HAP II Final Exam (Vocab and Labeling)
1/578
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
579 Terms
Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
sensory - olfaction / smell
innervates the nose (nasal mucosa)
Optic Nerve (CN II)
sensory - vision
innervates the eye
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
(motor)
somatic motor: momst eye movement
parasympathetic: pupillary dilation, accommodation
innervates the eye muscles
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
(motor)
somatic motor: contracts superior oblique muscle
innervates the superior oblique of eye
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
(mixed)
somatic sensory: skin of face, tongue, mucosa of mouth
somatic motor: mastication muscles (chewing)
innervates skin of face and tongue muscles
Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
(motor)
somatic motor: lateral movement of eye
innervates lateral rectus of eye
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
(mixed)
somatic sensory: outer ear; anterior 2/3 of tongue
somatic motor: facial expressions
parasympathetic: most gland secretions in the head
innervates the tongue, most skeletal muscle of the face, and lacrimal and salivary glands
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
sensory - hearing and equilibrium
innervates the inner ear (cochlea and vestibular apparatus)
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
(mixed)
somatic sensory: taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue; epiglottis
somatic motor: swallowing and breathing
parasympathetic: parotid gland secretion
innervates tongue, muscles in the pharynx, and parotid gland
Vagus Nerve (CN X)
(mixed)
somatic sensory: external ear cartilage
somatic motor: swallowing using muscles of pharynx and larynx
parasympathetic: all PS innervation of visceral organs from neck to transverse colon
innervates the external ear, muscles in pharynx and larynx, and all visceral organs from the neck to the transverse colon
Accessory Nerve (CN XI)
(motor)
somatic motor: turns head and shrugs shoulders
innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII)
(motor)
somatic motor: tongue protrusion and retraction
innervates the tongue
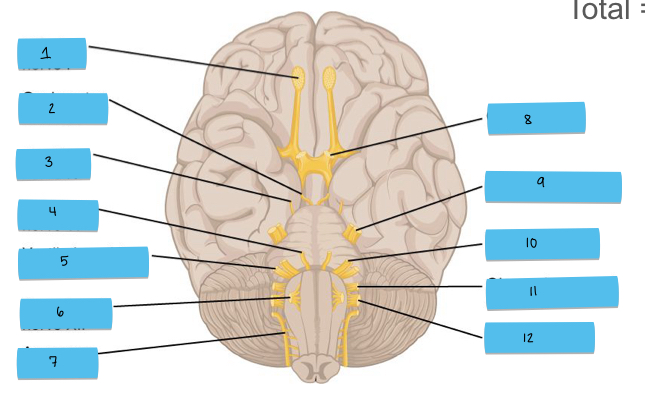
What is 1 pointing to?
olfactory nerve (CN I)
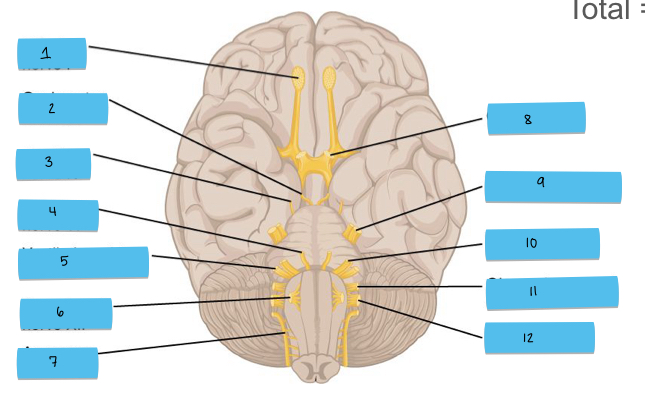
What is 2 pointing to?
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
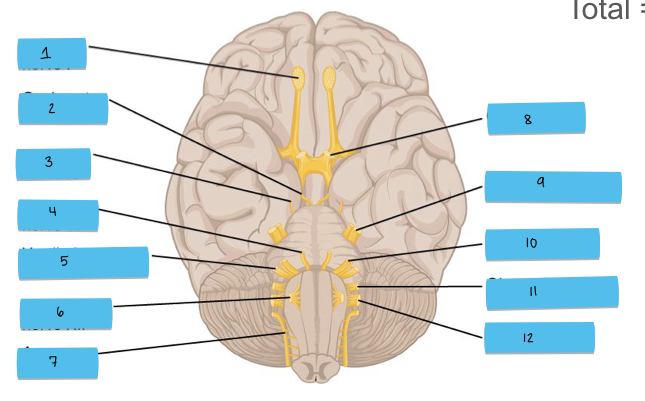
What is 3 pointing to?
