Experience 4: Comparing Metals and Nonmetals
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
the ability to be drawn into wires
ductility
the ability to be hammered or pressed into shapes
malleability
a material's ability to conduct heat
thermal conductivity
a material's ability to conduct electricity
electrical conductivity
the way light interacts with a material's surface
luster
an irregularity within a crystal that occurs at a point on the lattice
point defect
mixtures of two or more elements, at least one of which is a metal
alloy
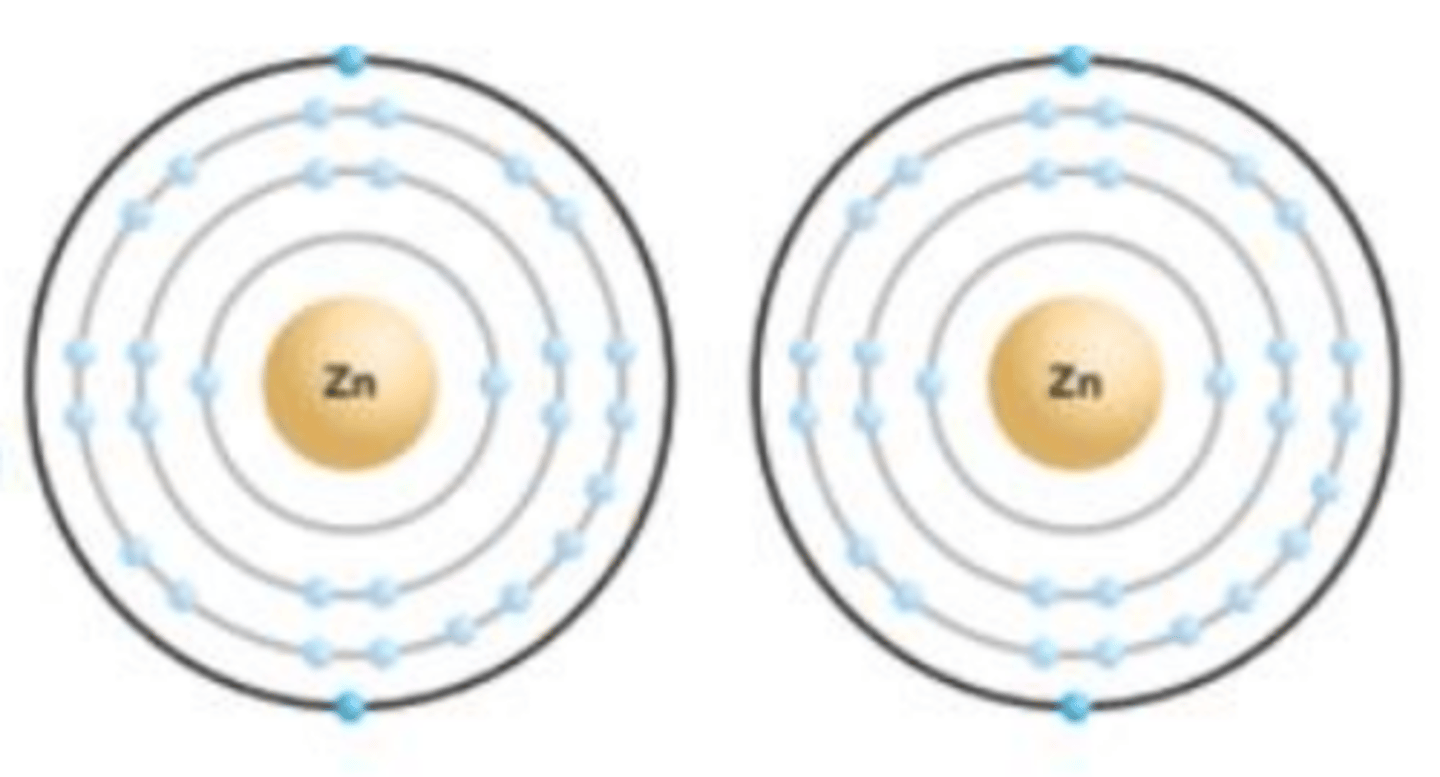
in metals, including zinc, electrons are not __________ to individual atoms. Instead, they move around ___________, holding them together in a ________________ structure
