L11 An introduction to assays
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is an assay

IC50, EC50, Ki, Kd
Ideally you want these numbers to be small as possible

What are PAINS
give a couple common examples
Molecules often detected in assays that are active owing to artefacts or lack of specificity. (Reaction with amino acids that are non-specific or interference with the assay mechanism)
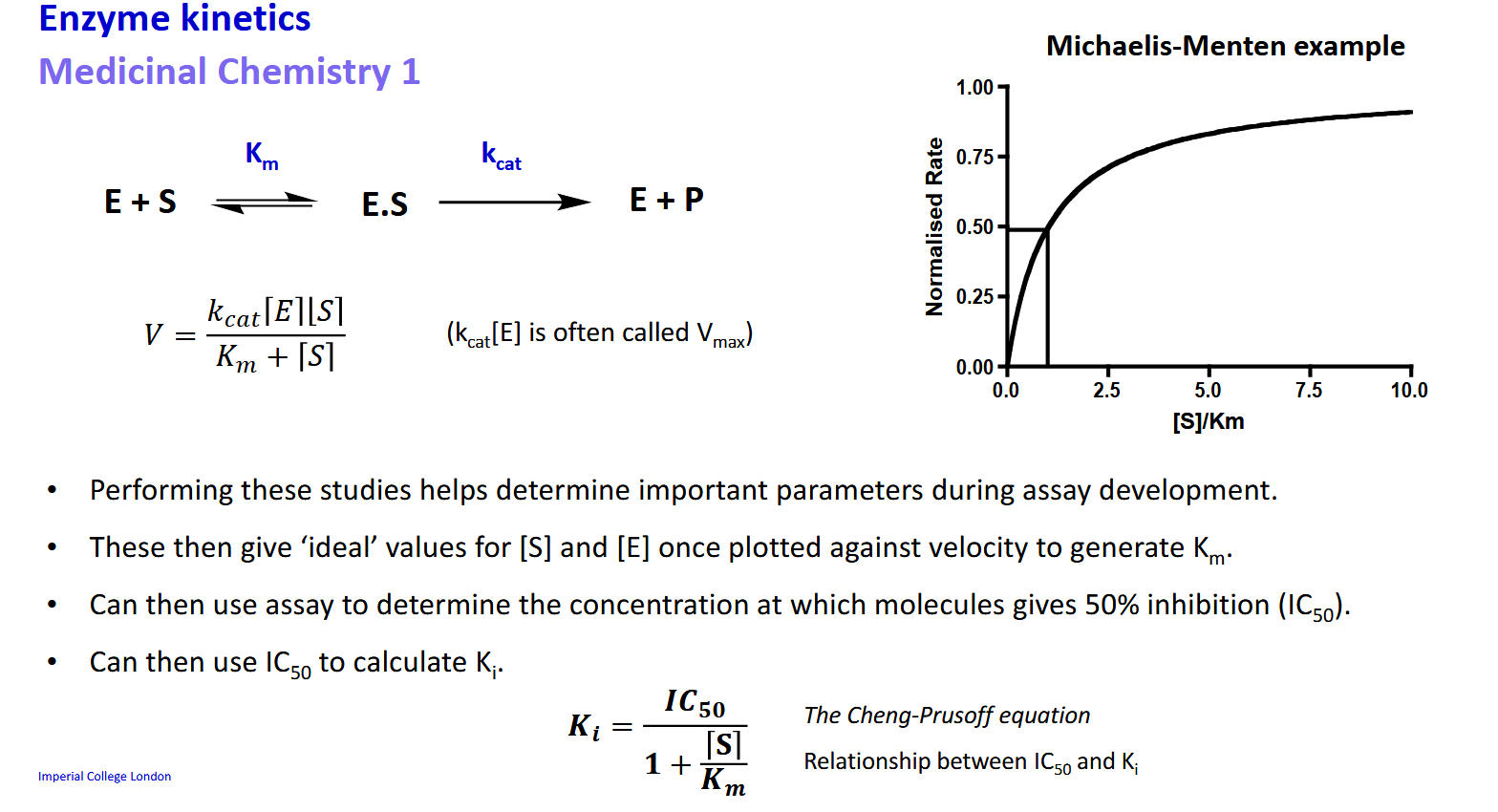
Enzyme kinetics - Km and kcat use in tandem with assays
What equation relates Ki to IC50 and why is this equation useful
Using these studies and an assay you can find the paramaters necessary to calculate Ki
Converting between Ki and IC50 may be necessary depending on the standard used by the lab/paper.
