RAD 214: Urinary & Venipuncture
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
functional
IVU
VCUG
Nonfunctional
retrograde cystography
retrograde urethrography
IVU patient prep
light evening meal
laxative
NPO 8 hours
enema the morning of the exam
IVU Room prep
contrast media drawn up
IV supplies
emesis basin
emergency cart
access to oxygen and suction
IVU: 1 minute projection
nephrogram or nephrotomogram
IVU: 5 min & 10-15 mins
KUB
IVU: 20 min projection
obliques
IVU: post void projection
done erect or prone
nephrogram
standard x ray of kidneys
center midway between xiphoid and crest
1 minute after injection
nephrotomogram
tomogram of the kidneys
CR:
midway between xiphoid and crest
uses tomogram cut measurement to determine how far apart images are taken
1 minute after injection
blurs region around kidneys
tomogram kidney cut size
initial fulcrum found by measuring abdomen at lower ribs and divide by 3
after how many minutes are your kidneys blushing?
1 minute
when do you start obliques?
when the ureters are full
10-15 mins
KUB (IVU)
patient supine
CR to iliac crest & MSP
entire urinary system, symphysis pubis
expose on expiration
Kidney Projection
10×12
patient supine
CR
between xiphoid and iliac crest & MSP
1 min after contrast injection
