AP Bio Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Pyrimidines
These base pairs have a single ring structure (U,C,T)
Purines
These base pairs have a double ring structure (A,G)
Semiconservative Replication
Each old DNA strand during replication pairs with a new one
Plasmids
a genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes, typically a small circular DNA strand in the cytoplasm of a bacterium or protozoan. Plasmids are much used in the laboratory manipulation of gene
Hydroxyl Terminus
Also known as the 3’ end of DNA. DNA is read from this end
Phosphate Terminus
Also known as the 5’ end of DNA. Nucleotides are added from this end
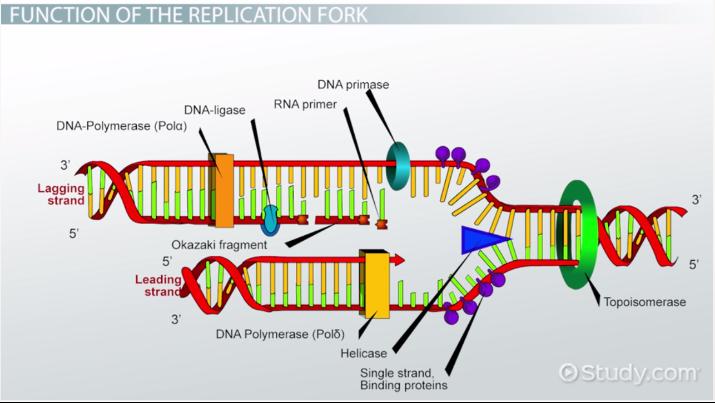
Leading Strand
This strand is synthesized continuously during DNA replication
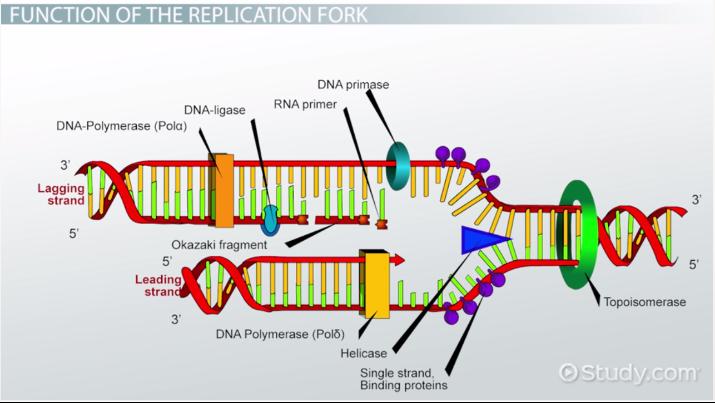
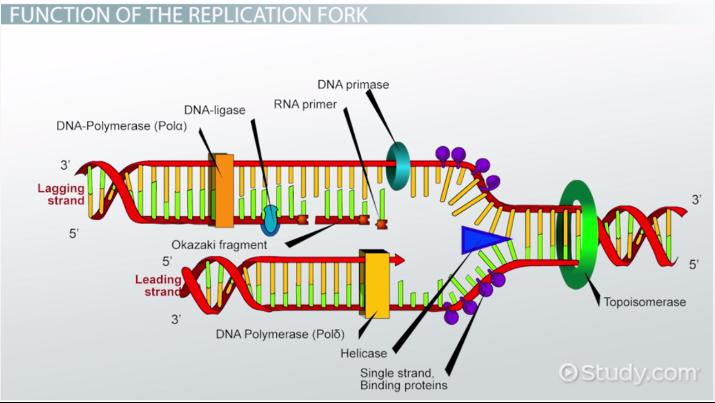
Lagging Strand
This strand is synthesized discontinuously during DNA replication s it goes “backwards”
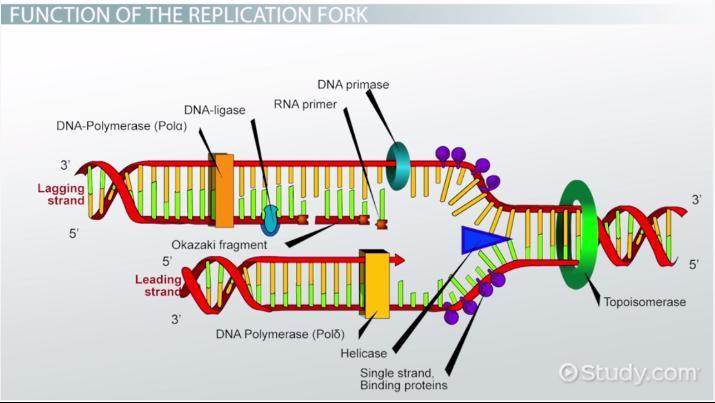
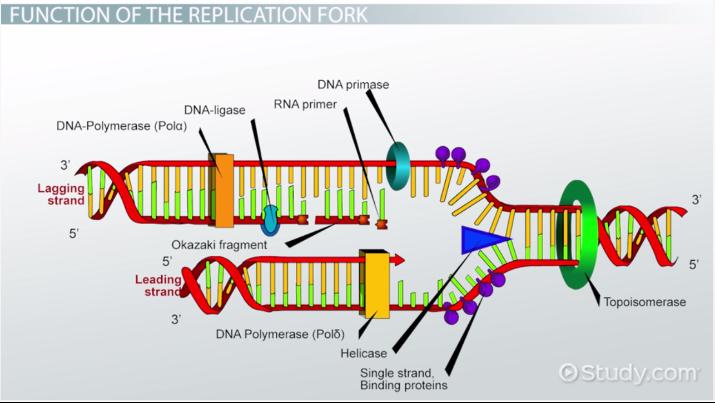
Helicase
This enzyme unwinds DNA strands
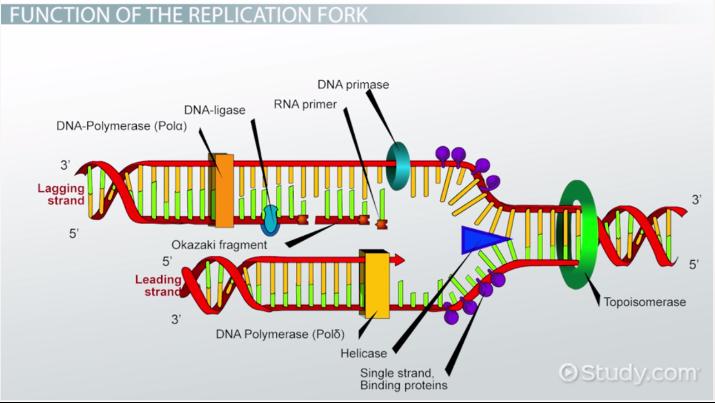
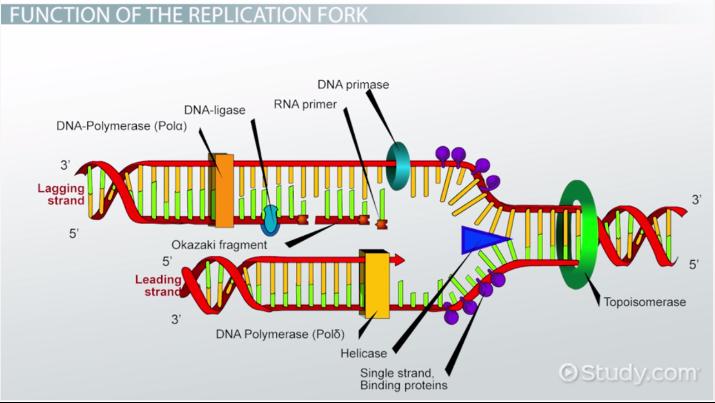
Topoismerase
This relaxes the supercoil at the replication fork
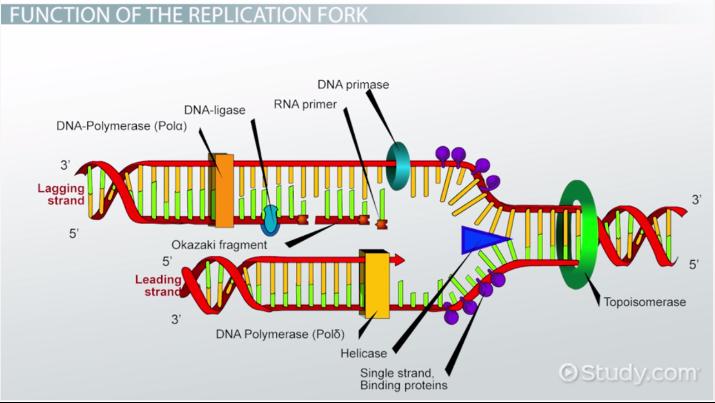
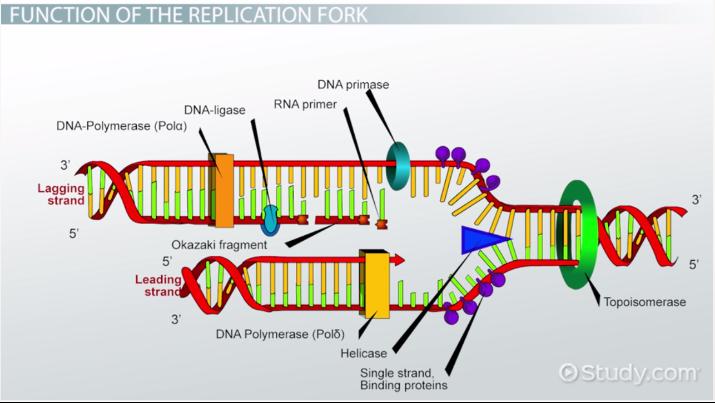
Ligase
This enzyme acts as a “glue” to join fragments on the DNA lagging strand during replication
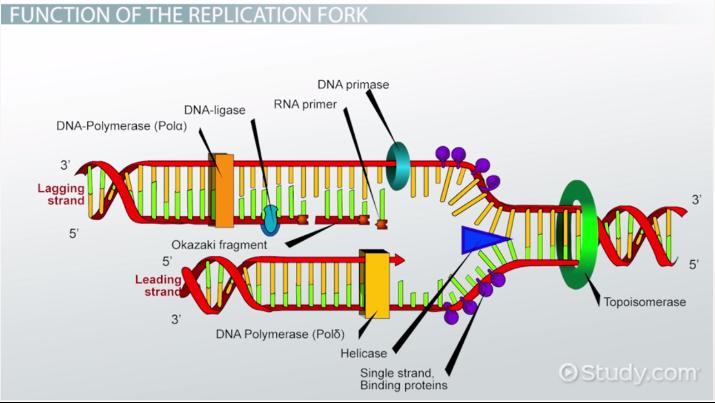
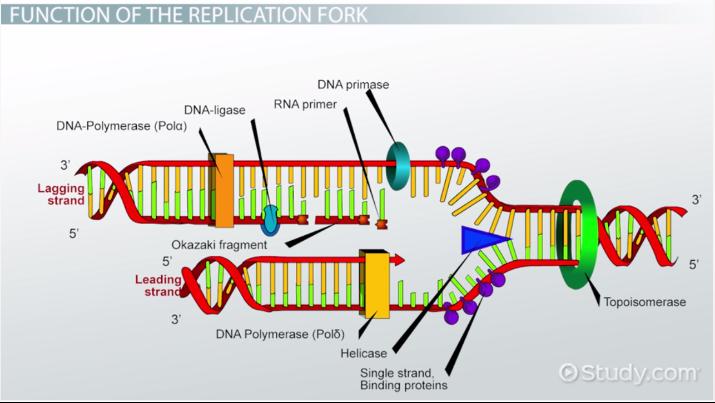
RNA Primase
This enzyme builds “chunks” of RNA on the lagging strand called Okazaki Fragments
