DEP - Exam 1
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Nativism
“Nature”, Built-in, what' you’re born with
Empricism
“Nurture,” environment
Nativism vs Empiricism
Thinks in terms of percentages
There’s no definite cut-off between nature vs nurture
the womb can be an environment
puberty occurs after birth (biological)
Similarities
What makes us the same
Differences
What makes us different
human variability
Ex:
babies may talk or walk at different times (no concrete value but there’s an average)
maturation, timing when one goes through puberty
Quantitative development
amount that changes
Ex: memory (storage capacity), # of words in vocabulary
Qualitative Development
changes in function, ability, use
Ex: adults can use their memory more efficiently/differently than children (use strategies to retrieve information)
Lifespan perspective
looking at the entire lifespan not just childhood
development doesn’t stop at puberty
There are (+) and (-) changes as one ages
biological (brain keeps developing), behavioral
Why do we study lifespans?
People have been living a lot longer
Covid decreased this by months
There more ____ people than we’ve ever had in history
elderly
infant mortality rates
# out of 1000 infants that die before 1
it’s gotten better but there’s still a long way to goo
Ex: in 1950, 30/1000 would die, now it’s less than 10
Age at retirement
getting older in the U.S. (65-67)
most people don’t retire completely (part-time job)
some Hispanics people may retire late (don’t have as much money)
Family size
related to where you live
larger in Africa, smaller in Europe
Family sizes are shrinking around the world
China revoked it’s only child policy (4M:1F)
Japan and Korea have low fertility rates
Male/Female ratio
in nature 103M:100F to account for the males that die (so there’s enough for breeding)
Each pregnancy a woman has a boy the likelihood of her having another one goes up slightly
age of mom may also be a factor
Medical Advantages
we can save more kids than we used to be able to
kg kid → over 95% will survive now
Super premature kids (22 weeks), usually can’t do as much as other kids (very small)
Conceptions of Childhood → Decartes
babies are born perfect, have a sort of “godliness” to them, then society corrupts them
they also have some knowledge of how the world works “built-in” (physics, math)
infants have a general idea of numbers and space
Conceptions of Childhood → John Locke
babies have blank slate “Tabula Rasa”
the world “writes” on it - knowledge comes from experience
Behaviorism: a child can be turned into anything through reward, punishment, and environment
Teaching is based on theory that we just “______”
pour into brains
we actually have to change those “naive” theories and views on the world
we’re not blank slates
Conceptions of Childhood → G. Stanley Hall
famous psychologist influenced by Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
recapitulation theory → by looking at one individual you get how the history of how that species evolved
if we evolve physically, we may evolve mentally and behaviorally
if you look at a child's development, it reflects the stages of human evolution, suggesting that childhood is a significant phase in understanding human nature
gave us the idea of adolescence and pushed child labor laws
thought males and females should be educated seperateley
worried about the “evils” of the world corrupting young minds (pool halls, comic books)
What are kids interests?
climb → apes
plants → agraian (growing plants)
animals → husbandry
machines → “industrial revolution” (gears)
virtual → virtual worlds, computers
Observation
no manipulation, watch subjects in natural environment
Ex:
kids start acting different when adult come in the room - our behavior changes depending on who’s around us
Experiment
observation + manipulation + observation again
IV: what’s manipulated
DV: what’s measured
subject variables: aspect of participants that we can’t manipulate because it’s built-in
Ex: sex/gender, age
Construct
idea that is being manipulated or measured
Ex: how we drive when distraction (driving video game)
Operationalism
The practice of defining constructs in measurable terms, allowing researchers to quantify variables and assess their relationship
actual manipulation/measure
correlation
A statistical measure that expresses the extent to which two variables change together, indicating the strength and direction of their relationship
1 variable varies, the 2nd variable also varies
correlation ≠ causation
Ex: as age increases so does conservatism (actually has to do with different generations)
longitudinal study
follow same participants over time (as they age)
get to see the deveopment of the same people
flaws:
attrition - people move or die
cohort effect
cross-sectional design
follow participants at same point in time (but are all different ages)
fast, can collect data quickly
flaw: cohort effect
Cohort effect
People born around the same time experience some of the same things influencing their behavior
Some things may be attributed to development, when it could just be something like the political climate
different generations and cohorts are different, not necessarily people themselves
Time-lag design
A research design that compares different cohorts at the same point in time to assess changes over time without the influence of age, often by measuring the same individuals at different ages.
gold standard form of research - controls cohort affects
Ex: comparing the intelligence of 20-year-olds in 2000, 2010, and 2020 to see how a generation's capabilities change
experimenter bias
The influence of a researcher's expectations or beliefs on the outcome and interpretation of their study. It can lead to skewed results and affects the objectivity of the research
they imply what they want
Ex: hint that smart kids talk early
subject bias
The tendency of participants in a study to alter their responses or behavior based on their perceptions of the research or the expectations of the experimenter. This can distort the findings and compromise the integrity of the research.