trochlear nerve (CN IV)
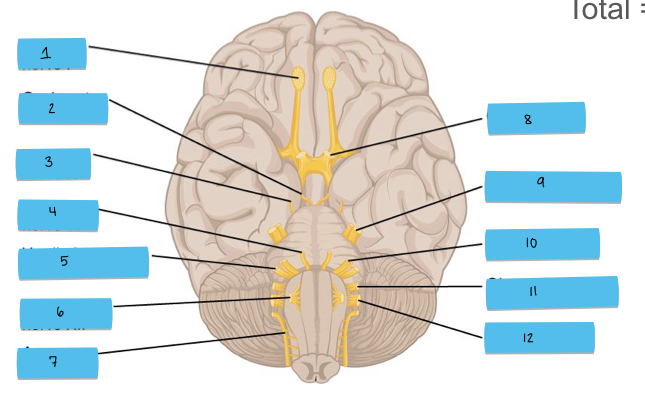
What is 4 pointing to?
abducens nerve (CN VI)
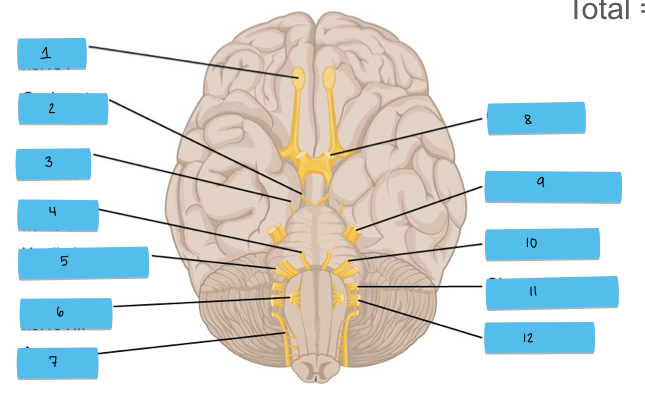
What is 5 pointing to?
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
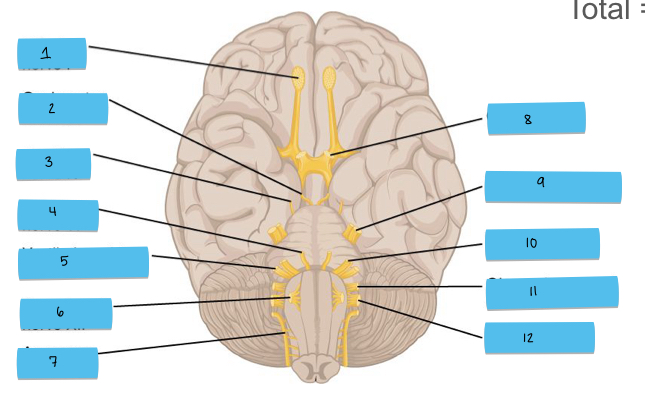
What is 6 pointing to?
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
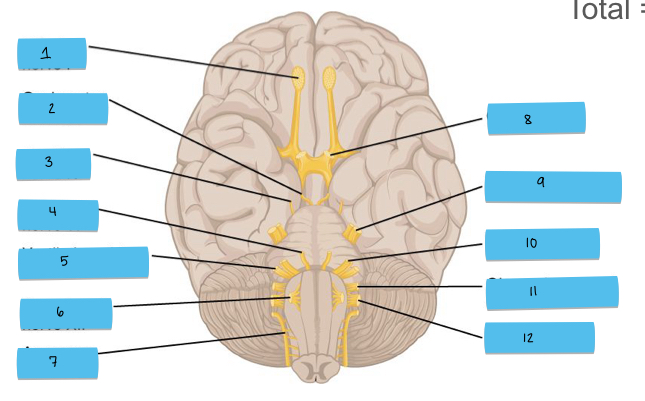
What is 7 pointing to?