bound; freely
crystalline
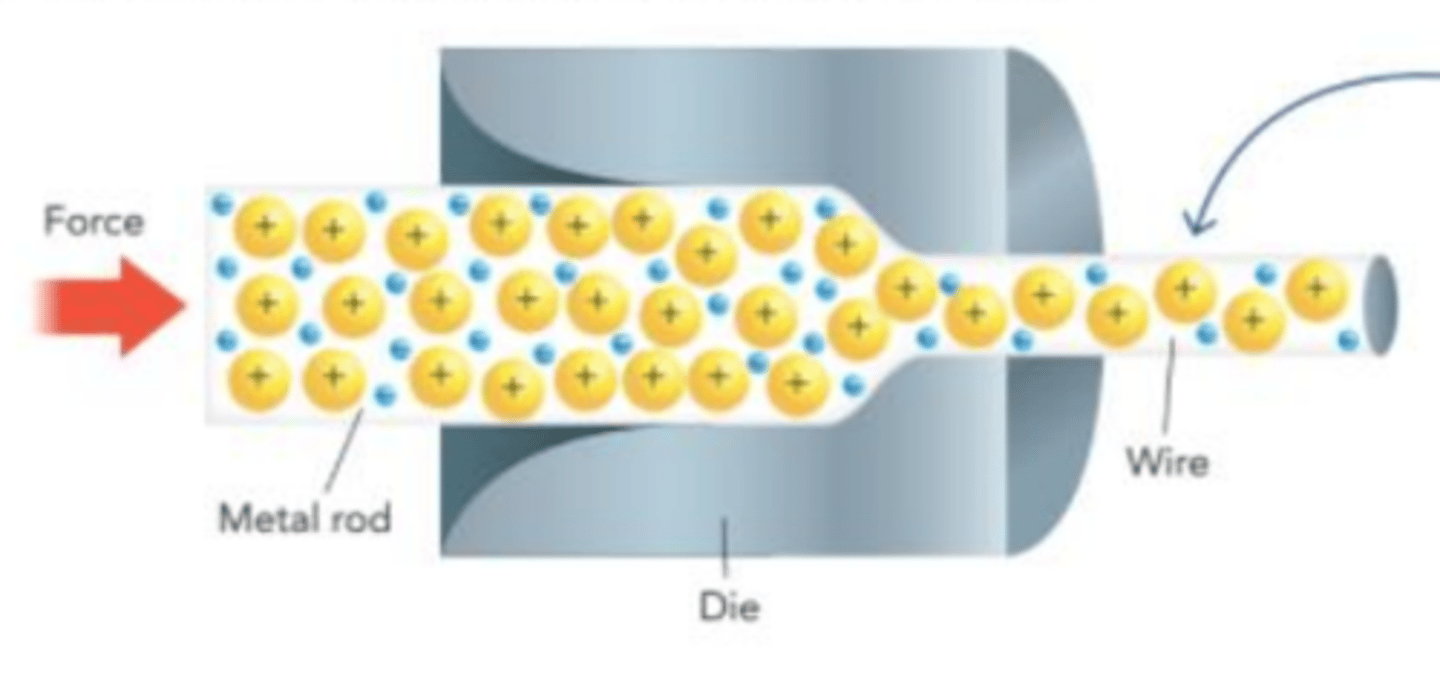
a sea of valence electrons allows metals to be _________________ ________ wire or ______________ without breaking
Ionic compounds __________ behave the same way
squeezed into; hammered
DON'T
Drifting electrons insulate metal cations from each other. When metal is forced through a die, the cations easily slide past one another, allowing the metal to be formed into wire. What is this an example of?
ductility
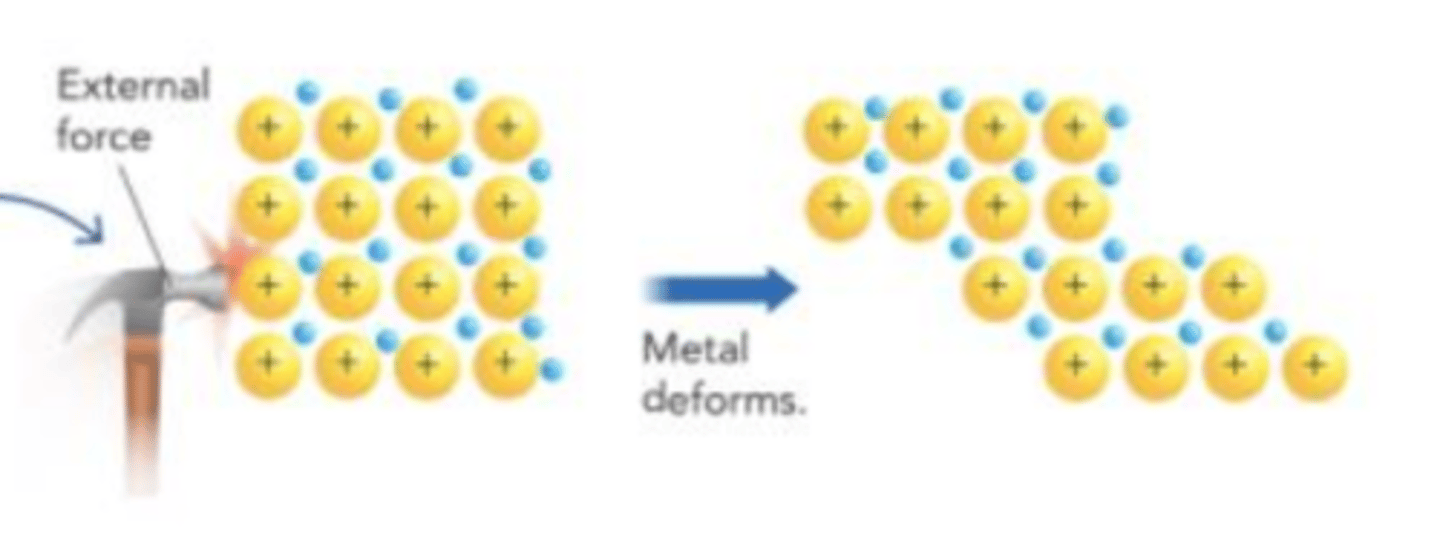
When pressure is applied to a metal, the cations can easily change position, so the metal changes shape without breaking. What is this an example of?
