14 Diseases of Equine Immune System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Immunodeficiencies
SCID and Failure of Passive Transfer in foals are both considered anaphylactic reactions or immunodeficiencies
Failure of passive transfer
What is the MOST COMMON immune deficiency in equine practice?
Secondary humoral deficiency in IgG antibodies from premature lactation/colostrum loss, poor quality colostrum, or lack of nursing within 24 hours of birth
What causes failure of passive transfer in foals?
Sticky, viscous, yellow
What will colostrum look like if it is high quality?
Decreases rapidly within first 24 hours of life
Ability to absorb colostrum decreases rapidly over HOW MUCH TIME in the foal's life?
2-4 L
HOW MUCH colostrum does a foal need to ingest in the first 24 hours of life to avoid failure of passive transfer?
c. unable to rise
e. weak/poor suckle reflex
Select the FOAL FACTORS for failure of passive transfer:
a. running milk pre-parturition
b. sick mare (placentitis)
c. unable to rise
d. recently moved to a new area, so not getting antibodies of importance at new place
e. weak/poor suckle reflex
Supplement with oral colostrum
If the foal is under 24 hours of age and you realize it may have failure of passive transfer, what can you do to correct it?
Intravenous plasma
If the foal is over 24 hours of age and you realize it may have failure of passive transfer, what can you do to correct it?
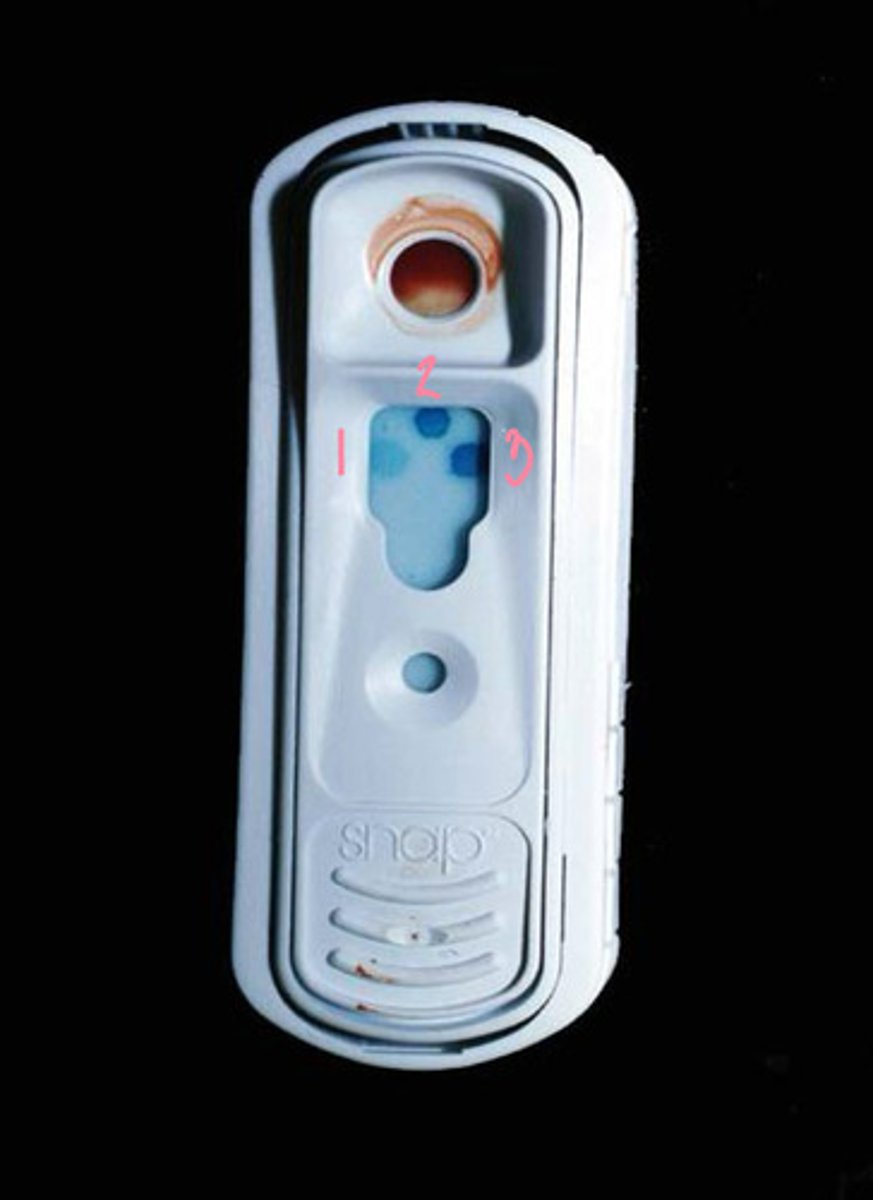
FAILURE OF PASSIVE TRANSFER:
1. IgG of 400
2. Foal sample that we compare to color of 1 and 3 dots
3. IgG of 800 = you WANT foal color to be close to this one = means they have had adequate IgG and DO NOT have failure of passive transfer
This test is testing the blood of a foal. What is this being used to test for, and what do each of the dots mean?