accessory nerve (CN XI)
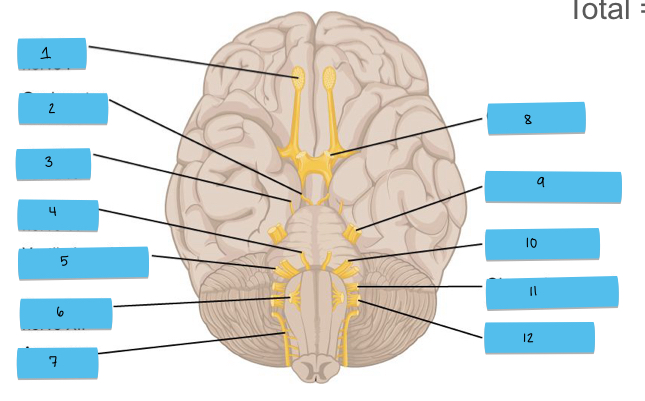
What is 8 pointing to?
optic nerve (CN II)
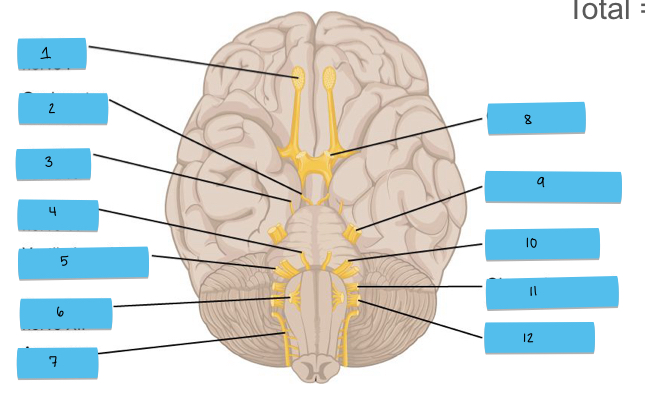
What is 9 pointing to?
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
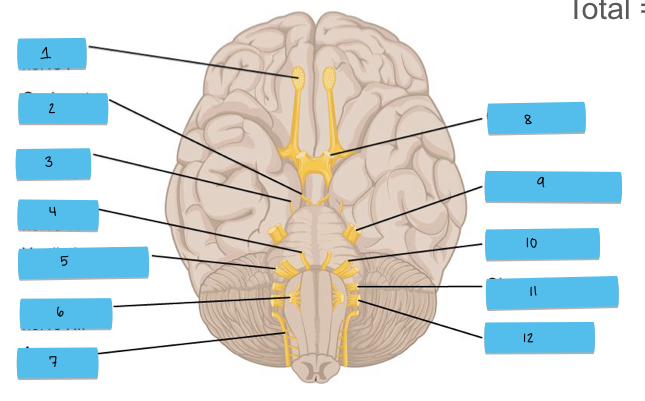
What is 10 pointing to?
facial nerve (CN VII)
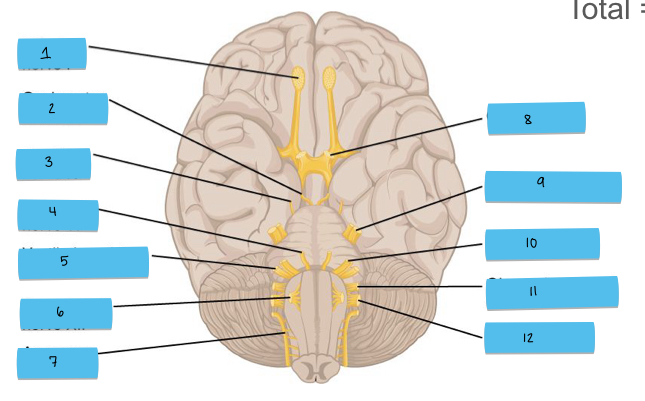
What is 11 pointing to?
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
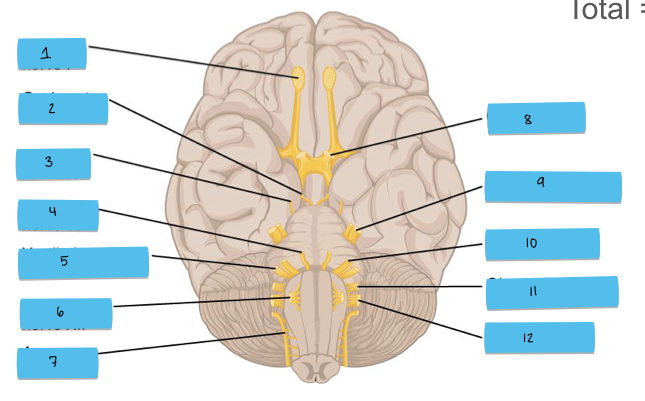
What is 12 pointing to?
