Unit 7 - terms
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Varying levels of consciousness (sleep/wakefulness)
Different states of awareness ranging from full alertness (wakefulness) to reduced awareness (sleep), including altered states like dreaming and hypnosis.
Example: Being fully alert in class vs. being drowsy right before falling asleep.
Psychodynamic therapies
Therapies based on Freud’s ideas that aim to uncover unconscious conflicts influencing behavior.
Example: A therapist helps a patient explore childhood experiences affecting current anxiety.
Free association
A technique where clients say whatever comes to mind without filtering, revealing unconscious thoughts.
Example: A patient says random words that lead to memories of unresolved conflict
Dream Interpretation
Analyzing dreams to uncover unconscious wishes or conflicts.
Example: Repeated dreams of falling may reflect feelings of losing control.
Circadian Rhythm
The body’s internal 24-hour biological clock that regulates sleep and wake cycles.
Example: Feeling sleepy at night and alert in the morning.
Stages of sleep
Distinct phases of sleep that repeat in cycles, including NREM and REM sleep.
Example: A sleeper moves from light sleep to deep sleep and then REM multiple times per night.
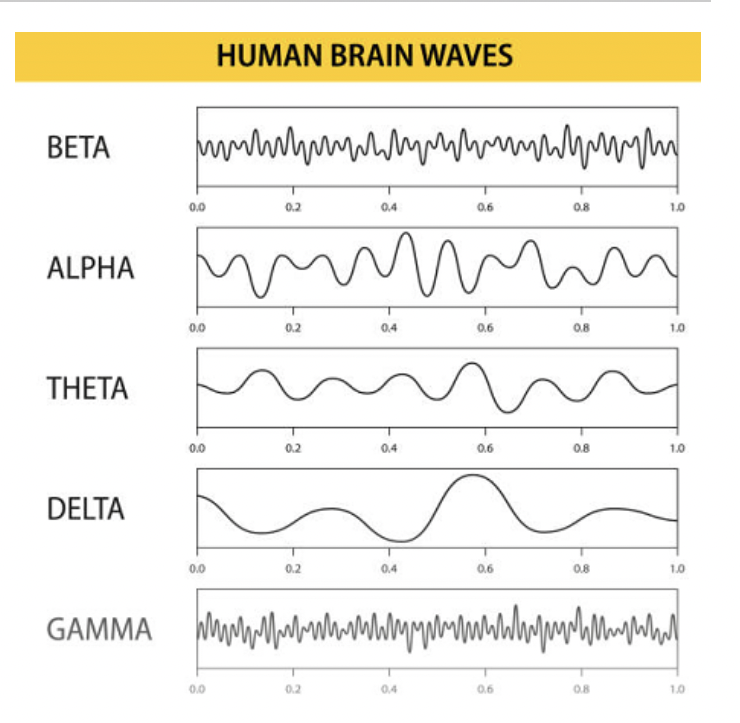
Spindles and Delta
Sleep spindles: Brief bursts of brain activity during NREM-2
Delta waves: Large, slow brain waves during deep sleep (NREM-3)
Example: Delta waves dominate during deep restorative sleep.
EEG patterns for each stage
Brain waves measured by EEG differ across sleep stages (theta, spindles, delta, REM-like waves).
Example: REM sleep EEG resembles wakefulness.
