Medicinal Drugs from Biodiversity
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Status of Philippine Biodiversity
high species diversity and high endemicity
archipelagic country (patchwork of islands)
tropical location of country (tropical biome)
extensive area of rainforest
Threats in Biodiversity
Why is there a decline?
hunting
used as pets or food
habitat destruction
species restricted to one or two islands (example: tarsiers)
climate change
medicine (overexploitation)
religious rites
Pharmacology
study of history, sources, physical and chemical properties of drugs
ways in which drugs affect the living systems
Two Main Branches of Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics
biological and physiological effects of drugs
drugs’ mechanisms of action
what the drug does to the body
Classification of Drugs’ Effect
Medicinal
Poisonous
Psychoactive
Pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug
drug’s journey in your body
4 Steps in Pharmacokinetics
ADME
Absorption: How the drug gets into your bloodstream.
Distribution: How the drug spreads to different parts of your body
Metabolism (or Biotransformation): How the body breaks down the drug
Excretion: How the body gets rid of the drug
Drug Administration
Oral
Enteral (medications that are administered into the gastrointestinal tract)
Rectal
Inhalation
Intramuscular Injection (using the deltoid muscle)
Subcutaneous injection (tissue layer beneath the skin)
Transdermal (usually patches applied to the skin)
Drug Tests
identifies the presence of: methamphetamine, cannabinoids, or THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
Pharmacotherapeutics
how drugs may be best used in treatment of illness
what’s the best drug and the right dose?
Pharmacognosy
where drugs come from
drugs derived from herbal and natural drug sources
studying compositions of natural substances to gain knowledge for developing synthetic versions
Executive Order 247
balance the potential benefits of using Philippine biodiversity with the need to protect it and share the profits fairly
Toxicology
study of poisons and poisonings
History of Pharmacology
Ancient Egypt: listed 700 remedies for ailments
First Century: Dioscorides prepared De Materia Medica which classified 600 plants for medicinal purposes
Sources of Drugs
Natural
Semisynthetic
Synthetic
Drug Uses
Symptomatic treatment
Prevention
Diagnostic drugs
Curative
Health maintenance
Contraception
Principles of Drug Action
Agonist effect
Antagonistic effect
Adverse drug effect
Therapeutic effect
Agonist effect
describes a drug's ability to bind to a receptor in the body and activate it, triggering a response that is similar to the body's own natural substances
example: morphine binds to opioid receptors in the brain, reducing pain
Antagonistic Effect
drug's ability to bind to a receptor and block it, preventing the body's natural substances (or other drugs) from activating the receptor
example: Naloxone is used to reverse the effects of opioid overdose
Adverse Effect
unwanted effect of the drug, also known as side effects
Therapeutic Effect
positive effect of the drug
Drugs from plants
Medicinal
Poisonous
Psychoactive
examples of drugs from plants
CCSSTTVDAOM
Caffeine
Cocaine
Silymarin
Scopolamine
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Theobromine
Vinblastine
Digixon/Digitoxin
Arecoline
Opium
Morphine
Poisonous plants
chrysanthemum
piscicide (Derris elitica)
Drugs from microorganisms
antimalaria
replication inhibitors on HSP 90
antibiotics
anti-inflammatory
apoptosis inhibiting compounds
anti-cell proliferating agent
cell lysis
drugs from marine organisms
Fucoidan extract
Portuguese man-o-war
Shell-less gastropods
Shells from crustaceans
newly discovered drugs
Ara-C
Bryostatin
Ecteinascidin
Descodermolide
Halichondrin B
Conus toxin
Ara-C (Cytarabine)
anticancer drug to treat acute myelocytic lymphoma
isolated from a shallow-water sponges
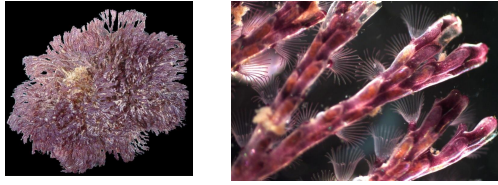
Bryostatin
Anticancer and immune modulating agent
Action: activation of protein kinase C mediation cell signalling pathways