vagus nerve (CN X)
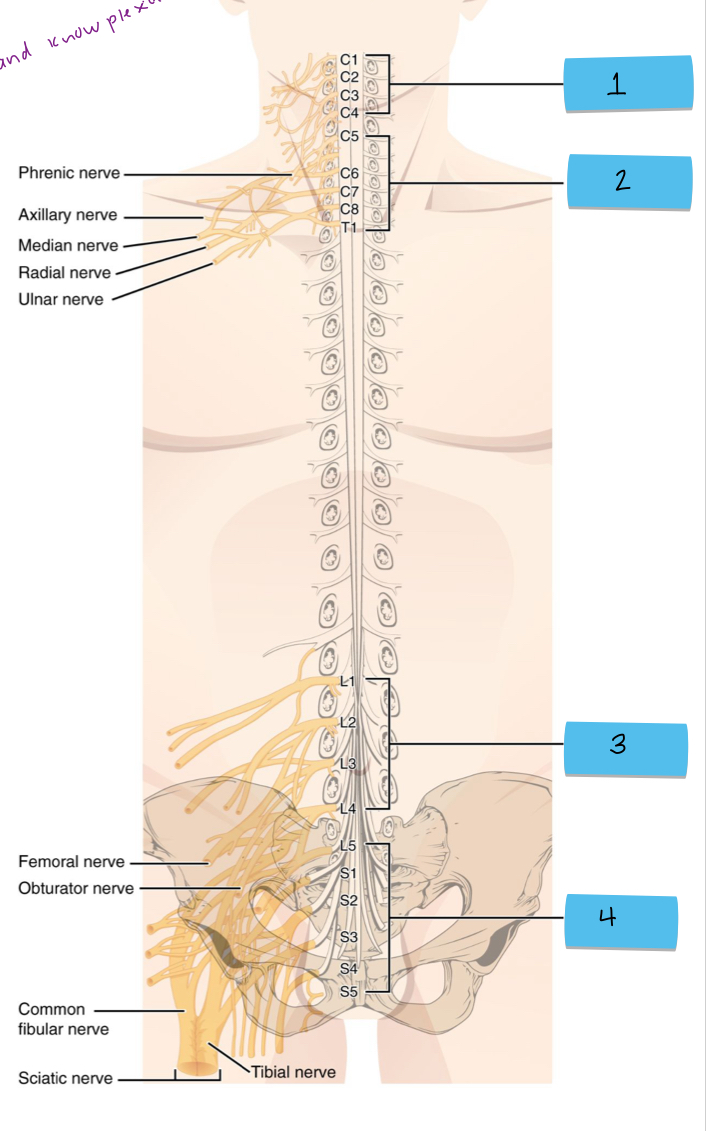
What is 1 pointing to?
cervical plexus
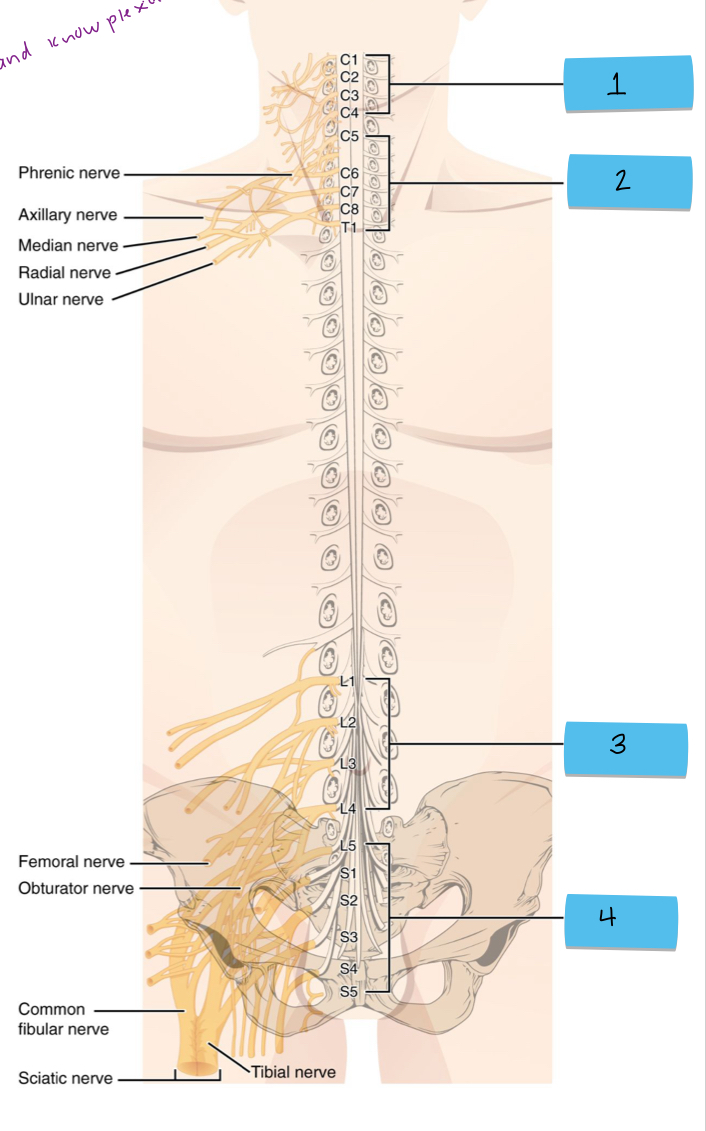
What is 2 pointing to?
