Classifications of Joints + Synovial Joints
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the two classifications of joints?
functional and structural
What are the types of functional joints?
synarthroses, amphiarthroses, and diarthroses
What are the types of structural joints?
fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
(F) immovable
Type: Synarthroses
Location: Sutures and gomphoses
(F) partially immovable
Type: amphiarthroses
Location: pubic symphysis, syndesmosis, synchondroses, and intervertebral disc
(F) freely movable
Type: diarthroses
Location: any synovial joint
(S) bones connected through fibrous tissue
Type: fibrous
Location: sutures, gomphoses, and distal tibiofibular joint, b/w radius and ulna, and tibia and fibula
(S) cartilage connects tissue between bones
type: cartilaginous
location: epiphyseal, symphyses, synchondroses
(S) bones connected with hyaline cartilage and surrounded by a joint capsule
type: synovial
locations: shoulder, wrist, elbow, fingers, hip, knee, ankle, and toes
what is syndesmosis membrane?
how is it classified?
where is it present?
greater distance between articulating surfaces and more dense irregular tissue
it is a functional amphiarthroses with structural fibrous tissue
present at distal tibiofibular joint
what is interosseous membrane?
how is it classified?
where is it present?
a substantial sheet of dense irregular connective tissue binding neighboring long bones
functional amphiarthroses with structural fibrous tissue
between radius+ulna, and tibia+fibula
what is synchondroses?
how is it classified?
where is it present?
joint where articulating material between bones is hyaline cartilage
functionally amphiarthroses, structurally cartilaginous
cartilaginous junction of the first rib with the manubrium of the sternum
what is symphyses?
how is it classified?
where is it present?
bones are fused by a layer of fibrocartilage
functionally amphiarthroses, structurally cartilaginous
pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs
