Sleep-Related Breathing disorders - Clin Med 3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What does this refer to
With EEG and Esophageal Manometry
SpO2
Respiratory rate and effort
Gas exchange
Heart rate
Eye and leg movements
Muscle electrical activity
Body position
Polysomnography assessment
What does a BMI of < 18.5 indicate
Underweight
What does a BMI of 18.5-24.9 refer to
Healthy weight
What does a BMI of 25.0-29.9 indicate
overweight
What does this BMI refer to > or equal to 30
obese
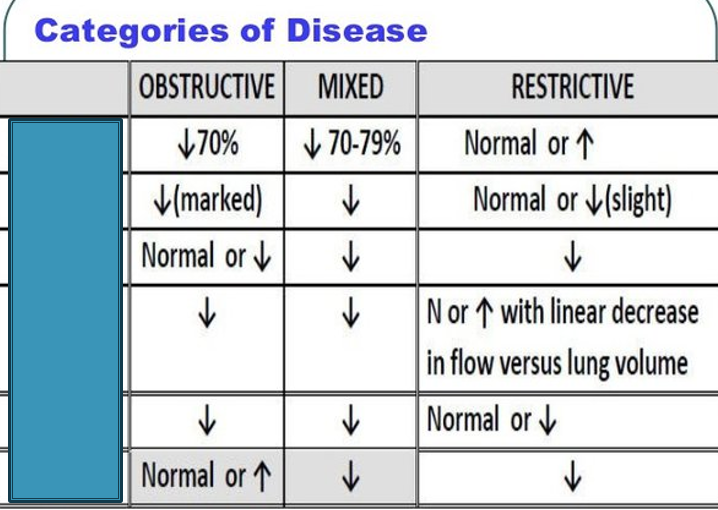
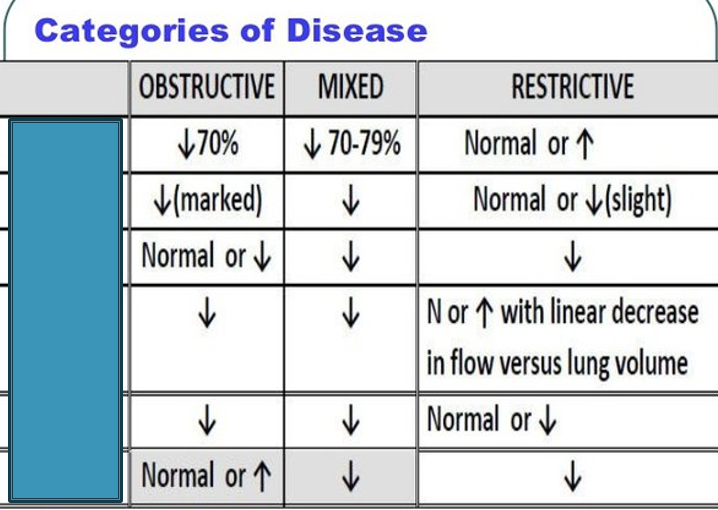
