Ch. 9 - Skeletal Muscle
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
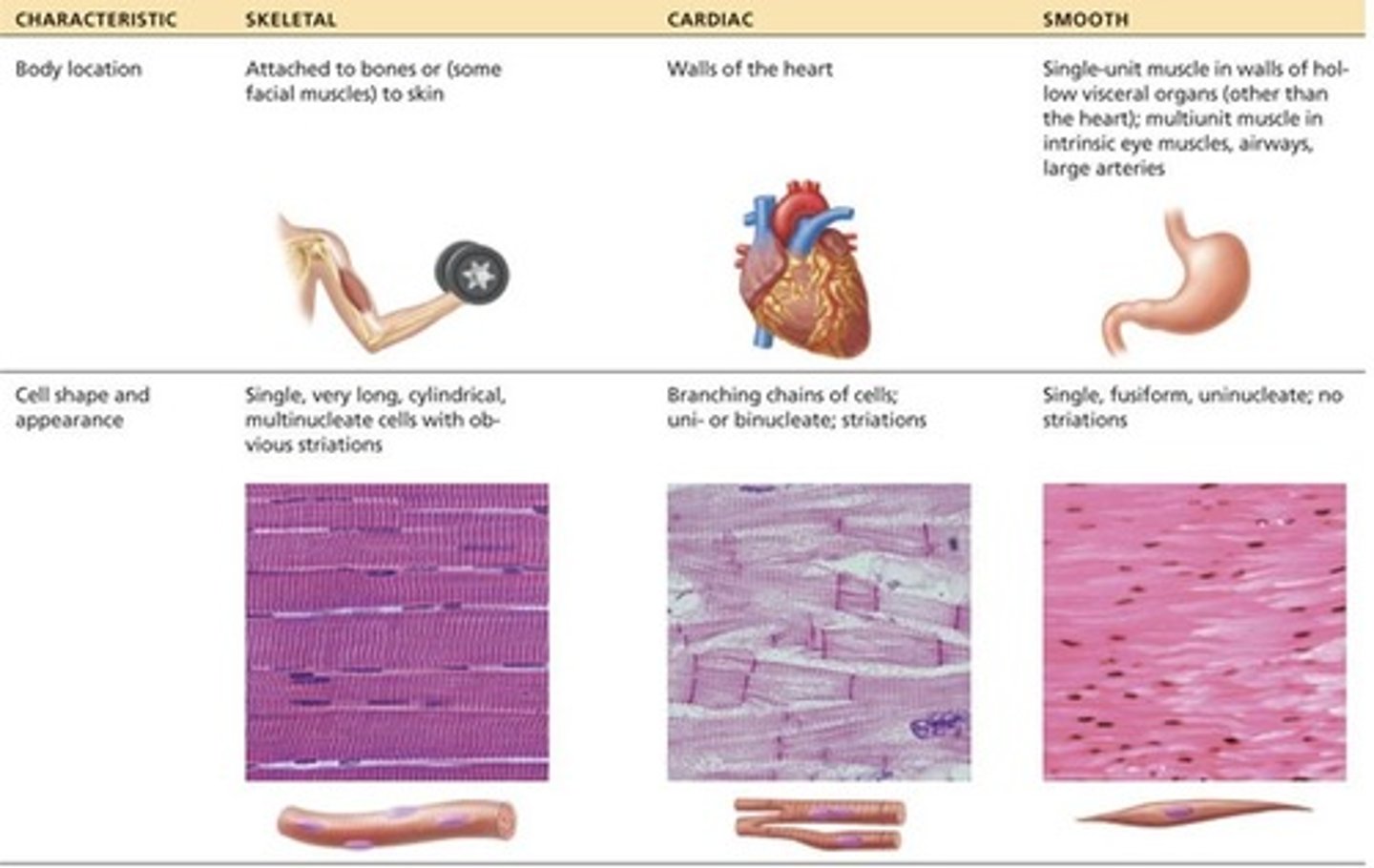
types of muscle tissue
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
muscle tissue functions
body movement
