Vertebrae Function/Joints
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards related to movement anatomy, thoracic and rib cage, sacral plexus, gait application, and lumbosacral plexus.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
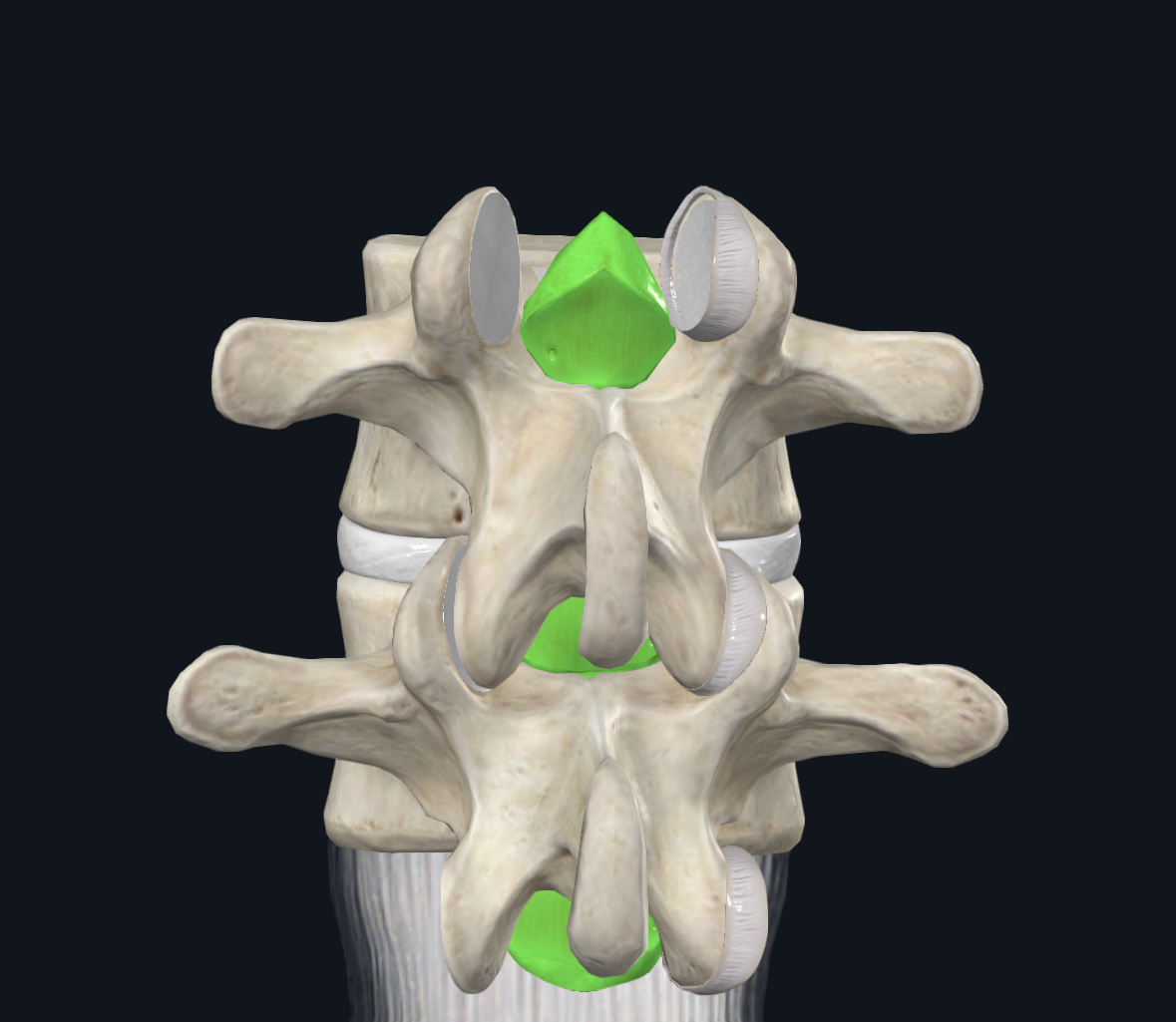
Ligamentum flavum function (limits…?)