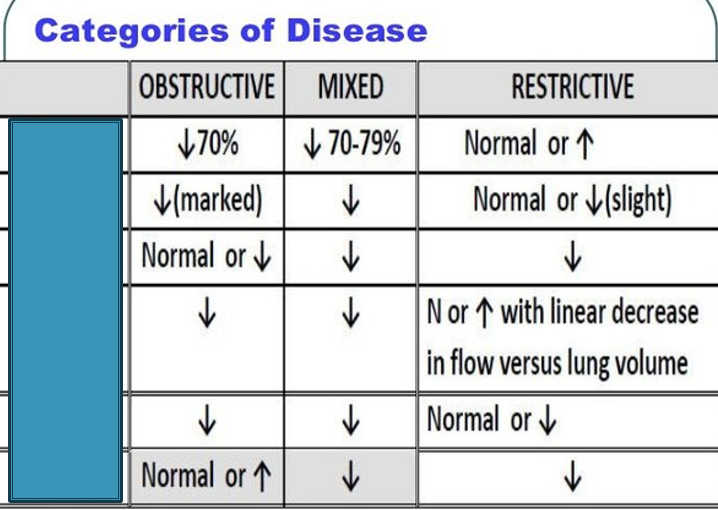
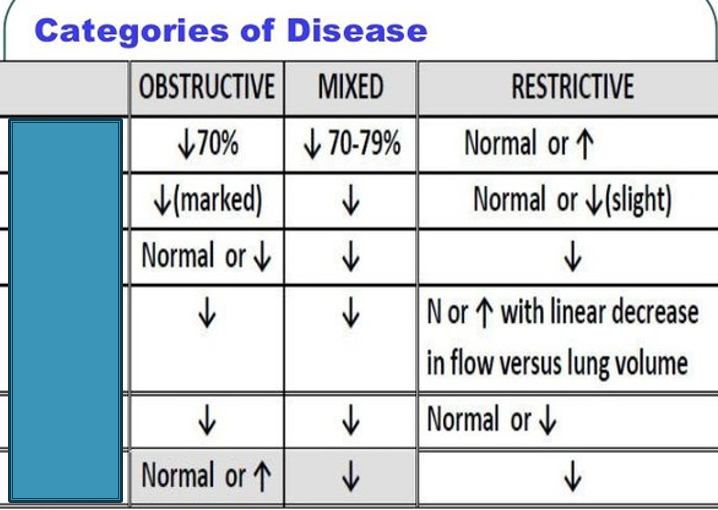
What is the first box
FEV1/FVC
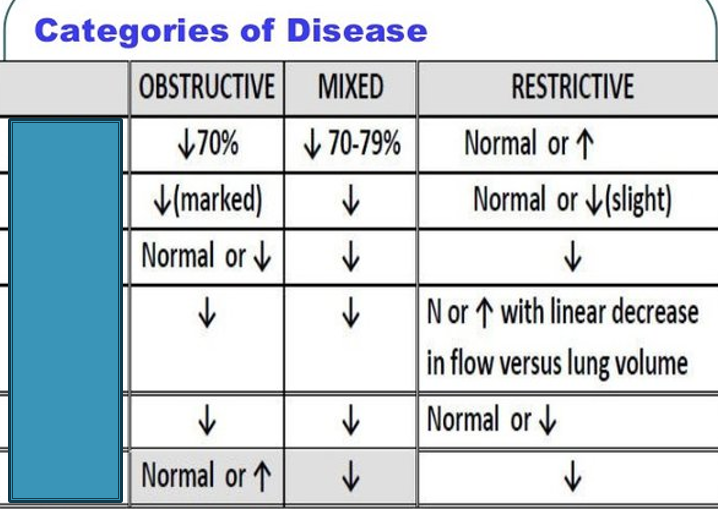
What is the second box
FEV1
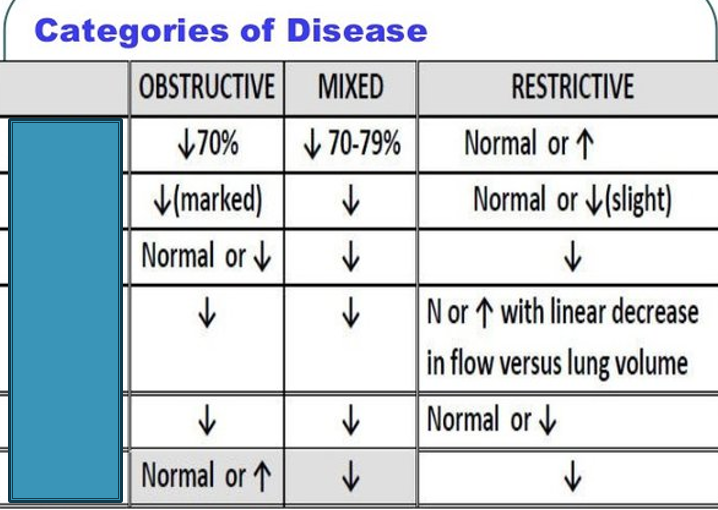
What is the third box
FVC
What is the 4th box
PEFR
What is the 5th box
MW
What is the 6th box
TLC
What does this refer to
A 56-year-old man presents to your office for excessive fatigue.
He complains of falling asleep all the time at work, which is “very distressing" as it has been affecting his work.
He denies sudden loss of muscle tone or hallucinations before or after falling asleep.