malleability
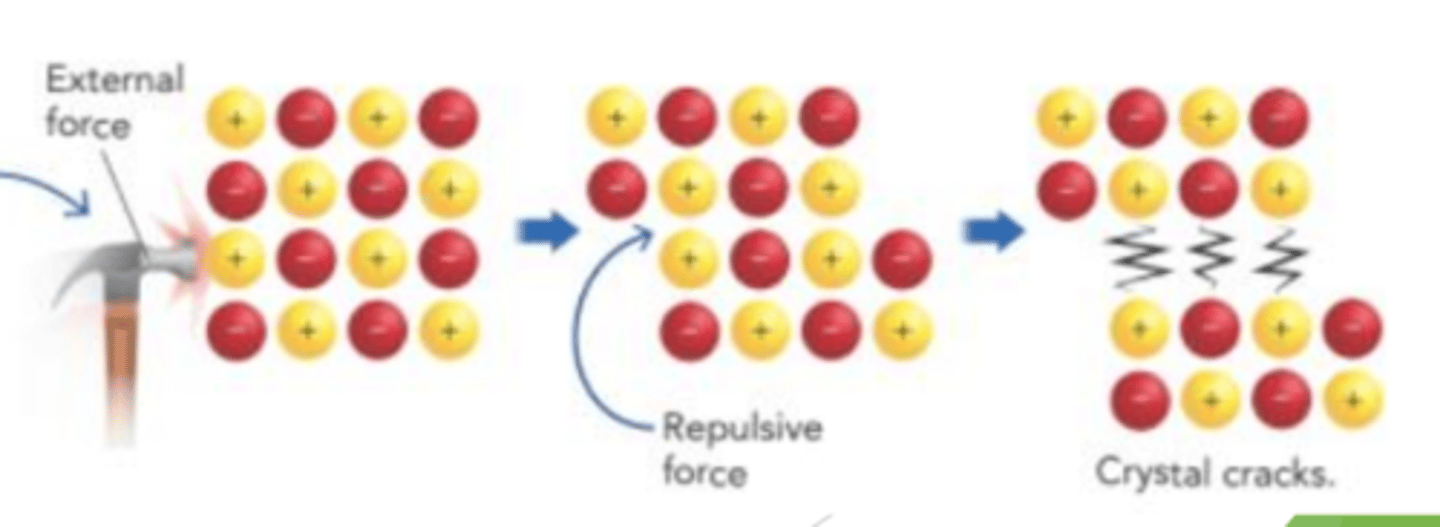
Applying pressure to an ionic compound tends to push the ions close together. The positive ions ________ each other, and the crystal ______________
repel
shatters
Because electrons can move around, they conduct heat more easily than ______ solids or _____________ ____________ solids.
ionic solids or covalent network solids
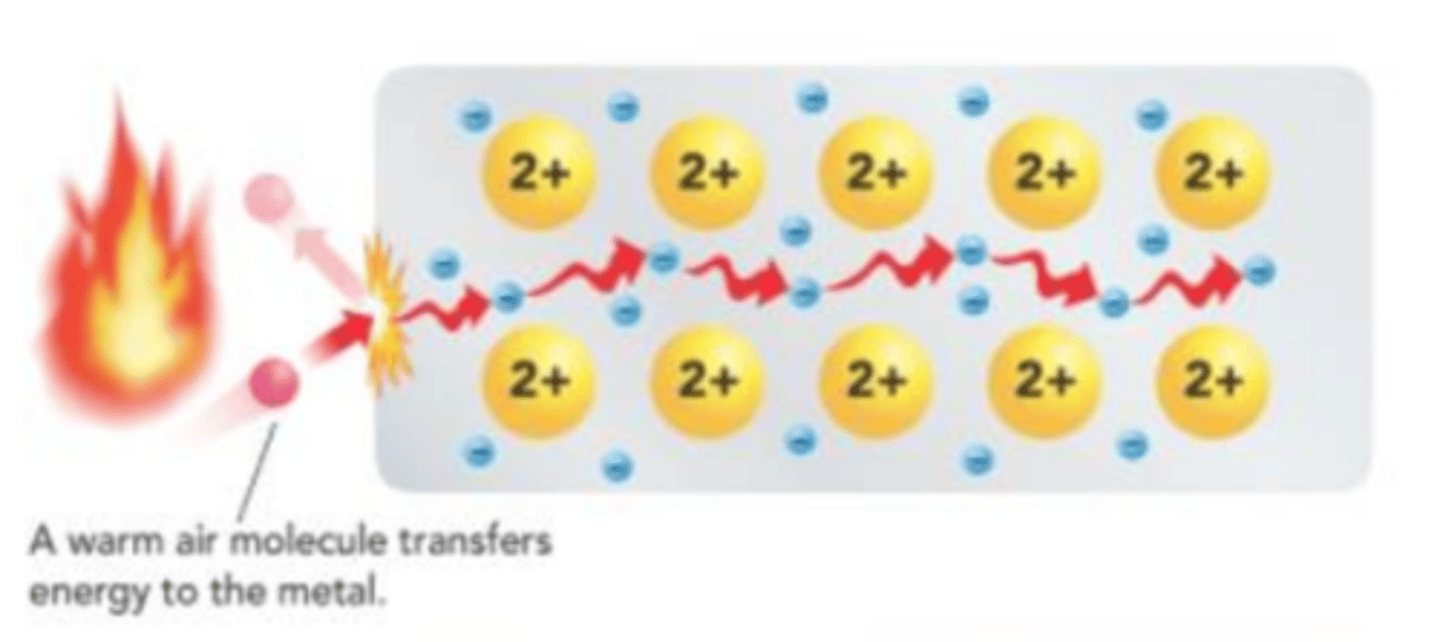
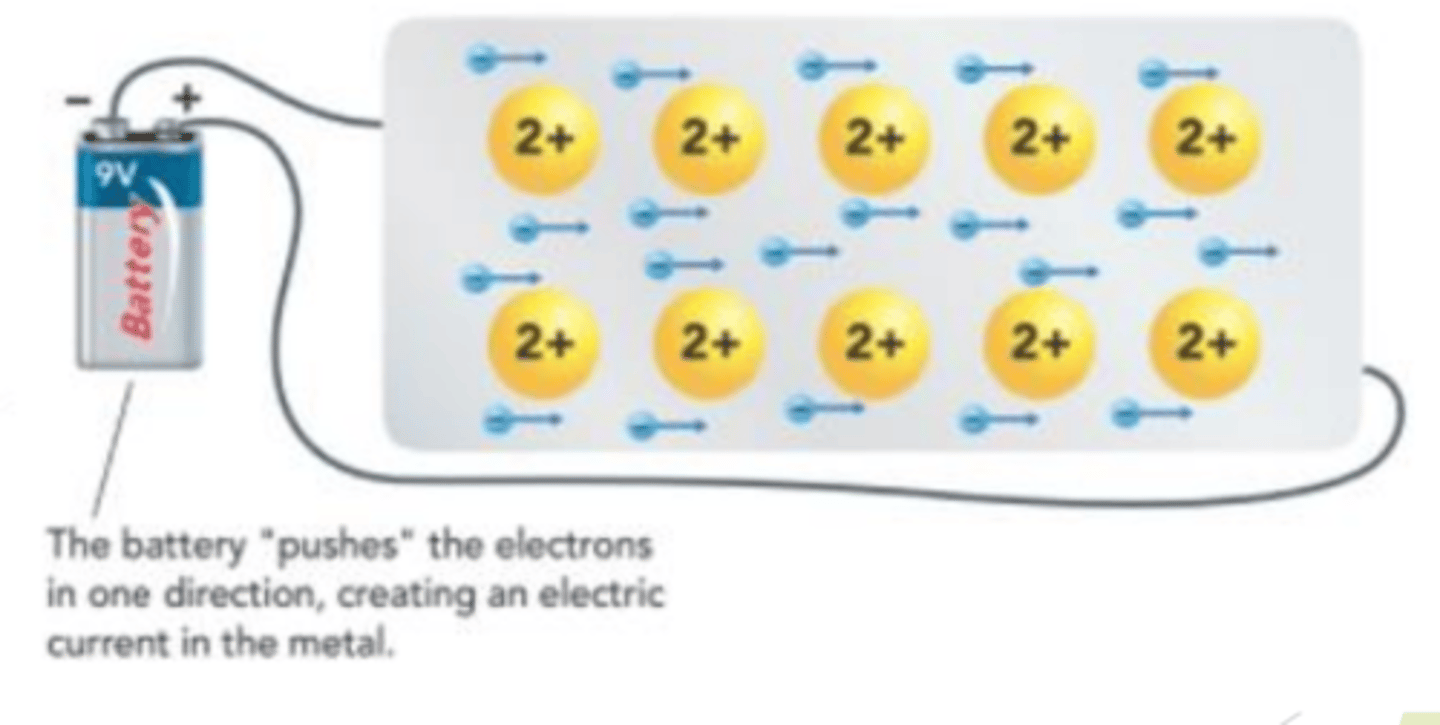
The delocalized electrons in metals can easily move, making metals __________ ________________ than ionic solids
more conductive
In a(n) _______________ defect, extra atoms are stuck where they don't belong
interstitial defect
In a(n) _______________ defect, different atoms take the place of existing atoms in the crystal lattice
substitution defect
In a(n) _______________ defect, atoms are missing from the lattice structure
vacancy defect
the tension on the surface of a water drop
surface tension
a substance that reduces surface tension and increases wetting
surfactant
in any solution, the dissolving medium is called the _______________
solvent
the dissolved particles (usually ions, but also polar molecules) are called the _______________
solute
the process of ion capture by the solvent is called _______________
solvation
a solution where water is the solvent
aqueous solution
a compound that conducts electric current when dissolved in an aqueous solution or in the molten state
electrolyte
a compound that does not conduct electric current in either an aqueous solution or in the molten state
nonelectrolyte
a solid, crystalline compound that contains water molecules as an integral part of its crystal structure
hydrate
the loss of water by a hydrate
efflorescence
a chamber used for maintaining a dry environment in chemistry labs
desiccator
because water is a polar molecule, its molecules are ________________ to each other
_______________ bonds hold water molecules together
attracted
hydrogen bonds