stabilize position
move substances in body
guard body entrances/exits
support soft tissue
produce heat
store nutrients
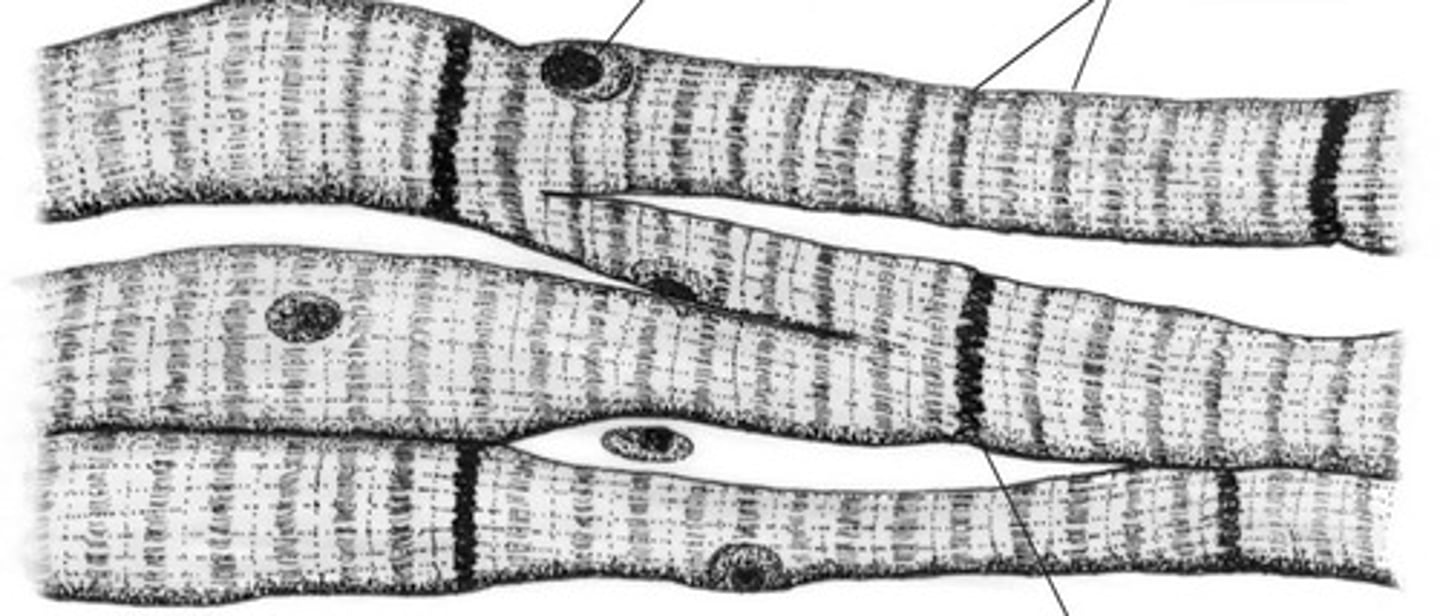
cardiac muscle tissue
involuntary
in heart wall
pumps blood