brachial plexus
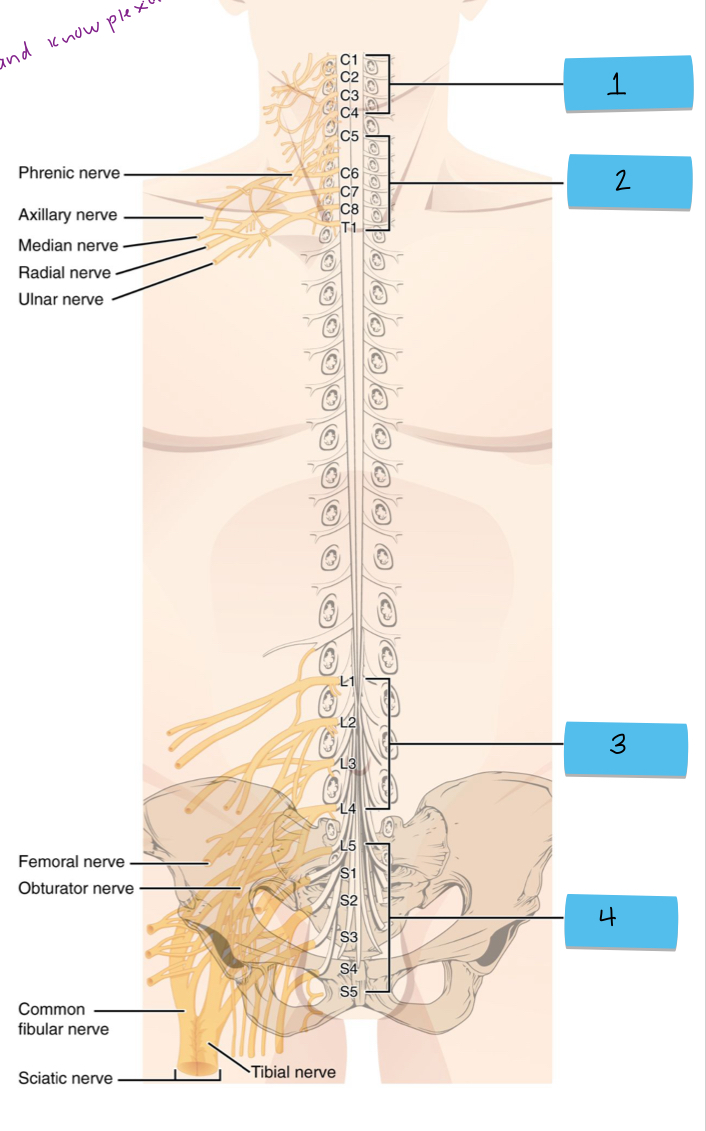
What is 3 pointing to?