what is epiphyseal?
how is it classified?
where is it present?
growth centers during endochondral bone formation
functionally synarthroses, structurally cartilaginous
epiphyseal (growth) plate that connects the epiphysis and diaphysis of a growing bone
What are the types of synovial joints?
planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, ball-and-socket joint
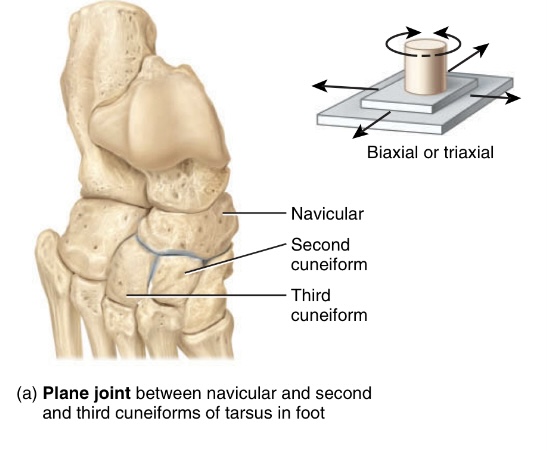
helps in maintaining flexibility and range of motion, with a flat and slightly curved articular surface
type: planar joint
type of motion: gliding and sliding
location: between the navicular and the 2nd + 3rd cuneiforms
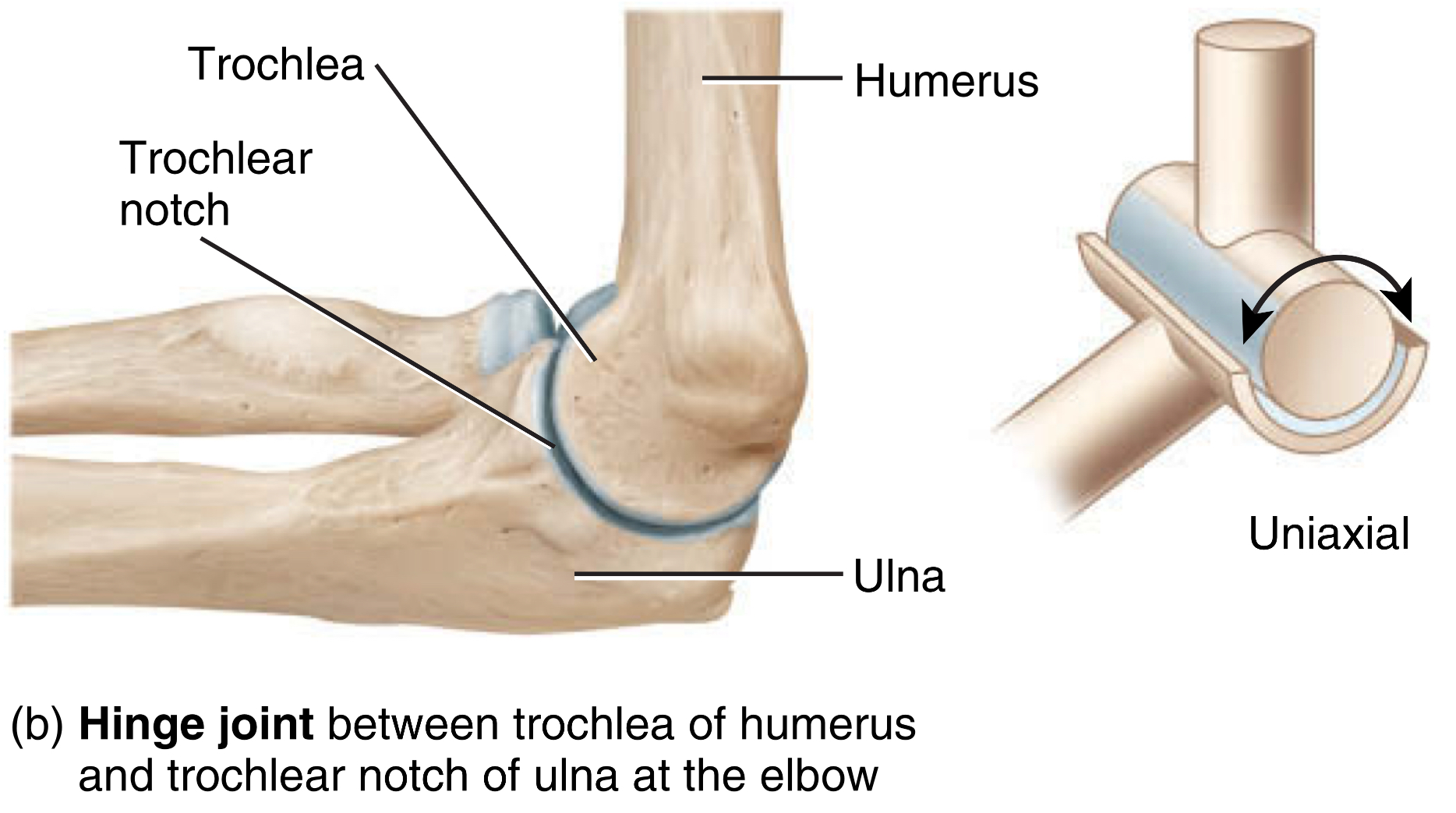
