BIMM 120_Midterm #1_Saier Milton
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
3 Laws of Biology
1. Biology Obeys Chemistry & Physics
-1st Law of Thermodynamics: Energy/matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
-2nd Law of Thermodynamics: Entropy increases in a closed system
-Cells are open systems that maintain order via metabolism by ↓ internal entropy, ↑ external entropy, and equilibrium = death.
2. All Life Is Membrane-Bound
-Life consists of membrane-encased cells.
-Cells grow and divide independently; viruses are not living.
-Life is genome-encoded, but early life required symbiosis due to incomplete genomes.
3. All Life Evolved
-All life shares a common ancestor
-Evidence: Universal genetic code
-Darwin’s natural selection acts on genotype & phenotype. Early evolution = cooperation. Later evolution = increasing competition as independence arose
Metagenomics:
-Environmental DNA → PCR → sequencing → genome assembly. Revealed unculturable organisms and expanded the tree of life (Castelle & Banfield, 2018).
Timeline of Life on Earth
-Bacteria → Archaea → Eukaryotes (evolved from Asgard archaea).
Lamarck vs Modern View
-Lamarck: First to propose that organisms evolve and that traits acquired by use/disuse (incorrect).
-Modern biology: All biological information is genome-encoded.
-Bioinformatics & phylogeny best predict function and evolutionary relationships.
Transport Classification DataBase (TCDB):
Classifies transporter proteins by function and evolutionary history.
Cooperation & Competition (Saier, 2025)
-Early evolution: cooperation dominated (metabolic handoff, symbiosis)
-Later evolution: increasing competition as genomes became complete.
-Simple → complex through integration, not competition alone.
Partial Microbes (CPR, DPANN, Asgard):
-Early microbial lineages with reduced genomes, metabolic incompleteness, cannot live independently, and rely on obligate symbiosis.
CPR (Candidate Phyla Radiation) Bacteria:
Very small genomes and cell size, incomplete metabolic pathways, lack full biosynthesis, survive only with hosts, and simplified ribosomes present.
DPANN Archaea
Reduced genomes, attach to hosts, form biofilms, and show gene sharing.
Asgard Archaea:
Contains eukaryotic signature proteins (ESPs) that support eukaryote origin.
Isoprenoids & the “Lipid Divide”:
-Isoprenoids are essential metabolites.
-Lipid Divide: Archaea: MVA pathway; Bacteria: MEP pathway. Some CPR bacteria lack MEP, showing the divide is oversimplified and ancient.
Metabolic Handoffs:
One organism’s waste is another's substrate, enabling survival in nutrient-poor environments.
Nanoarchaeum equitans:
Obligate symbiont of Ignicoccus with compact genome that redirects host metabolism. Model how early cooperation led to endosymbiosis and complex cells.
Endosymbiont Theory:
-Mitochondria evolved from proteobacteria.
-Plastids (chloroplasts) evolved from cyanobacteria.
Nucleotides & Bonding
-Purines: 2 rings (A, G)
-Pyrimidines: 1 ring (U, T, C)
-C:G = 3 H-bonds (stronger); A:T / A:U = 2 H-bonds (weaker)
-Bond strength depends on geometry (linear > bent).
Codon Position Importance:
-Importance Order: P2 > P1 > P3
• P2: Determines amino acid chemistry
(a) P2 = A → hydrophilic
(b) P2 = T → hydrophobic
(c) P2 = C/G → semi-polar
• P1: Controls P3 importance
(a) P1 = A/T: P3 changes AA
(b) P1 = C/G: P3 is silent
• P3: Wobble position → often synonymous (no AA change)
Codons & Termination during Translation Rules
-Initiation codons: AUG > GUG > UUG/CUG → all read as fMet (Always Give Unconditional Cuddles)
-Initiation wobble = P1
-Stop codons: UAA > UAG > UGA
-Weaker H-bonds → easier polypeptide release.
-Highly expressed genes: use abundant/common codons.
-Lowly expressed genes: tolerate rare codons.
-Codon redundancy protects against harmful mutations.
mRNA–tRNA Asymmetric
-Pairing is direction-dependent (A:T ≠ T:A; C:G ≠ G:C).
-Stronger binding: tRNA purine : mRNA pyrimidine
Ancient vs Modern Plagues
-Ancient plagues (Justinian, Black Death) spread via commerce (Silk Road).
-Modern plagues spread via close contact (e.g., wet markets) and air travel.
