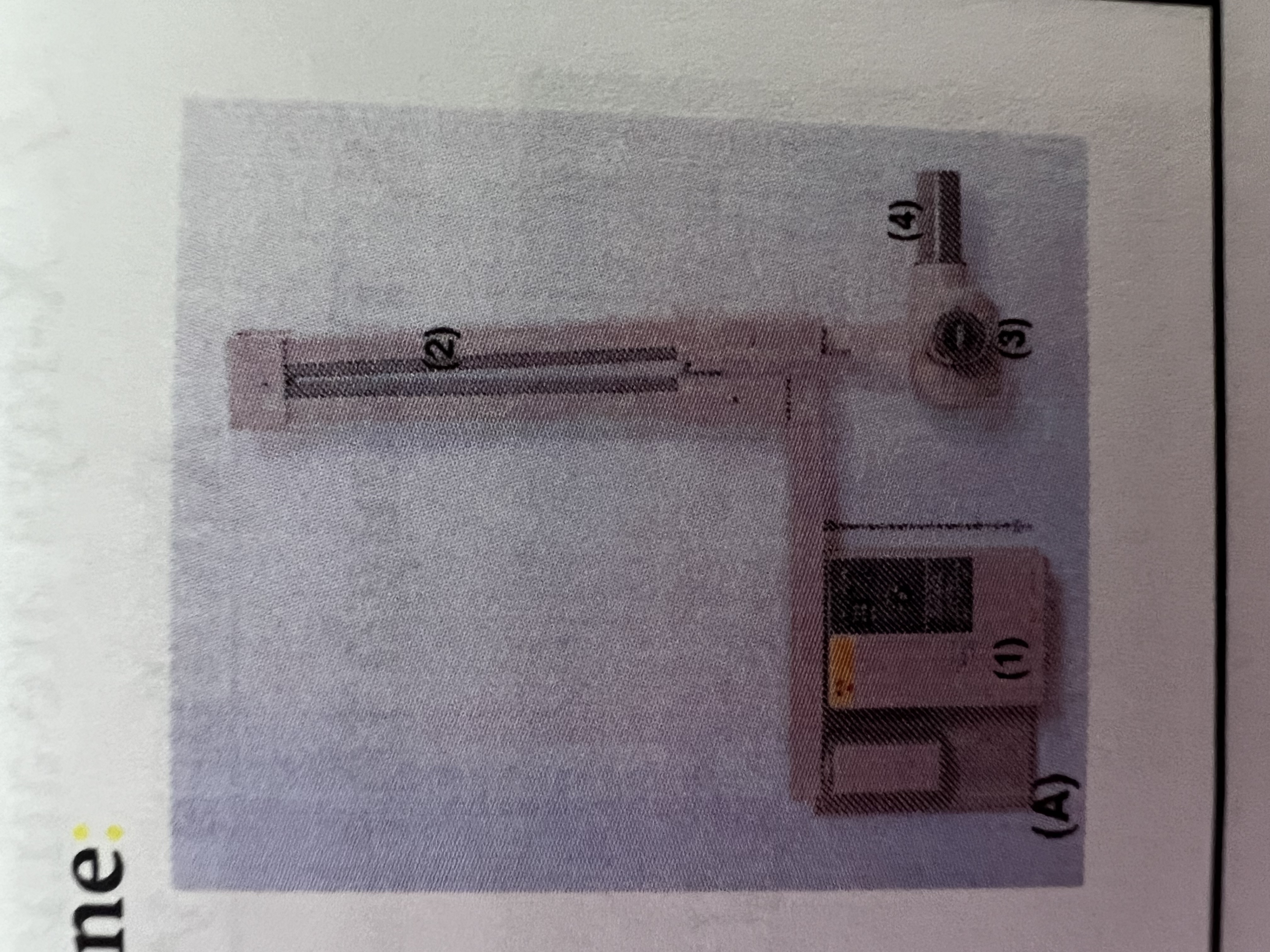
#4 is the
Tube
What are the two sides in the Tube Head?
cathode (negative side) and anode (positive side)
2 components found in the Cathode?
Coil or Filament, and the Focusing cup
5 components found in the Anode side?
Tungsten Target, aperture window, aluminum filter, lead diaphragm/collimator, cone/PID
Film is coated on both sides with…
Crystals
The larger the crystals on the film
The faster the film is developed
3 types of intra oral X-rays?
Bitewings, PA Radiographs, Occlusal Radiographs
3 types of extra oral X-rays?
Panoramic (PAN), Cephalometric (Ceph), Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
What 2 solutions are used to process film?
Developer and Fixer
Composition of Fixer solution?
Sodium Thiosulfate and Acetic Acid
Composition of Developer Solution?
Hydroquinone and Elon