12) Capillaries & bulk flow
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
How are substances exchanged b/w CAPILLARY & INTERSTITAL FLUID?
1) diffusion (across/b/w cells)
2) transcytosis (via vesicles)
3) bulk flow (main one)
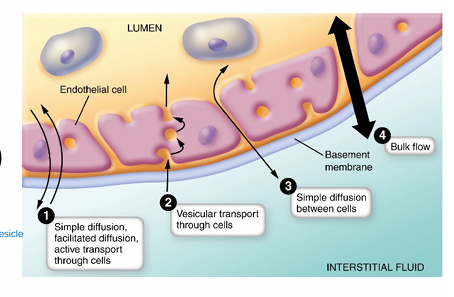
What is BULK FLOW?
What is bulk flow driven by?
1) mass Mm of fluid & solutes through pores
2) PRESSURE GRADIENTS
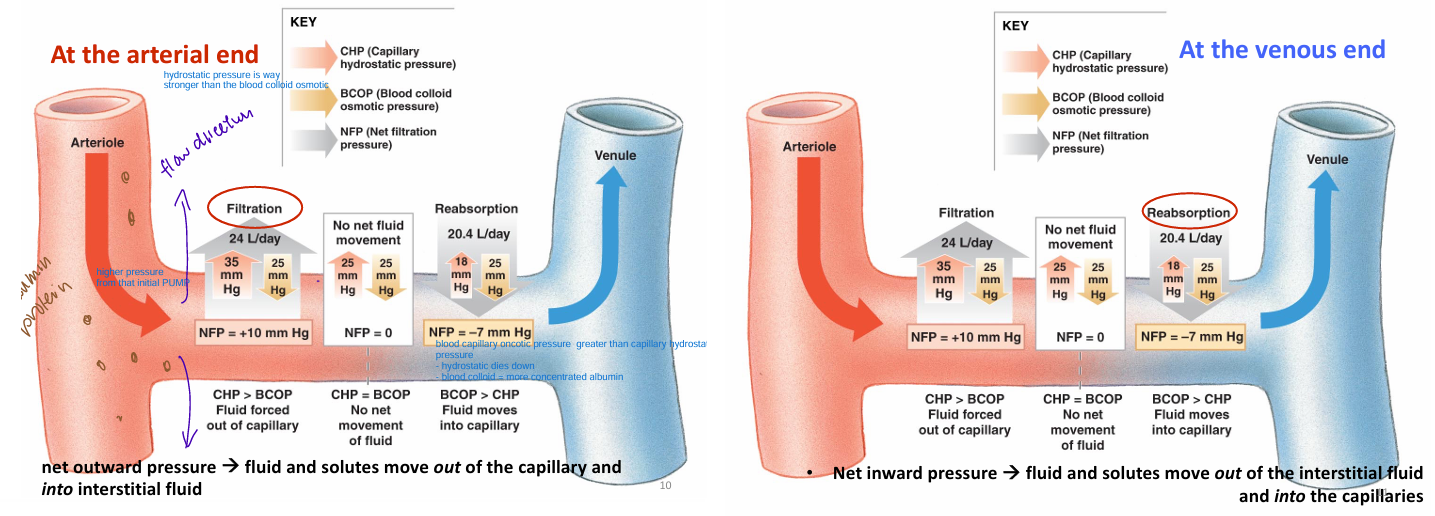
What is filtration in terms of bulk flow?
Mm from high pressure in CAPILLARIES
to low pressure in interstitial space
What is reabsorption in terms of bulk flow?
Mm from high pressure in INTERSTITIAL SPACE to low pressure in capillaries
What pressure PROMOTE filtration?
1) Capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP)
- pressure of blood pushing against BV wall
2) Interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure (IFCOP) (usually negligible)
- small amt of protein in interstitium
→ osmotic pressure (pulls water OUT)
What pressures REABSORBS (against filtration)
1) Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)
- osmotic pressure caused by large proteins (albumin) in capillaries
2) Interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure (IFHP) (usually negligible)
- difficult to measure; usually don’t consider
What is NFP?
Net filtration pressure = direction of bulk flow
Mm of fluid/solutes across the capillary walls
NFP positive = filtration (fluid outwards)
NFP negative = reabsorption (fluid inwards)
1) At the arterial end, the __ is greater than _.
2) At the venous end, the __ is greater than _.
1) capillary hydrostaic pressure; blood colloid osmotic pressure
2) blood colloid osmotic pressure; capillary hydrostaic pressure
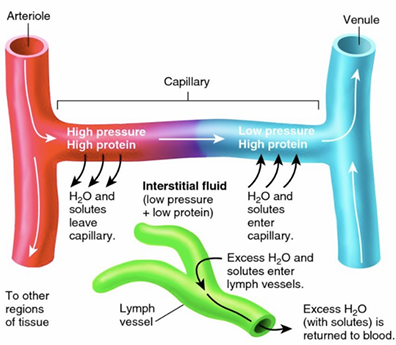
What is the role of lymphatic vessels?
*note: 85% of filtered fluid is reabsorbed BACK into the capillaries
that excess 15% filtered fluid/solute
→ enters lymphatic vessels as LYMPH
→ returns to systemic circulation
~3L of excess interstitial fluid is return to circulation each day by lymphatic system