Types of enzymes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Why are enzymes specific ?
They are specific to a particular substrate due to the shape of the active site
What are catabolic reactions and what is an example ?
They break things down , and metabolic pathway energy is required .
E.g: respiration (breaking down glucose for energy
E.g : Digestion
What are anabolic reactions?
They build things up , and are chemical reactions that are required for growth.
E.g: Photosynthesis
What is activation energy ?
Minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
What are extra cellular enzymes?
Enzymes that catalyse reactions outside of a cell
What are intracellar enzymes ?
Enzymes in the cytoplasm , so catalyse reactions inside the cell
What are hereotrophs and what is an example ?
They consume other organisms and break down nutrients. E.g: Proteins into amino acids
What is an external digestive system ?
They secrete enzymes onto the food source outside of their bodies . E.g: flies
How do extra cellular enzymes work and what are two examples of them ?
Molecules need to be broken down into smaller molecules before they pass inside the a cell so enzymes released from the cell that are extracellular can do this (as they work outside the cell )
E.g: Fungi work outside of organisms
Single-celled organisms release into their surrounding environment
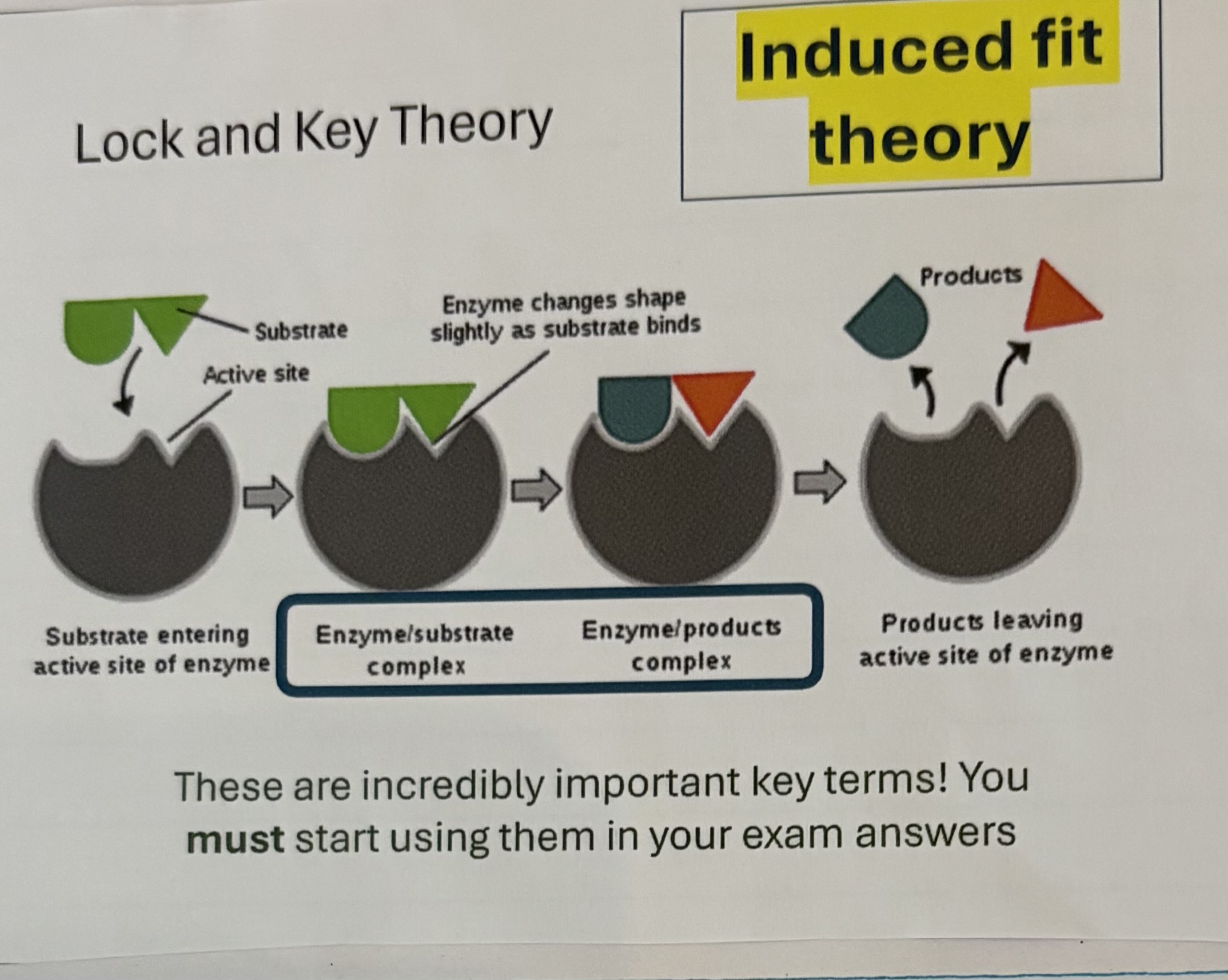
What happens in the lock and key theory ?