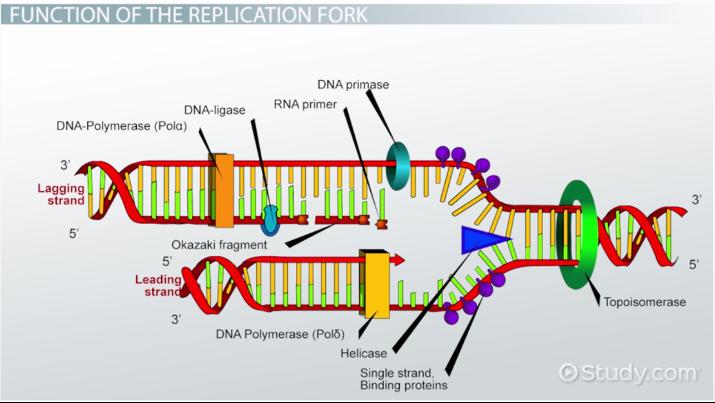
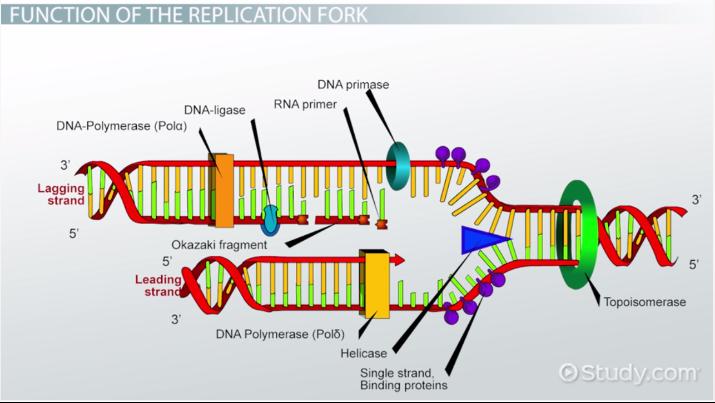
Okazaki Fragments
short sections of DNA formed at the time of discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand during replication of DNA
mRNA
This type of RNA is a temporary RNA version of a DNA recipe
DNA Replication
The act of copying DNA that happens during S Phase. This happens in the NUCLEUS
RNA transcription
This is making an RNA copy of DNA
A tiny specific portion is made into mRNA on a gene by gene basis
rRNA / Ribosomal
This type of RNA makes up ribosomes
tRNA
This RNA shuttles amino acids to ribosomes and brings them into place
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
The steps of RNA transcription
AUG
Start Codon
Antisense Strand
The template DNA being copied in RNA transcription
Sense Strand / Coding Strand
The strand not being copied in RNA transcription
RNA Polymerase
This enzyme adds RNA nucleotides to the 3’ side (building 5’ to 3’)
Processed
In eurkaryotes, RNA must be ______ before leaving the nucleus
Exons
Coding regions for proteinsI
Introns
Non-coding regions of mRNA
Spliceosome
Intron remover
Poly(A) Tail
This is added to protect an mRNA strand with codons at the 3’ end
GTP Cap
This is added to protect an mRNA strand with codons at the 5’ end
Translation
Transforming an mRNA into a protein (on ribosomes in the cytoplasm and the rough ER)
Anti-codon of tRNA bonds with the mRNA codon
Codon
A group of 3 nucleotides —> each represents an amino acid
Anticodon
On the other end of tRNA opposite of the codon (3 complementary nitrogenous bases)
Wobble Pairing