unbalanced forces pulling inward on a drop of water cause it to _________________ the amount of surface area by beading up on some surfaces
minimize
a molecule at the ___________ of the drop will experience only attractive forces from below. Because these attractive forces are ________________ there is a net pull on the molecule into the drop
surface
unbalanced
a molecule in the ____________ of the drop will experience attractive forces from all sides. Because these attractive forces are ______________, there is no net pull on the molecule
middle
balanced
the rate at which a solute dissolves
dissolution rate
contains the maximum amount of solute for a given quantity of solvent at a constant temperature and pressure
saturated solution
the amount of solute that dissolves in a given quantity of a solvent at a specified temperature and pressure to produce a saturated solution
solubility
a graph of the solubility as a function of temperature
solubility curve
areas in the ocean where the oxygen concentration is so low that animal life suffocates
hypoxic zones
contains more solute than it can theoretically hold at a given temperature
supersaturated solution
solutions are called ____________________ _______________ because they have a uniform appearance and composition
homogeneous mixtures
_____________________ _______________ are not uniform in composition and are not considered solutions
heterogeneous mixtures
a heterogeneous mixture containing particles, called the dispersed phase, that are spread throughout another substance, called the dispersion medium
a colloid
a heterogeneous mixture from which particles settle out upon standing
suspension
in a solution, individual molecules and ions of the solute and solvent are _________ ________________
mixed together
most ____________ contain charged particles of clumped molecules or ions that are spread throughout the dispersion medium
colloids
a ________________ is a mixture from which particles settle out upon standing
suspension
when light scatters by particles in a colloid or in a very fine suspension