Ex: telling the experimenter their kids talked super early (meaning they’re smart)
Sigmund Freud
A psychologist known for developing psychoanalysis, focusing on unconscious motives and childhood experiences.
psychoanalyzed his daughter
great observer and reminded us that childhood is important (abuse is bad)
5 stages of psychosexual development
oral stage (0-2)
anal stage (2-3)
phallic stage (3-4)
latency period (4-12)
genital stage (12+)
Oral stage (0-2)
mouth (pleasure) → sucking, nursing, drinking, talking
adults will succumb to smoking, drinking etc. if they don’t go through this stage
Anal stage (2-3)
anal pleasure → potty training, kids are interested in their anus (biggest achievement)
very anal as an adult if not successful
phallic stage (3-4)
kids interested in sex
boy interested in phallus - looking, touching
girls wondering they don’t have one (penis envy)
Oedipal complex vs. Electra Complex - dependent on the idea that child lives in 2 parent heterosexual household
Oedipal Complex
boy love mom, jealous of dad
resolution: realizing they can have their own as adult
Electra Complex
girl want dad because he has a penis
resolution: get own “dad”/penis an adult (bf)
Latency period (4-12)
not interested of any previous forms of pleasure from other stages for awhile
“trauma” from experiencing those stages
Genital stage (12+)
actual sexuality, sexual urges, puberty
Jean Piaget
theories are based on observing his 3 children
coined the term schema → everthing we use to organize knowledge and understand the world
He proposed stages of cognitive development
sensorimotor (0-2)
preoperational (2-5/7 shift)
concrete operational (5/7-12)
formal operational (12+)
he emphasized not rushing kids - natural unfolding, can’t be rushed (de’collage)
Schema
organized knowledge base - everything we know about a topic
How knowledge is built (based on schemas/piaget)
Equilibration → adjusting mental schemas to fit new experiences
Assimilation → not changing schema
sub-type: letting something in, but saying it’s a bad example
Accommodation → change schema
Ex: balls come is many different shapes and sizes
Sensorimotor period (0-2)
coordinating senses + motor movement
piaget’s strongest stage
Pre-operational (2-5/7)
kids will have a lot of false beliefs about the world
Concrete operational (5/7-12)
around 5/7 kids will become more logical - correlates with going to school
only about things that are in front of them
Formal operational (12+)
kids are logical and can reason abstractly
Piaget’s weakest stage
he acted like kids were adults at this stage
De’collage
unevenness in development
Lev Vygotsky
Marxism shaped his thinking
work is influence by Piaget (wrote letters to each other)
interest in langauge, culture, and social aspects + how they influence cognition and how we think
emphasized the role of social interaction in cognitive development, proposing that children learn through guided interactions with more knowledgeable others. His concepts of the Zone of Proximal Development and Scaffolding illustrate how support can facilitate learning
Vygootsky’s Stages of Language and Speech
Social stage (0-3) - kids talk to get things done (want something)
Egocentric speech (3-7) - talking to themselves, externalization of thinking, giving themselves directions
Inner speech (7+) - external speech goes inside mind (internal dialogue)
it’s been proven that not everyone has an internal dialogue
Language = Thought - very much related/develop together
Scaffolding
parents, teachers, caregivers etc. can give children higher support to reach further to help build them up
teach them to do things they wouldn’t be able to do without help but within reason (Zof PD)
Zone of Proximal Development
skills that are coming soon (naturally), a little boost will help them get there
The Zone of Proximal Development refers to the range of tasks that a child can perform with guidance but not yet independently. It highlights the significance of scaffolding in education, where support is provided to bridge the gap between what a learner can do alone and what they can achieve with assistance
teachers will model these skills - can’t over or under teach
Ethology
The study of animal behavior in natural environments, emphasizing the evolutionary basis and adaptations of behaviors
some things happens in nature and humans are animals so some of the things apply to us
Ethologists: Konrad Lorez, Eric Lenneberg, John Bowlby
Konrad Lorenz
studied Geese and is known for his research on imprinting/attachment, demonstrating how young animals recognize and follow their caregivers
Geese follow the first thing they see after their born, if theres nothing after 24 hrs they follow nothing
There’s a critical period where something must happen or it never will
Eric Lenneberg
There’s a critical period with language (puberty)
Ex: Genie Wiley - never learned how to talk or develop language
John Bowlby
children must attach to parents in the first few years or they won’t be able to attach to anyone late in life
Sensitive period
A developmental window during which an individual is particularly receptive to certain environmental stimuli, significantly impacting learning and attachment
easier to develop skills during this time
The brain and critical periods
the brain constantly has critical periods
may individual differences on when these critical periods close or if they do at all
Lateralization of the brain
2 sides of the brain do 2 different things
most research is done on right-handed people without familial sinistrality
ambidextrious people migt have longer critical periods
High socio-economic status could people = longer ________ _____
critical periods
supportive environment, don’t have to mature as quickly
Ecological systems theory - Urie Bronfenbrenner
framework for understanding the various systems that influence human development, including immediate environments, social interactions, and broader societal factors over time.
