DC ANATOMY CH6 Integumentary
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
What is the primary function of apocrine glands?
- production and secretion of yellowish sweat
- can be viscous milky sweat
- contains fatty substances and proteins
what is the primary function of eccrine glands?
Thermoregulation (regulating temperature)
what is another term for eccrine glands?
merocrine
What type of tissue makes up the reticular layer? characteristics included
- coarse dense & fibrous CT
- makes up most of dermis (80%)
- elastic fiber (stretch-recoil)
- collagen (strength)
- cleavage lines found here
what type of tissue makes up the papillary layer? characteristics included
- superficial to reticular layer
- dermal papillae lie on top of dermal ridges
- give rises to epidermal ridges (CT)
what is another term for all the ridges?
friction ridges
What are the classifications of burns?
- First degree
- Second degree
- Third degree
What is the characteristics of first degree burn?
- EPIDERMAL/EPIDERMIS damage only
- localized redness, edema (swelling), and pain
- SUPERFICIAL BURN
What is the characteristics of second degree burn?
- BLISTERS appear
- epidermal & upper dermal damage (epidermis/dermis)
- AKA PARTIAL-THICKNESS BURN
What is the characteristics of third degree burn?
- entire thickness of skin affected
- AKA FULL-THICKNESS BURN
- skin turns gray-white, cherry red, or blackened
- nerve endings are destroyed (meaning not painful)
- skin grafting is usually necessary
- debridement
In a third degree burn where the nerve endings are destroyed, is it painful for the patient?
Yes, because they can't feel anything. (because of the nerves being destroyed)
What are the THREE colors that a third degree burn can cause?
- gray-white
- cherry red
- blackened
What gives the nail bed its color?
- underlying capillaries
Where is the nail bed located?
its the epidermis underneath the keratinized nail plate
What is cyanosis?
- BLUISH discoloration
- caused by LOW OXYGENation of hemoglobin
What is erythema?
- REDDENING of skin
- caused by fever
- caused by hypertension
- caused by inflammation
- caused by allergy
What is pallor?
- blanching OR pale white
- caused by anemia
- caused by low blood pressure (BP)
- caused by fear
- caused by anger
What is jaundice?
- yellow cast
- in eyes
- caused by liver disease
What is bronzing?
- inadequate steroid hormones
- ADDISON'S DISEASE
what is hemoglobin?
- pinkish hue of fair skin
- lower levels of melanin
What is carotene?
- yellow-orange pigment
- obvious in palms/soles
What is bruises?
- black/blue
- caused by CLOTTED BLOOD beneath skin
What are all the skin cancers?
- basal cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma
- melanoma
What is basal cell carcinoma and its characteristics?
- most common
- least malignant
- stratum basale cells proliferate
- slowly invade the dermis & hypodermis\
- treatment: surgical excision
What is squamous cell carcinoma and its characteristics?
- second most common
- metastasize
- involves keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
- scaly redden papule on scalp, ears, lower lip, or hands
- treatments: radiation therapy OR surgical removal
What is melanoma and its characteristics?
- most dangerous
- cancer of melanocytes
- highly metastatic
- resistant to chemotherapy
- treatments: wide surgical excision accompanied by immunotherapy
What is considered the most dangerous skin cancer?
melanoma
What is considered the least dangerous skin cancer?
basal cell carcinoma
what is the phrase for the layers?
- Come Let's Get Sun Burned
- Come Let's Go Sun Bathe
- Corneum Lucidum Granulosum Spinosum Basale
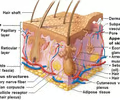
What are the characteristics of epidermis layer?
- keratinized stratified squamous epithelium cells
- AVASCULAR
- cells: kerantinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans, Merkel
- includes CLGSB
What are the characteristics of stratum corneum?
- Avascular
- flattened, non-nucleated, keratinized dead epithelial cells
- function to protect deeper cells from environment
- prevents water loss
- DEAD CELLS
- constantly shedding (sloughing)
- 3/4 (75%) of epidermal thickness
- MOST SUPERFICIAL LAYER
What are the characteristics of stratum lucidum?
- found in ONLY THICK SKIN (palms & soles of feet)
- DEAD CELLS
- cells look clear
- nuclei, organelles, & cell membrane no longer visible
What are the characteristics of stratum granulosum?
- avascular
- cell appear changes since nuclei & organelles disintegrate
- keratinization begins
- cells accumulate LAMELLAR GRANULES
- CELLS START TO DIE
- 3-5 layers of flatted granular cells
- contains shrunken fibers of keratin & shriveled nuclei
What are the characteristics of stratum spinosum?
- intermediate keratin filaments attached to desmosomes that allow them to resist tension & pulling
- KERATINIZED LAYER
- ABUNDANT MELANOSOMES
- DENDRITIC CELLS
- many layers of cells that becomes flattened
- centrally located large oval nuclei
- developing fibers of keratin
What are the characteristics of stratum basale?
- MOST DEEP
- VASCULAR
- layer of stem cells that actively divide (ACTIVE MITOSIS)
- single row of cuboidal or columnar cells
What are the characteristics of dermis layer?
vascular connective tissue (CT)
What happens to blood vessels in COLD environments?
blood vessels CONSTRICT in cold environments
What happens to blood vessels in HOT environments?
blood vessels DILATE in hot environment
What is melanin?
- pigment synthesized in skin made by melanocytes
- exposure to sunlight stimulates production
What is melanocytes?