striations visible microscopically
intercalated discs
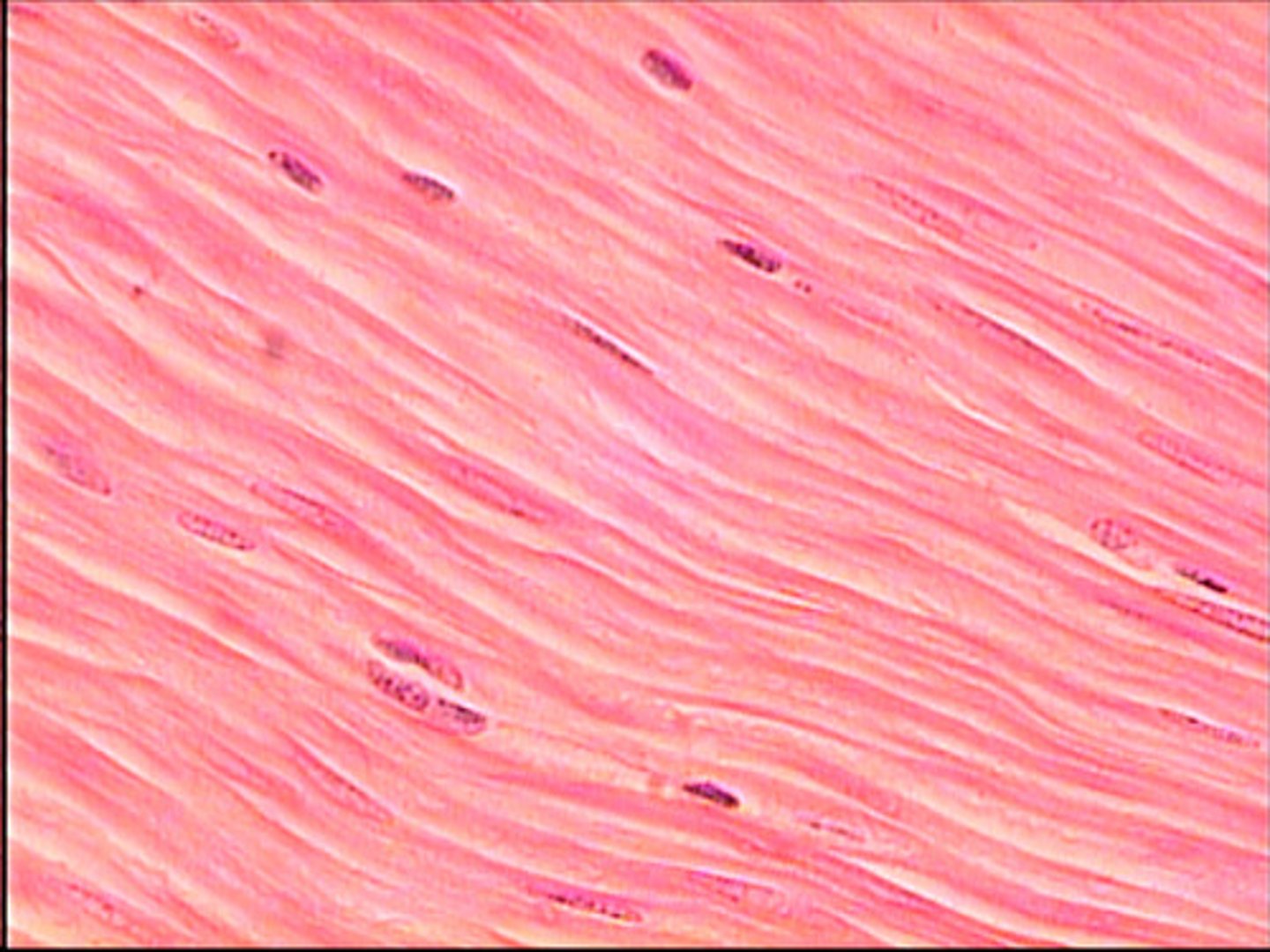
smooth muscle tissue
Involuntary
walls of hollow internal structures
no striations
skeletal muscle tissue
Voluntary
movement - pulling on bones
