EKG rhythms
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
normal sinus rhythm
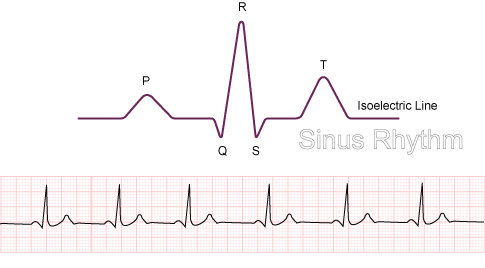
sinus bradycardia
slow heart rate (<60 bpm)
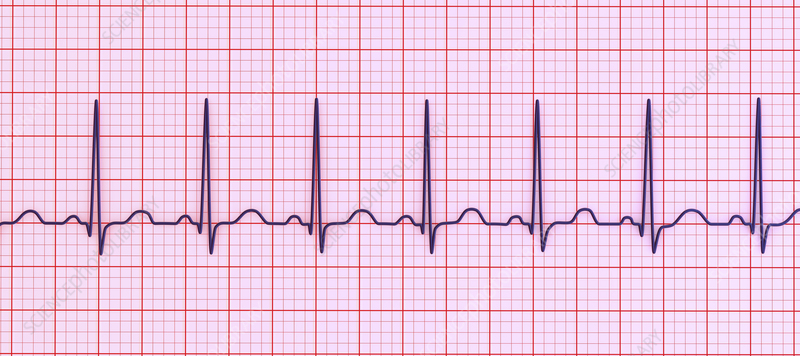
sinus tachycardia
fast heart rate (>100 bpm)
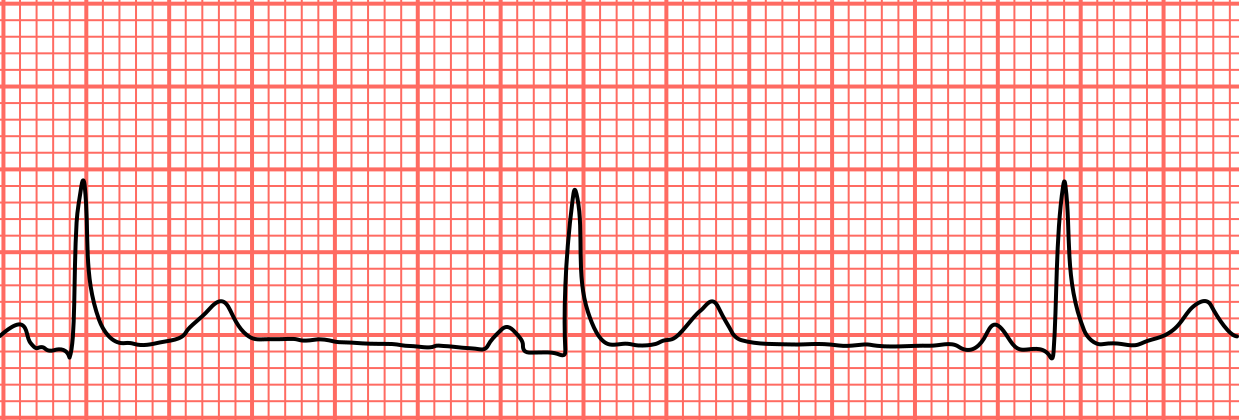
atrial fibrilllation
irregular atrial activity
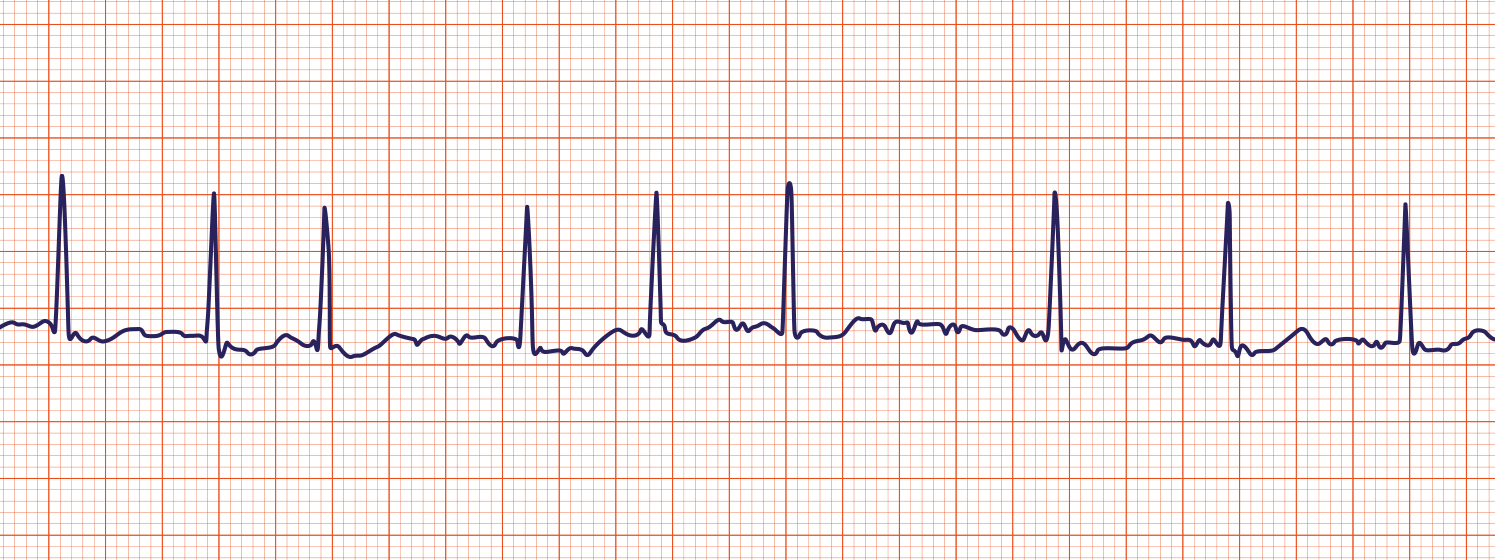
Atrial flutter
rapid, regular atrial activity
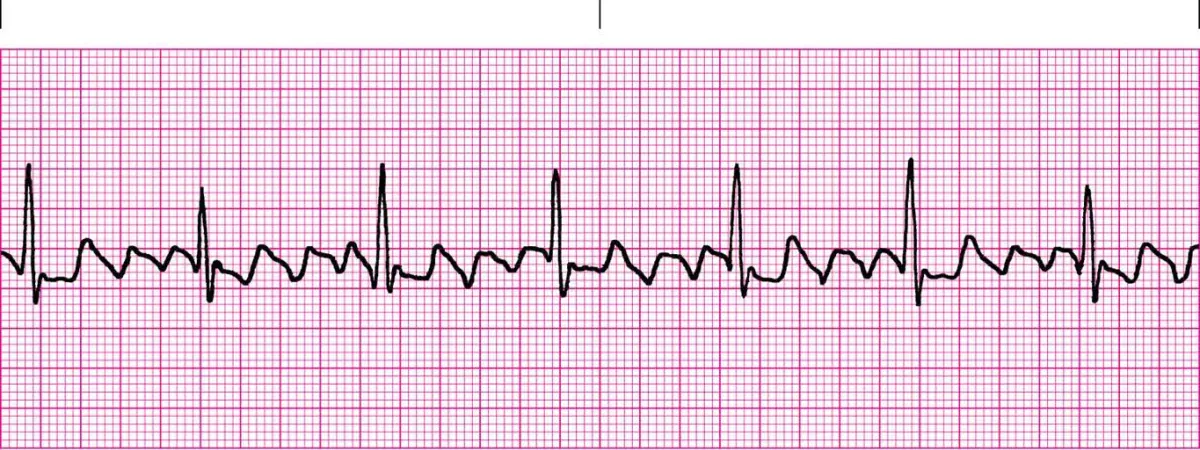
ventricular fibrillation
chaotic ventricular rhythm