Tyndall effect
when a beam from a flashlight is directed on beakers known to contain a colloid, a suspension, and solution, which of the following will not exhibit the Tyndall effect?
the solution
Metals are ___________, and can be drawn into a wire.
A. Conductive
B. Malleable
C. Magnetic
D. Ductile
D. Ductile
______________ describes the way a substance reflects light, or SHINES.
A. Magnetism
B. Brittleness
C. Luster
D. Ductility
C. Luster
_______________ describes how well the substance can be hammered into sheets.
A. Malleability
B. Conductivity
C. Ductility
D. Luster
A. Malleability

If a substance breaks easily, it is said to be ________________.
A. Magnetic
B. Conductive
C. Brittle
D. Ductile
C. Brittle

Metalloids are the best conductors of electricity
A. True B. False
B. False
Nonmetals are usually GOOD conductors of heat and electricity.
A. True B. False
B. False
Nonmetals are not attracted to magnets.
A. True B. False
A. True
Metals are the most conductive elements on the Periodic Table.
A. True B. False
A. True
Metals can be drawn into a wire.
A. True B. False
A. True
Metals lack luster, are brittle, and do not conduct electricity.
A. True B. False
B. False
If a substance breaks easily, it is said to be ________________.
A. Magnetic
B. Conductive
C. Brittle
D. Ductile
C. Brittle
Metals are usually silver-grey in color.
A. True B. False
true
Metals usually have high melting points.
A. True B. False
t
Metals are soft and bend or break easily.
A. True B. False
f
Which of these grouping of elements could have the characteristic of luster ?
Metal
Nonmetal
metalloids
Both metals and metalloids
Both metals and metalloids
Which of these is a property of metals?
It's malleable
It can't conduct electricity
They are used in food
It's very brittle
It's malleable
Brittle
Metal
Nonmetal
Nonmetal
All of the following would classify an element as a metal except?
Dull
Luster
Malleable
Hard
Dull
Iron is a good conductor, malleable and magnetic. What type of element is Iron?