The substrate is held by the enzyme so that the right atom groups are close enough go to react
R-groups in the active site of the enzyme will interact with the substrate . Temporary , weak bonds are formed
These temporary bonds will put strain on the bonds within the substrate , this will support the reaction in taking place
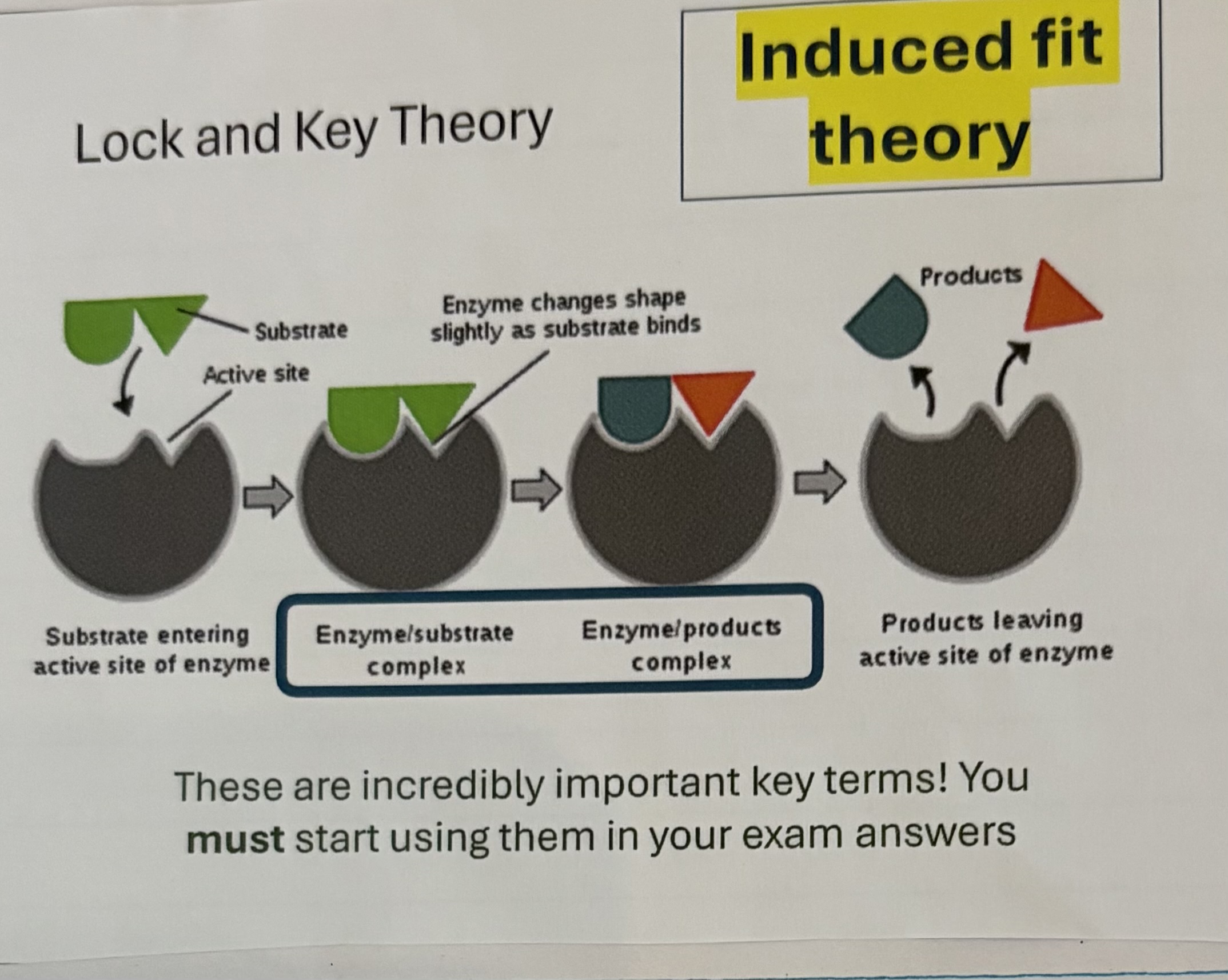
What is induced fit theory ?
Enzyme not initially a perfect fit so the active site changes shape slightly to fit the enzyme perfectly
The interactions between the substrate and enzyme are weak as they have weak bonds between each other because they enzyme wont stay for long
Changes occur in the tertiary structure which strengthens the the bonding and puts strain on the substrate molecule
This leads to a weakening of the bonds in the substrate and lowers the activation energy