Microsystem
Mesosystem
Exosystem
Macrosystem
Chronosystem
Microsystem
direct impact on person of interest (parent, friend, teacher, pet etc.)
Mesosystem
members of microsystem interact without person, indirectly influencing them
Ex: parent-teacher conference
Exosystem
interactions with microsystem, external environmental settings that indirectly influence the person, such as a parent's workplace or community services
Macrosystem
reigning cultural time period
Ex: where you live, political climate
Chronosystem
how much change you have - the dimension of time that encompasses changes over the life course, including life transitions and socio-historical events
change affects us
Ex: pre-ww2 births vs post-ww2 births
Genes
smallest unit of inheritance
dominant vs. recessive
Chromosomes
groups of genes
22 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (1 from mother, 1 from father)
46 total
Genotype
genes we have
Phenotype
expression of genes + environment - “what we get”
Epigenetics
the study of how environmental factors influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence
extra “note” that say which genes we should use or express
Ex: Holocaust, Dutch Famine
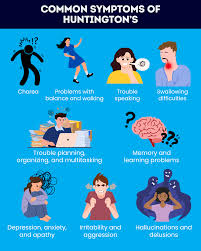
Huntington’s Disease
dominant gene
doesn’t manifest until late 30’s early 40’s
destroys brain - eats white matter
progressive motor and cognitive decline → early death
can be tested for its
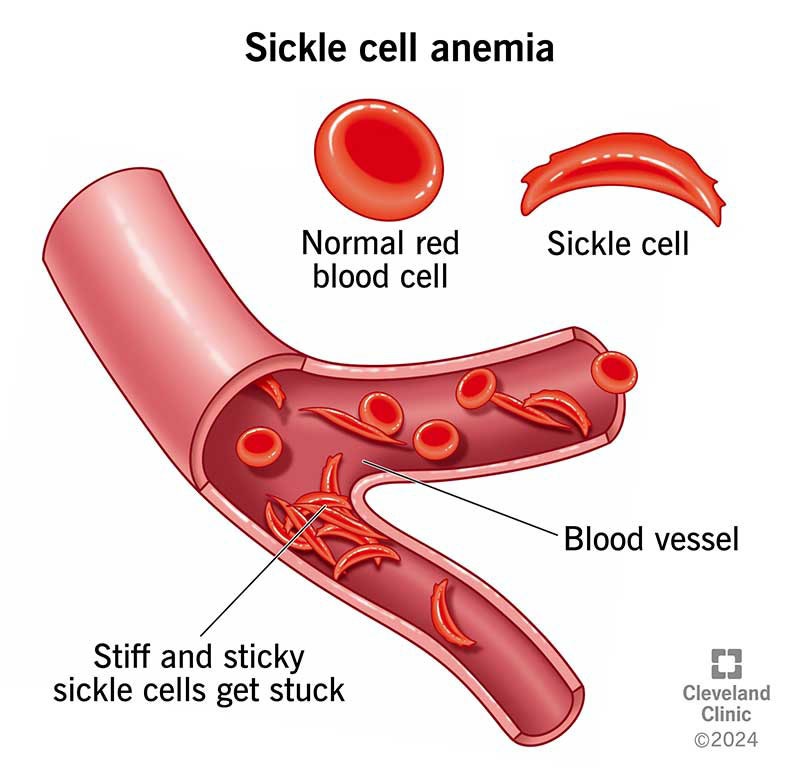
Sickle Cell Anemia
misshaped or “sickled” red blood cells
cells don’t carry enough oxygen, gets stuck in blood vessels
recessive trait - caused by mutation in hemoglobin gene
more common in those of African or South American descent
sickled cells can’t carry malaria
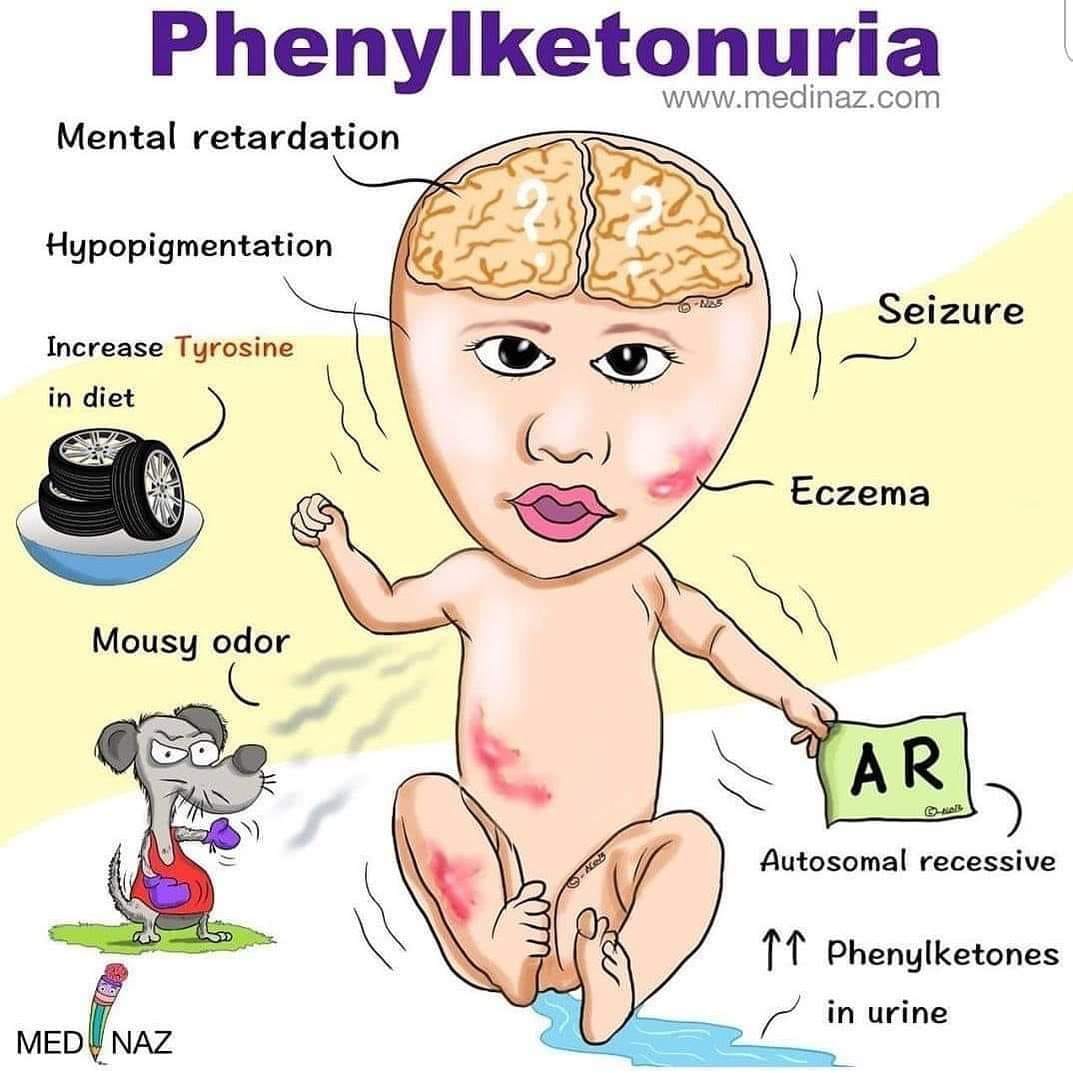
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
mutation in the PAH gene
inability to break down phenylalanine (a protein)
can result in severe intellectual disability if untreated - accumulates in brain, loss of skills
managed through a strict diet low in phenylalanine
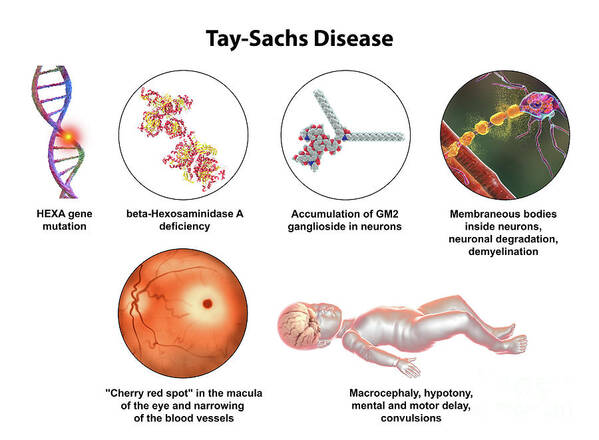
Tay-Sachs
caused by a mutation in the HEXA gene
