Demand Side Policies
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Monetary and Fiscal Policies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What are demand side policies?
Aim to shift AD in an economy
What are the two types of demand-side policies?
Fiscal and monetary
What are fiscal policies?
Involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence AD which the government sets up
What are monetary policies?
Involves adjusting interest rates and the money supply to influence AD, organised by the Central Bank
What are interest rates?
The cost of borrowing money and the reward for saving
What are the goals of monetary policies?
To achieve macroeconomic objectives
A low and stable inflation rate
Low unemployment
Reduce business cycle fluctuations
Promote a stable economic environment for long term growth
To control the level of exports and imports (net external balance)
What does nominal mean?
The fact that the metric has not been adjusted for inflation
What is nominal interest rates?
The headline rate presented by commercial banks - there has been no adjustment to the interest rate based on the inflation rate
What is real interest rates?
The nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate
can also be calculated by CPI
What are expansionary monetary polciies?
Involves reducing interest rates, increasing quantitative easing or depreciating the exchange rate aiming to increase AD in the economy
What do expansionary monetary policies aim to do with AD?
Shift AD to the right

What is a real life example of the use of expansionary monetary policies?
The USA during the 2008 Global Financial Crisis
US Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to almost zero, making borrowing cheaper and supporting both business investment and consumer spending
Used quantitative easing to increase liquidity into the financial system by buying long term assets, lowering longer term IR. This helped to stabilise the financial markets, increase asset prices and support a slow return to growth by encouraging investment
How did the real life example of expansionary monetary policies impact the macroeconomic aims?
Economic growth increases
Inflation rises
Unemployment may fall as output is increasing and more workers are required
Net external demand worsens (higher PL exports may decrease with rising incomes, imports may increase)
What are contractionary monetary policies?
Include increasing interest rates, decreasing or stopping quantitive easing, and appreciating the exchange rate with the aim to decrease AD in the economy
What does contractionary monetary policies aim to shift AD?
Shift AD to the left
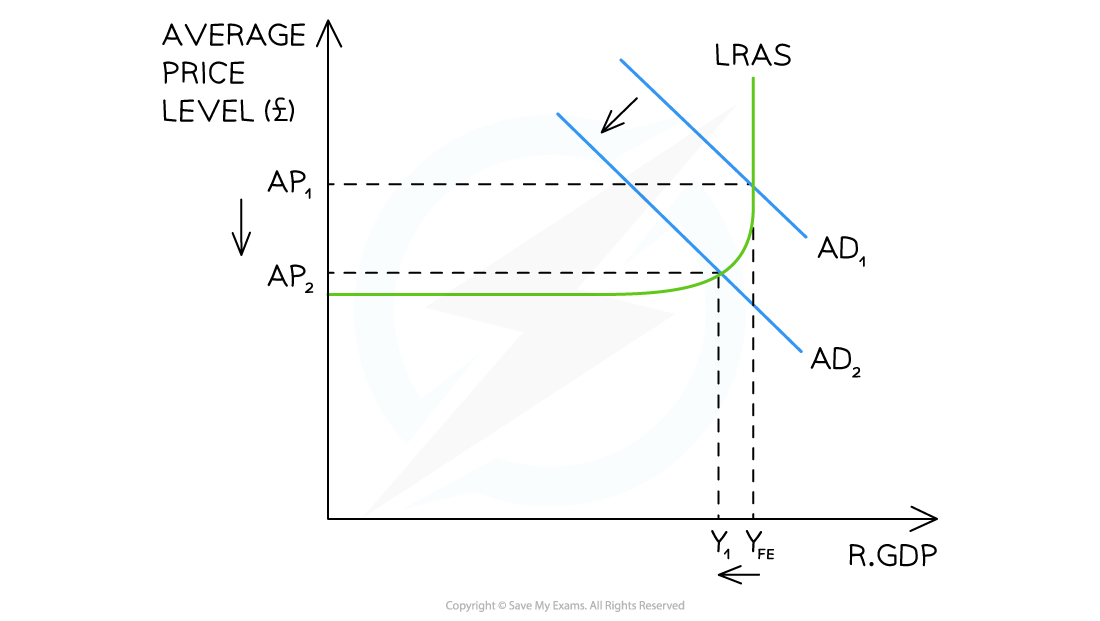
What is a real life example of contractionary monetary policies?
European Central Bank 2011
Inflation rate was rising above 2% due to weak recover from 2008 financial crisis
Raised the interest rates from 1% to 1.5%
Consumption: Higher mortgage and loan costs reduced household spending.
Investment: Costlier loans discouraged investment in infrastructure and business expansion.
Aggregate Demand (AD): Overall AD decreased, helping to control inflation but exacerbating unemployment in weaker Eurozone economies.
In this real life example of contractionary monetary policies, what was the impact of macroeconomic aims?
Economic growth slows down
Inflation eases
Unemployment may increase as output is falling and fewer workers are required
Net external demand is likely to worsen as both exports (too expensive because of higher exchange rate) and imports (imports increase but households have less income to spend) reduce
What is the process of money creation by the commercial banks? (aka Fractional Banking)
Involves a cycle of lending and deposit creation