SCID = severe combined immunodeficiency
What is the primary AND humoral cellular immunodeficiency in foals caused by a failure to produce B and T lymphocytes?
Inherited
SCID is an autosomal recessive inherited or acquired condition in Arabians
IgM, lymphopenia
What immunoglobulin is reported to be low in foals with SCID? What other CBC value will be low?
2-3 months, meaning they present normal at birth but develop infection after maternal antibodies wane
Horses tend to develop signs of SCID around WHAT age?
Less than 6 months = because they are highly susceptible to infections and unable to recover
What is the lifespan of foals that develop SCID and WHY?
c. IgE mediated hypersensitivity
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is type 1:
a. immune-complex mediated hypersensitivity
b. IgG mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity
c. IgE mediated hypersensitivity
d. Cell mediated hypersensitivity
b. IgG mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is type 2:
a. immune-complex mediated hypersensitivity
b. IgG mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity
c. IgE mediated hypersensitivity
d. Cell mediated hypersensitivity
a. immune-complex mediated hypersensitivity
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is type 3:
a. immune-complex mediated hypersensitivity
b. IgG mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity
c. IgE mediated hypersensitivity
d. Cell mediated hypersensitivity
d. Cell mediated hypersensitivity
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is type 4:
a. immune-complex mediated hypersensitivity
b. IgG mediated cytotoxic hypersensitivity
c. IgE mediated hypersensitivity
d. Cell mediated hypersensitivity
1
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is anaphylaxis?
2
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is immune mediated hemolytic anemia
2
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is immune mediated thrombocytopenia?
2
Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is neonatal isoerythrolysis?
Large release of histamine from reaction to allergen
What causes the systemic signs that come from anaphylaxis?
1: anaphylaxis
A horse has a history of recent vaccine reaction and presents with hives (urticaria), sweating, dyspnea, and hypotension. What hypersensitivity reaction do you think is happening here?
FALSE: For anaphylaxis type 1 hypersensitivity reaction in horses, previous sensitization IS NOT required for a horse to have a reaction.
TRUE OR FALSE: For anaphylaxis type 1 hypersensitivity reaction in horses, previous sensitization IS required for a horse to have a reaction.
a. dexamethasone
b. epinephrine or temporary tracheostomy
d. hypertonic saline + epinephrine for cardiovascular collapse
Select the following appropriate treatments for anaphylaxis in horses:
a. dexamethasone
b. epinephrine or temporary tracheostomy
c. vitamin E or selenium injection
d. hypertonic saline + epinephrine for cardiovascular collapse
e. phenylephrine for urticaria
f. IM penicillin at 2x normal dose
Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia
What is the name of the hypersensitivity reaction that comes from IgG targeting RBCs, often a result of RBC membrane changing from a disease process or drug reaction?
IgG
Which Ig is the issue with Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia?
Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia (type II rxn)
A horse presents with pale white mucous membranes and chronic weight loss. The horse has fever and lethargy. The horse is EIA and Piroplasmosis negative and has a regenerative response on bone marrow cytology. Thoughts?
Coombs test
What is the diagnosis for Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia in horses?
EIA, Piroplasmosis
What 2 other top differentials should you be considering for a horse with Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia?
ONLY with intravascular hemolysis
Why would a horse have hemoglobinuria with immune mediated hemolytic anemia?
Regenerative
With immune mediated hemolytic anemia, horses will have regenerative or nonregenerative bone marrow on cytology?
Washed, patient-derived RBCs are mixed with equine-specific Coombs reagent; if antibodies are present on the RBC, the reagent causes the cells to agglutinate (clump), confirming immune destruction = primarily used to test for IMHA
What does a positive coombs test mean? How does the test work?
Immune mediated thrombocytopenia (type II rxn)
A horse presents with SEVERE thrombocytopenia but normal PT and PTT clotting times. The horse is EIA and Piroplasmosis negative with a normal bone marrow aspirate. The horse has petechial hemorrhage, hyphema (blood in eye), and epistaxis. Thoughts?