EEG Pattern - Awake and alert
Beta
fast, low amplitude
problem solving, concentration
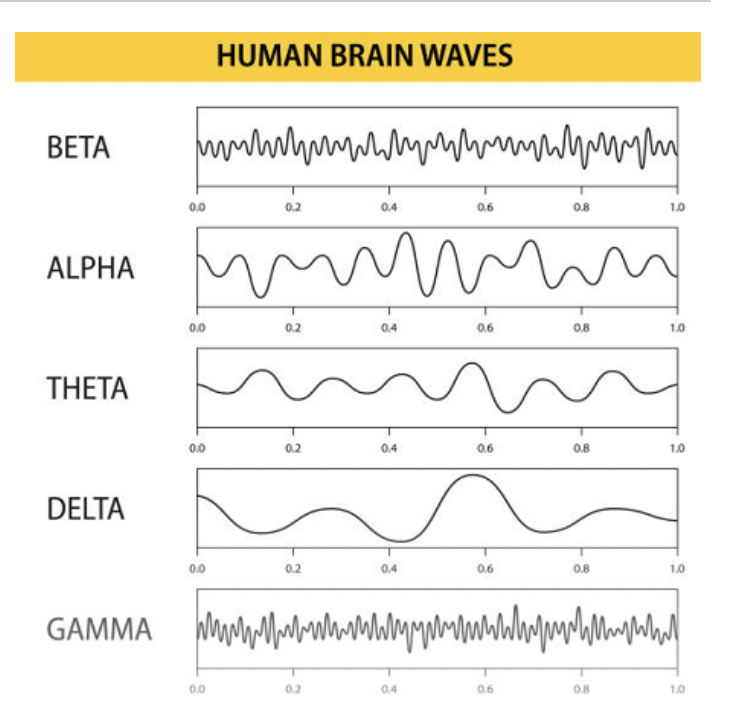
EEG Pattern - Awake but Relaxed
Alpha
slower than beta
meditating, or resting
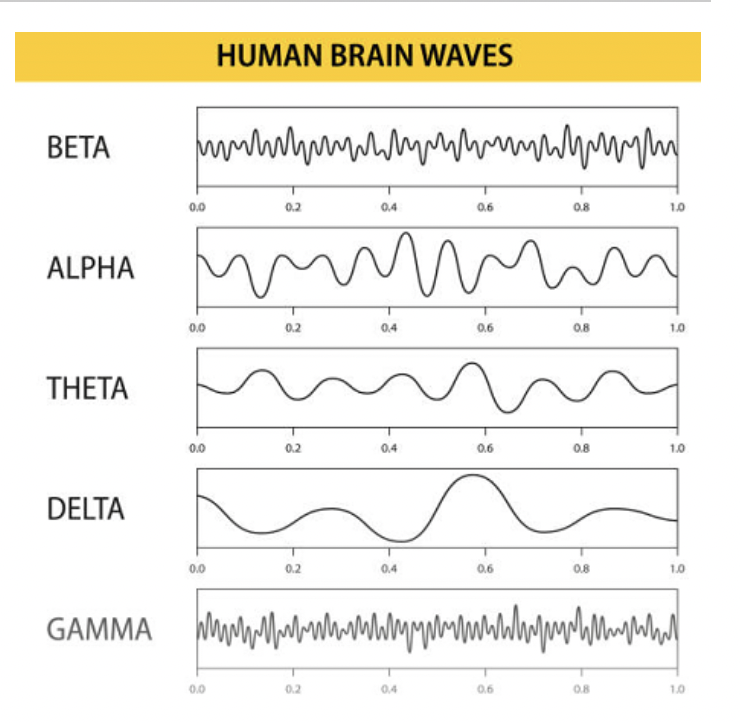
EEG Pattern - NREM 1
Theta
light sleep
hypnagogic sensations
drifting in and out of sleep
EEG Pattern - NREM 2
Theta waves + spindles + k complexes
spindles = short bursts of rapid activity
asleep but easily awakened
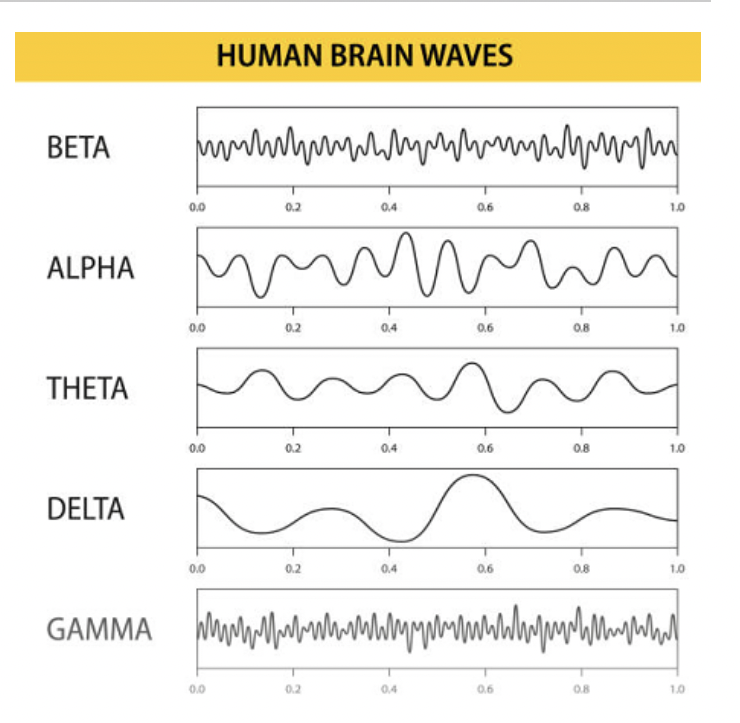
EEG Pattern - NREM 3
Delta Waves
slow, high amplitudes
deep sleep
sleepwalking, night terrors
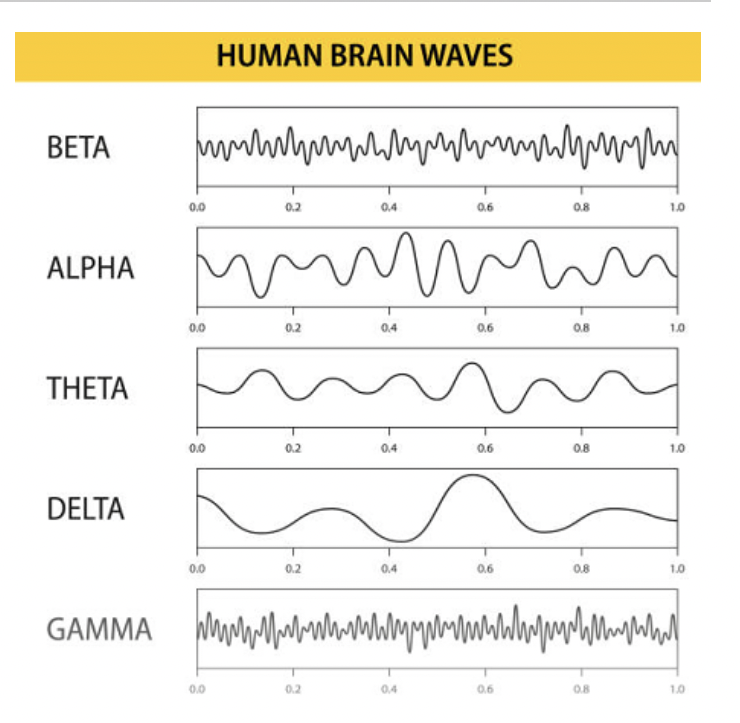
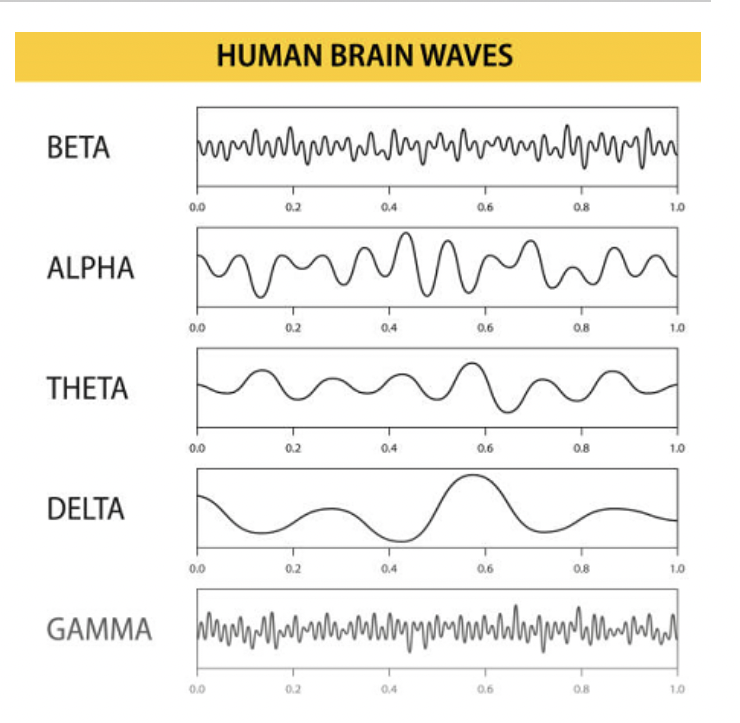
EEG Stage - REM (paradoxical sleep)
Kind of like Beta
A sleep stage where the brain is active, eyes move rapidly, but muscles are paralyzed.
Example: Vivid dreaming occurs even though the body cannot move.
Hypnagogic sensations
Hallucination-like experiences during the transition from wakefulness to sleep.
Example: Feeling like you’re falling just as you fall asleep.
Dreaming and REM
Most vivid and emotional dreams occur during REM sleep.
Example: Complex story-like dreams happen late in the night.
REM increases throughout the night
REM periods get longer with each sleep cycle.
Example: Most REM sleep happens in the early morning hours.
REM rebound
The tendency to experience increased REM sleep after being deprived of it.
Example: After pulling an all-nighter, REM sleep increases the next night.