What are the steps of the money creation process?
Initial Deposit
Reserve Requirement
Lending and loan creation
Deposit expansion
Money supply expansion
What is the initial deposit?
A consumer deposits a certain amount into a commercial bank
What is the reserve requirement?
Banks are required by the Central Bank to hold a certain percentage of their deposits as reserves to meet the demands of customers who want a portion of their money back
What is the lending and loan creation?
Banks keep a fraction of the deposit and lends out the remainder to borrowers
What is the deposit expansion?
The loaned amount is then received by the borrower, who deposits the funds into their own bank account
The new deposits can be used by the other bank as the basis for creating further loans
The cycle continues as banks retain a portion of the new deposits as reserves lend out the rest, leading to further loan creation, deposit expansion and potential new rounds of lending
What is the money supply expansion?
New loans and subsequent deposit creation increase the overall money supply in the economy
The original deposits has effectively multiplied into multiple deposits across the banking system
What are different tools of monetary policies?
Open market operations
Minimum reserve requirements
Quantitative easing
Changes to the base rate
What is open market operations?
Buying and selling government securities (bonds) by the Central Bank in the open market
Transactions typically conducted with commercial banks and other financial institutions
What are bonds?
The government borrows money from private firms and individuals and promises to pay it back in the future with some interest
What is the impact of open market operations on money supply?
By buying the government bonds back from private owners, the CB injects money into the system
Selling the government bonds withdraws money from the free circulation as private institutions receive bonds and the CB receives cash
What is the impact of open market operations on interest rates?
When the CB buys back government bonds, it increases the commercial bank reserves, making it easier to lend money
Increased lending capacity leads to more funds available in the market, potentially lowering interest rates
When the CB sells government bonds, it reduces commercial bank reserves making it harder to lend money - decreasing lending capacityWhat and increasing interest rates
What are minimum reserve requirements?
The regulations set by the CB that mandate the minimum percentage of customer deposits that commercial banks must hold as reserves
Reserves typically in the form of cash or deposits held within the CB
CB specifies the reserve ratio, which is the percentage of customer deposits that banks must hold as reserves
What is the objective of minimum reserve requirements?
Ensure the stability and soundness of the banking system
CB aims to enhance liquidity and solvency of banks
Provides a buffer against deposit with-drawls or unexpected financial shocks
What is the impact of minimum reserve requirements on money supply?
Banks required to hold a higher reserve ratio = less money available to lend or invest and the money supply decreases
Banks allowed to decrease their reserve ratio = more money available to lend or invest and the money supply increases
What is the base rate?
The interest rate at which the CB lends money to commerical banks
What are changes to the base rate?
Have a ripple effect through the economy
Called a transmission mechanism

What is a transmission mechanism?
Has an activator and several steps in a process resulting in a particular outcome
What are some key vocab for transmission mechanism?
Official rate: the base rate of interest from the CB
Market rates: The interest rates set by commercial banks for heir customers (savings and loans)
Asset prices: The price of any resource/good that can provide future economic benefits
Exchange rate: The price of one currency in terms of another
Net external demand: The demand for a country’s exports
Inflation: A sustained increase in the average price level of goods/services in an economy
What is quantitative easing?
A monetary policy tool used by the CB to stimulate the economy when traditional monetary policy measures (eg IR cuts) have become less effective

