Abrasion, Polishing- Dental Materials
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is abrasion?
Wear or material loss from a substrate as a result of scratching or other mechanical means.
What is two-body abrason?
Abrasive particles are tightly bonded to the abrasive instrument that is removing material from the substrate surface
Like sandpaper
What is three-body abrasion?
Involves the use of non-bonded abrasives
Abrasive particles are free to translate and rotate between two surfaces
What is airbone particle abrasion?
Abrasive particles are propelled against a substrate by air pressure to remove surface material
What factors affect the rate of abrasion?
Hardness between the abrasive and substrate
Particle size of abrasive
Particle shape of abrasive
Speed and pressure
Lubrication
What scale describes the resistance of scratching of one material by another?
Mohs Hardness Test
How is pumice create?
Super-heated, highly pressurized rock is violently ejected
from a volcano
Why are hard gold alloys used in dentistry in terms of hardness?
Equally hard as dentin, less hard than enamel

What does the indentation hardness test calculate?
The size or depth of the indentation and the amount of force are used to calculate a hardness value
Test names: Brinell, Knoop, Vickers
Particle Size of Abrasive
Superfine- <10 μm
Fine- 10 to 20 μm
Medium- 20 to 100 μm
Coarse- 100 to 500 μmF
What does lubrication help with in abrasion?
Reduce heat build-up
Wash away debris to prevent clogging
The most efficient abrasion occurs when the difference in hardness between the abrasive and the substrate is?
Larger
Low speed rpm?
<20000 rpm
Med speed rpm?
20,000-200,000 rpm
High speed rpm?
>200,000 rpm Air-driven
What is air turbine?
Balance between speed and torque. It is faster and consistent with cutting and grinding
Are electric handpieces or air-driven handpieces louder (high-pitched)?
Air-driven handpieces
Finishing vs polishing difference?
Finishing: Put a final surface on. The refinement procedure of substrate surface
Polishing: To make smooth and glossy surface by abrasion
What are the types of finishing and polishing instruments?
Carbide Burs
Diamond Burs
Dental Stones
Rubber Wheels
Disk & Strips
What are carbide burs composed of?
Bur Shank: Stainless steel
Cutting Blades: Tungsten Carbide
What are carbide burs used for?