organ made of mostly skeletal tissue + CT, nerves, blood vessels
muscle cell = muscle fiber

muscle tissue properties
excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
Excitability
can produce electrical signals (action potentials)
Contractility
ability to shorten (contract) when stimulated
Extensibility
ability to stretch without being damaged
Elasticity
ability to return to original shape after being stretched
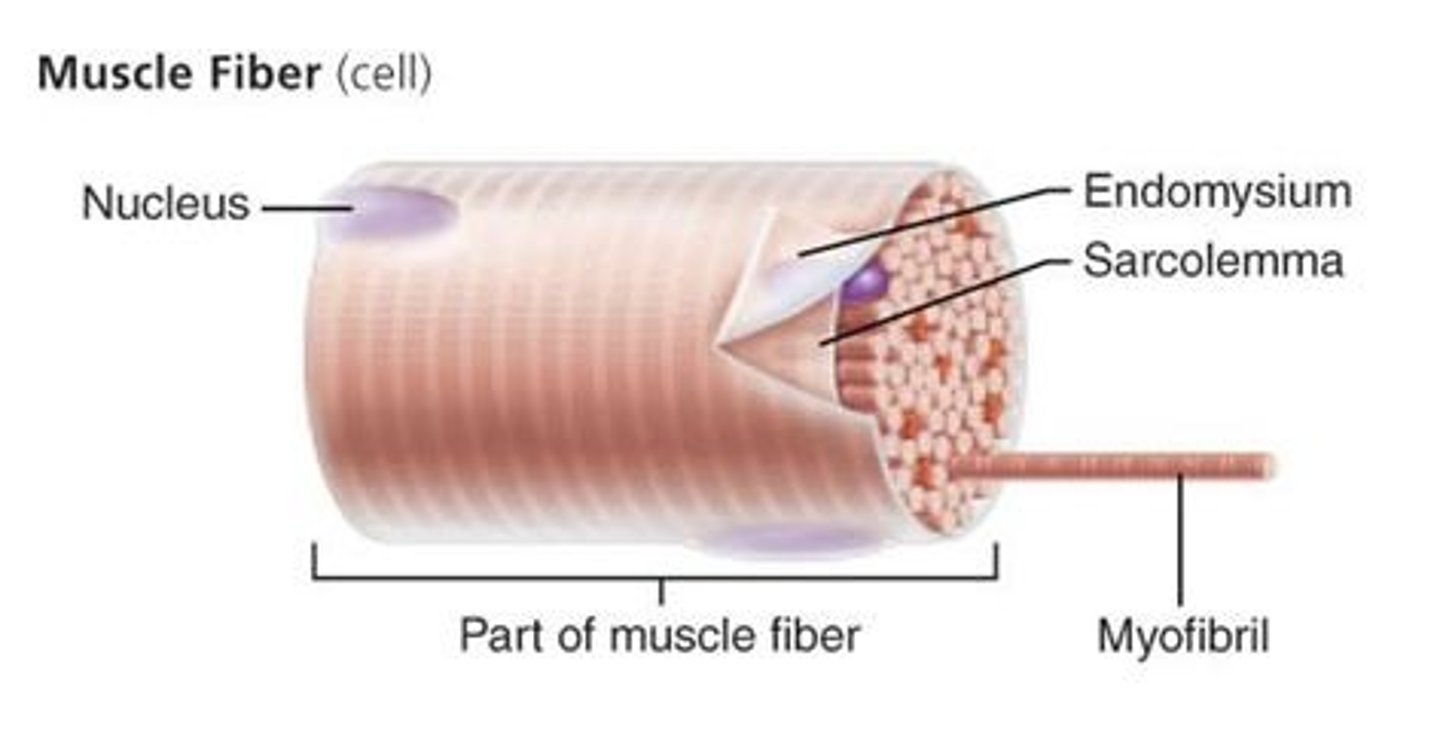