How does quantitative easing link with transmission mechanism?
CB buys bonds > commercial banks receive cash for their bonds > liquidity in the market increases > commercial banks lower lending rates > consumers and firms borrow more > consumption and investment increases > AD increases > inflation increases
What are the strengths of monetary policies?
CB can operate independently and can consider the long term outlook
Contractionary policies often effective during inflationary gaps - targets inflation and maintains stable prices
Frequency policy alterations (4-8 times a year) allows for constant adjustments to macroeconomic variables - can be quickly amended or reversed
What are the weaknesses of monetary policies?
Conflicting goals eg. economic growth puts upward pressure on inflation
Expansionary policies is less effective during a deflationary gap - the larger output gap the less effective, consumers may not respond to lower IR when confidence is low
Expansionary policies leads to cheaper credit which can inflate asset prices in the long term
IR has limitations of downward adjustment - the closer it gets to zero, the less effective changes are
QE may help solve current issues in the market, but the extra money supply may lead to rapid inflation once the market fundamentals have improved
What is the difference between QE and open market operations?
QE: CB creates new electronic credits which basically ‘prints’ new money to ease liquidity in the market
Open market: uses existing reserves
What are expansionary fiscal policies?
Reduces taxes or increases government spending to generate further economic growth with the aim to increase AD

What are contractionary fiscal policies?
Increasing taxes or decreasing government spending to slow down economic growth or reduce inflation with the aim to decrease AD

How are fiscal policies usually presented by?
Annually by the Government through the Government Budget
What is government budget?
A document that presents the government revenue and expenditure plans for the fiscal policies ahead
What is a balanced budget?
Government revenue = government expenditure
What is a budget deficit?
Government revenue < government expenditure
What is budget surplus?
Government revenue > government expenditure
How is a budget deficit financed?
Through public sector borrowing which then gets added to the public debt
What are different sources of government revenue?
Taxation
Sale of goods/services
The sale of government owned assets
How is taxation a source of government revenue?
Direct taxes are imposed on income and profits and paid directly to the government by the individual or firm
Indirect taxes are imposed on spending - the supplier is responsible for sending the payment to the government
Depends on the PED and PES producers are able to pass on a proportion of the indirect tax to the customer
The less a consumer spends the less indirect tax they pay
How is the sale of goods/services a source of government revenue?
Government owned firms sometimes charge for the goods/services that they provide
How is the sale of government owned assets a source of government revenue?
Privatisation can generate significant government revenue during the year in which the government sells the asset
What is privatisation?
The transfer of ownership and control of firms/assets from the State (public sector) to the private sector
What is government expenditure?
Represents a significant portion of the AD in many economics
How is government expenditure broken down?
Current expenditures
Capital expenditures
Transfer payments
What is current expenditure?
Includes the daily payments required to run the government and public sector (eg. wages and salaries for public teachers) and the payments for goods/services (eg. medicine for government hospitals)
What is capital expenditure?
Investments in infrastructure and capital equipment
What are transfer payments?
Payments made by the government for which no goods/services are exchanged (eg. unemployment benefits). This type of government spending does not contribute to AD as income is only transferred from one group of people to another
What are the goals of fiscal policies to achieve macroeconomic objectives?
Maintain a low and stable inflation rate
Maintain low unemployment
Reduce the business cycle fluctuations
Redistribute income so as to ensure more equity
Control the level of exports and imports (net external balance)
What is the business cycle?
The stages of economic growth the economy moves through including boom, slowdown, recession and recovery
What is redistributing income?
The transfer of income from households or firms that earn more to households that earn less
What happens when a fiscal policy is made?
Creates a ripple effect in the economy impacting the macroeconomic objectives of the economy
What happens when changes to fiscal policies occurs or when changes to AD occurs?
Influence several of the components of AD
Help achieve at least one goal of fiscal policies
What is a real world example of expansionary fiscal policies?
2008 Global Financial Crisis may countries such as the US implemented fiscal policies. For instance, they introduced the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act ($831 billion stimulus package) to boost demand through infrastructure investment and tax cuts
How does the real world example of expansionary fiscal policy impact the macroeconomic aims?
Economic growth increases
Inflation rises but unemployment will decrease to meet demand
What is a real world example of contractionary fiscal policies?
Post pandemic, many countries experienced inflationary pressures due to high consumer demand and supply chain disruptions. The US Federal Reserve signaled fiscal tightening, alongside monetary policy tightening, to curb demand and control inflation
In this real world example for contractionary fiscal policies, what were the impacts on the macroeconomic aims?
Economic growth slows down
Inflation eases
Unemployment may increase as fewer workers are needed
Net external demand improves (less income, imports may fall)
What is the Keynesian Multiplier?
A ratio of change in real income to the injection that created the change
What is the Keynesian Multiplier process?
Based on the idea that one individual’s spending is another individual’s income
Extra consumption = extra income > spend more > expenditure is now income for the next level of individuals
What is a result of the successful rounds of spending?
The final increase in national income is much larger than the initial injection
What is the size of the multiplier dependent on?
The size of leakages that occur during the process
The higher the leakages, the smaller the multiplier
Therefore, the multiplier can work in reverse > when injections are reduced
Where does the initial injection shift AD?
To the right
What are marginal propensities?
The proportion of the next dollar earned that a consumer saves, consumes, is taxed, or purchases imports with. They are calculated for economies and provide insight into how each additional dollar of income is allocated
What is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and the formula for it?
The proportion of additional income that is spent on consumption (C)
MPC = ∆C/∆Y
What is marginal propensity to save (MPS) and the formula for it?
The proportion of additional income that is saved (S)
MPS = ∆S/∆Y
What is marginal propensity of tax (MPT) and the formula for it?
The proportion of additional income that is paid in tax (T)
MPT = ∆T/∆Y
What is marginal propensity to import (MPM) and the formula for it?
The proportion of additional income that is spend on imports (M)
MPM = ∆M/∆Y
How can the multiplier be caluclated?
Focusing on the MPC: Multiplier = 1/(1-MPC)
Focusing on the withdrawals: Multiplier = 1/MPW = 1/(MPM+MPS+MPT)
What is the significance of the multiplier in shifting AD?
The greater the withdrawals, the smaller the value of the multiplier (vice versa)
The greater the MPC, the higher the value of the multiplier (vice versa)
What happens when one of the factors that impact disposable income change the multiplier?
Taxes increase = value of the multiplier reduces
IR increases = savings increase + consumption decrease = multiplier reduces
Exchange rate appreciates = level of imports increase = multiplier decreases
Confidence in the economy increases = consumption increase = multiplier increases
Why is it useful for governments to know the value of the multiplier?
Can use it to judge the likely economic growth caused by increased spending
Why is there a time lag for the multiplier?
Takes time for the successive rounds of income to work through the economy
What are the strengths of using fiscal policies?
Spending can be targeted at specific industries
Highly effective in restoring confidence during a deep recession
Redistributes income through taxation
Reduces negative externalities through taxation
Increased consumption of merit/public goods
Short term government spending = increase in AS of an economy
What are economic stabilisers?
Automatic fiscal changes that occur as the economy moves through stages of the business cycle