Limits flexion
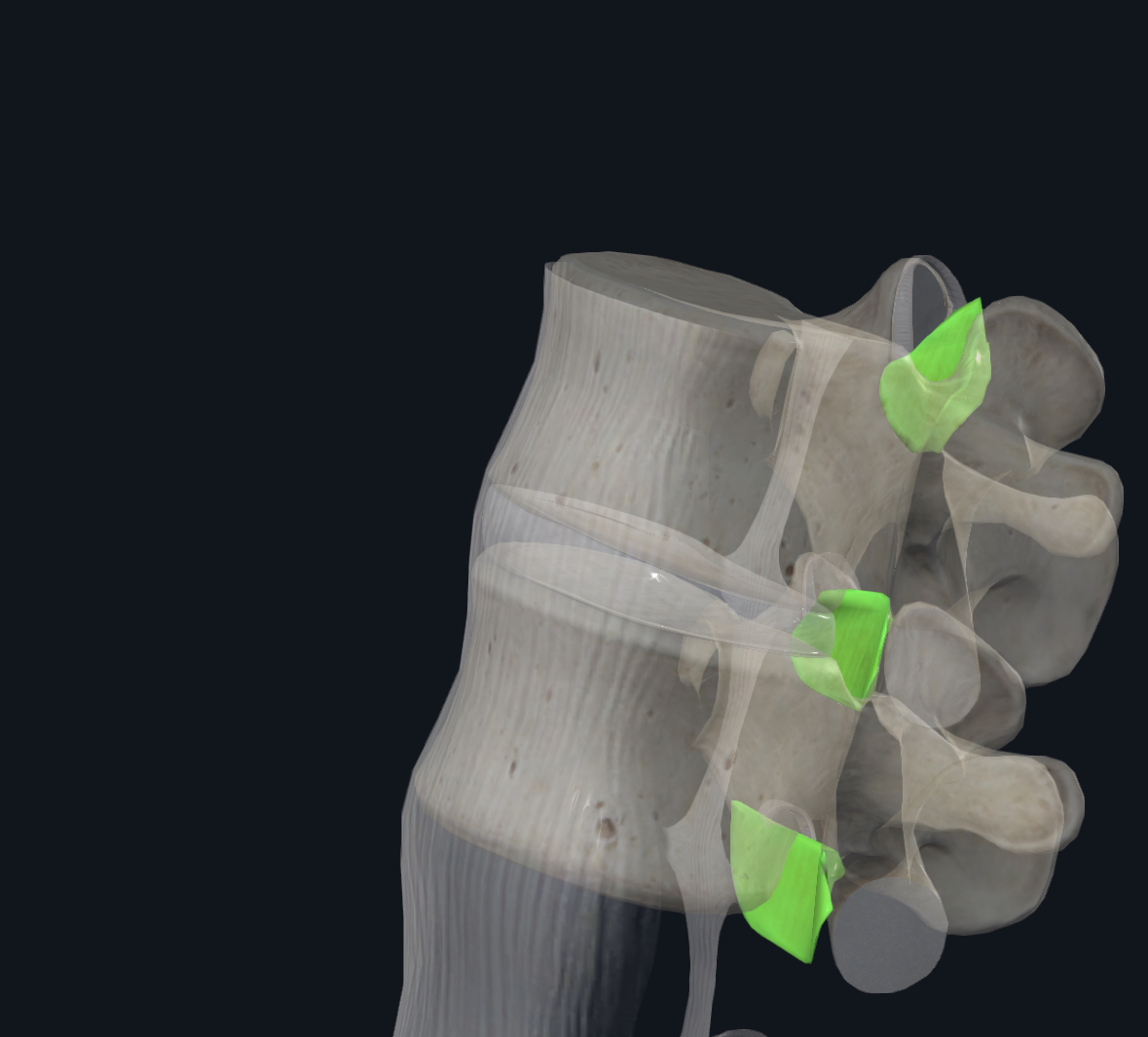