Contouring and finishing
What are diamond burs made of?
Stainless steel shank
Powdered diamond abrasive
Metallic bonding material
Diamond burs should always be used with?
Water spray
What are types of dental stones?
Silicon carbide
Aluminum oxide
Diamond stone
What are rubber wheels used for?
Used for fine grinding to remove coarse scratched from rough grinding
made by molding aluminum oxide, (silicone carbide and chromium oxide) in a rubber matrix
What are disks made of?
Stiff plastic or paper backing coted with abrasive particles
What is commonly used to finish and polish interproximal areas?
Polishing strips
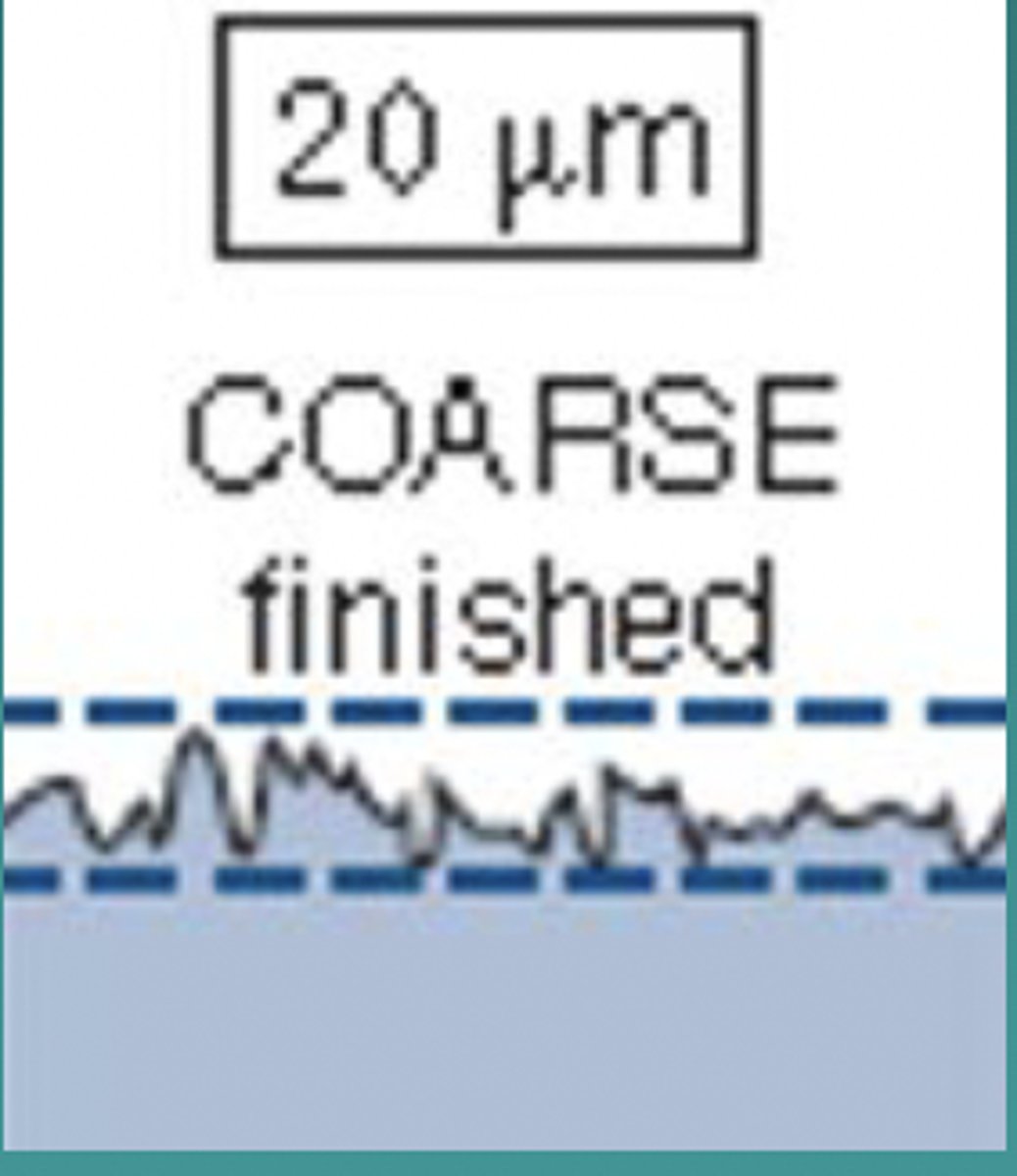
If a scratch is larger than 0.5 microns, the surface will look?
Dull, the light scatters
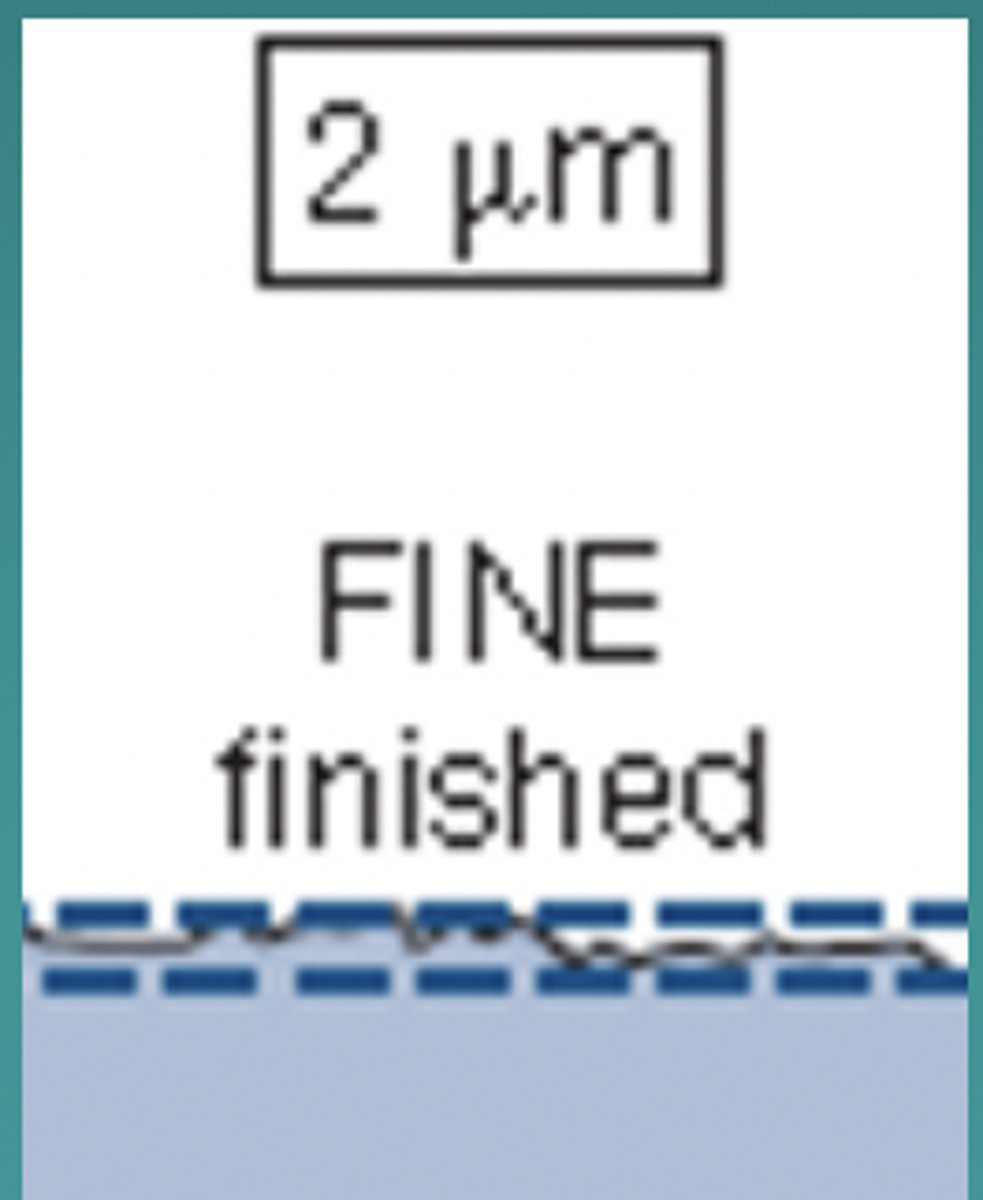
What # of microns does the tongue feel like the surface is smooth?
<2 microns
What are the three most common types of coolant?
Air, water, and air-water spray
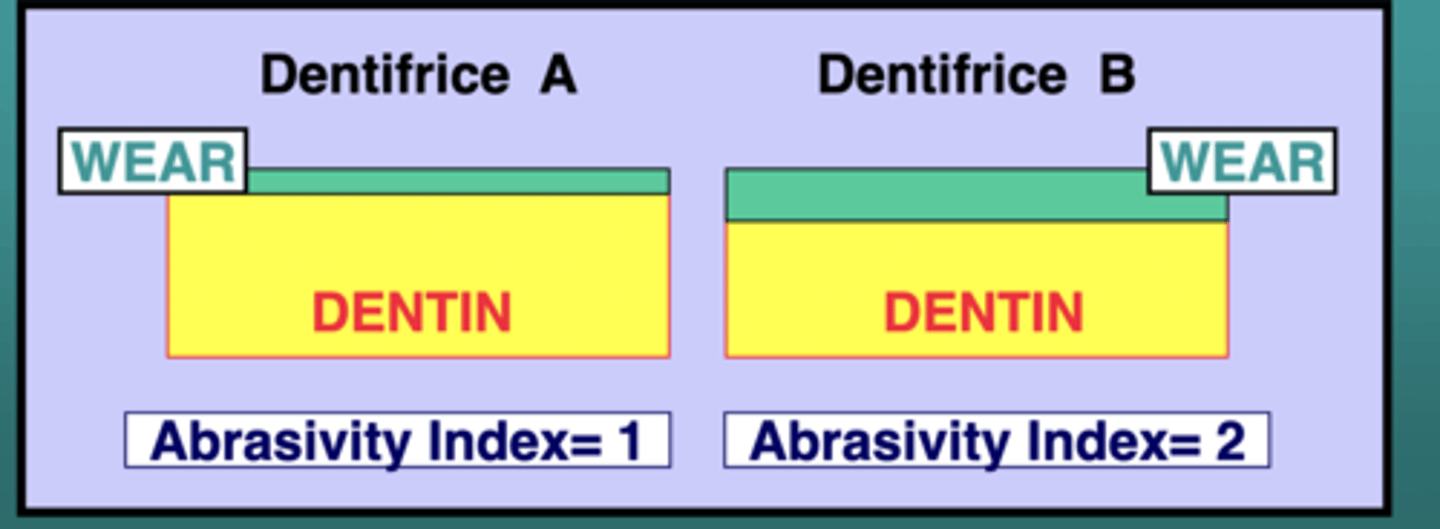
What does the abrasivity index measure?
A measure of the amount of material abraded from a dentin surface in a given time period
What sequence of grit do you use for efficient abrasion?