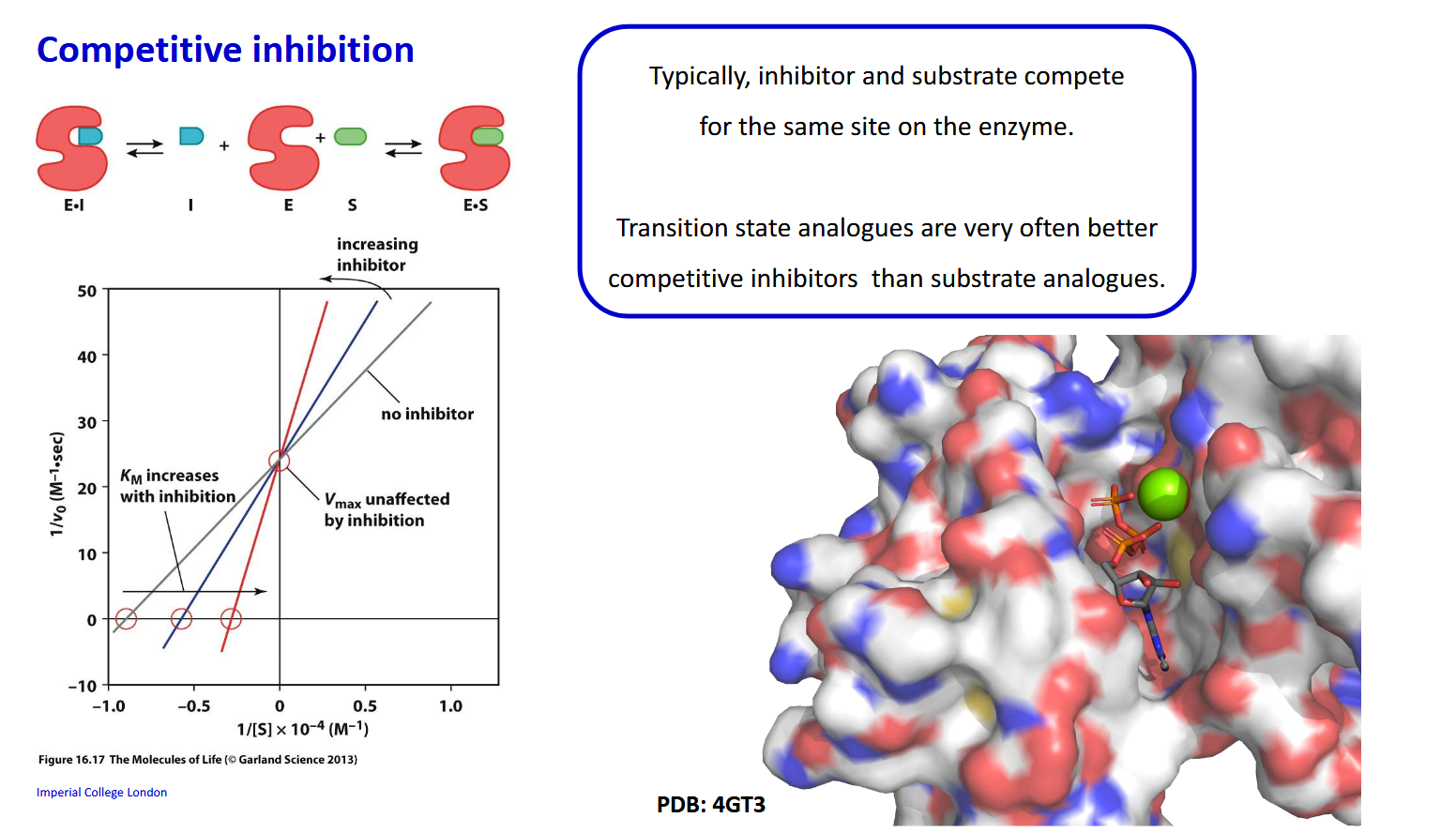
Competitive inhibition - How does Km and Vmax change with increasing inhibitor
Km increases with inhibition as binding affinity has effectinvely dropped. Vmax is unaffected as a large substrate concentration is gonna outcompete the inhibitor
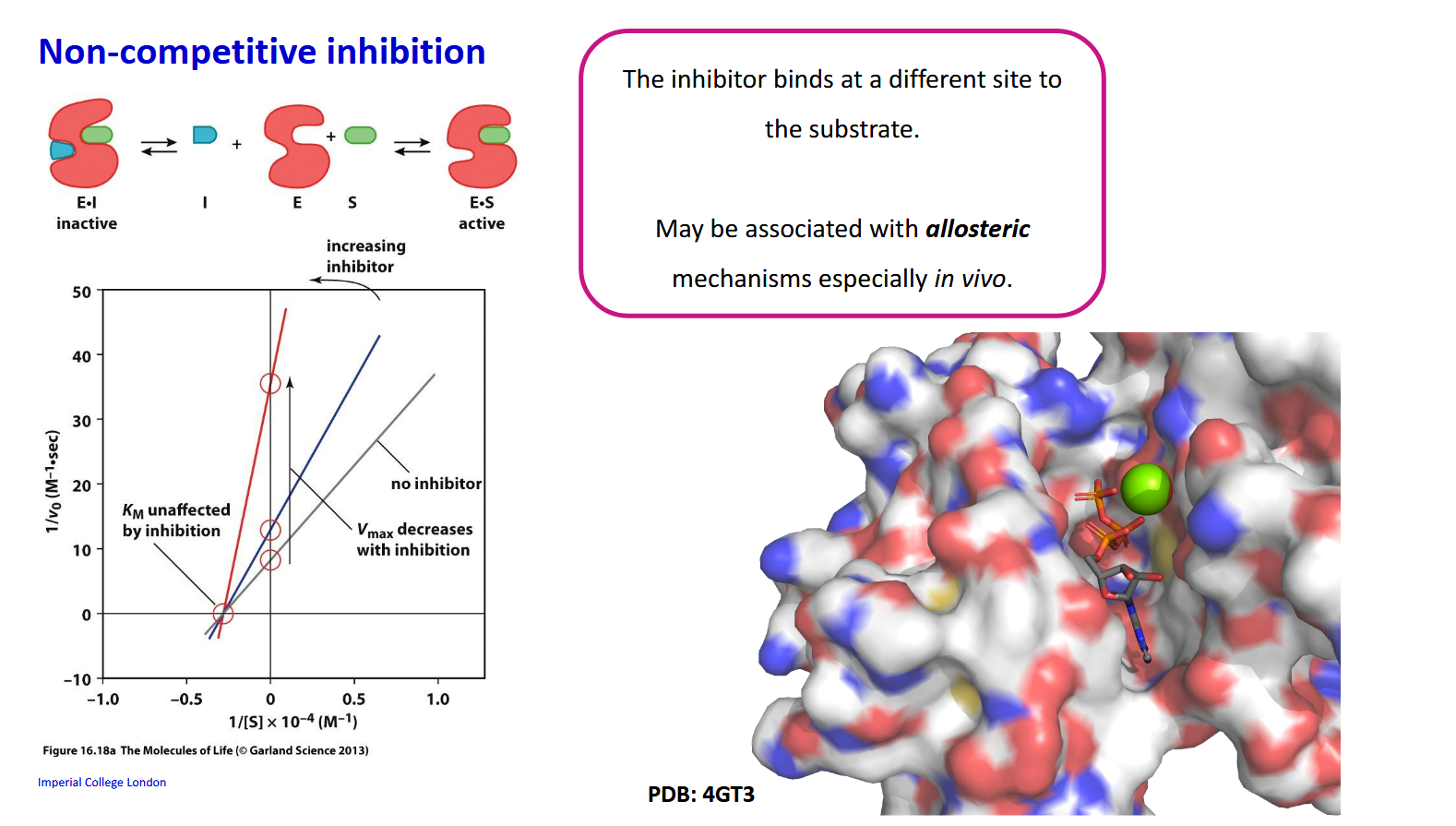