Ecteinascidin
Ascidian Ecteinascidia turbinata
Treatment for ovarian cancer

Descodermolide
From sponge Discodermia
Potent immunosuppressive
Inhibits cell proliferation by interfering microtubule network assembly

Halichondrin B
Sponge Lissodendoryx
like the action of Descodermolide
Conus toxin
Conus spp.
Bioactive compounds for poison, tranquilizer, muscle relaxant
Interfering nerve conduction
Cocaine
local anesthesia
Erythroxylum coca
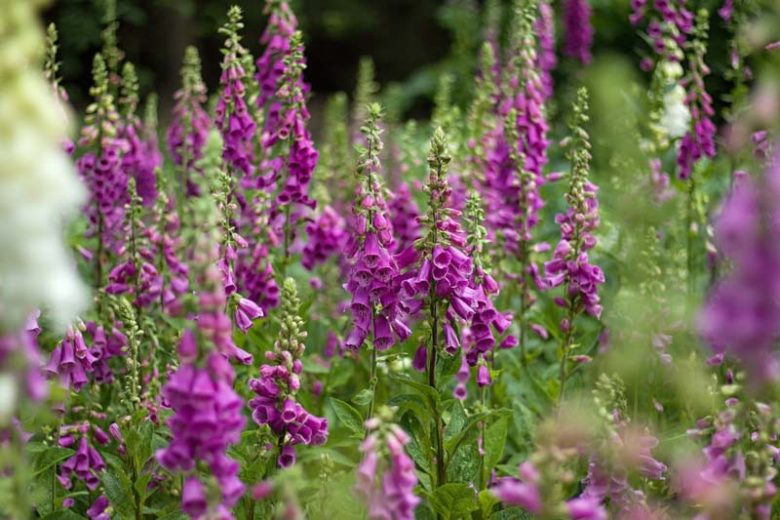

Digoxin / Digitoxin
cardiotonic
stain
Digitalis purpurea (Lady’s glove)

Scopolamine
sedation
psychoactive drug
Datura spp.
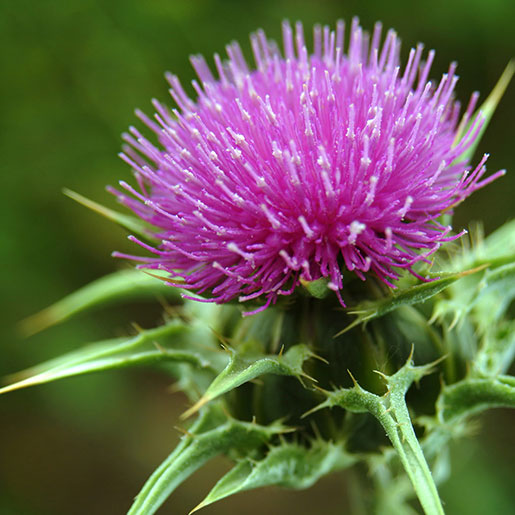

Silymarin
antihepatotoxic (prevents liver disease)
Silybum marianum (milk thistle)
some found in bitter gourd