Neonatal isoerythrolysis
What hypersensitivity disease is caused by blood group incompatibility between the mare and foal, leading to destruction of the foal's RBC following colostrum consumption?
1. foal inherits non-compatible blood type from sire
2. mare is sensitized to foal RBC antigen so she has produced antibodies
3. foal consumed colostrum containing antibodies against its' own RBC
What 3 conditions must ALL OCCUR for neonatal isoerythrolysis to be true?
Aa or Qa, donkey factor is also highly antigenic
What is the incompatible blood type of the foal often inherited from the sire in neonatal isoerythrolysis?
Mules
note: but thoroughbreds are technically highest risk
What type of equid most commonly gets neonatal isoerythrolysis?
Normal at birth = signs 6-72 hours after birth
What point in time after birth will foals start to develop signs of neonatal isoerythrolysis?
Neonatal isoerythrolysis (type 2 rxn)
A foal 20 hours old presents with pale yellow mucous membranes, discolored urine, progressive lethargy and weakness. The PCV, RBC, and hemoglobin are decreased. Bilirubin is increased and there is hemoglobinuria. Thoughts?
a. withhold milk
c. supportive care, dec. stress, fluids
d. alternative source of colostrum supplementation
Select the following treatments which will work for foals UNDER 24 hours of age with neonatal isoerythrolysis:
a. withhold milk
b. blood transfusion (washed mare RBC or compatible donor)
c. supportive care, dec. stress, fluids
d. alternative source of colostrum supplementation
b. blood transfusion (washed mare RBC or compatible donor)
c. supportive care, dec. stress, fluids
Select the following treatments which will work for foals OVER 24 hours of age with neonatal isoerythrolysis:
a. withhold milk
b. blood transfusion (washed mare RBC or compatible donor)
c. supportive care, dec. stress, fluids
d. alternative source of colostrum supplementation
Hyperbilirubin induced neurologic damage
What is kernicterus, which can occur as a complication of neonatal isoerythrolysis?
If test is positive (agglutinates) at 1:8 dilution or lower, do NOT let the foal nurse
You do a jaundiced foal agglutination test on the mare to identify her risk for producing a neonatal isoerythrolysis foal before birth. If the test agglutinates at WHAT DILUATION, the foal should NOT NURSE?
Lymphoma
What is the most common hematopoietic neoplasm in horses?
Multicentric
Which form of lymphoma is the MOST COMMON and widespread in horses
c. multicentric
Which form of lymphoma in horses is widespread, affecting lymph nodes and multiple organs like spleen, liver, GI, and kidney?
a. alimentary
b. mediastinal
c. multicentric
d. cutaneous
a. alimentary
Which form of lymphoma in horses occurs in older horses, mostly in the small intestine, causing colic, diarrhea, and malabsorptive weight loss?
a. alimentary
b. mediastinal
c. multicentric
d. cutaneous
b. mediastinal
Which form of lymphoma in horses is the most common neoplasia of the thorax, causing respiratory distress, coughing, and distended jugular vein?
a. alimentary
b. mediastinal
c. multicentric
d. cutaneous
d. cutaneous
Which form of lymphoma in horses carries the best prognosis, causing multifocal subcutaneous nodules which may exude yellow fluid?
a. alimentary
b. mediastinal
c. multicentric
d. cutaneous
FALSE: While it is true you must get their financial and personal consent to treatment, they should be told that treatment is often PALLIAIVE and NOT curative
TRUE OR FALSE: With lymphoma, owners should be told that treatment is often curative and you should get their financial and personal consent to the treatment.
a. excision of solitary mass
b. radiation
d. glucocorticoids
f. chemotherapy
Select which of the following are adequate treatments for lymphoma in horses:
a. excision of solitary mass
b. radiation
c. euthanasia first always
d. glucocorticoids
e. monoclonal antibody treatment
f. chemotherapy
Corticosteroids, Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide
Name three immunosuppressors which can be used as immune response modifying treatments in horses:
Stop giving medications, treat underlying disease, dexamethasone
What do you do to treat immune mediated thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia in horses?
Mycobacterial products, proprionibacterium acnes
Name immunostimulants which can be used as immune response modifying treatments in horses:
IgE --> IgG
When you immunomodulate using allergen hyposensitization, the goal is to switch the immune response from an IgE one (type 1) to WHAT OTHER Ig?