lumbar plexus
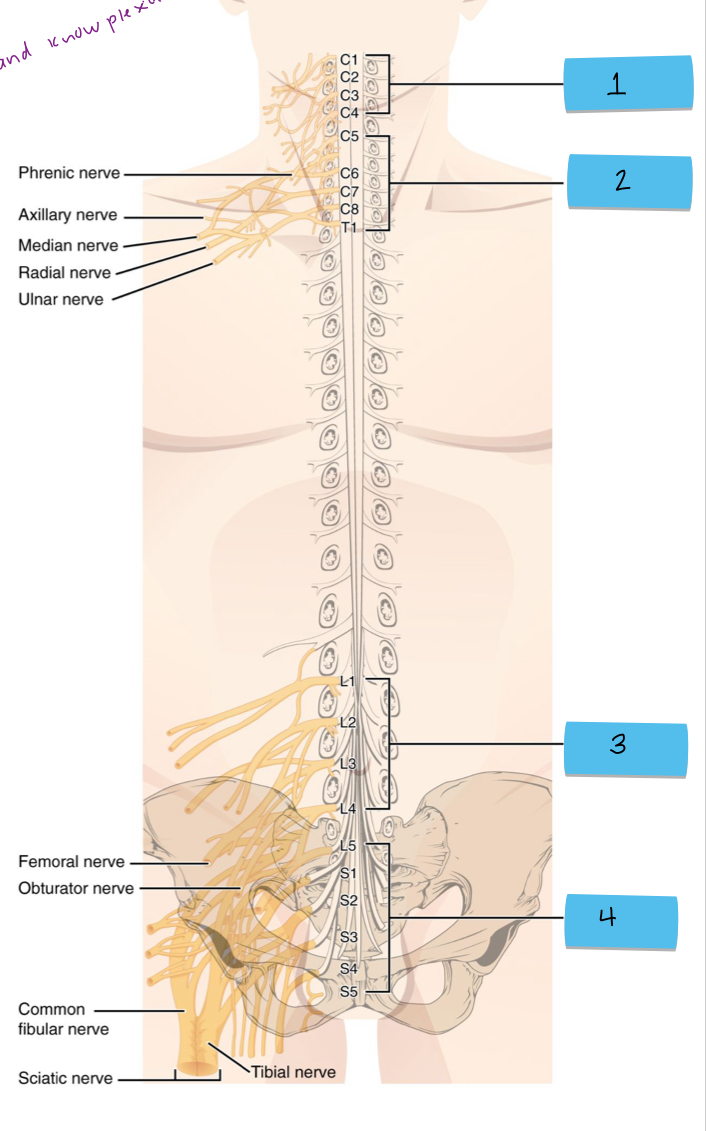
What is 4 pointing to?
sacral plexus
Dorsal portion of spinal cord
posterior; receives sensory info from body
Ventral portion of spinal cord
anterior; sends motor command from brain to body
Dorsal horn
gray matter in posterior spinal cord; synapse site for incoming sensory neurons; interneurons; within the CNS direction of info. flow)
Ventral horn
gray matter in anterior spinal cord; contains motor neuron cell bodies; motor neurons; within CNS (direction of info. flow)
Dorsal root
posterior side of spinal cord; carries sensory input into the spinal cord; sensory neurons (afferent); toward CNS (direction of info. flow)
Ventral root
anterior side of spinal cord; carries motor output away from the spinal cord; motor neurons (efferent); away from CNS (direction of info. flow)
Dorsal root ganglion
on dorsal root (outside spinal cord); contains cell bodies of sensory neurons; sensory neuron cell bodies; sends signals to dorsal horn
Sensory input pathway and motor output pathway
sensory input pathway: sensory neurons — dorsal root ganglion — dorsal root — dorsal horn (synapse)
motor output pathway: ventral horn (motor neuron cell bodies) — ventral root — muscles
Exteroceptors
found near body surfaces (skin, eyes, ears, etc.); detects external stimuli from outside the body;
ex: touch, temperature, pain (from skin), vision, hearing, smell (most of special senses)
Interoceptors
found inside the body (viscera, blood vessels); detects internal stimuli from organs and tissues; often not perceived
ex: blood pressure, pH, oxygen levels, stretch in GI tract (chemical changes, temperature, pain, thirst, hunger, etc);
Proprioceptors
found in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments, and connective tissues around bones and muscles; detects body position and mvoement awareness (via stretch receptors)
Nonencapsulated
nonmyelinated and have small bulbous ends; mostly in epithelia and connective tissue; free nerve endings (bare dendrites); light touch, pain, temperature, itch
Encapsulated
nerve endings wrapped in connective tissue capsule; mostly in dermis, joints, muscles; precise touch, pressure, stretch, vibration, proprioception
Mechanoreceptors
mechanical forces (pressure, touch, vibration, stretch); located in skin, muscles, ears, vessels, organs
Thermoreceptors
temperature changes; located in skin and hypothalamus
Photoreceptors
light changes; located in retina of the eye
Chemoreceptors
chemical changes (smell, taste, blood interstitial fluid); found in nose, tongue, blood vessels
Nociceptors
pain (extreme cold, heat, intense pressure, inflammation); located almost everyehere (especially skin & organs); often stimulate subtypes of the other receptors
Free nerve endings of sensory neurons (receptors)
structural class / where: nonencapsulated (most body tissues)
functional location: exteroceptors, interoceptors, proprioceptors
functional stimulus: thermoceptors, chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, nociceptors
Modified free nerve endings (Merkel cells and discs) receptors
structural class / where: nonencapsulated (basal epidermal layer)
functional location: exteroceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (light pressure)
Hair follicle receptors
structural class / where: nonencapsulated (surrounding hair follicle)
functional location: exteroceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (hair deflection)
Tactile corpuscles (Meissner’s) receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (dermal papillae in hairless skin)
functional location: exteroceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (light pressure, discriminative / precise touch, low frequency vibration)