The third position of a codon is more flexible with pairing (ex: might pair G and U)
A Site
This site on the Ribosome attaches new RNA
P Site
This site on the Ribosome is in charge of creating the polypeptide
E site
This site on a ribosome is the exit site
Initiation
This is when RNA polymerase attaches to a promoter in transcription
Elongation
This is when RNA polymerase makes the RNA strand during transcription
Termination
When RNA polymerase leaves the DNA after completing transcription
Initiation
In translation, this is when a ribosome attaches to mRNA
Elongation
In translation, addition of amino acids (brought by tRNA). Link with peptide bonds
Termination
In translation, when the ribosome reaches the end of an mRNA strand (stop codon)
3
A ribosome reads mRNA in groups of ____ called codons
Transcription Factors
These encourage or inhibit DNA unwinding and polymerase bonding
Epigenetic Changes
These are changes to the DNA package (usually too tightly wrapped around histones, meaning that DNA cannot be read) caused by he environment
Operons
In bacteria, a gene cluster is controlled by a single promoter
Structural Genes
These code for enzymes
Promoter Gene
RNA polymerase binds here to begin transcription
Operator
This controls whether transcription occurs (IN BACTERIA)
Regulatory Gene
This gene codes for a repressor (blocks transcription)
Post-Transcriptional Regulation
In this gene regulation process, unneeded DNA is destroyed
Post-Translational Regulation
In this gene regulation process, a cell makes a protein but does no use it
Base Substitution / Point Mutations