nephrons fill with contrast in the renal parenchyma before contrast moves into collecting system
IVOblique
AP/ PA
oblique patient 30°
CR to
iliac crest & spine
10 minute mark
14×17
expiration
IVU Oblique evaluation
side up kidney = area of interest
parallel to IR
side down ureter = area of interest
free from superimposition
RPO (IVU)
right kidney
left ureter
LPO(IVU)
right kidney
left ureter
ureteral compression
enhances filling of pelvicalcyceal system & proximal ureters
allows renal collecting system to hold contrast logner
what if ureteral compression cannot be used?
use trendelenburg instead
Retrograde Cystography
nonfunctional
retrograde filling of the bladder by gravity only
contrast media delivered through catheter
150-500 ml
done under fluoro
AP/ posterior obliques
AP Axial Bladder
patient supine
CR
angled 10-15° caudal
2” superior to symphysis pubis & MSP
10×12 crosswise
bladder not superimposed by pubic bones
Oblique Bladder
45-60° patient oblique (LPO/RPO)
contrast filled bladder
LPO/RPO
not superimposed by lower limbs
60° oblique bladder
better visualizes posterolateral aspect of bladder and UVJ
kidney blushing
nephrons fill with contrast in the renal parenchyma before contrast moves into collecting system
venipuncture needle size
18-22 gauge needle
upright post void