Coarse-Medium-Fine-Superfine
Straight Carbide Bur Blade Design vs Spiral Carbide Blade Design
Straight: One blade on tooth
Spiral: Several blades on tooth
Carbide Blade Design 3 angles + 2 faces
Rake Angle: Cutting edge strength
Edge Angle: Blade strength
Clearance Angle: provide a stop and space
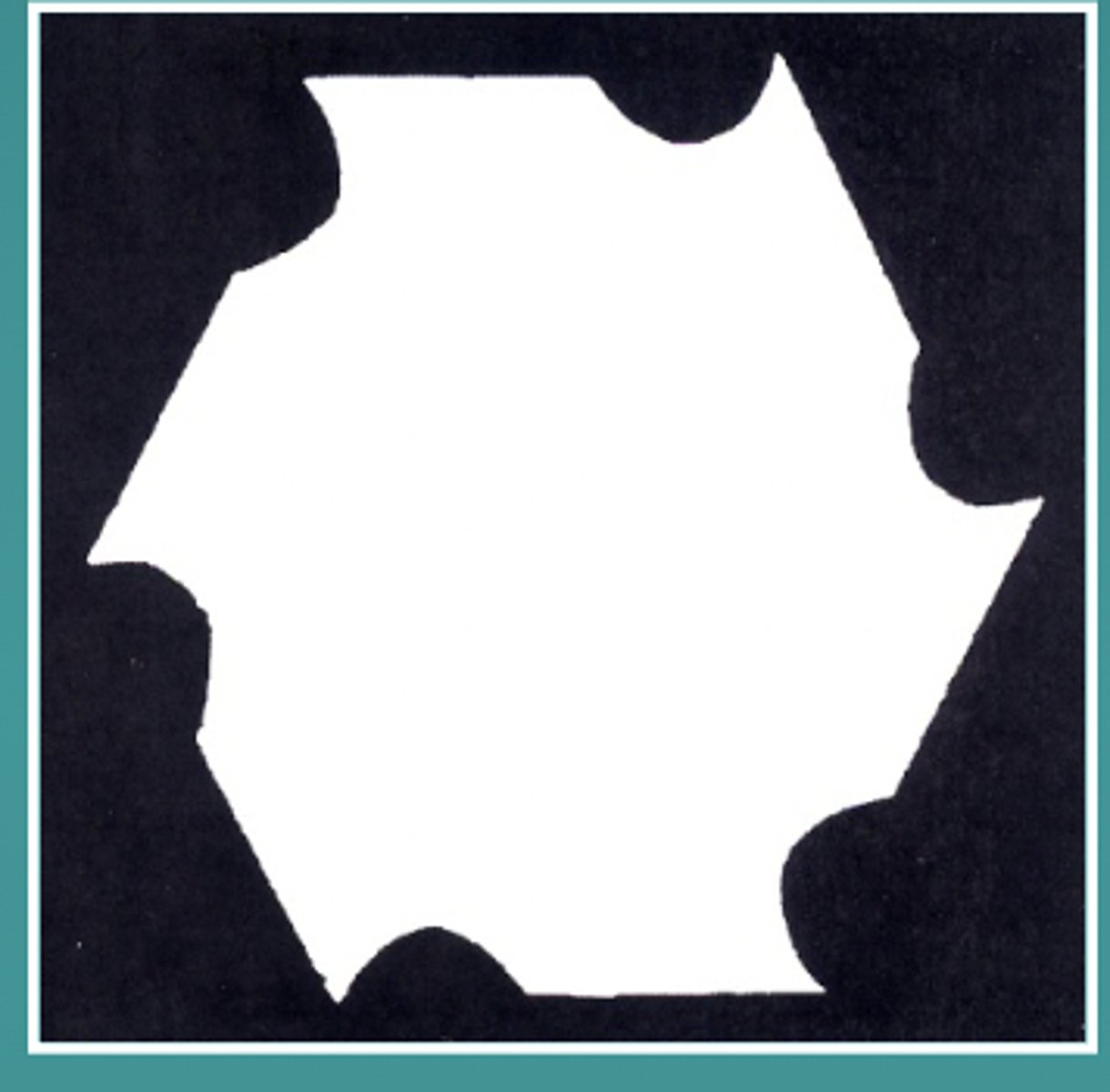
Carbide Positive Rake Angle
The radius lies outside the blade, the rake angle is positive.
For soft &weak materials

Carbide Negative Rake Angle
The radial line lies behind the rake face and entirely within the blade
For hard & Brittle materials
What does a large rake angle mean?
A large rake angle means lower strength of the cutting edge
What is the Carbide edge angle?
Internal angle at the edge formed by the two faces of the bur blade
Related to the resistance of the blade to fracture
What is the Carbide clearance angle?
The angle between the clearance face immediately behind the edge and a tangent to the path of rotation
Which bur is better for end-cutting to produce lower heat and have more blade edges for cutting?