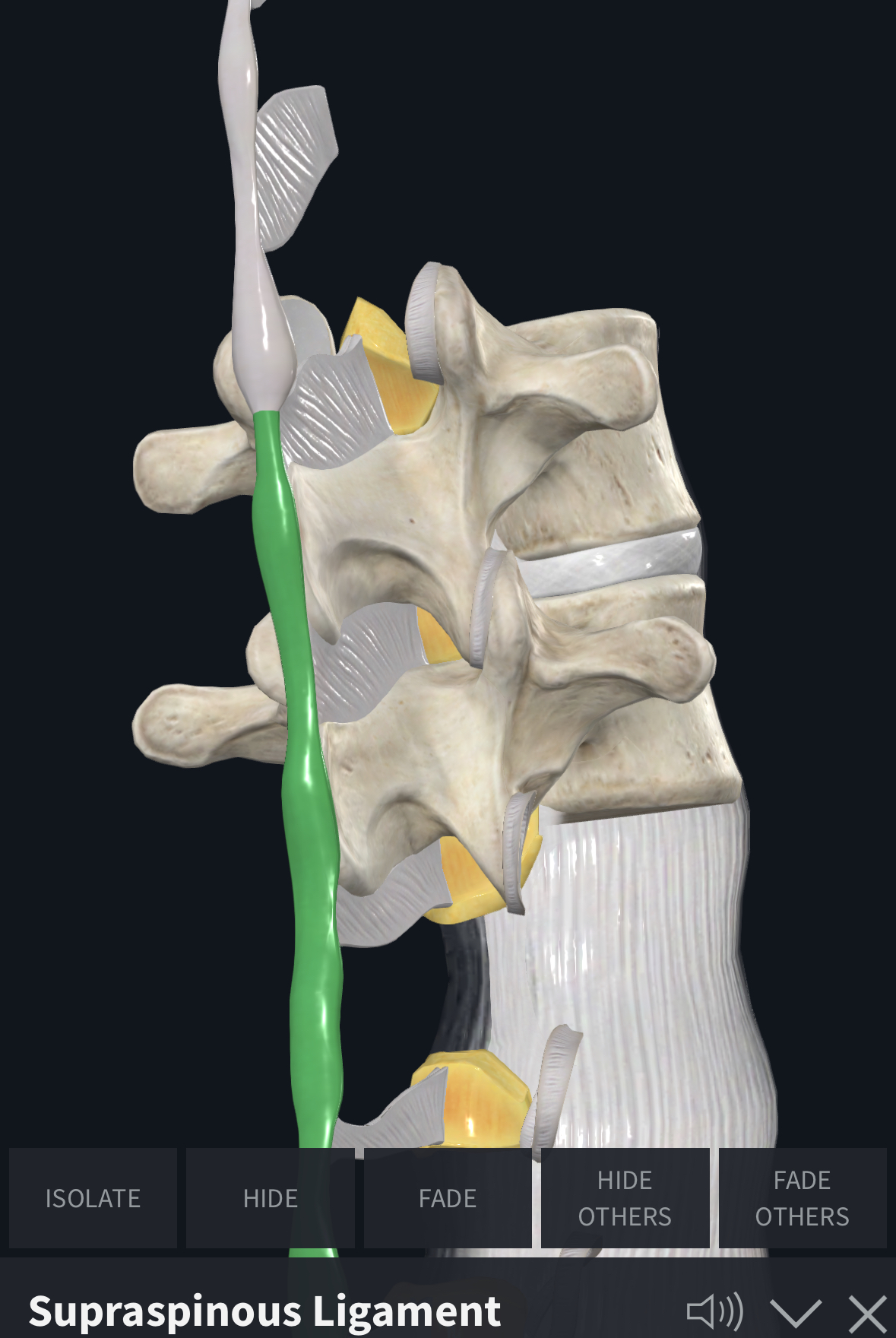
Supraspinous ligaments function (limits…?)