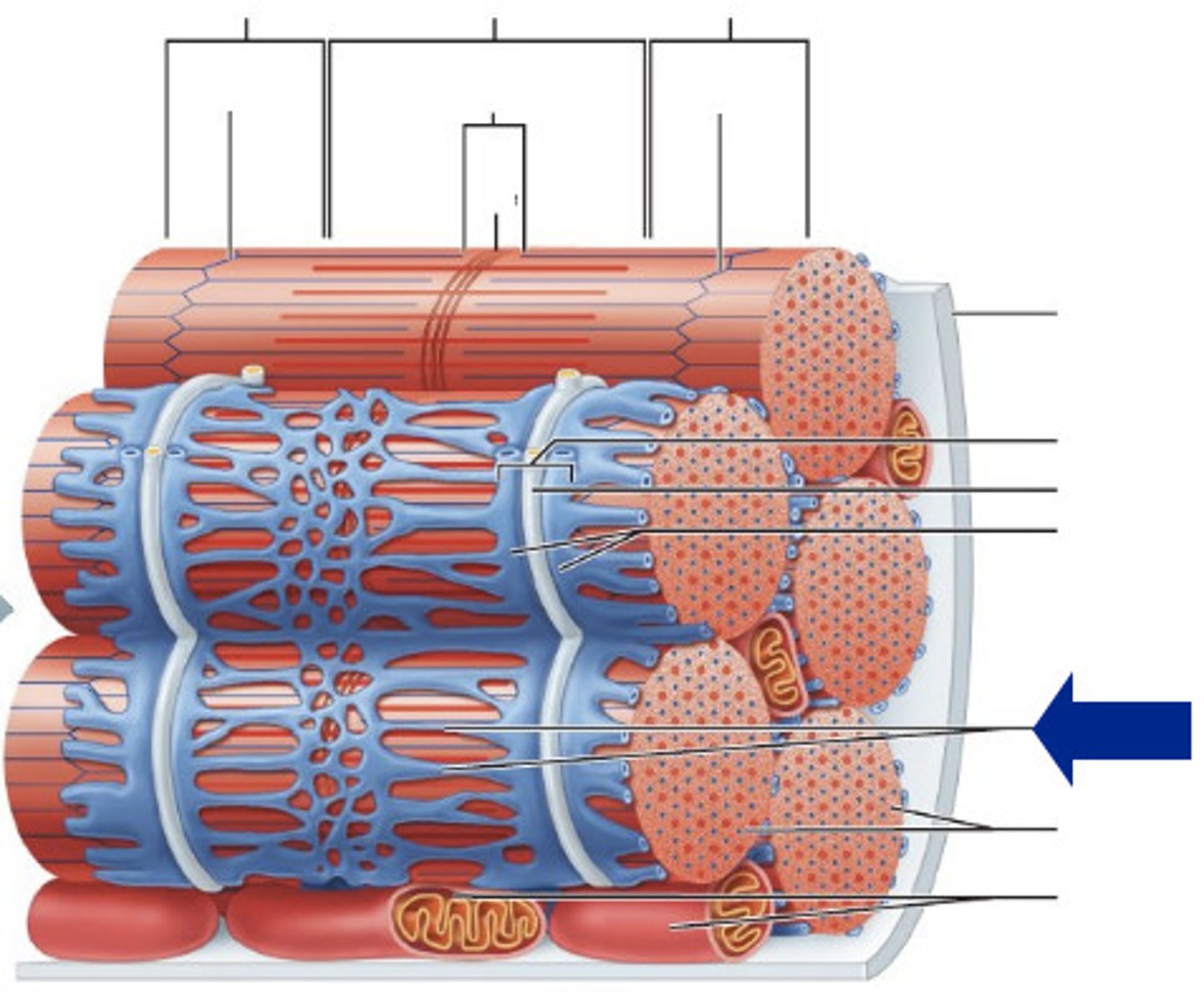
Skeletal muscle structure
epimysium, perimysium, endomysium
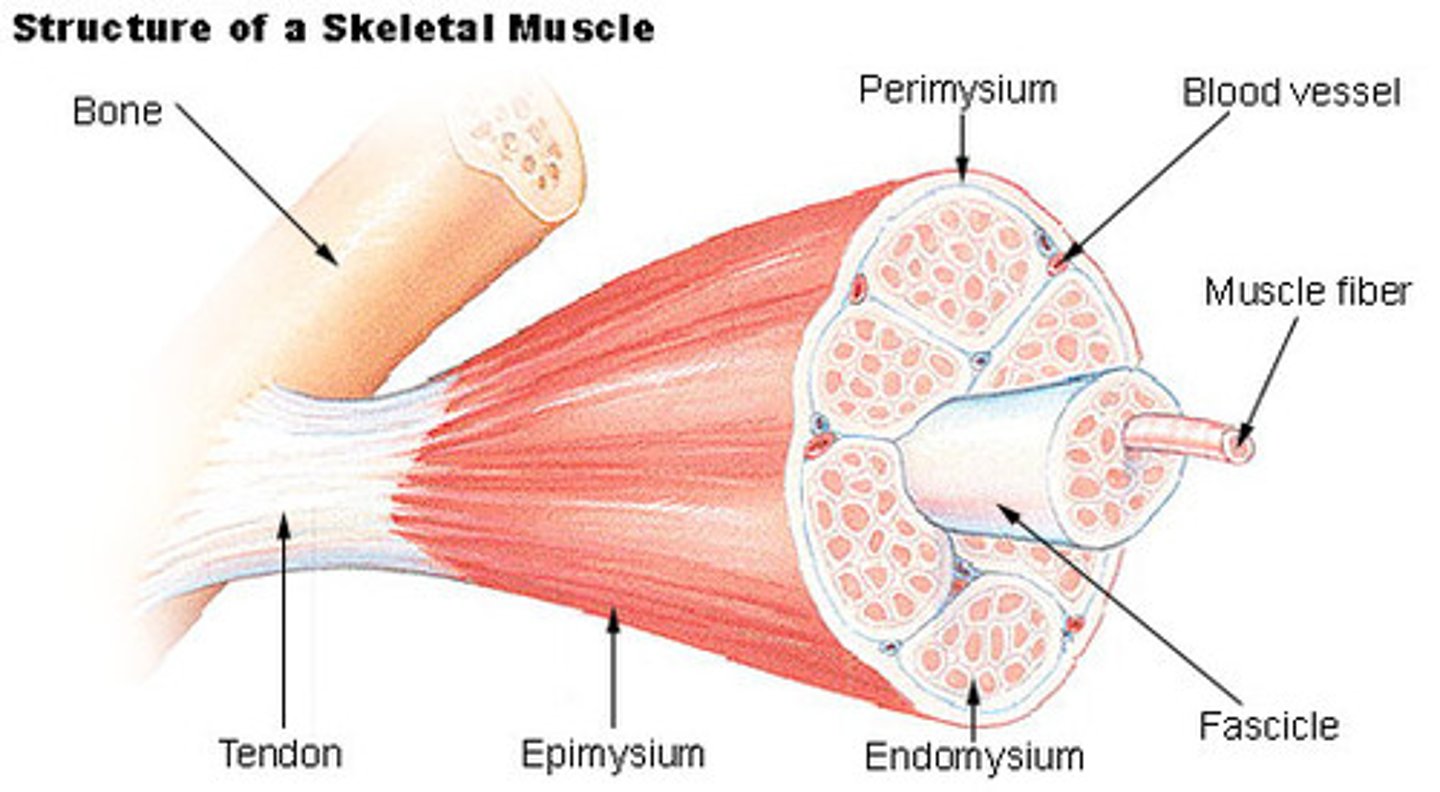
Epimysium
dense sheath of collagen fibers surrounding muscle