Lamellar corpuscles (Pacinian) receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (dermis, hypodermis, tendons, ligaments, joints)
functional location: exteroceptors, interoceptors, some proprioceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (deep pressure, stretch, high frequency vibration)
Bulbous corpuscles (Ruffini endings) receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (deep in dermis, hypodermis, joints)
functional location: exteroceptors, proprioceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (deep pressure, stretch)
Muscle spindles receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (around muscle fascicles)
functional location: proprioceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (muscle stretch, length)
Tendon organs receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (around tendons)
functional class: proprioceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors (tendon, stretch, tension)
Joint kinesthetic receptors
structural class / where: encapsulated (capsule of synovial joint)
functional location: proprioceptors
functional stimulus: mechanoreceptors, nociceptors
Somatic reflec arcs
receptors, sensory neuron, integration center (interneuron), motor neuron, effector
not perceive because doesn’t go to cortex; stays in spinal cord
Receptor level
detection at sensory receptors
Circuit level
processing in ascending pathways (spinal cord)
Perceptual level
processing in sensory area of the brain
Somatosensory cortex
receives and processes sensory input from the body; located in postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe
Motor cortex (primary motor cortex)
sends motor output to skeletal muscles; located in precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe; sends signals via upper motor neurons — spinal cord — lower motor neurons — efectors (muscles)
Phasic receptors
detect changes in the environment; respond quickly at first then stop firing if stimulus remain; fast adapting
ex: Meissner’s corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, olfactory receptors
Tonic receptors
detect continuous stimuli; continue firing as long as stimulus is present; slow adapting
ex: nociceptors, proprioceptors, muscle spindles
Perceptual detection (sensory perception)
ability to detect that a stimulus occured (usually need several inputs summed)
Magnitude estimation (sensory perception)
ability to determine the intensity or strength of a stimulus
Spatial discrimination (sensory perception)
ability to localize the stimulus on the body
Feature abstraction (sensory perception)
ability to identify complex aspects of a stimulus
Quality discrimination (sensory perception)
ability to differentiate submodalities of a sense (different categories?)
Pattern recognition (sensory perception)
ability to recognize familiar patterns or combinations of stimuli
Graded (receptor) potential
temporary change in membrane voltage that happens when a stimulus (touch, taste, light) activates a sensory receptor; located on receptor membranes or dendrites; signal is local (fades with distance); summation (can add up if multiple stimuli happen close together); can lead to action potential if strong enough
Receptor potential
specific type of graded potential that occurs in sensory receptor cells (photoreceptors, olfactory neurons, mechanoreceptors); generated when a sensory stimulus causes ion channels to open or close; changes membrane potential based on stimulus strength; may trigger NT release (photoreceptors) or trigger action potentials
Transducin
G-protein found in photoreceptor cells in the retina; involved in visual signal transduction pathway
What is the order of light as it passes through the eye?