Carbide burs
Which bur is more effective for tooth preparation beveling enamel margins and enameloplasty?
Diamond burs
What does dental stones consist of?
Consist of abrasive particles that have been sintered together or bound with an organic resin to form a cohesive mass
What are dental stones used for?
Contouring and finishing restorations, and where maximum abrasion is needed
What are rubber polishers used for?
Adjusting and polishing acrylic material
Don't apply heavy pressure as it can produce excessive friction heat
What are disks used for?
Used for gross reduction, contouring, finishing, & polishing restorations
What is the role of larger abrasive particles and small abrasive particles?
The larger abrasive particles remove large amounts of material from the substrate, and the smaller particles smooth out the roughness produced by the larger particles.
What is the process of polishing dental restorations?
Polishing of a surface relies on using sequentially smaller and smaller abrasives.
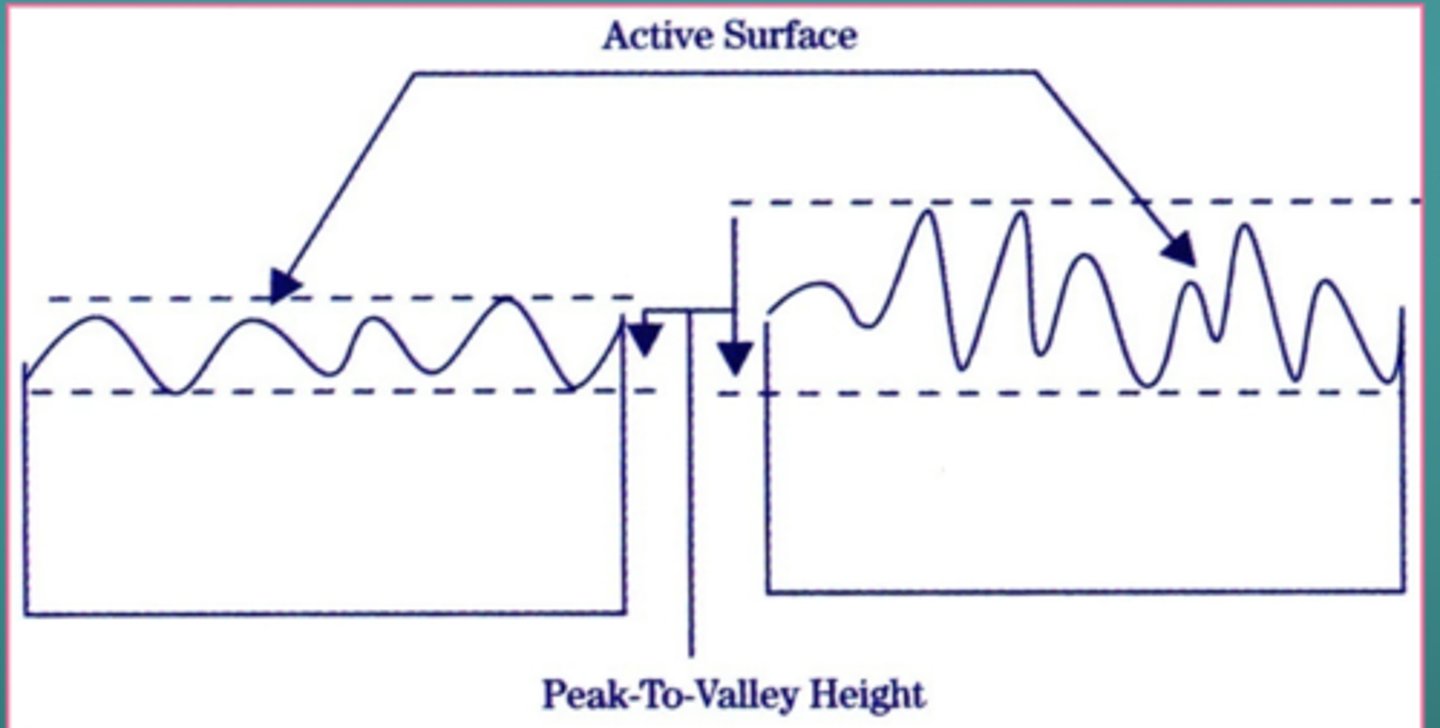
How does proper polishing affect peak-to valley heigh and active surface area of restoration?
Proper polishing reduces peak-to-valley height and active surface area of the restoration
What # of microns does the tongue feel like the surface is rough?
>20 microns
What is Dentifrice, toothpaste?
Dental Prophylaxis Paste; Used for removing debris and residual stains from the teeth and for polishing the tooth surface and restoration