patient erect or prone
CR to
upright: 1” below iliac crest & MSP
prone: iliac cest & MSP
bevel insertion degree
always insert bevel up at 20-45° angle
kidneys are surrounded by
adipose tissue allowing them to be seen on x ray
kidney movement
up and down with breathing or position change
kidney functions
production and elimination of urine
removes nitrogenous waste
regulate water levels in the body
regulate acid/base balance & electrolyte levels of the blood
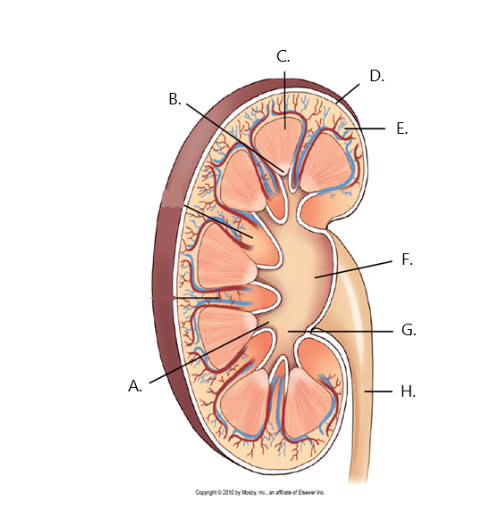
A
minor calyx
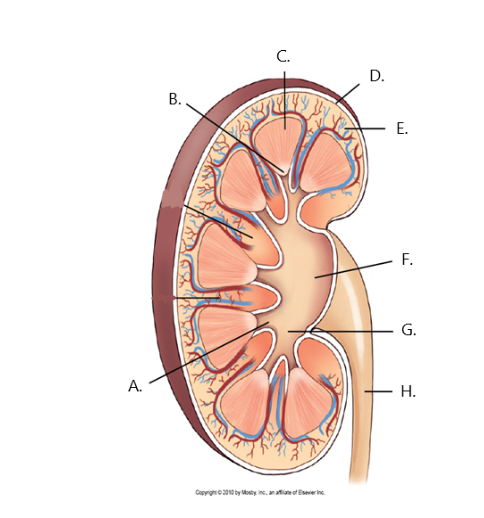
B
renal papilla
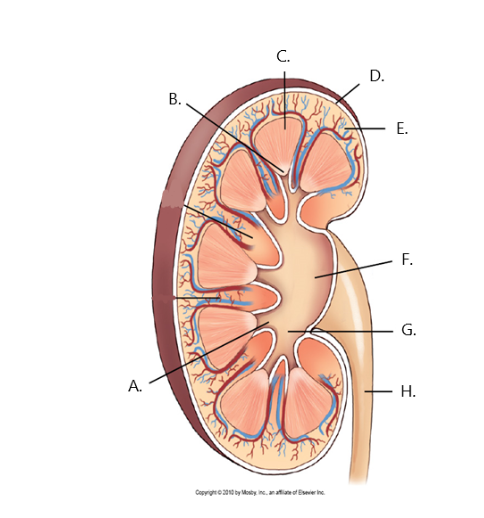
C
renal medulla
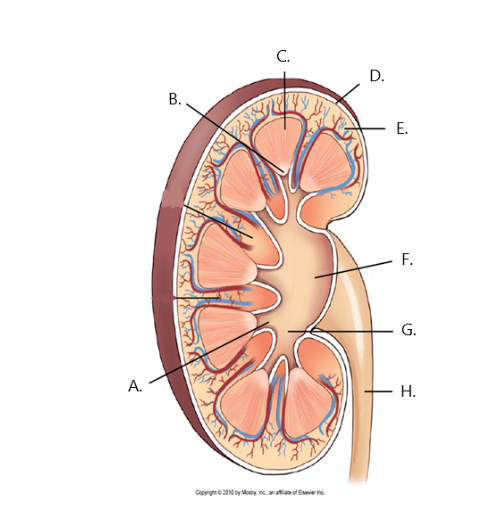
D
fibrous capsule
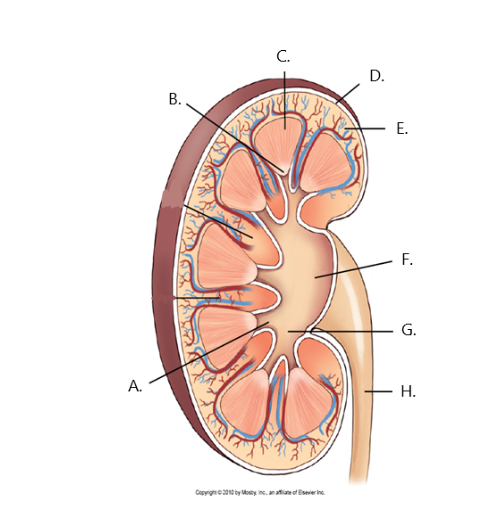
E
cortex
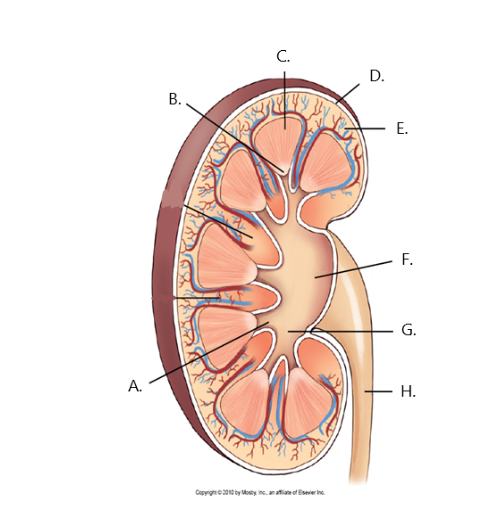
F
renal pelvis
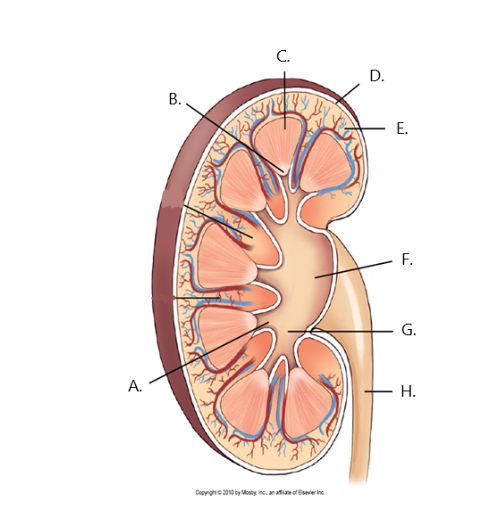
G
major calyx
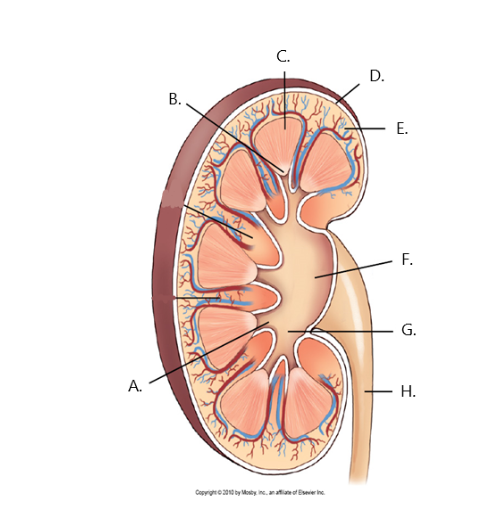
H
ureter
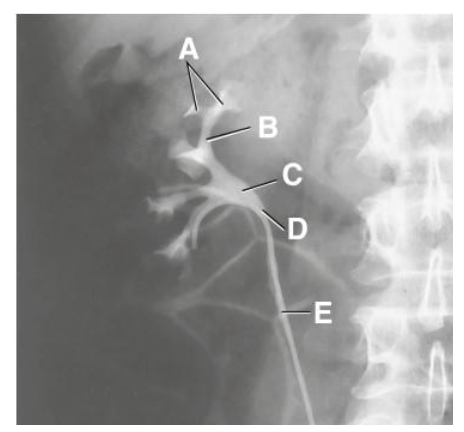
A
minor calyx
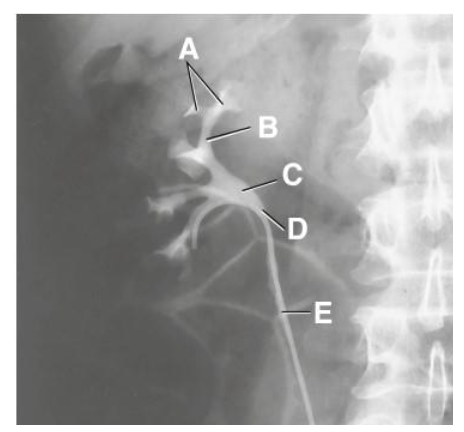
B
major calyx
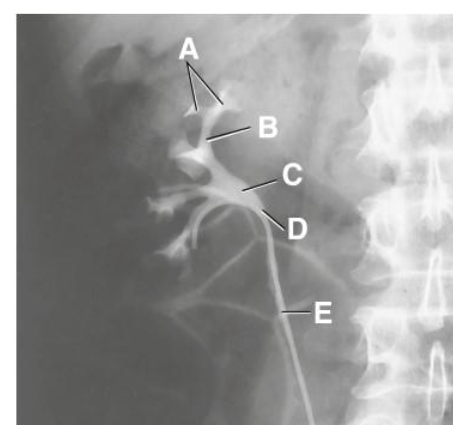
C
renal pelvis
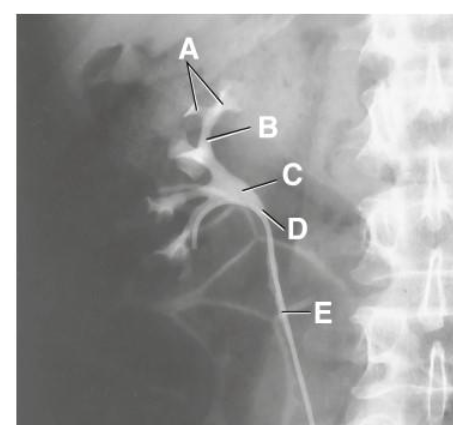
D
ureteropelvic junction
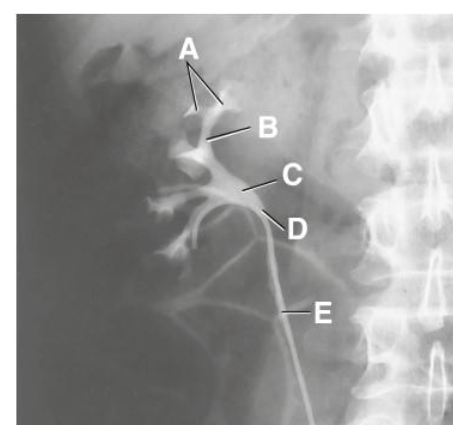
E
proximal ureter
function of ureters
transport urine between the kidneys and bladder
where do the ureters begin?