- produce melanin
- ALL HUMANS HAVE SAME NUMBER OF MELANOCYTES
What is melanosomes?
- carries melanin
- melan is PACKAGED in melanosomes
Color (skin) shade differences are due to...
- different amounts of melanin
- the form of melanin
hat is the order of the layers SUPERFICIAL to DEEP?
stratum corneum -> stratum lucidum -> stratum granulosum -> stratum spinosum -> stratum basale
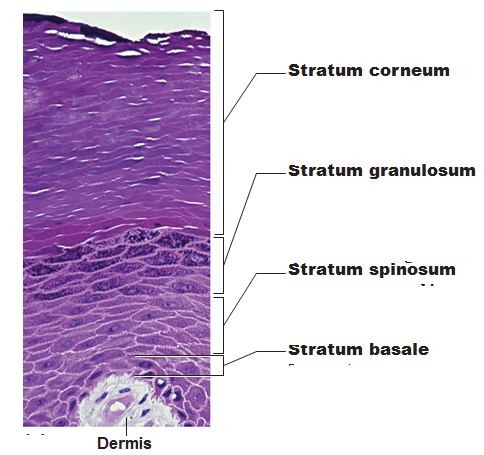
What is the order of the layers DEEP to SUPERFICIAL?
stratum basale -> stratum spinosum -> stratum granulosum -> stratum lucidum -> stratum corneum
What are the major regions of the hair shaft?
medulla, cortex, & cuticle
What is medulla?
central core of large cells & air spaces
What is cortex?
sever layers of flatten cells surrounding medulla
What is cuticle?
outer layer consisting of overlapping layers of single cells
Major regions of the hair shaft
REFER TO PICTURE IN SLIDES/TEXTBOOK
What is the most important risk that leads to skin cancer?
- OVEREXPOSURE TO UV RADIATION
- frequent irritation of skin
What are Langerhans cells?
- star-shaped MACROPHAGES
- patrols DEEP EPIDERMIS
- ACTIVIATES the IMMUNE system
What are Merkel cells?
sensory receptors that sense touch
What is the lamellated corpuscle?
- CT cells
- act as sensory receptors
- reacts to PRESSURE & SENSATION in skin & joints
define alopecia
- hair thinning
- in both sexes after age 40
How is alopecia different than alopecia areata?
- Areata: when the immune system attacks follicles
- autoimmune system disorder
What glands produces ear wax?
- ceruminous glands
- lines the external ear canal
- cerumen = earwax
What is the characteristics and functions of keratinocytes?
- produces keratin
- MAJOR CELLS of the epidermis
- connected by desmosomes denritic cells
- marcophages that ACTIVATE immune system (HORMONES)
What is the characteristics and functions of dendritic cells?
- (Langerhans) marcophages activates immune system
- engulfs foreign antigens and present to WBCS
What is the characteristics and functions of tactile cells?
(Merkel) sensory receptors that sense touch
What is the characteristics and functions of melanocytes?
- produces the pigment melanin
- packaged into melanosomes
- protects nucleus from UV damage
- spider shaped cells
What cells can be found in the dermis?
- fibroblasts
- macrophages
- mast cells
- white blood cells (WBC)
What makes the dermis strong and flexible?
- collagen = strong & resilient
- elasticity / elastin = flexible
What are the two major layers of the dermis?
papillary & reticular
Which layer makes up the greater percentage of the dermis?
reticular makes up 80% of the dermis
What are the two types of sudoriferous glands?
- eccrine (merocrine) sweat glands
- apocrine sweat glands
What are the locations of the apocrine glands?
- axillary areas (EX: armpits)
- anogenital areas
What are the locations of eccrine (mecocrine) glands?
- palms
- soles
- forehead
abundant in all three location
Why would a physician use the rule of nines?
- to evaluate burns
- estimate volume for fluid loss
- body broken into 11 sections
What are desmosomes and what might they do to the skin?
- intracellular junctions
- allows cells to resist tension & pulling
- strong adhesion
- water resistant
How does the skin fight infection?
- dendritic cells engulf foreign antigens (Langerhans & macrophages)
- keratinocytes layers keeps pathogens out (epidermis layer serves as physical/chemical barrier)
(top 2 are more important)
What is the importance of cleavage (tension) lines?
- incisions parallel to cleavage lines heal more readily
- important to surgeons
define keratin
- protein that gives skin & hair its protective properties
- toughening of skin
- found in epidermis
define apotosis
programmed cell death
define striae
- silvery white scars
- AKA stretch marks
- caused by EXTREME STRETCHING of skin\
- leaves dermal tears
define vellus hair
pale fine body hair of CHILDREN and adult females
How does melanin protect you?
- acts as chemical barrier keeping skin protected from UV radiation
- melanosomes transfer to keratinocytes -> protects nucleus from UV damage
define hair root
smooth area within the scalp where keratinization goes on
define arrector pili
- small band of smooth muscle attached to the follicle
- responsible for goosebumps
define hair papilla
- dermal tissue containing a knot of capillaries
- supplies nutrients to hair
define hair matrix
divides the area of bulb that produces hair cells
define eponychium
nail fold that projects onto surface of nail body (cuticle)
define hyponchium
area under the free edge of the plate that ccumulates dirt
define vernix caseosa
- sebaceous gland secretion
- protects the skin of the fetus
- while in watery amniotic fluid
What is another name for sweat glands?
sudoriferous glands
layers of the skin as seen on diagram
refer to slides/textbook
- epidermis
- dermis
- hypodermis (this is CT)