His wife reports that he snores at night.
A physical examination demonstrates an obese, lethargic man with unremarkable findings.
Sleep apnea
What does this refer to
A serious, common, underdiagnosed sleep disorder that is characterized by disordered breathing resulting in numerous hypoxic episodes throughout sleep preventing the patient from restorative sleep
Two specific etiologies
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Central sleep apnea
Sleep Apnea
What classification of severity of sleep apnea is below
AHI > 30 (more than 30 episodes per hour)
Severe obstructive sleep apnea
What classification of severity of sleep apnea is below
AHI 15-30
Moderate obstructive sleep apnea
What classification of severity of sleep apnea is below
AHI 5-15
Mild obstructive sleep apnea
What does this refer to
M > F
MC obese and middle-aged patients
Risk ↑ with obesity, hypothyroidism and tobacco use
Exacerbated by EtOH, sleep medications, or illnesses causing nasal obstruction
Affects > 936 million people worldwide
> 80% are undiagnosed
Epidemiology of Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Anatomical
Characterized by obstructive apneas, hypopneas, and/or respiratory effort-related arousals (RERAs)
Repetitive complete or partial collapse of the upper airway during sleep
Central sleep apnea (CAS)
Neurological
Can be caused by heart failure, stroke, high altitude sleeping
Etiology of Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to

Clinical history of sleep apnea
What does this refer to
No abnormal findings
What to assess
Oropharyngeal crowding
Enlarged tonsils
Excessive soft tissue
Enlarged uvula or tongue
Nasal septum deviation
Short neck
Physical exam of sleep apnea
What does this refer to
Narcolepsy
distinguishing factor
clinical features such as cataplexy, hypnagogic hallucinations, sleep attacks, and sleep paralysis
can be differentiated on polysomnography
Respiratory disease (e.g., chronic obstructive lung disease)
distinguishing factor
positive medical history and polysomnography results
Differential diagnosis sleep apnea
What does this refer to

Workup for Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to
Polysomnography with Apnea-Hypoxia Index (AHI)
15 obstructive apneas/hour
5 apneas/hr and snoring/breathing pauses with daytime somnolence
The gold standard and diagnostic study for sleep apnea
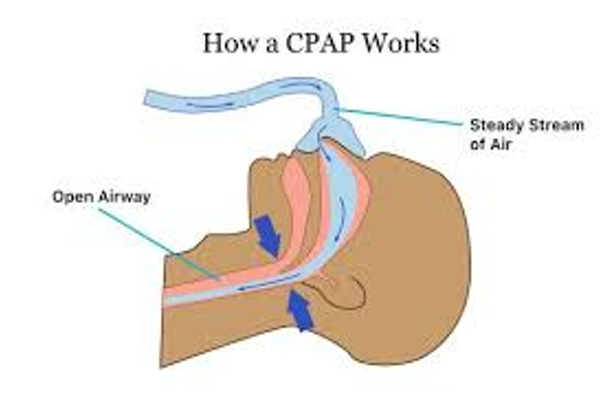
What does this refer to
Weight loss
Weight loss medications
Exercise
Severely obese & failure of conservative treatment
Weight loss surgery
Surgical intervention (non-responders)
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
Nasal septoplasty
Tracheostomy
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
Clinical intervention Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to

Clinical management Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to
Weight loss and exercise
Low fat, low sodium, low sugar, low carb diet
Meals
Eat smaller meals more frequently instead of 3 larger meals daily
Complementary and alternative management Sleep Apnea
What does this refer to

Morbidity/mortality/Complications Sleep Apnea