inability to break down certain sugars
accumulates in brain, no cure - leads to neurodegeneration and early death in infancy
lose movement, language
die before age of 3 - multi-organ failure
more common in Jewish and Middle Eastern descent
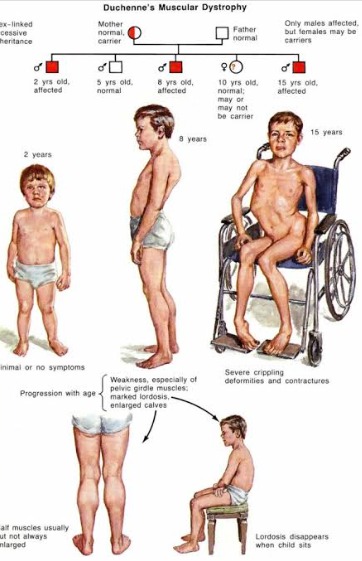
Muscular Dystrophy
muscles fail to develop
affects walking + moving
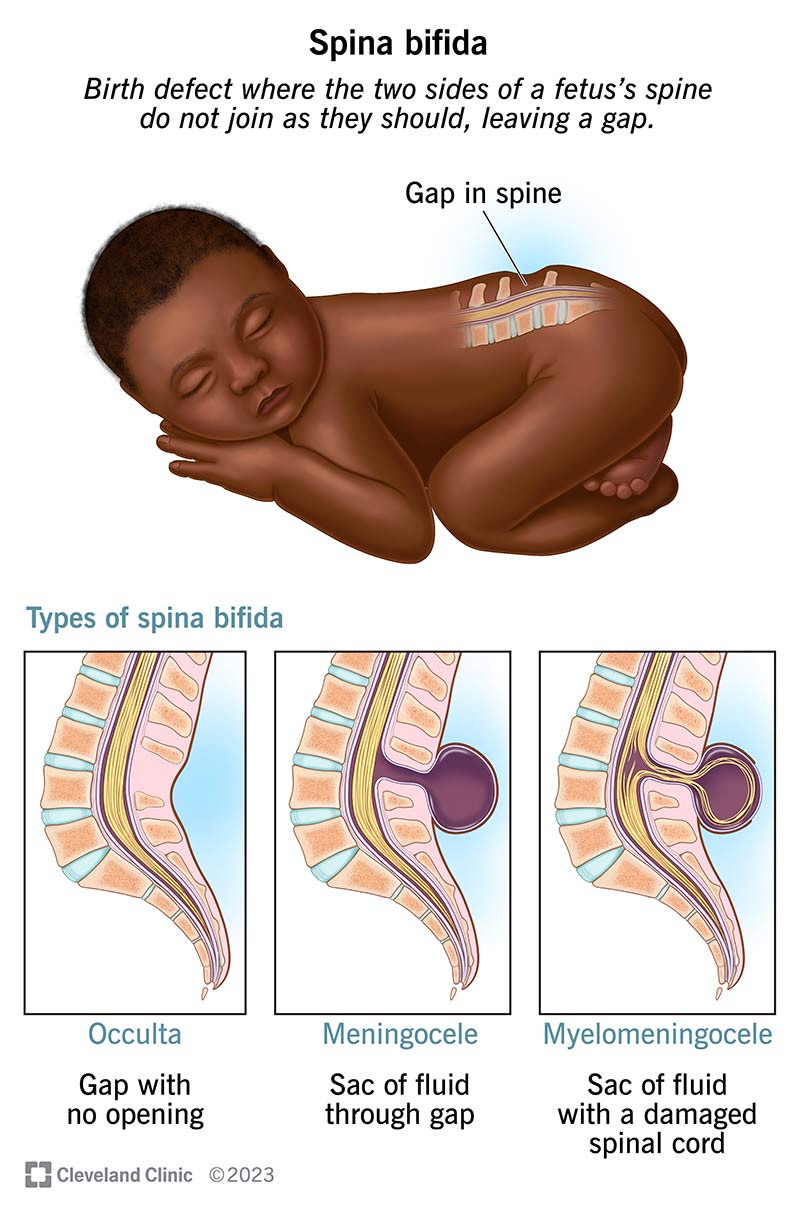
Spina Bifida
spine/neural tube doesn’t close completely
spinal fluid may leak out, spinal nerves may form a sac
treatment:
folic acid as a preventative measure
prenatal surgery - shoves it back in
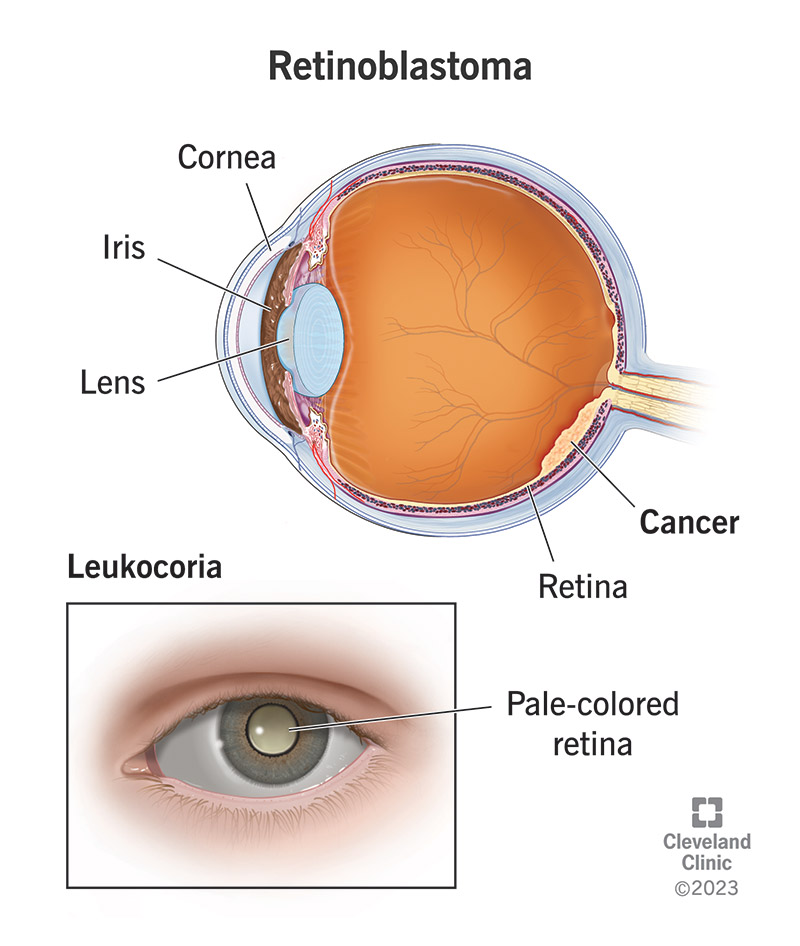
Retinoblastoma
cancer in retina
starts very young
abnormal eye - doesn’t “look full”
death if untreated - reaches brain
Trisomy
extra chromosome - 3 instead of a pair
Deletion
loss of a chromosome segment, resulting in missing genetic material
Translocation
chromosome in the wrong spot - a chromosome segment is moved from one chromosome to another
Mosacism
abnormal chromosome set - individual has two or more genetically different cell lines, resulting from mutations during early cell division