What are the effects of automatic stabilisers in a recession?
Automatically be lower tax revenue due to the nature of progressive taxation - as income falls households are taxed less
Unemployment rises, the government will pay higher unemployment benefits/transfer payments which households will then use for consumption
Both of them will result in real GDP being higher than it would otherwise been
What are the effects of automatic stabilisers during an economic boom?
Automatically be higher tax revenue due the nature of progressive taxation - as income rises households are taxed more
Unemployment falls = government will pay less unemployment benefits/transfer payments which households don’t get, therefore decreasing consumption
Both will result in real GDP being lower than it would otherwise been - automatic disflationary effect
What are the weaknesses of fiscal policies?
Political pressures
Unsustainable debt
Conflicts between objectives
Time lags
Crowding out
What is meant by political pressures as a weaknesses?
Polices can fluctuate significantly with new governments are elected
Long term infrastructure projects may lack follow-through
What is meant by unsustainable debt as a weaknesses?
Increased government spending can create budget deficits which are added to the national debt
Repaying this debt may lead to austerity on future generations
What is national debt?
The cumulative total past government borrowing which has to be repaid (with interest)
What is austerity?
Strict policies that cut government spending to reduce budget deficit and repay debt
What is meant by conflicts between objectives as a weakness?
By solving one objective, another one is affected
What is time lags as a weakness?
Difficult to predict when desired effect on the economy will occur, fiscal policies also take a longer time to plan and implement than monetary policy
What is meant by crowding out as a weakness?
Refers to the phenomenon where expansionary fiscal policies, specifically government spending, can result in a reduction of private sector spending or investment
Government borrowing results in competition with others in the economy who want to borrow the limited amount of savings available
This competition causes the real interest rates to rise and private investment decreases

Why are private firms put off from borrowing loanable funds?
Due to the increased rate of interest and investment falls, resulting in AD decreasing
Private firms have been crowded out of the market by the government actions