What is the left box
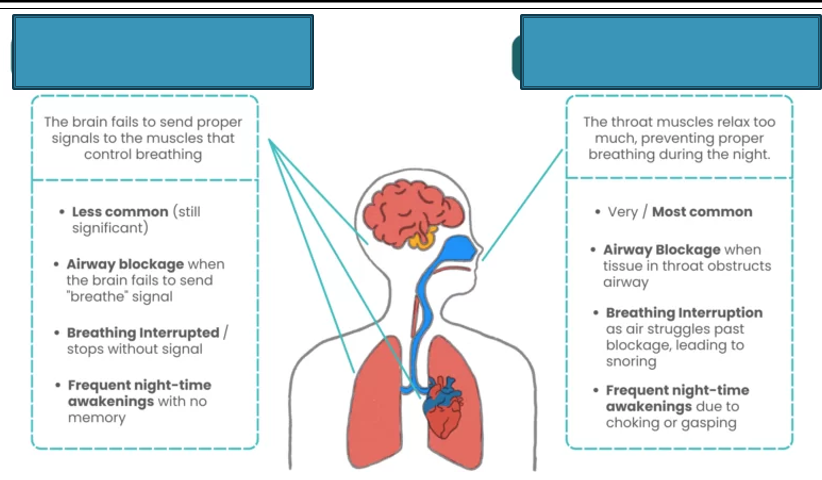
Central sleep apnea (CSA)
What is the right box
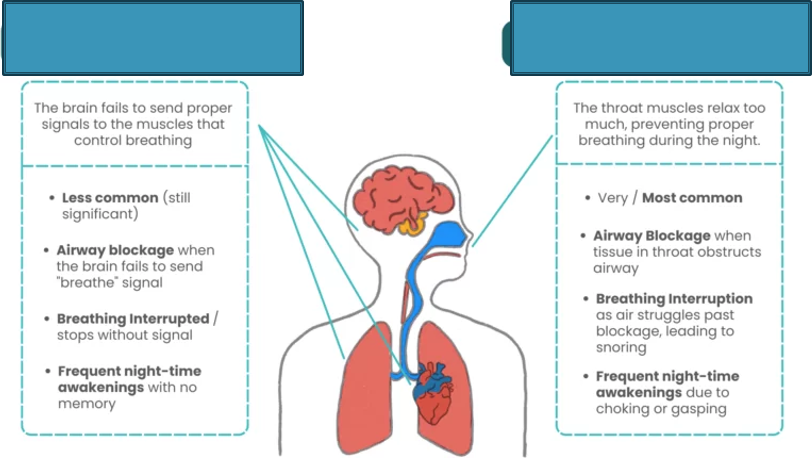
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
What does this refer to
Poor breathing in some people with obesity
Inefficient respiration —> ↓ O2 and ↓ CO2 levels in the blood
Also known as Pickwickian syndrome
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
MC in obese patients
Epidemiology Obesity Hypoventilation Synfrome
What does this refer to
Exact cause unknown
Hypothesis
Excess weight against chest wall makes it more difficult to deep breathe and quickly enough
Results in defect in the brain’s control over breathing
Results in acidemia
If in a stable condition kidneys have enough time to correct acidemia
What is the expected ABG in the unstable patient
pH ↓ (acidotic, usually < 7.35)
CO2 ↑
HCO3 ↓
What is the expected ABG in the stable patient
pH: 7.35-7.45
CO2: 35-45
HCO3: 22-26
Etiology Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
Main sx due to lack of sleep
Poor sleep quality
Daytime sleepiness
Depression
Headaches
Fatigue
Chronic hypoxia with elevated CO2
SOB/DOE
Chronic fatigue/fatigue with minimal activity
Clinical History Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
BMI > or equal to 30kg/m2
Cyanosis
Lips
Fingers/toes
Skin
SaO2 ↓
R side HF (HF due to a respiratory problem —> cor pulmonale)
Sx
Edema
SOB/DOE
Fatigue with minimal activity
Physical exam Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What is a ddx for obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Sleep apnea
What does this refer to
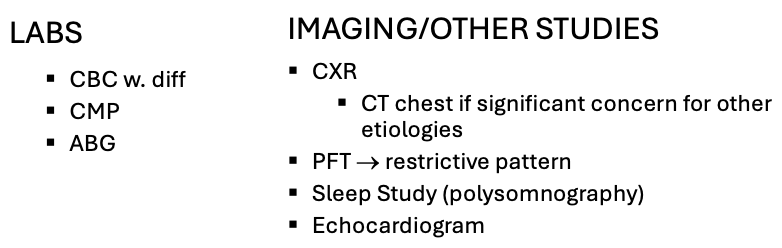
Workup Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to

Workup – best initial test/how’s it diagnosed? Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
Weight loss and exercise
CPAP or BiPAP
Supplemental O2
Tracheostomy for severe cases
Interventions can be initiated (and/or changed) inpatient or outpatient
Weight loss can reverse OHS
Clinical intervention Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
Weight loss drugs
GLP-1
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
Weight loss diet
Exercise
Complementary and alternative management Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to

Morbidity/mortality Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
May lead to heart/blood vessel problems, severe disability, or death
Complications
Depression, agitation, irritability
Increased risk for accident/mistakes if able to work
Intimacy/sex problems
Cardiac complications
HTN
Cor pulmonale
Pulmonary HTN
Prognosis/complications Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
What does this refer to
Rare disorder
Similar to OSA but doesn’t meet the criteria (not as severe)
May be classified between snoring and sleep apnea
Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Typically of average weight
Epidemiology Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Often caused by partial narrowing in the retropalatal and retroglossal areas of the airway
Soft tissue relaxation not allowing for proper airflow during sleep