Activation-synthesis theory (dreams)
Dreams result from the brain trying to make sense of random neural activity.
Example: The brain turns random signals into a story-like dream.
Consolidation theory (dreams)
Dreams help process and store memories.
Example: Dreaming about a test after studying all day.
Wish-Fulfillment (Freud & dreams)
Dreams represent unconscious desires, often symbolic.
Example: Dreaming of success reflects hidden wishes.
Latent Content
The hidden, symbolic meaning of a dream.
Example: A journey symbolizing personal growth.
Manifest Content
The literal storyline of a dream.
Example: Dreaming you’re climbing a mountain.
Sleep & memory consolidation
Sleep strengthens learning and memory storage.
Example: Getting sleep improves recall after studying.
Sleep & physical restoration
Sleep allows the body to repair tissues and restore energy.
Example: Growth hormone is released during deep sleep.
Insomnia
Persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep.
Example: Lying awake for hours every night.
Narcolepsy
A disorder involving sudden sleep attacks and REM intrusion.
Example: Falling asleep during a conversation.
REM sleep behavior disorder
Loss of muscle paralysis during REM, causing people to act out dreams.
Example: Punching or kicking while dreaming.
Sleep apnea
A disorder where breathing repeatedly stops during sleep.
Example: Loud snoring followed by gasping
Somnambulism
Sleepwalking during deep NREM sleep.
Example: Walking around the house while asleep.
Pineal Gland (Melatonin)
A gland that secretes melatonin, regulating sleep cycles.
Example: Melatonin increases at night to induce sleep.
Psychodynamic view of personality
Personality is shaped by unconscious conflicts and early childhood experiences.
Example: Adult fears rooted in childhood trauma.
Psychosexual Stages
Freud believed personality develops through conflicts at each stage, each centered on an erogenous zone.
If conflicts are not resolved, a person becomes fixated, meaning part of their personality remains stuck at that stage.
oral - anal - phallic - latency - genital
oral stage (birth - 1 year)
Erogenous zone: Mouth (sucking, biting, chewing)
Primary conflict: Weaning from the breast or bottle
Key theme: Dependence vs. independence
Pleasure comes from oral activities.
The infant relies on caregivers for nourishment and comfort.
Fixation occurs if needs are over- or under-gratified.
Possible adult fixations:
Smoking, nail-biting, overeating
Excessive dependency or passivity
Sarcasm or verbal aggression (oral-aggressive)
anal stage (1 - 3 year)
Erogenous zone: Anus (bowel and bladder control)
Primary conflict: Toilet training
Key theme: Control vs. flexibility
Pleasure comes from controlling bodily functions.
Parents’ responses to toilet training are critical.
Too strict or too lenient training can cause fixation.
Possible adult fixations:
Anal-retentive: overly neat, rigid, perfectionistic, stubborn
Anal-expulsive: messy, careless, impulsive
phallic stage ( 3 - 6 years)
Erogenous zone: Genitals
Primary conflict: Sexual desire toward opposite-sex parent
Children become aware of anatomical sex differences.
Development of sexual identity occurs.
Key concepts:
Castration anxiety (boys): fear of losing the penis due to attraction to mother
Electra complex / penis envy (girls): attraction to father and resentment toward mother
Resolution:
Child identifies with same-sex parent, adopting their values → formation of superego
Possible fixation outcomes:
Vanity, recklessness
Difficulty with authority or relationships
latency stage (6 years - puberty)
Erogenous zone: None (sexual energy is dormant)
Primary focus: Social, academic, and skill development
Sexual impulses are repressed.
Energy is redirected toward friendships, hobbies, and learning.
Important for developing communication and coping skills.
Fixation:
Freud believed fixation is unlikely at this stage.
genital stage (puberty +)
Erogenous zone: Genitals
Primary focus: Mature sexual relationships
Sexual urges reawaken in socially acceptable ways.
Successful resolution of earlier stages leads to healthy adult relationships.
Emphasis on intimacy, reproduction, and balance between love and work.
Outcome:
Psychological health if earlier conflicts were resolved
Difficulty with intimacy if fixations remain
Unconscious
A vast reservoir of unacceptable thoughts, wishes, urges, and traumatic memories that are actively kept out of awareness because they create anxiety. Freud believed this level strongly influences behavior.
Example: Repressed childhood conflicts shaping adult relationships.
Preconscious (subconscious)
Information not currently in awareness but easily retrievable when needed; acts as a bridge between conscious and unconscious.
Example: Recalling your address when asked.
