Week 3- enzymes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
substrate specificity vs reaction specificity
Substrate- some enzymes are highly specific for one molecule (substrate)
Reaction- Some enzymes act on many substrates, but perform same reaction
coenzyme
When the co factor needed with enzyme is organic (has carbon)
6 classifications of enzymes
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydroases
Isomerses
Lyases
Ligases
Oxidoreductases
enzymes that catalyse redox reactions (oxidases and reductases, hydroases for two hydrogens present)
Transferases
transfer from one group to another
Hydroases
catalyse hydrolysis
Isomerases
catalyse conversion of one isomer to another
Lyases
catalyses addition or removal of molecule to create or break double bond
dehydrase (removal H2O)
Synthase (addition of small molecule to double bond)
Ligases
Bond formation accompanied by energy release from hydrolysis reaction
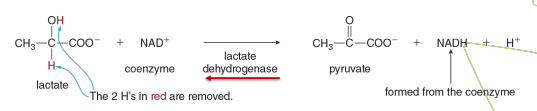
Example of Oxidoreductases
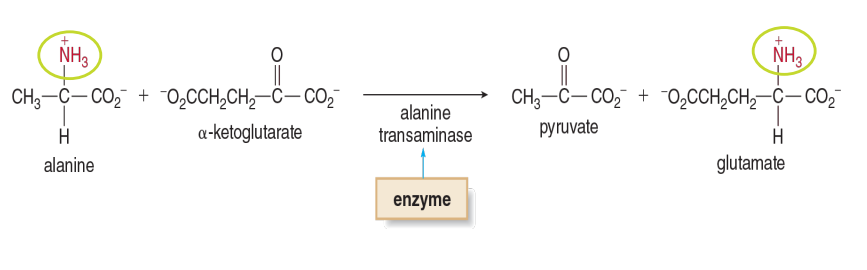
Example of Transferases
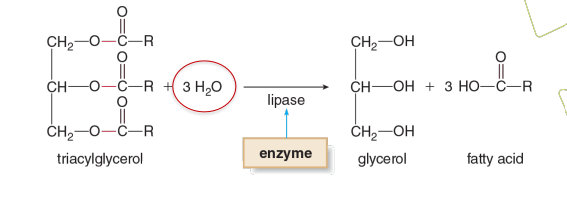
Example of Hydroases
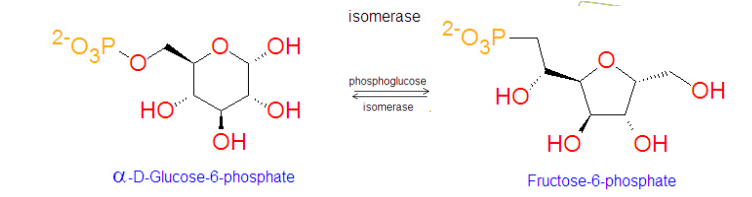
Example of Isomerses
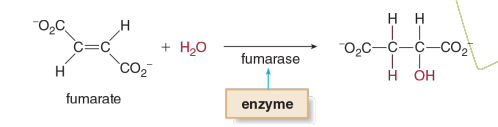
Example of Lyases
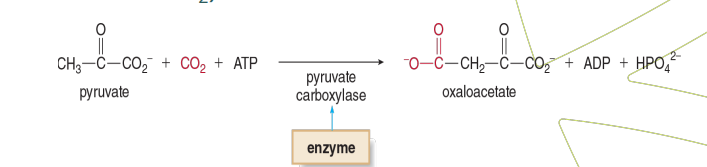
Example of Ligases
How are enzymes named?
[The substrate its acting on] [the type of classification]
lock and key model
Shape of active site on substrate matches enzyme exactly
Induced fit model
The shape of the active site is more flexible to fit enzyme
How enzymes work with temp and pH
Optimal temp 37 degrees
pH optimal 7.4
increase with inc temp but cant go outside 37 or will lose function/denature
allosteric enzymes
Have a regulator bound to them (not at the active site tho) to control them
Negative allosteric control
Occurs when the regulator binds and makes the active site less able to bind substrate
Positive allosteric control
Occurs when the regulator binds and makes the active site more able to bind substrate
3 types of enzyme inhibition
Irreversible-penicillin
Reversible- competitive and non-competitive
Proenzyme-pepsin and trypsin
zygmogen
proenzymes- ie. pepsin and trypsin digestive enzymes active when it reaches destination
How do proenzymes activate?
They carry extra amino acids and let go once at their destination causing them to carry out desired function
Competitive vs non-competitive reversible enzymes
Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor binds to the active site.
Competes with the substrate.
Can be overcome by adding more substrate.
Non-Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor binds to an allosteric site (not the active site).
Changes enzyme shape, reducing activity.
Cannot be overcome by more substrate.
An enzyme that catalyses the conversion of L-sugars to D-sugars is?
Isomerases
A kinase catalyses which of the following types of chemical reactions?
A. Hydrolysis
B. Oxidation-reduction
C. Phosphorylation
D. Isomerization
phosphorylation
An oxidase catalyzes which of the following types of chemical reactions?
A. Hydrolysis
B. Oxidation
C. Phosphorylation (transfer of a phosphate group)
D. Decarboxylation
Oxidation-reduction
Which type of enzyme catalyzes the breaking of bonds using water?
A. Ligase
B. Isomerase
C. Oxidoreductase
D. Hydrolase
Hydrolase
A decarboxylase enzyme performs which type of reaction?
A. Adds water across a bond
B. Transfers electrons
C. Removes a group without using water or oxidation
D. Rearranges atoms within a molecule
Removes a group without using water or oxidation
An isomerase catalyzes what kind of reaction?
A. Combines two molecules
B. Rearranges atoms within a molecule
C. Transfers phosphate groups
D. Breaks bonds using water
Rearranges atoms within a molecule
Lactate dehydrogenase is what type of enzyme used for what type pf reaction
Oxidoreductase used for an oxidation-reduction
Alanine Transaminase is what type of enzyme
Transferase
Liptase is what type of enzyme
Hydrolase
phosphoglucose isomerase is what type of enzyme
Isomerase
fumerase is what type of enzyme
Lyase
Pyruvate hydroxylase is what type of enzyme?
Ligase
Which enzyme transfers phosphate groups one molecule to another?
Transferase
Which type of enzyme breaks bonds using water?
Hydrase