-Sanitation & ventilation reduce spread.
-Hippocrates separated medicine from superstition.
Black Death (Bubonic Plague)
-Caused by Yersinia pestis via fleas on rodents.
-Symptoms: buboes
-30–60% mortality in Europe.
-Disease blamed on miasma (foul, polluted air) → believed solution: spice-filled masks.
-Treatment: Quarantine and burning houses.
Smallpox
-Caused by the Variola virus.
-Variolation: direct smallpox exposure.
-Vaccination: cowpox exposure → safer immunity. 1st successful vaccine.
Influenza
-RNA virus (Types A, B, C).
-Strain A causes most pandemics
-Surface proteins:
(a) Hemagglutinin (H): host cell entry
(b) Neuraminidase (N): viral release
-Important Strain:
(a) H1N1 (Swine flu): Influenza A from avian → pig → human. Pigs are “Mixing Bowls” because they have avian + human receptors enable co-infection → reassortment → novel (more virulent strains).
(b) H5N1 (Avian flu): Influenza A from wild birds. Highly virulent with poor human immunity. Dangerous due to its high mutation rate.
Antigenic Drift vs Shift:
-Antigenic Drift: small, gradual mutations (e.g. seasonal flu).
-Antigenic Shift: major reassortment between animal & human viruses → pandemics.
-Influenza uses BOTH
Why do we need new flu vaccines every year?
-Due to antigenic drift: H and N constantly mutate to allow immune escape.
~⅔ effective; excellent at preventing death.
1918 Influenza (H1N1)
-Zoonotic: avian → pig → human.
-High mortality and altered WWI.
-Ages 25–44 most affected due to the cytokine storm.
Transmissibility and Virulence:
-Transmissibility: ability to spread.
-Virulence: disease severity.
Virus Evolution: “Think Like a Virus”
-Evolution favors higher transmissibility and lower virulence.
-Less host damage (killing/disfigure) = better spread.
-Cough-inducing toxins aid transmission.
COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)
-Zoonotic: bats → animals → humans.
-Origin linked to wet markets & close animal–human contact but spread via air travel.
-Spike (S) protein binds ACE-2 receptors for cell entry.
-Spike mutations allow vaccine escape and new waves.
SARS & MERS:
1. SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome)
-Linked to live animal markets.
-Bats → animals → humans.
-Transmission via direct animal contact.
2. MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome)
-Coronavirus related to SARS.
-Bats → camels → humans.
-Higher virulence and respiratory failure than SARS-CoV-2.
-Limited spread due to high lethality + camel geography.
Ebola & Marburg Viruses
-Enveloped RNA filoviruses that causes hemorrhagic fever.
-Reservoir: fruit bats.
-Spread via bodily fluids, bush meat, human-animal contact
-Highly deadly due to: Rapid replication, immune evasion, systemic tissue damage
HIV
-Zoonotic: SIV → humans (primates).
-Enveloped RNA retrovirus causing AIDS.
-Spread via blood, sexual contact, and bush meat.
-Retrovirus: RNA → DNA integration into host genome.
-High mutation rate due to error-prone replication.
-No cure or vaccine, but antivirals suppress replication, making HIV a chronic disease.
Poliomyelitis
-Enters gut → bloodstream → CNS.
-Kills motor neurons → paralysis
-Iron lung used for respiratory failure.
-Vaccines:
(a) Salk: inactivated (killed), injected, very safe.
(b) Sabin: attenuated, oral, strong immunity.
Measles
-Most infectious virus known.
-MMR vaccine is highly effective.
-High R₀ → outbreaks if unvaccinated.
-95% herd immunity required.
Prion Diseases
-Infectious misfolded proteins (not viruses) cause normal proteins to misfold → chain reaction
-Diseases: Kuru (cannibalism) and BSE (Mad Cow) → vCJD in humans.
-Spread via oral exposure; replicate in Peyer patches.
Why Are So Many Diseases Zoonotic?
-75% of emerging diseases are zoonotic (animals)
-Drivers: Wet markets, Bush meat, Farming & agriculture
-No plant virus causes human epidemics.
Why Are Bats Ideal Reservoirs?