Metal
Nonmetal
Metalloid
Pretty
Metal
A student is given a sample of an unknown substance. He is asked to determine if it is classified as a metal, a metalloid, or a nonmetal. He discovered that the unknown element conducted some heat and electricity, had a shiny luster, and broke easily. This element is most likely a
metal
nonmetal
metalloid
cannot be determined
metalloid
Which table below correctly lists the properties of metals and nonmetals? *
A
B
C
D
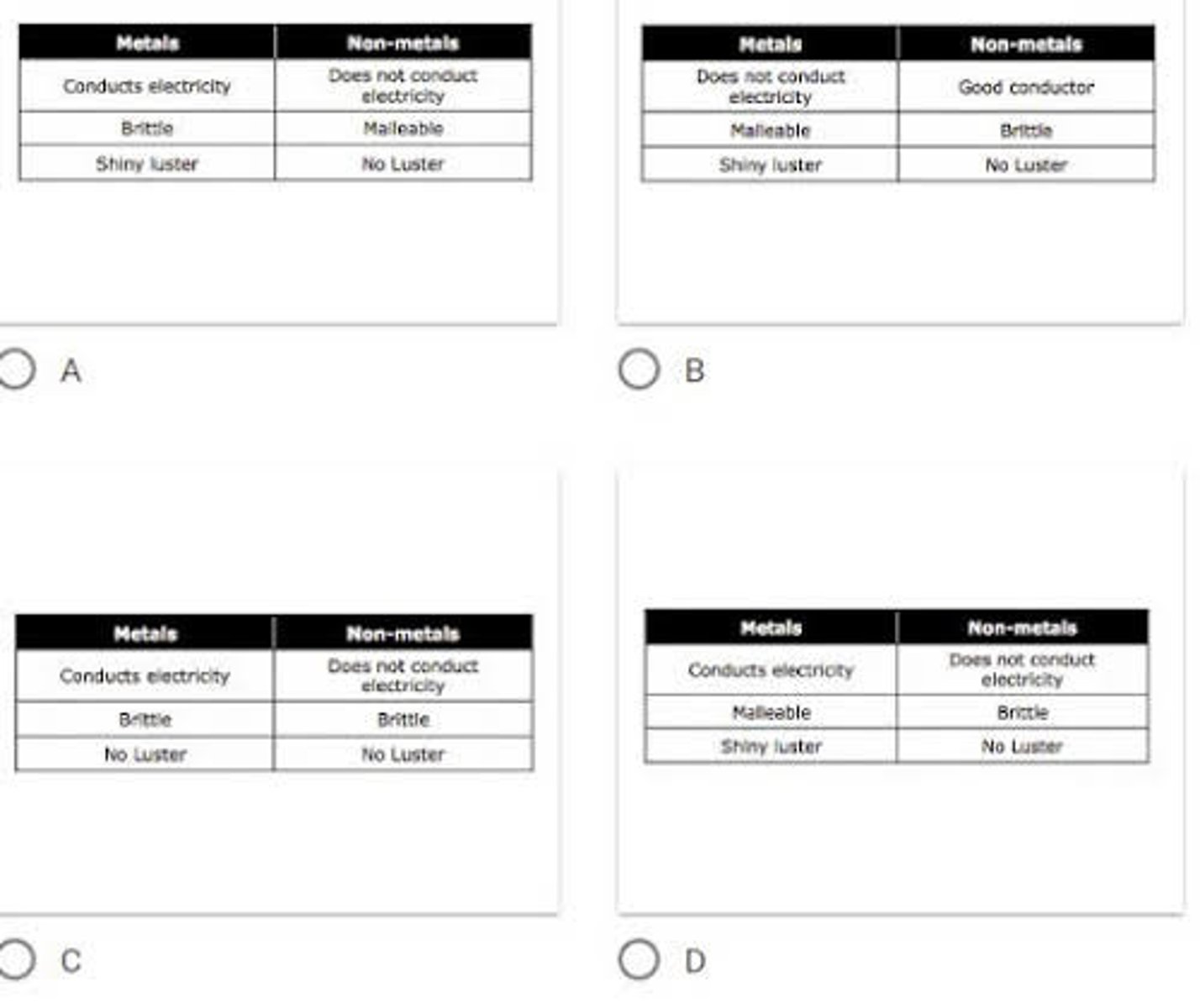
answer
d
Which of the following is a property of a non-metal?
Conducts electricity and heats well
Can be hammered into thin sheets
Is brittle and breaks easily
Has a shiny, metallic luster
Is brittle and breaks easily
All of the following are properties used to classify elements as metals, non-metals, and metalloids EXCEPT —
texture
conductivity
luster
malleability
texture
A student tested the conductivity of four elements using an incomplete electrical circuit. When the element is placed in the circuit, the bulb lights up brightly, lights up dimly, or does not light up at all based on the element's ability to conduct electricity. The table below shows the results of her investigation. Based on the results of the conductivity test, which element is classified as a metal?