Id
Primitive, unconscious part of personality driven by the pleasure principle, seeking immediate gratification of instincts (sex, hunger, aggression).
Example: Wanting something immediately without considering consequences.
Ego
Rational, mostly conscious part that operates on the reality principle, mediating between the id, superego, and real-world demands.
Example: Delaying gratification to avoid punishment.
Superego
Moral conscience that internalizes societal norms and values, striving for perfection and producing guilt when standards are violated.
Example: Feeling guilty for lying.
Defense Mechanisms
Defense mechanisms are unconscious strategies used by the ego to reduce anxiety caused by conflicts between the id and superego.
compensation
Overemphasizing strengths to cover weaknesses.
Example: Excelling academically to offset poor social skills.
repression
Pushing distressing thoughts out of awareness.
Example: Forgetting traumatic events.
Denial
Refusing to accept reality.
Example: Ignoring a serious diagnosis.
Displacement
Redirecting emotions to a safer target.
Example: Yelling at a sibling instead of a boss.
Projection
Attributing one’s feelings to others.
Example: Accusing others of jealousy.
Rationalization
Creating logical excuses for behavior.
Example: “I failed because the test was unfair.”
Reaction formation
Acting opposite to true feelings.
Example: Being overly nice to someone you dislike.
Regression
Reverting to earlier behaviors under stress.
Example: Thumb-sucking.
Sublimation
Channeling impulses into socially acceptable actions.
Example: Aggression into sports.
intellectualization
Avoiding emotion by focusing on facts.
Example: Analyzing illness clinically
identification
Adopting traits of others.
Example: A child mimicking a parent.
Carl Jung
Neo-Freudian who emphasized spirituality and shared unconscious elements.
Collective Unconscious (Jung)
Shared universal memories across humanity. Archetypes, symbols, myths, stories. Collectively shape how humans think, feel, dream, and tell stories
Example: Common mythological themes.
Archetypes (Jung)
Universal symbolic patterns.
Example: The hero or mother figure.
Inferiority Complex (Alder)
Feelings of inadequacy motivating behavior.
Example: Overachieving to prove worth.
Womb Envy (Horney)
Men’s envy of women’s reproductive ability.
Example: Seeking dominance to compensate.
Hypnosis in therapy -pain and anxiety reduction; does not recover repressed memories or allow for regression in age
Used to reduce pain and anxiety; does not recover repressed memories or enable age regression.
Example: Hypnosis for chronic pain relief.
Hysteria/ Hysterical Fits
Physical symptoms without medical cause, believed to result from unconscious emotional conflict. Tied to the conversion disorder
fainting
paralysis
blindess
Example: Sudden paralysis without injury.
Emil Kraepelin
Early psychiatrist who classified mental disorders scientifically.
Normal vs Psychosis
normal: contact with reality
Psychosis: loss of reality testing
Example: Delusions or hallucinations indicate psychosis.
Neurotic vs Psychotic
Neurotic: distressed but reality-based
Psychotic: detached from reality
Neurosis
chronic anxiety without loss of reality.
Example: Phobias.
psychoanalytic theory
Behavior is driven by unconscious conflicts and childhood experiences.
how to treat neurosis: Psychoanalysis to uncover unconscious conflict.
Iceburg metaphor
Mind is mostly unconscious beneath awareness.
Illustrates that most mental life occurs below awareness; the conscious mind is only the visible tip, while unconscious forces drive behavior.
Example: Conscious thoughts are just the “tip.”
castration anxiety
Freud’s idea that boys fear punishment during the phallic stage.
electra complex/ penis envy
Girls’ attraction to father and envy of males (Freud).
consciousness
Our awareness of ourselves and our environment.
Example: Knowing you’re tired and deciding to go to sleep.
divided consciousness
Mind can process information simultaneously.
Example: Driving while daydreaming.
daydreaming (evolutionary perspective)
Mental simulation for planning and problem-solving.
Example: Imagining future scenarios.
night terrors
Intense fear during NREM-3, no memory afterward.
Example: Screaming during sleep
REM w/o atonia
During REM sleep, the muscle paralysis (atonia) does not occur
talk, shout, punch, kick in bed
restless leg
Uncomfortable sensations causing urge to move legs at night.
alfred adler
Neo-Freudian who emphasized social interest and inferiority.
Karen Horney’s
Neo-Freudian who emphasized social and cultural factors, rejected Freud’s views on women.
Freud’s treatment of neurosis
Free association
Dream analysis
Bringing unconscious conflicts into conscious awareness