Limit flexion
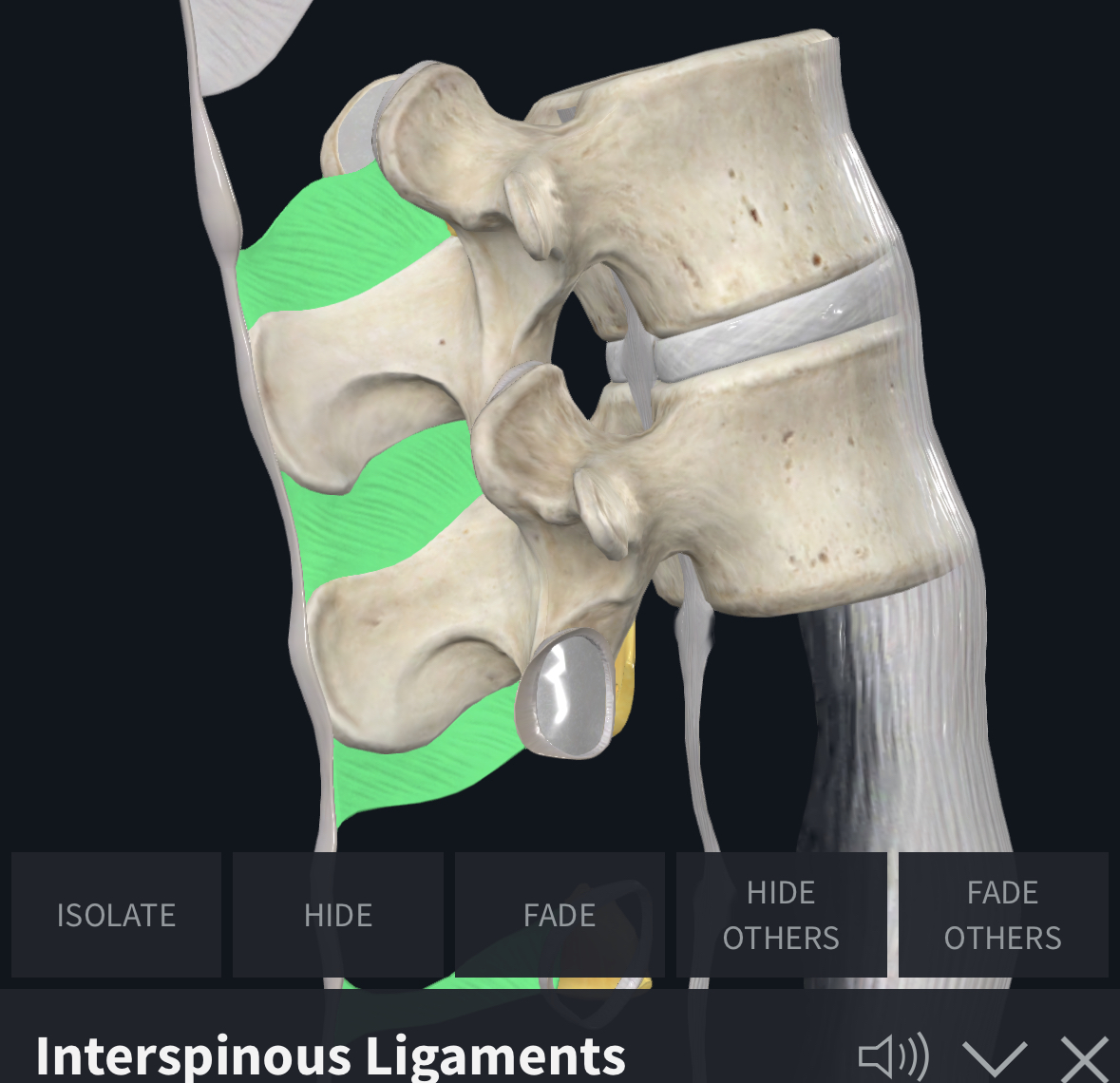
Interspinous ligaments limit…?