Tongue falling back
Leads to frequent respiratory-related arousals from sleep (RERAs)
Etiology Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Non-refreshing sleep
Snoring
Excessive daytime sleepiness
Unexplained daytime tiredness
Difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep (insomnia
Heavy breathing during inhalation
Morning HA
Clinical History Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Linked to significant cognitive and behavioral problems in children
Learning disabilities
ADD +/- hyperactivity
Aggression
Clinical History Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
No acute findings
BMI
Healthy (not overweight) 18.5-24.9
If UARS complications
HTN
Physical exam Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
OSA v CSA
OHS
Often misdiagnosed as
Idiopathic insomnia
Idiopathic hypersomnia
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Fibromyalgia
ADD +/- hyperactivity
Depression
Differential diagnosis Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to

Workup Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
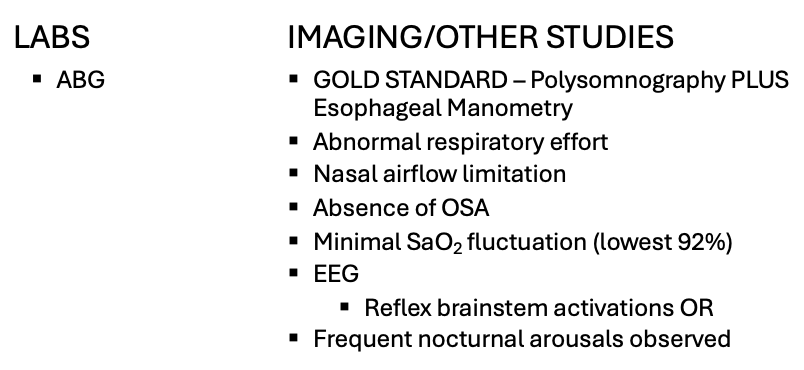
Workup – best initial test/how’s it diagnosed? Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Avoid EtOH and sedative medications
Optimal sleep position
Weight loss if “overweight”
CPAP
Oral appliances
Mandibular advancement splint (MAS)
Surgery to enlarge the airway
Clinical intervention Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What is the clinical pharmacotheapeutics upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS)
None
What does this refer to
Healthy diet and exercise to maintain optimal BMI
Complementary and alternative management Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to

Morbidity/mortality Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
Treatment compliance improves symptoms and quality of life
May progress to sleep apnea if untreated/non-compliance
Prognosis/complications Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS)
What does this refer to
= RV + ERV + TV + IRV. Total amount of air the lung can hold
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
What does this refer to
The maximal amount of air that can be exhaled as fast as possible after a maximal inhalation. The result of this test is then compared to a predicted normal based on age, height, and weight, ethnic origin & smoking history
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
What does this refer to
the amount of volume of air that has been exhaled at the end of the 1st second of forced expiration
Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1)
If BOTH the FVC and the FEV1 are less than 80%
predicted there is a restrictive disease present. FEV1 is also used to determine the severity of disease – more on that later.
Step 1 of Determining Restrictive Disease
FEV1/FVC result (<80% of predicted → OBSTRUCTIVE)
Step 2 of Determining Restrictive Disease
If FEV1/FVC is > 80%, look at FVC and FEV1 results individually. If both < 80% → RESTRICTIVE
Step 3 of Determining Restrictive Disease
FEV1/FVC and FVC are both decreased below 80% → MIXED defect