light — cornea — pupil — lens — vitreous humor — retina
Parasympathetic control over the pupil
sphincter pupillae muscle contracts: pupil contricts (size decreases)
Sympathetic control over the pupil
dilator pupillae muscle contracts: pupil dilates (size increases)
Photons
tiny packets/particles of light energy; enter the eye — hit retina — trigger visual process
Photoreceptors
specialized cells in retinae that detect light (rods and cones)
Rods
sensitive to low/dim light (night vision); don’t detect color; detect peripheral vision; low resolution
Cones
detect bright light and color; high resolution; concentrated in the fovea (detailed vision)
Phototransduction and ion flow in light
photons activate transducer; transducin activates PDE which breaks down cGMP into GMP; reduced cGMP causes cGMP-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels to close; Na+ and Ca2+ ions stop flowing into the cell but K+ ions continue to exit; photoreceptor hyperpolarizes (membrane potential become more -); hyperpolarization reduced glutamate release at the synpase with bipolar cells; change in glutamate release alters bipolar cells activity which starts the visual signal cascase to the brain
Phototransduction and ion flow in dark
photoreceptors are depolarized (more + inside); cyclic GMP (cGMP) levels are high keeping cGMP-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels open on the photoreceptor’s outer membrane; Na+ and Cl- ions flow into cell and creat inward current call dark current; keep photoreceptor slightly depolarized allowing it to continuously release NT glutamate to bipolar cells
Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
enzyme activated during phototransduction in photoreceptors; when light actviated rhodopsin it triggers transduction which activates PDE; breaks down cGMP into GMP; causes cGMP-gated ion channels to close (photoreceptor hyperpolarization)
Bipolar cell
type of neuron in retina that connects photoreceptors to ganglion cells; recevie NT signals (like glutamate) from photoreceptors; ON bipolar cells activated when glutamate decreases (light condition); OFF bipolar cells activated when glutamate increases (dark condition); transmit signals to ganglion cells
When does glutamate decrease / increase?
decreases in light
increases in dark
Ganglion cell
final output neuron of retina; receives input from bipolar cells; axons form optic nerve which carreis visual info to the brain; generate action potential that travel along optic nerve
Cyclic GMP (cGMP)
secondary messenger molecule inside photoreceptor cells; in the dark cGMP levels are high which keeps ion channels open (photoreceptor depolarizes); when PDE breaks down cGMP in light the ion channels close (photoreceptor hyperpolarizes)
Photoreceptor depolarizes
dark; cGMP levels are high; cGMP-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels stay open; (+) ions flow into cell causing it to stay depolarized; cell continuously releases glutamate at teh synapse with bipolar cells
Photoreceptor hyperpolarizes
light hits photopigement (rhodopsin) activating transducin which activates PDE which breaks down cGMP; cGMP-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels close; K+ keeps flowing out of cell making the inside of the cell more negative (hyperpolarized)
Glutamate
primary NT released by photoreceptors; released continuously in the dark due to depolarization; light-induced hyperpolarization reduces glutamate release
Rhodopsin
light sensitive photopigment found in rods (dim lighting); made of opsin (protein) and 11-cis-retinal; triggered by photon (retinal changes shape); activated tranducin — PDE — decrease cGMP — signal
11-cis-retinal
inactive (before light hits); bound to opsin in rhodopsin; keeps rhodopsin ready to detect light; when combined with opsin it forms rhodopsin
all-trans-retinal
active (after light hits); released after activation; triggers activation of rhodopsin; breaks away from rhodopsin after light is absorbed; release begins singal transduction (G-protein pathway)
Retinal
light sensor (derived from vitamin A); 11-cis-retinal (fits into opsin to form active photopigment) and all-trans-retinal (created after light hits it)
Opsin
protein (in photoreceptor cell); holds retinal in place and triggers signal cascase when retinal changes shape; doesn’t absorb light directly but amplified effect of retinal’s shape change
rodes: opsin and 11-cis-retinal = rhodopsin
cones: different opsin and retinal = photopsins (red, green, blue light)
Ciliary muscles
behind the iris; change the shape of the lens to focus on objects at different distances (accommodation)
objects near: muscles contract and lens becomes thicker and rounder
objects far: muscles relax and lens becomes thinner and flatter
Flattened lens vs bulging lens
flattened lens: focusing on distant objects
bulging lens: (rounded) focusing on closer objects
Emmetropic eye
normal vision; focal point is on retina
Myopic eye
nearsighted; focal point is in front of the retina (eyeball is too long)
How are myopic eyes corrected?
concave lens moves focal point further back (to normal position)
Hyperopic eye
farsighted; focal point is behind retina (eyeball is too short)