anterior to its respective kidney
follows natural curve of vertebral column
urine is forced down the ureters by
peristalsis and gravity
urine enters the bladder
posterolateral at the ureterovesical junction (UVJ)
proximal point of constriction
uteropelvic junction (UPJ)
renal pelvis funnels into smaller ureter
middle point of constriction
pelvic brim
iliac blood vessels cross over the ureters
distal point of constriction
ureterovesical junction (UVJ)
where the ureter joins the bladder
common site for calculus to become lodged
ureterovesical junction (UVJ)
urinary bladder function
reservoir for urine
urinary bladder capacity
350-500 ml
urinary bladder shape
empty = flattened
full = oval
rugae
numerous folds of the inner mucosa
trigone
smooth, triangular portion of the inner mucosa
bladder calculi
calcifications within the bladder or signs of obstruction of urinary system
cystitis
inflammation of urinary bladder
Polycytic renal disease
cysts scattered throughout one kidney or both
Hydronephrosis
distention of the renal pelvis & calyces of the kidneys
result from obstruction of ureters & renal pelvis
Pyelonephritis
inflammation of kidney & renal pelvis
Renal Obstruction
caused by debris, calculus, thrombus or trauma
renal calculi
calcifications that occur in luminal aspect of the urinary tract
can lead to
renal obstruction
hydronephrosis
patients with acid urine & high calcium levels = renal stones more often
Venipuncture Veins
median cubital
cephalic
basilic
venipuncture
puncture of a vein for withdrawal of blood or injection of a solution such as contrast media for urographic proceudres
Kidneys sit how many degrees to MCP
30°
IVU oblique which kidney is shown ?
kidney closest to IR
IVU oblique which ureter is shown?
ureter furthest (upside) from IR
IVU
functional
visualize the collecting portion of the urinary system
assess the functional ability of the kidneys
evaluate the urinary system for pathology or anatomic anomalies
IVU Contraindications
iodine allergy
anuria
multiple myeloma
diabetes
renal disease
CHF
pheochromocytoma
sickle cell anemia
patient on metformin
renal failure
Retrograde Urography
nonfunctional
retrograde filling of the urinary system
done in OR
patient sedated
modified lithotomy position
Voiding Cystourethrography (VCUG)
functional
study of the urethra
done under fluoro
retrograde filling of bladder by gravity only
followed by removal or catheter and imaging while patient is voiding
venipuncture tourniquet placement
3-4 inches above injection site
BUN normal ranges
8-25 mg/100 mL
Cr normal ranges
0.6-1.5 mg/dL
extravasation
leakage of iodinated contrast media outside of the vessel and into the surrounding tissues
AKA: infiltration
Phlebitis
inflammation of a vein
pain, redness, swelling
mild (non allergic) systemic reaction
does not require drug intervention or medical assistance
side effects
metallic taste
warmed, flushed feelings
anxious
lightheadedness
moderate systemic reaction
anaphylaxis / true allergy
requires medical assistance
moderate to severe hives
laryngeal swelling
bronchospasm
angioedema
hypotension
tachycardia
severe systemic reaction
life threatening requires immediate medical attention
hypotension
bradycardia
cardiac arrhythmias
convulsions
cardiac arrest
respiratory arrest
no pulse
premedication
A combination of diphenhydramine and solumedrol over a 12 hour period
urinary system basic anatomy
kidney (2)
ureter (2)
urethra (1)
bladder (1)
kidneys sit how many degrees to MSP and why?
20° due to the psoas muscle
what vertebral level do the kidneys sit at
T12-L3
congenital anomalies
duplicate ureter and renal pelvis
ectopic kidney
horseshoe kidney
malrotation
duplicate ureter and renal pelvis
double collecting system & double ureter
sometimes just double ureter
ectopic kidney
normal kidney that didnt ascend to abdomen stays in pelvis
horseshoe kidney
connected at upper or lower pole
most common in lower pole 95°
malrotation
renal pelvis not medial but anterior and posterior
the kidneys and ureters are located in the ____ space
retroperitoneal
what structure creates a 20° angle between the upper and lower pole of the kidney
psoas muscle
ionic contrast
hypaque, conray, renografin
Osmolality: High
Chance of Reaction: High
increases osmolality of the blood
nonionic
omnipaque, isovue, optiray, amipaque
Osmolality: Low
Chance of reaction: Low
more water soluble
fewer patient reactions
ureteral compression contraindications
Possible ureteral stones
Abdominal mass
AAA
Recent abdominal surgery
Severe pain
Acute trauma
ureteral compression alternative
trendelenburg position
retroperitoneal
kidneys
proximal ureters
infraperitoneal
distal ureters
urinary bladder
urethra
which kidney sits more superior?
left kidney