helps with articulating bones with a cylindrical-shaped bone and fitting into a trough like surface
type: hinge joint
type of motion: uniaxial movement, flexion and extension
location: distal humerus and proximal ulna
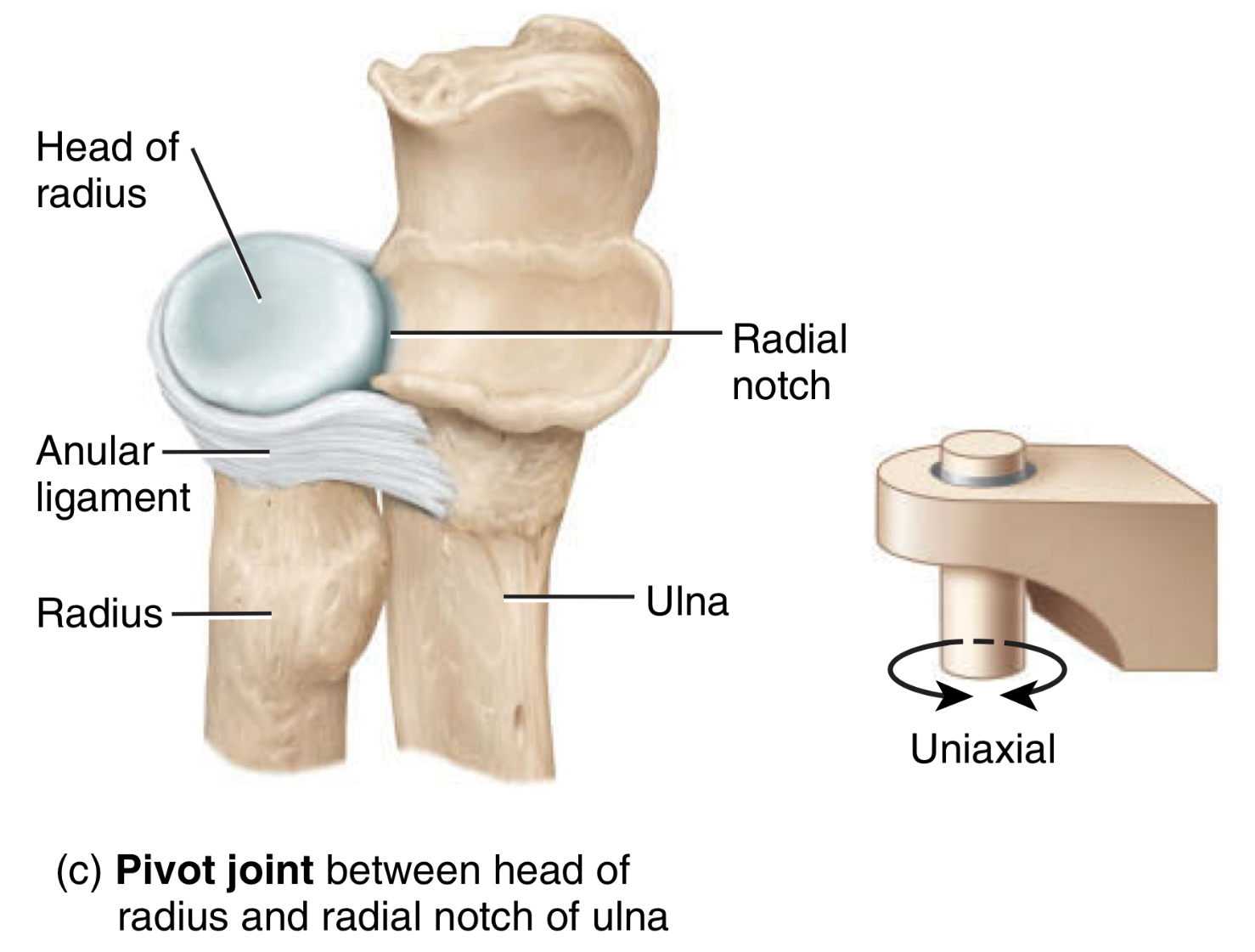
cylindrical bone fits into a ring-like structure
type: pivot joint
type of movement: allows bones to rotate into a ring-like structure
location: atlantoaxial joint, radioulnar joint
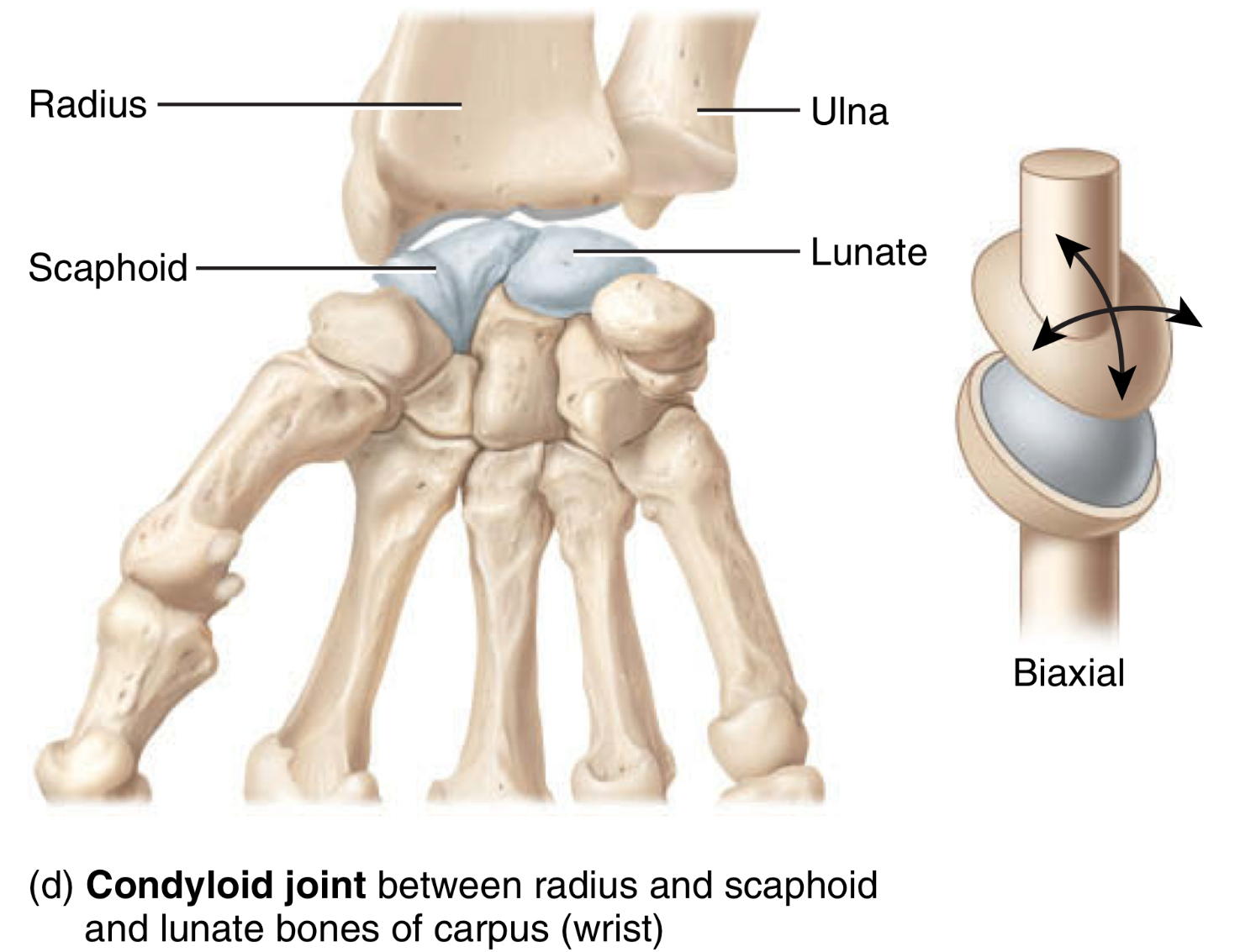
convex oval shape projection of bone fits intro the oval shaped depression of another bone
type: condyloid joint
type of movement: two dimensional movement, flexion and extension, abduction and adduction