connected to deep fascia
Separates muscle from other tissues/organs
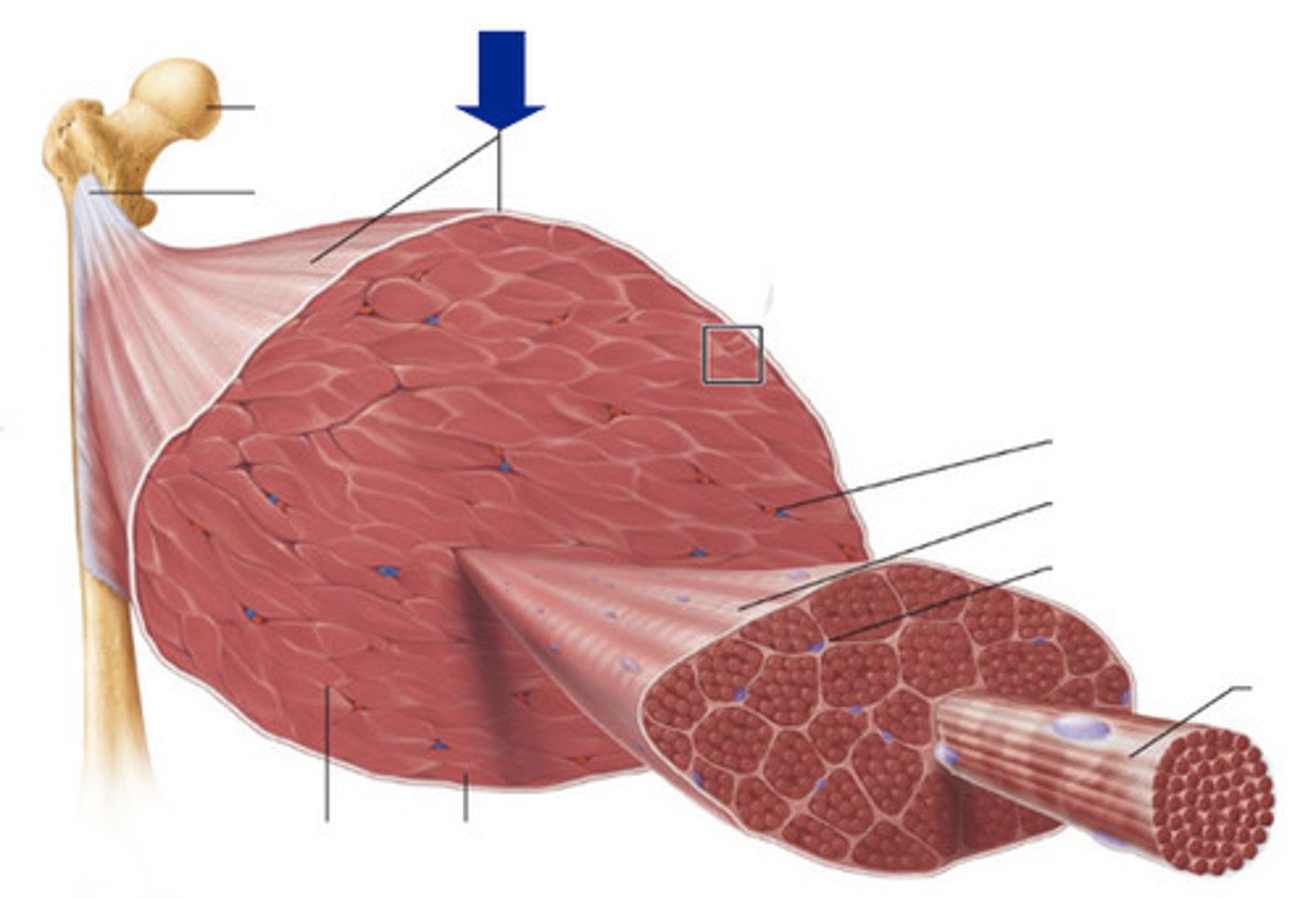
muscle fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
Perimysium
fibrous layer surrounding fascicle