Tetrahydrocannabinol
diuretic
decrease ocular tension
Cannabis sativa
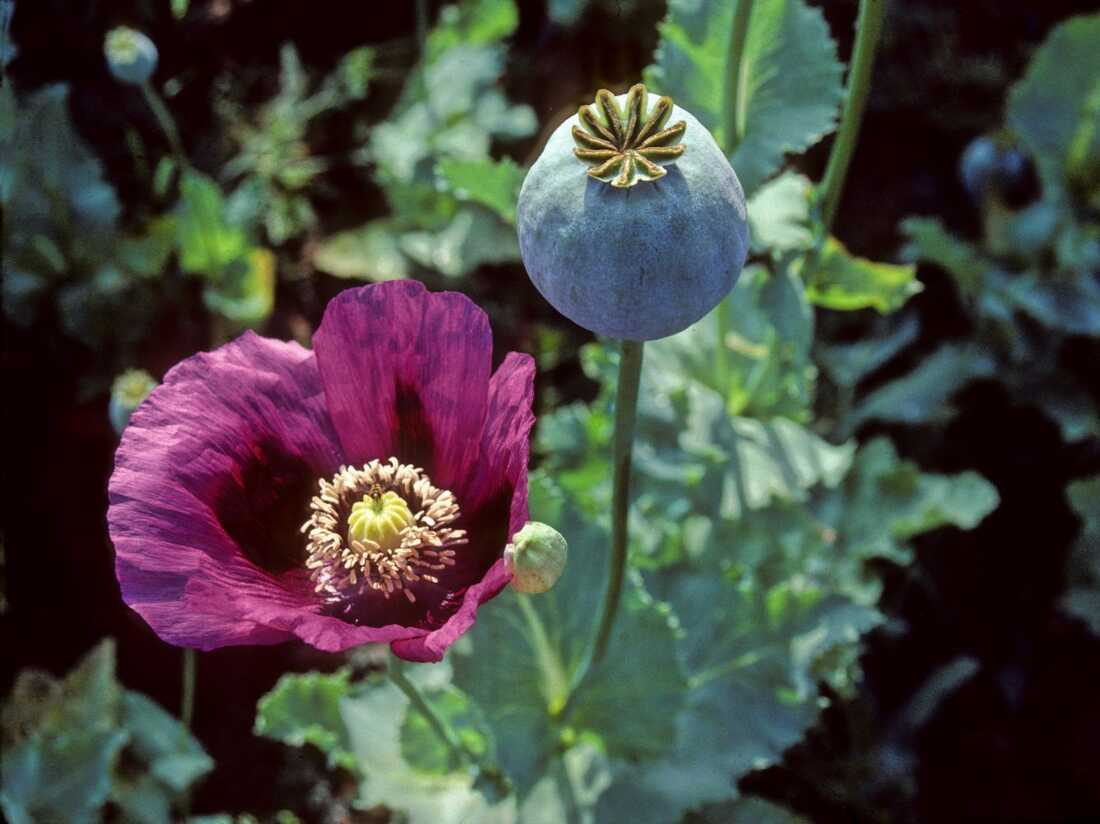

Opium
staying awake
vasodilation
Papaver somniferum
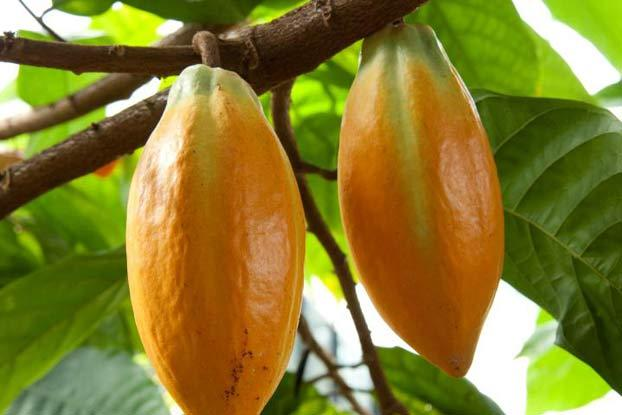