only some cells affected
Ex: variability with down syndrome
Chimerism
2 sets of DNA - an individual has two or more genetically distinct cell lines originating from different zygotes. This can result from the fusion of embryos or blood transfusions
Ex: Lydia Fairchild “not related” to biological kids, absorbed twin in utero resulting in a mixture of cells with different genetic compositions.
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
extra chromosome on 21st pair
related to age of egg - “zipper doesn’t work as well” at older age
a lot variability - mosaicism (Hannah)
markers:
wide set eyes
thin, long smile
some have heart problems or hearing difficulties
mental slowness
_______ is always affect when having an extra chromosome
intelligence
Trisomy 9/16
complete is incompatible w/ life
mosaic forms minimal problems
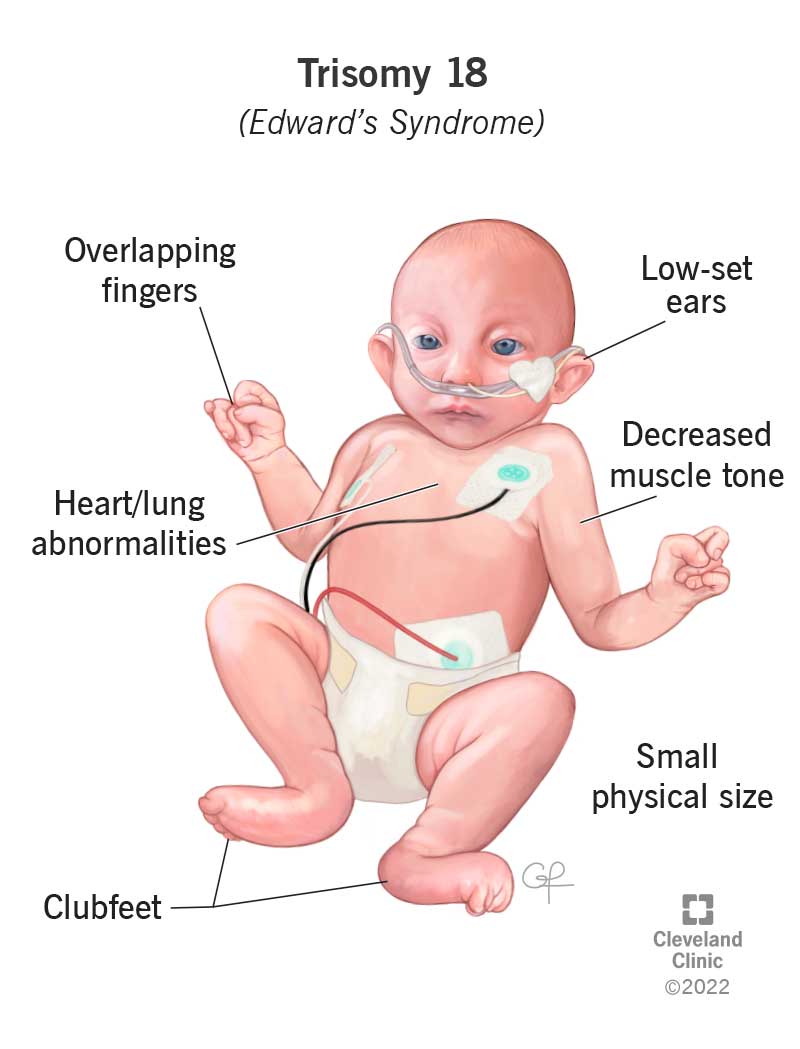
Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
condition caused by an extra chromosome on the 18th pair