Non-competitive inhibition - How does Km and Vmax change with increasing inhibitor
Km is unaffected by inhibition as the binding affinity to intact enzymes remains constant but Vmax decreases with inhibition
What is uncompetitive inhibition and how is Km and Vmax affected
Both Km and Vmax decrease with inhibition. Km decreases as [ES] is decreased as [ESI] is formed
![<p>Both K<sub>m</sub> and V<sub>max </sub>decrease with inhibition. K<sub>m</sub> decreases as [ES] is decreased as [ESI] is formed </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a59377e7-362e-4852-a917-abfe6ea6b708.png)
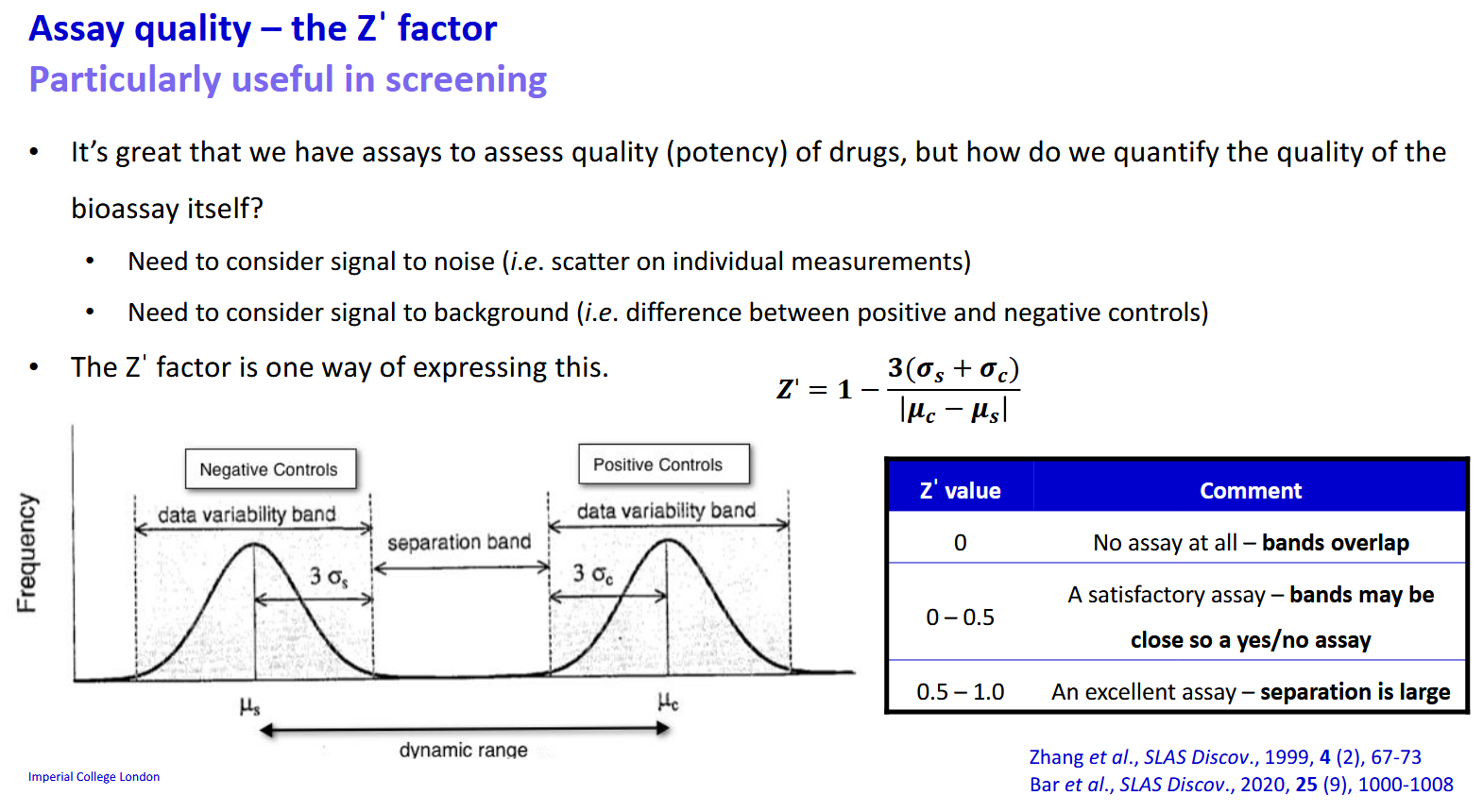
How can we assess the quality of an assay mathematically
The Z’ factor - measures signal to noise and signal to background.