Theobromine
diuretic
vasodilator
Theobroma cacao
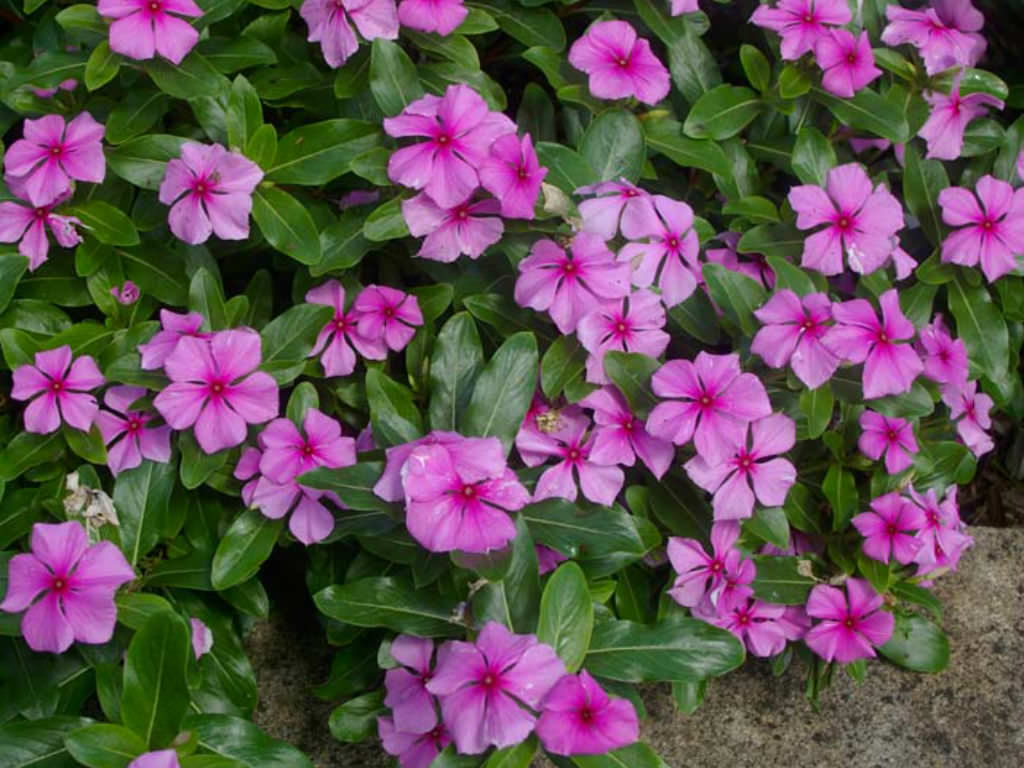

Vinblastine
antitumor
antileukemic
Catharanthus roseus (rosy periwinkle)
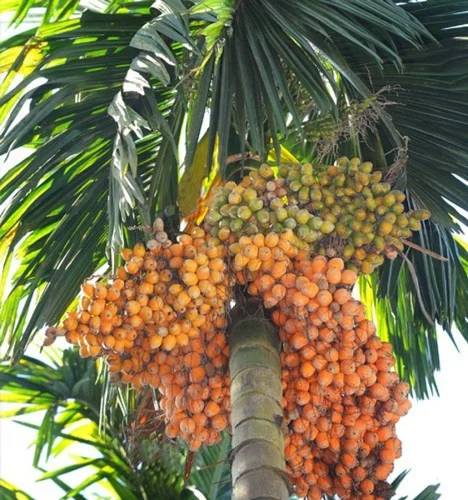

Arecoline
anti-helminthic
Areca catechu
masticated
Caffeine
CNS stimulator
mimics neurotransmitter response
cardiovascular response
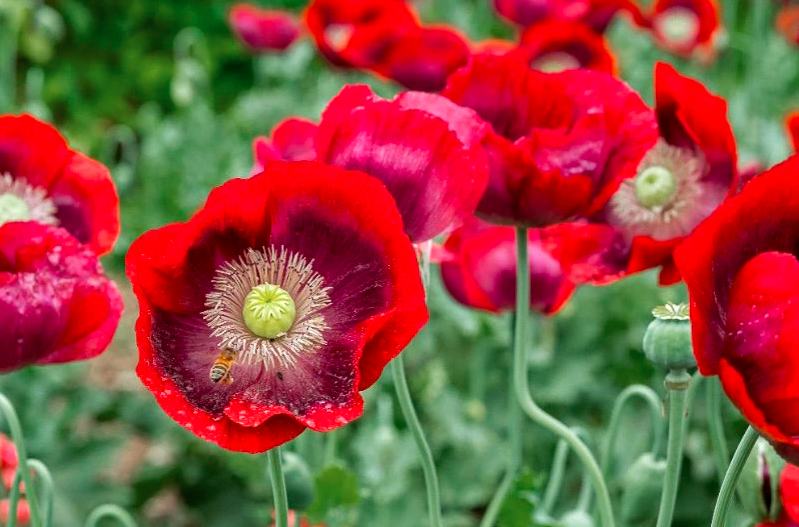

Morphine
analgesic
eye dilator
antispasmodic
Papaver somniferum