Limit Flexion
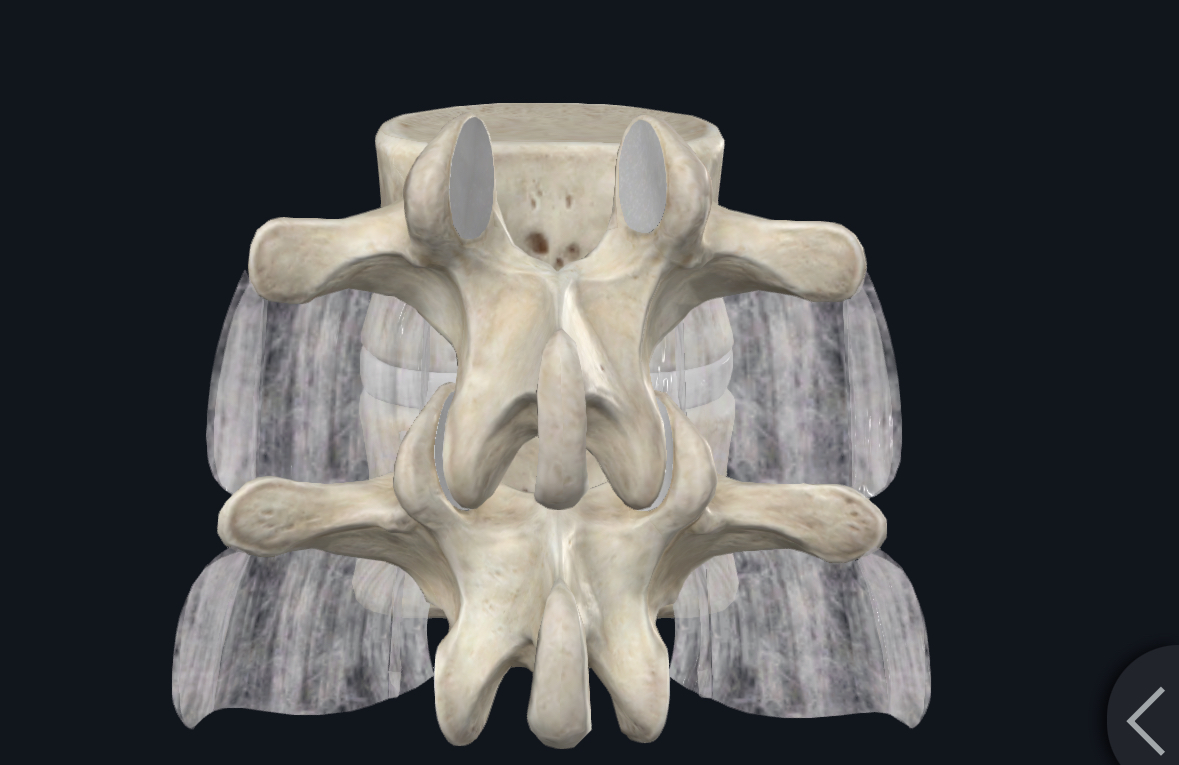
Intertransverse ligaments limit…?
contralateral lateral flexion
Capsule of the apophyseal joints function
Adds stability to the vertebral column; limits extension or excessive lordosis in the cervical and lumbar regions
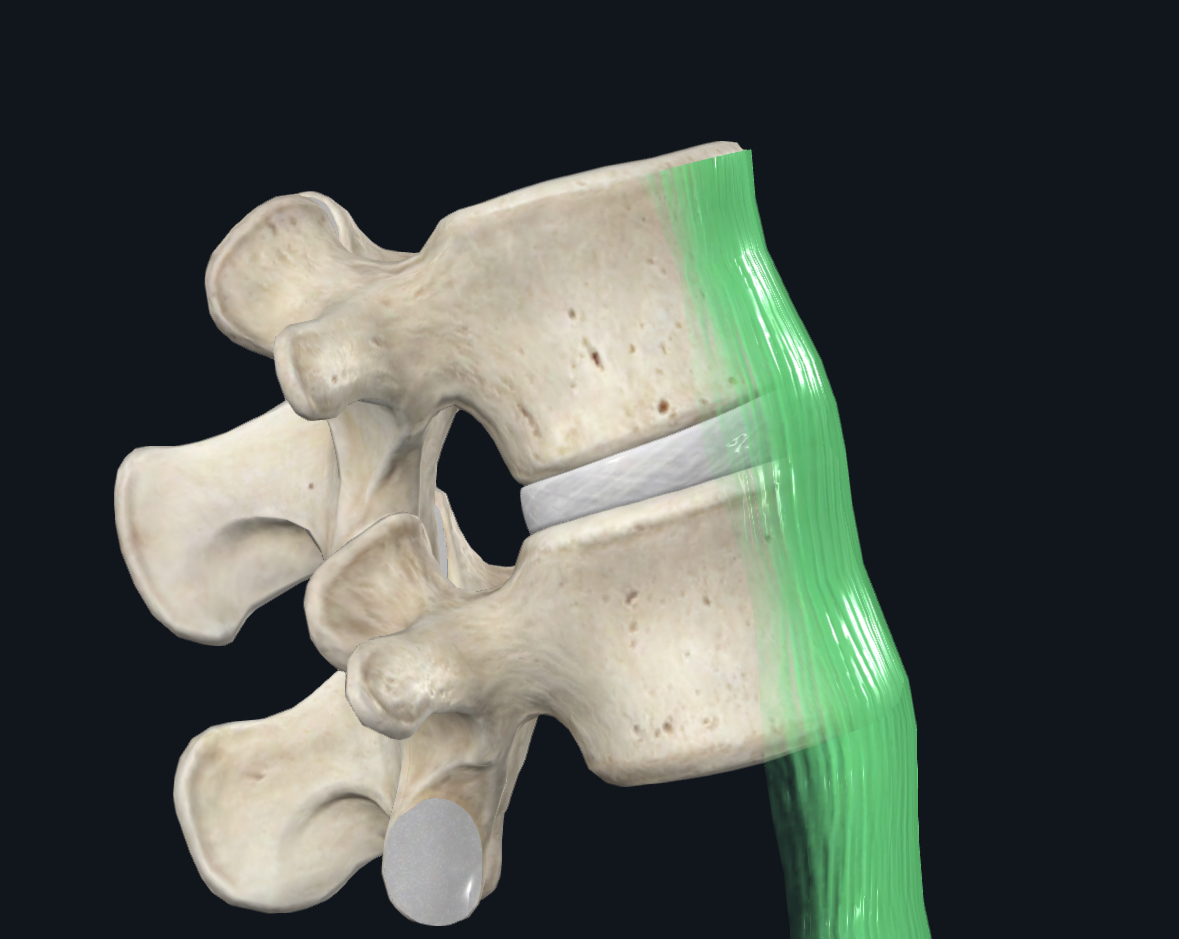
Anterior longitudinal ligament function
Stabilizes the vertebral column; limits flexion; reinforces the posterior annulus fibrosus
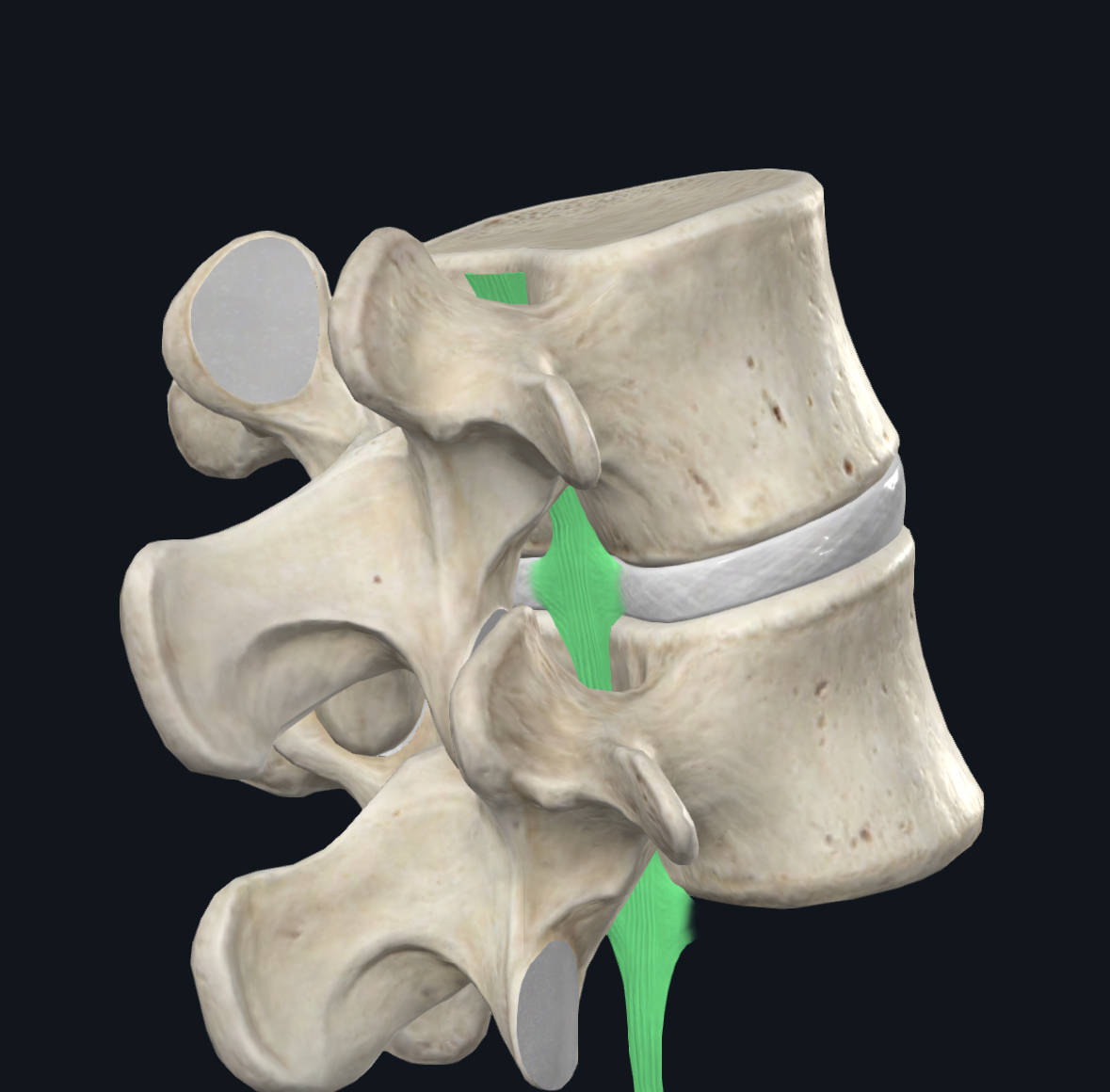
Posterior longitudinal ligament function
Strengthens and supports the apophyseal joint
Costal facets
Articulation with the posterior aspect of the ribs
Thoracic Cavity
Ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum define the volume of the thoracic cavity.
Facet Joint Orientation in Cervical Spine
Supero-lateral
Facet Joint Orientation in Thoracic Spine
Postero-lateral
Facet Joint Orientation in Lumbar Spine