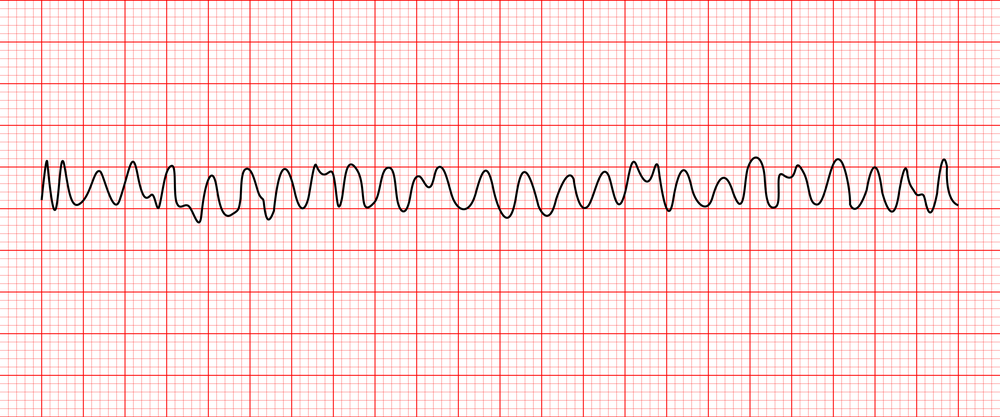
ventricular tachycardia
rapid ventricular rhythm
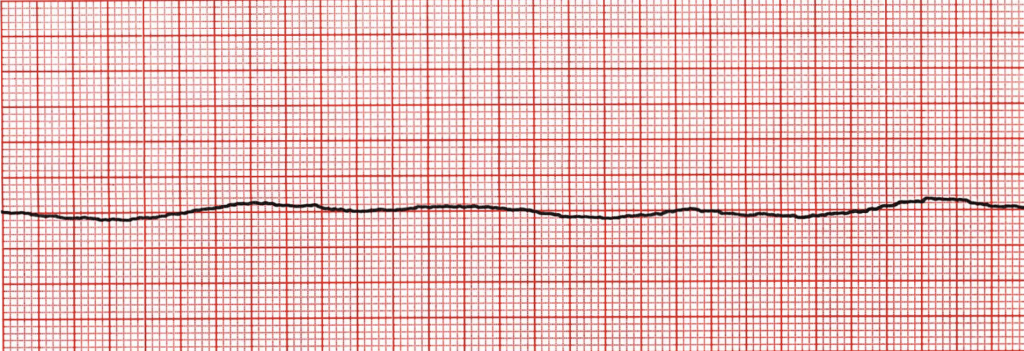
asystole
flatline
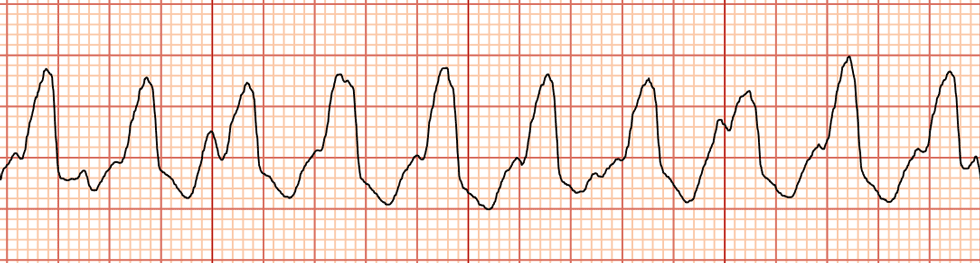
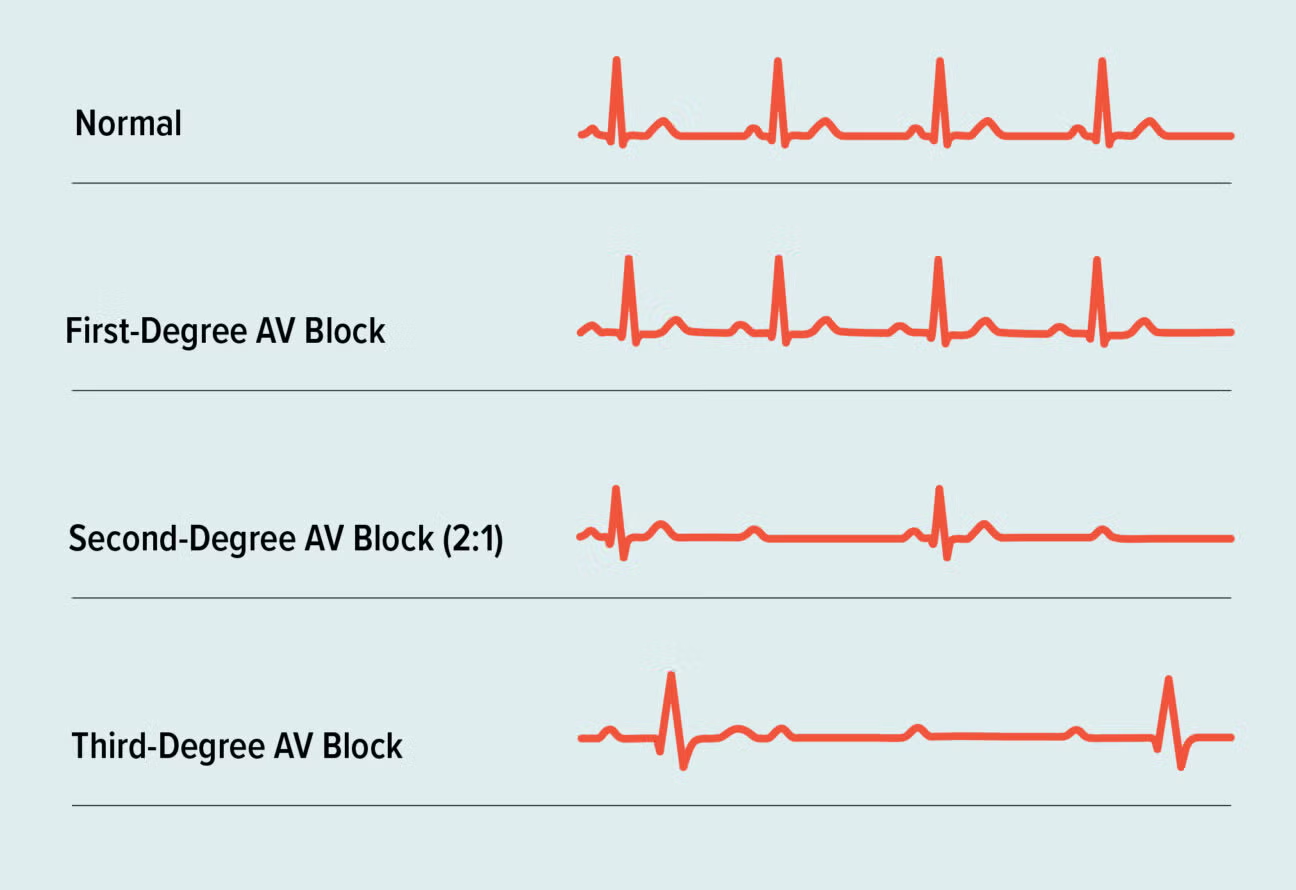
heart block
delay or blockage in conduction system
1500 method
most appropriate with fast rhythms (must be regular), count squares between two R waves, divide 1500 by that number
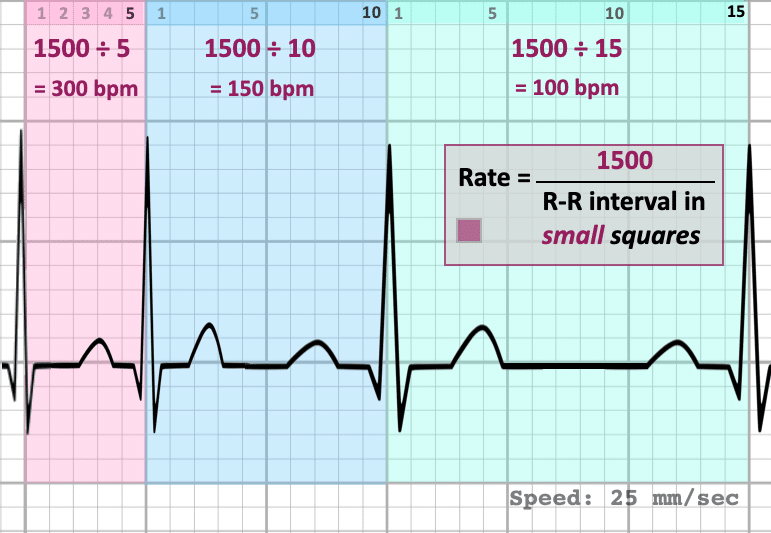
6 second method
used for estimating, especially irregular rhythm, count number of QRS complexes in two of the sections (30 boxes), multiply by 10

Lead I
records impulses between left and right arms
lead II
between right arm and left leg
lead III
between left arm and left leg
AVL
left leg and right arm with left arm tracing
AVR
left arm and left leg assist with the right arm tracing
AVF
right and left arms assist with left leg tracing
V1
fourth intercostal space, right of sternum
V2
fourth ICS, left of sternum, directly across from V1
V3
midway between V2 and V4
V4
fifth ICS, midclavicular line
V5
fifth ICS, midway between V4, and V6, at the anterior axillary line
V6
fifth ICS, at the midaxillary line
Ambulatory monitoring (holter monitor)
24hr or longer
portable ekg
bathe prior
loose-fitting clothing
record symptoms in log book
avoid bathing and showering
Stress testing
EKG monitor during exercise
some patients receive meds
avoid caffeine
eat a light meal 2 hrs before
take meds as usual
loose-fitting clothing
test stopped if bad symptoms
V7
left posterior axillary line, same horizontal plane as v6
v8
tip of scapula at the level of V6
v9
left parapspinous region at level of v6