often results in severe developmental delays and physical abnormalities
extreme mental slowness
misformed crest
difficulty flexing
associated with low birth weight and a small head
die very young

Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
genetic disorder caused by an extra chromosome on the 13th pair
leads to severe intellectual disability and physical abnormalities
live for mins-hrs
fragile x phenomenon
a lot of disorders/ailments are carried on the x chromosome - affects males more severely
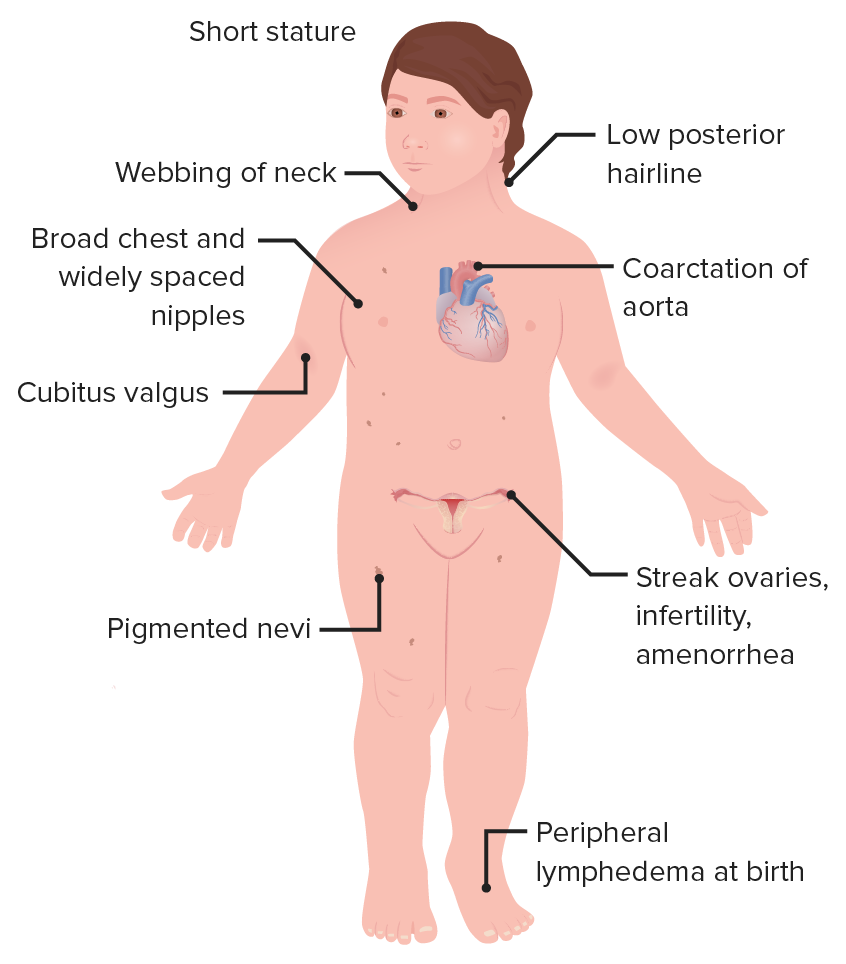
Turner Syndrome
female - XO (deletion on 23rd pair)
drop in IQ + spacial skills
physical markers:
webbed neck
extremely short
wide-set nipples
discolored spots
sterile
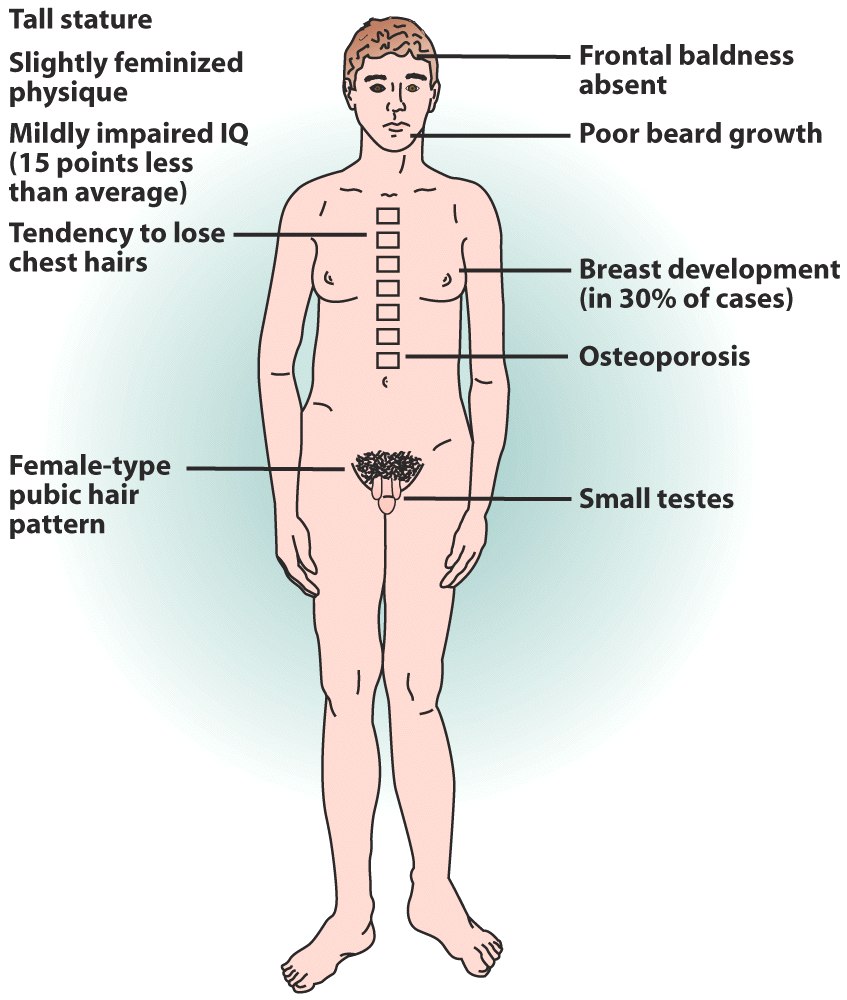
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
male - XXY (duplication)
markers:
less masculinized
breast development
wider hips
female hair growth patterns
poor quality sperm (low motility)
drop in intelligence

Supermale Syndrome
Male - XYY
random mutation
markers:
very tall
more acne