A single nucleotide base is substituted for another
Nonsense Mutation
When the original codon is replaced with a stop codon —> early termination
Missense Mutation
The original codon is replaced with a different amino acid
Silent Mutation
The original codon is replaced with a different one, but it still codes for the same amino acid
Insertion / Deletion
A type of gene rearrangement: The gain or loss of DNA or a gene —> DEVASTATING CONSEQUENCES (frameshift)
Frameshift
This gene rearrangement shifts how a sequence is read (sets of 3 become jumbled) and results from an insertion or deletion
Duplications
A type of gene rearrangement: an extra copy of gene causes new traits and results from unequal crossing over
Inversions
A type of gene rearrangement: change in orientation
Translocation
A type of gene rearrangement: 2 chromosomes break and rejoin so DNA is lost / replaced / or interrupted
Transposons
A type of gene rearrangement: gene segments are cut and pasted throughout a genome
Conjugation
Bacteria swap DNA to create genetic diversity
Recombinant DNA
A type of biotechnology: Combining DNA from multiple sources
Polymerase Chain Reaction / PCR
A type of biotechnology: amplifying genes
Transformation
A type of biotechnology: bacteria is induced to do something based off of a human gene (transcribe and translate)
Gel Electrophoresis
A type of biotechnology: DNA fragments (alleles) are separated by weight and charge
DNA Sequencing
A type of biotechnology: determining the order of nucleotides
Alternative Splicing
a cellular process in which exons from the same gene are joined in different combinations