Hydrogen
Arsenic
Krypton
Copper
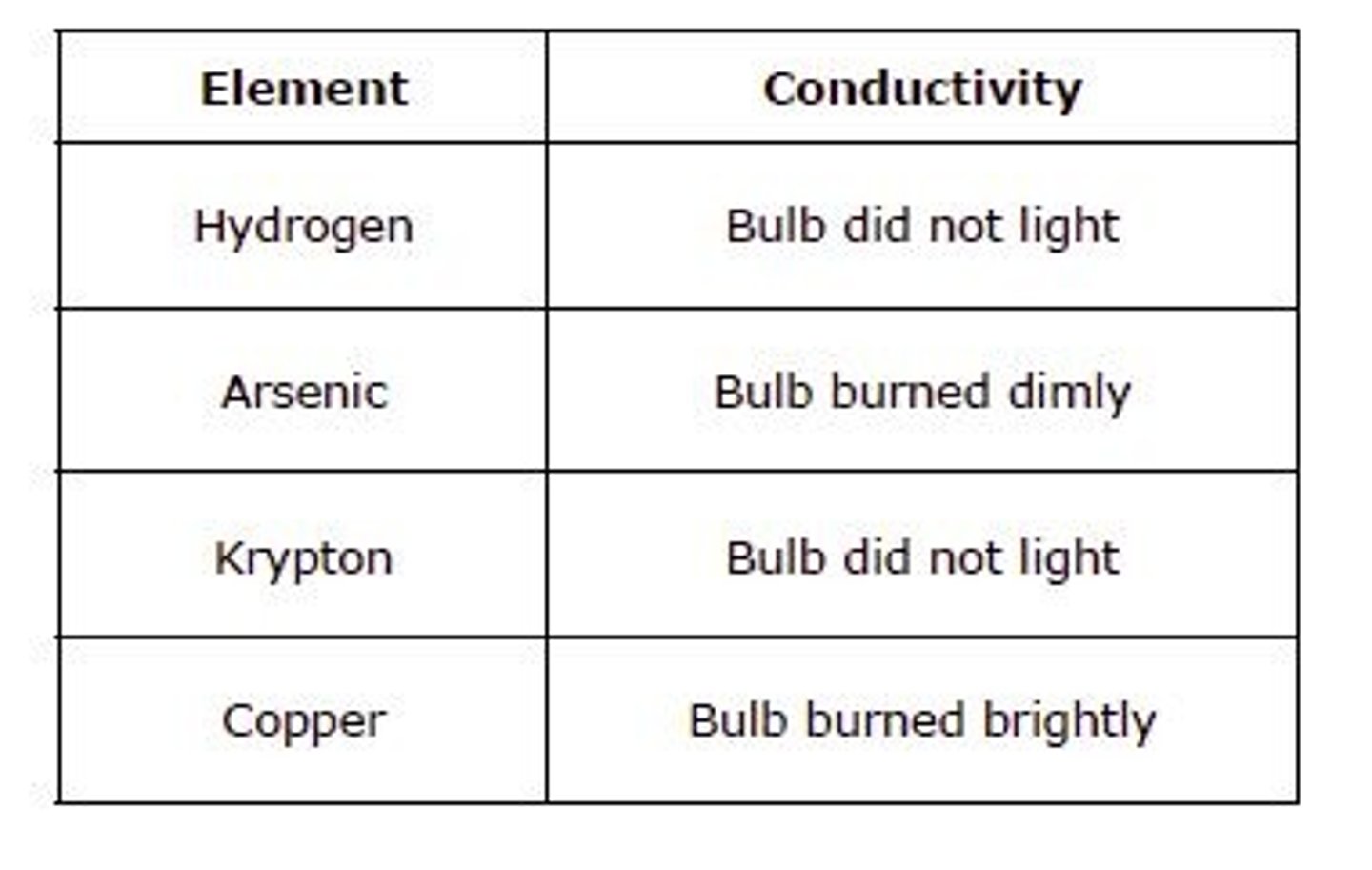
answer
copper
Which of the following correctly lists the three main groups of elements from greatest conductivity to least conductivity?
Nonmetals -metalloids-metals
metals-nonmetals-metalloids
metalloids-metals-nonmetals
metals-metalloids-nonmetals
metals-metalloids-nonmetals
The table shows the properties of four elements. Which element in the table is classified as a metal?