drop in intelligence (lower average)
make bad decisions, end up in jail
XXX Syndrome
Female
slight drop in intelligence
minimal symptoms, might be taller
Androgen Insensitive Females
Genetic males (XY)
androgen receptors do not respond to male hormones (insensitive to androgens), resulting in female reproductive anatomy
normal female external characteristics but lack a uterus
markers:
tall
thin
large breasts
less body hair
don’t get period/sterile
technically intersex but identify as female
Guevedoces (Penis 12 Syndrome)
Inbreeding (small breeding population) → Dominican Republic, New Guinea
raised as a girl, penis formed at 12
undescended penis (hidden)
sex reassigned at 12
95% identify as hetero males
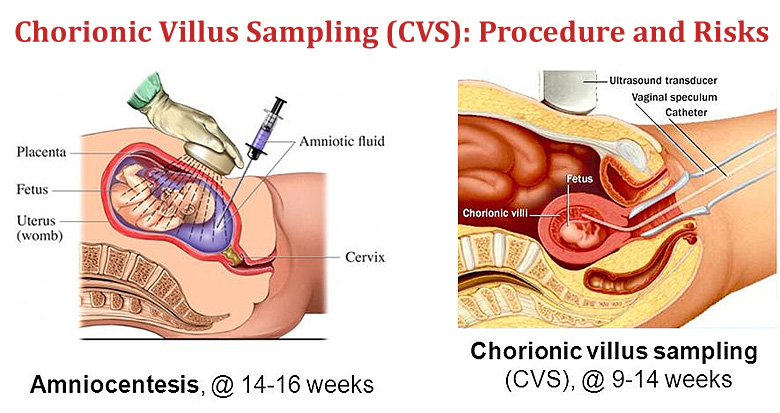
Prenatal Testing
older mom cut-off is at 35 - be offered genetic testing for fetal abnormalities such as Down syndrome
currently recommended to give all pregnant women testing regardless of age
amniocentesis → remove cells, tell them, done at 20 weeks
chorionic villus sampling → only done for huge genetic risk, 45+ mothers