location: between radius, scaphoid, and lunate
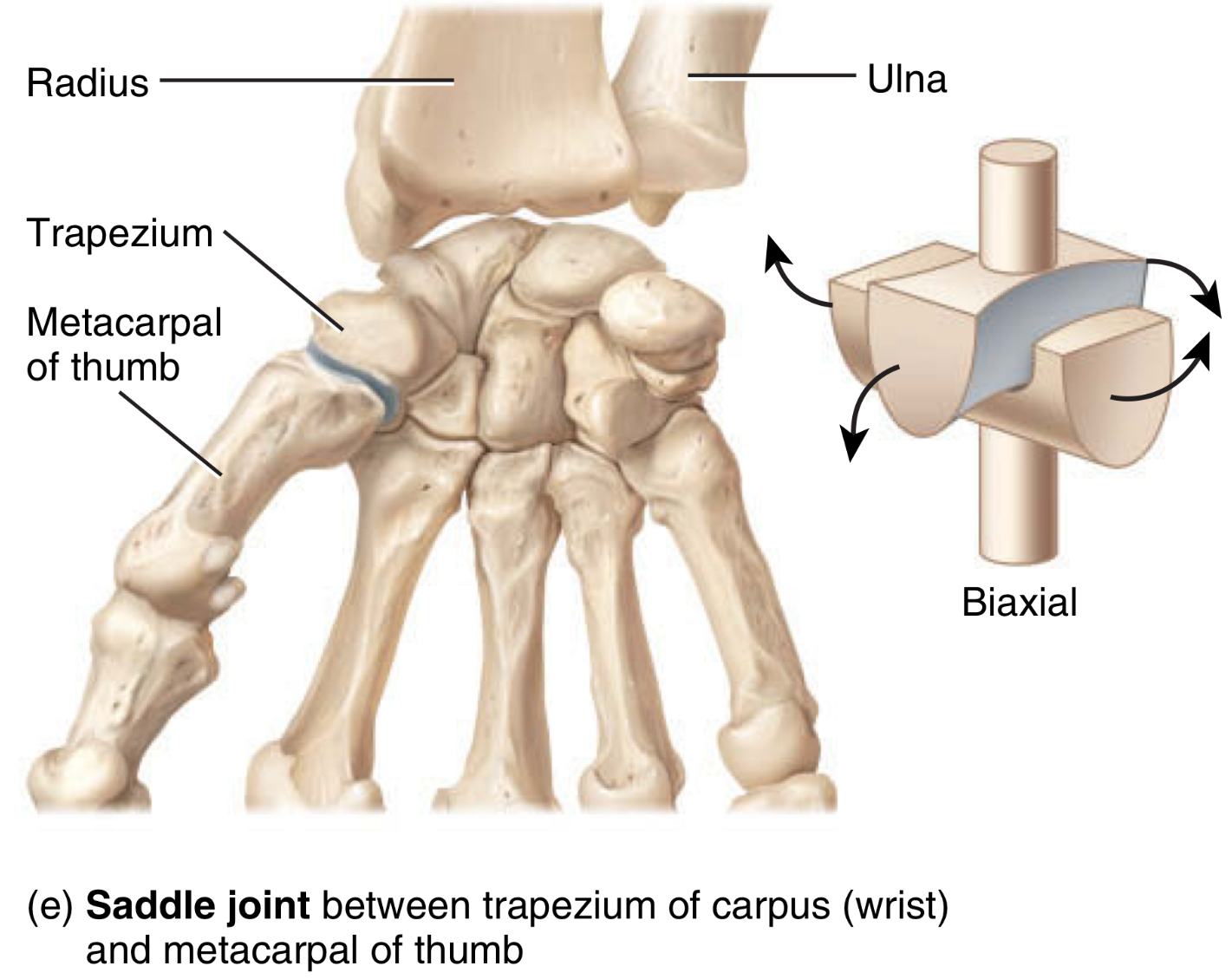
reciprocal concave and convex surfaces fit into concave depression
type: saddle joint
movement: 2 dimensions, flexion + extension, and abduction + adduction
location: between trapezium of carpus and first metacarpal of the thumb
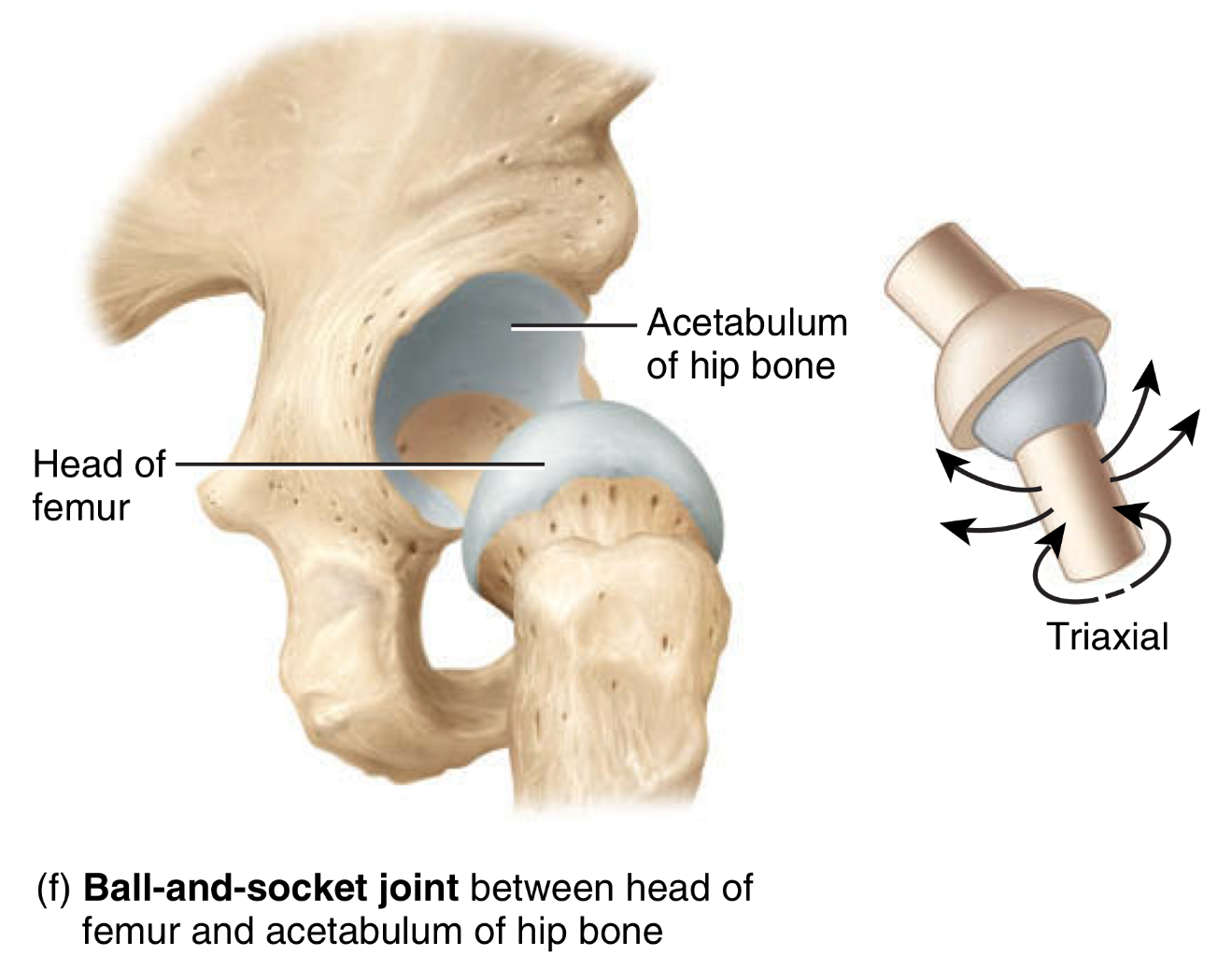
ball shaped bone end that fits into a cup-like depression of another bone, the most extensive range of motion
type: ball-and-socket-joint
movement: flexion + extension, abduction + adduction, and rotation
location: between head of femur and acetabulum of hip bone, and humerus and scapula