Medial
Upper Ribs (# & motion)
1-7 (Pump-handle motion)
Lower Ribs (# & motion)
8-10 (Bucket-handle motion)
Floating Ribs (# & motion)
11-12 (immobile)
Sciatic Nerve is…
the LARGEST NERVE in the BODY
Foot Slap
Inability of the dorsiflexor muscles to slowly control plantar flexion
High Stepping Gait
To clear the foot from the ground, the hip and knee must be excessively flexed to advance the leg
Vaulting Gait
Standing on tip-toes creates extra clearance for the contralateral (long) leg to clear the ground during swing
Weak Quadriceps Gait
Forward lean of the trunk shifts the line of gravity anterior to the medial-lateral axis of the knee
Genu Recurvatum
Over-stretched posterior capsule of the knee or paralysis of the knee flexor muscles fails to limit knee extension
Walking With Hip or Knee Flexion Contracture
Increased tightness in tissues that normally allow full hip and knee extension
Weak Gluteus Maximus Gait
Leaning the trunk posteriorly during the stance phase shifts the body's line of gravity posterior to the hip, reducing the demands on the hip extensor muscles
Uncompensated Weak Hip Abductor (Trendelenburg) Gait
The hip abductors of the stance (left) leg are unable to produce enough force to hold the pelvis level; thus the pelvis (and often the trunk) uncontrollably leans to the opposite (right) side
Compensated Weak Hip Abductor (Trendelenburg) Gait
Purposely leaning the pelvis and trunk to the same (left) side as the weak hip abductor muscles. This compensation shifts the line of gravity to the left, closer to the axis of rotation of the stance hip
Hip Hiking Gait
Elevating, or hiking, the pelvis provides extra clearance for the advancing leg
Hip Circumduction
Circumduction creates extra clearance to advance the functionally long leg