Manganese
Sulfur
Silicon
Neon
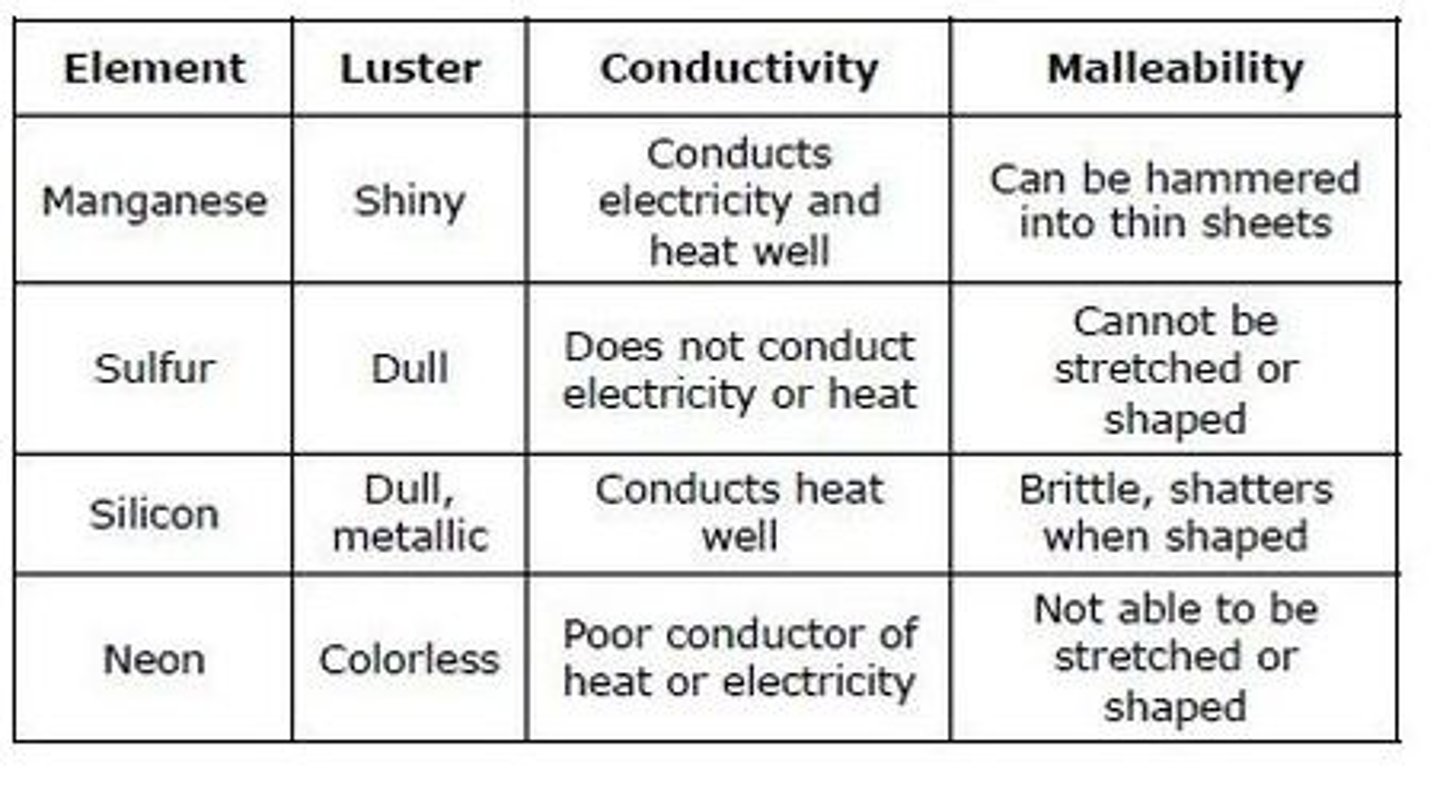
answer
manganese
Silicon is a semiconductor and has properties of both metals and nonmetals. What type of element is Silicon?
Metal
Nonmetal
Metalloid
Pretty
Metalloid
´Elizabeth was examining elements and their physical properties. She described an element is her science journal as having no shine, an insulator, and very brittle. What would this element be: a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid?
metal
nonmetal
metalloid
nonmetal
If a substance is magnetic it is most likely a
metal
non-metal
metal
Fe-Ca-Cu
metal
metalloids
non metal
metal
Boron- Silicon
metal
metalloids
non metal
metalloids
N- O-H-He
metal
metalloids
non metal
non metal
As conductors of heat and electricity metals are:
Good conductors
Semi-conductors
Poor conductors
Good conductors
As conductors of heat and electricity non metals are:
Good conductors
Semi-conductors
Poor conductors
Poor conductors
As conductors of heat and electricity metalloids are:
Good conductors
Semi-conductors
Poor conductors
Semi-conductors
Have luster/shiny -- metals:
Have luster
Some like metals some
like non metals
dull
Have luster
Have luster/shiny -- non metals:
Have luster
Some like metals some
like non metals
dull
dull
Have luster/shiny -- metalloids:
Have luster
Some like metals some
like non metals
dull
Some like metals some
like non metals
Other properties of metals:
1. Malleable
Ductile
High density
2.Some like metals some
like non metals
3. Solids are brittle
Low density
1. Malleable
Ductile
High density
Other properties of nonmetals:
1. Malleable
Ductile
High density
2.Some like metals some
like non metals
3. Solids are brittle
Low density
3. Solids are brittle
Low density
Other properties of metalloids:
1. Malleable
Ductile
High density
2.Some like metals some
like non metals
3. Solids are brittle
Low density
2.Some like metals some
like non metal