-High body temperature, strong antioxidant systems, and enhanced DNA repair mechanism from high-energy flight
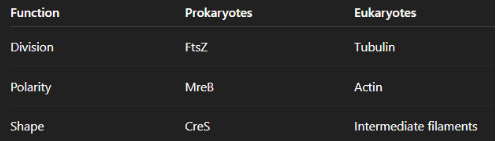
Bacterial Shapes
-Cocci (circular): Earliest bacterial shape. Requires FtsZ for cell division
-Rod: Requires MreB for shape and elongation
-Spiral: Require CreS (Crescentin) for spiral shape
FtsZ:
Tubulin-like, GTP-binding protein that forms a Z-ring at midcell to recruit the divisome and build the septum during binary fission. Without FtsZ, cells elongate but cannot divide (filamentous), and it is temperature-sensitive due to protein instability at high heat.
MreB:
Actin-like protein that guides sidewall peptidoglycan synthesis to maintain rod shape; loss causes rods to become cocci (often reversible).
CreS (Crescentin):
Intermediate-filament–like protein that localizes to one side of the cell to restrict growth and create curved/spiral shapes (e.g., Helicobacter pylori). Loss of CreS causes cells to become straight rods.
ParM:
An actin-like protein that ensures equal segregation of low-copy-number plasmids by forming filaments that push plasmids to opposite poles before cell division.
High vs low -copy-number plasmids (ParM):
-High: No ParM needed; random segregation is sufficient.
-Low: Require ParM for active segregation into daughter cells.
MamK:
Actin-like protein in magnetotactic bacteria that organizes magnetosomes into a chain that aligns with Earth’s magnetic field.
-Magnetite (Fe₃O₄): Aerobic.
-Greigite (Fe₃S₄): Anaerobic.
Big Picture: Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Channels
passive transport down gradients without energy. Ex: aquaporins
Carriers
bind substrates and change conformation to transport them passively or actively
(a) Symporter: same direction
(b) Antiporter: opposite directions
Pumps
Move substrates against concentration gradients using energy.
(a) Drug efflux pumps: antibiotic resistance
(b) P-type ATPases: use ATP directly
(c) F-type ATPase: transports ions (H⁺ or Na⁺) using the proton motive force to convert ADP + Pi into ATP, H⁺ flows from outside to inside causing counterclockwise rotation, while ATP hydrolysis drives clockwise rotation
(d) H⁺ pyrophosphatases: pump H⁺ via P–P bond hydrolysis
2 Main Ways Some Bacteria Use Light (to generate ATP):
1. Bacteriorhodopsin-based phototrophy
2. Photosynthesis (using electron transport chains)
1. Bacteriorhodopsin-based phototrophy
-Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven transmembrane proton pump with retinal bound to lysine via a protonated Schiff base. Light converts retinal from all-trans to 13-cis, pumping H⁺ out of the cell to create a proton motive force, which F-type ATP synthase uses to make ATP; no electron transport chain is required.
Bacteriorhodopsin vs Bacterial Rhodopsin
-Bacteriorhodopsin: light-driven pump; light provides energy to move H⁺ against gradient, creating a proton motive force for ATP synthesis.
-Bacterial rhodopsins: light-gated channels; H⁺ flows down existing gradient (not light) to provide energy.
Photosynthesis Bacteria
1. Oxygenic: Only cyanobacteria; use chlorophyll, H₂O, and CO₂ to produce O₂, and can fix N₂.
2. Anoxygenic: Do not produce O₂; use bacteriochlorophylls and alternative electron donors (e.g., H₂S), live in low-light environments, and include purple sulfur/non-sulfur and green sulfur bacteria (extremely O₂-sensitive).
FtsZ and Bacterial Cell Division:
1. Polymerization: FtsZ binds GTP and polymerizes at the + end.
2. Depolymerization: GDP-FtsZ is unstable and dissociates from the – end.
3. Dynamics: Filaments show dynamic instability and treadmilling.
4. Z-ring: FtsZ forms a midcell Z-ring beneath the plasma membrane.
5. FtsA: ATP-binding protein anchors and stabilizes the Z-ring.
6. Divisome: Z-ring recruits the divisome to build peptidoglycan inward.
7. Separation: Septum completes, cells separate, and FtsZ is reused.
Bacteriorhodopsin-based phototrophy (short steps):
1. Retinal starts all-trans (Schiff base protonated).
2. Light → retinal all-trans → 13-cis.
3. H⁺ released outward from Schiff base.
4. Cytoplasmic H⁺ restores all-trans retinal.
5. Outward H⁺ pumping creates PMF, which ATP synthase uses to make ATP.