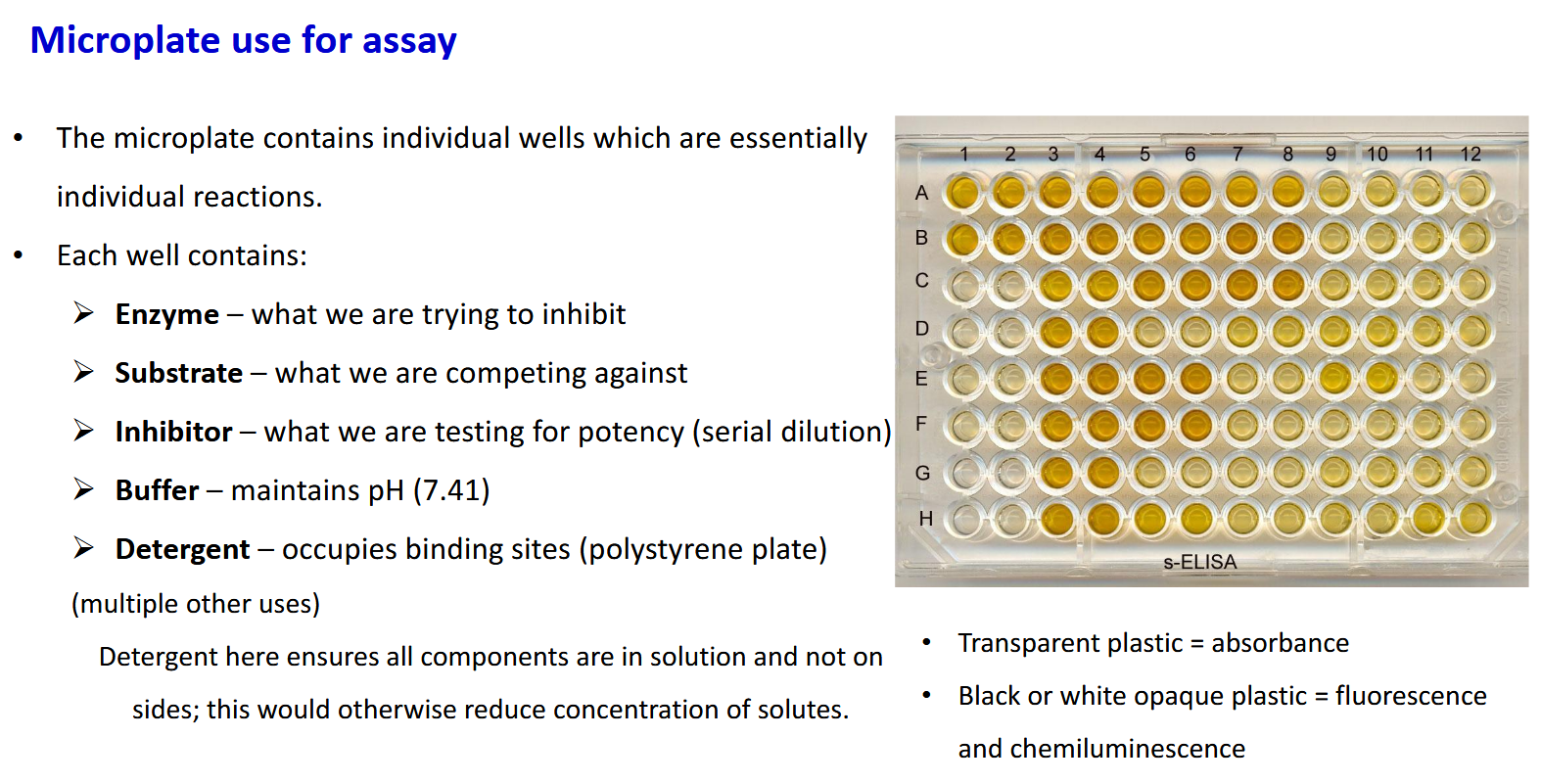
Microplate assay features - what does the detergent do
Dtergent ensures the compoents are not bound to the sides of the plate
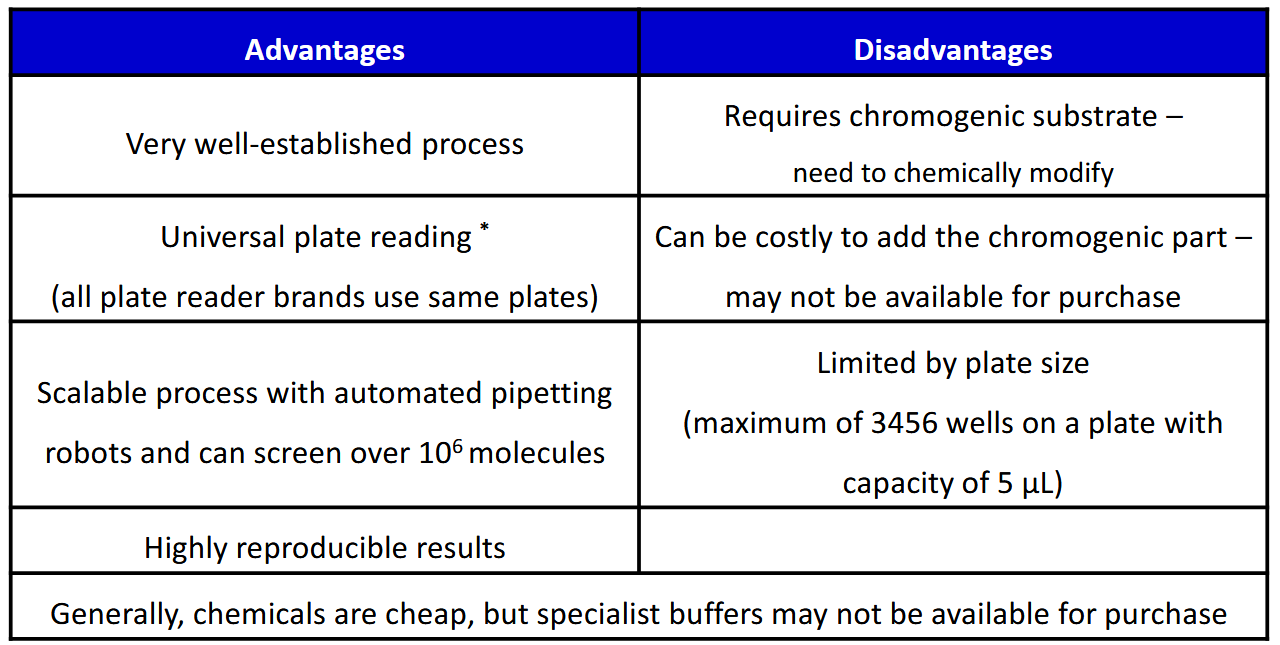
Advantages and disadvantages of microplate assasy
Well-established, familiar process with instruments that are readily available at most labs and standardised.
The process can also be automated by robots