contain collagen, elastic fibers w/ blood vessels & nerves to supply them
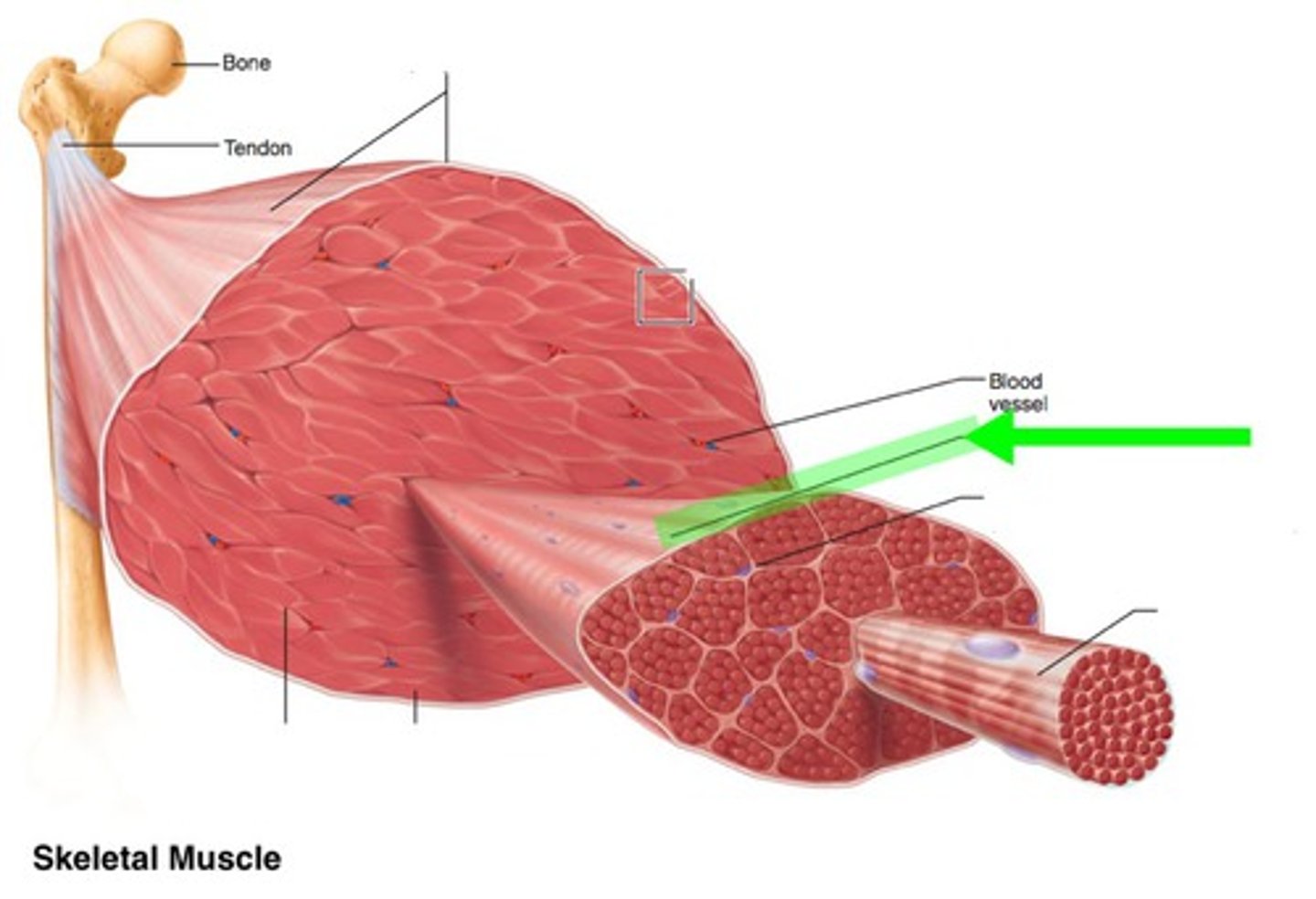
Endomysium
surrounds a muscle fiber
areolar CT
collagen and elastic fibers
blood vessels
nerves
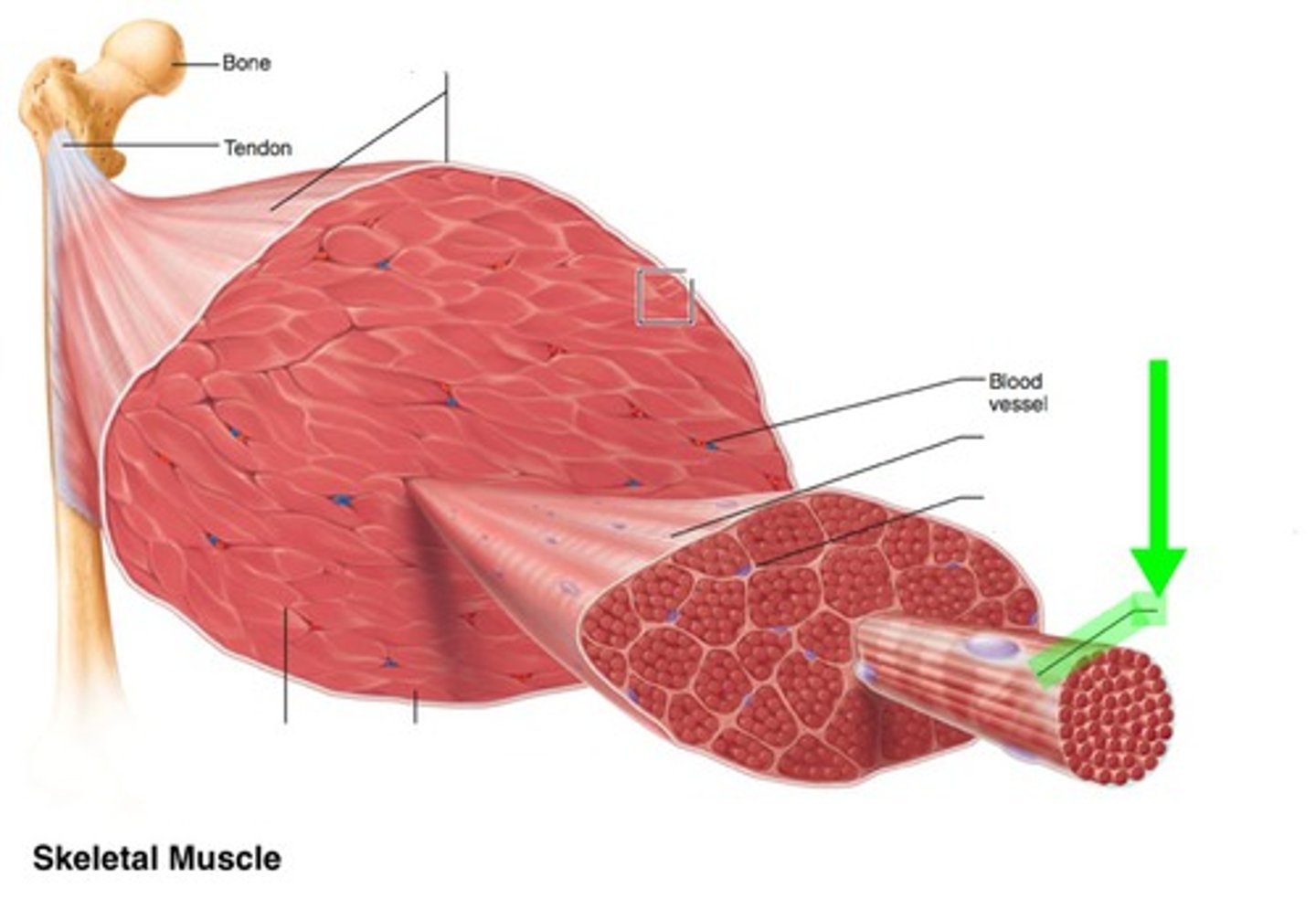
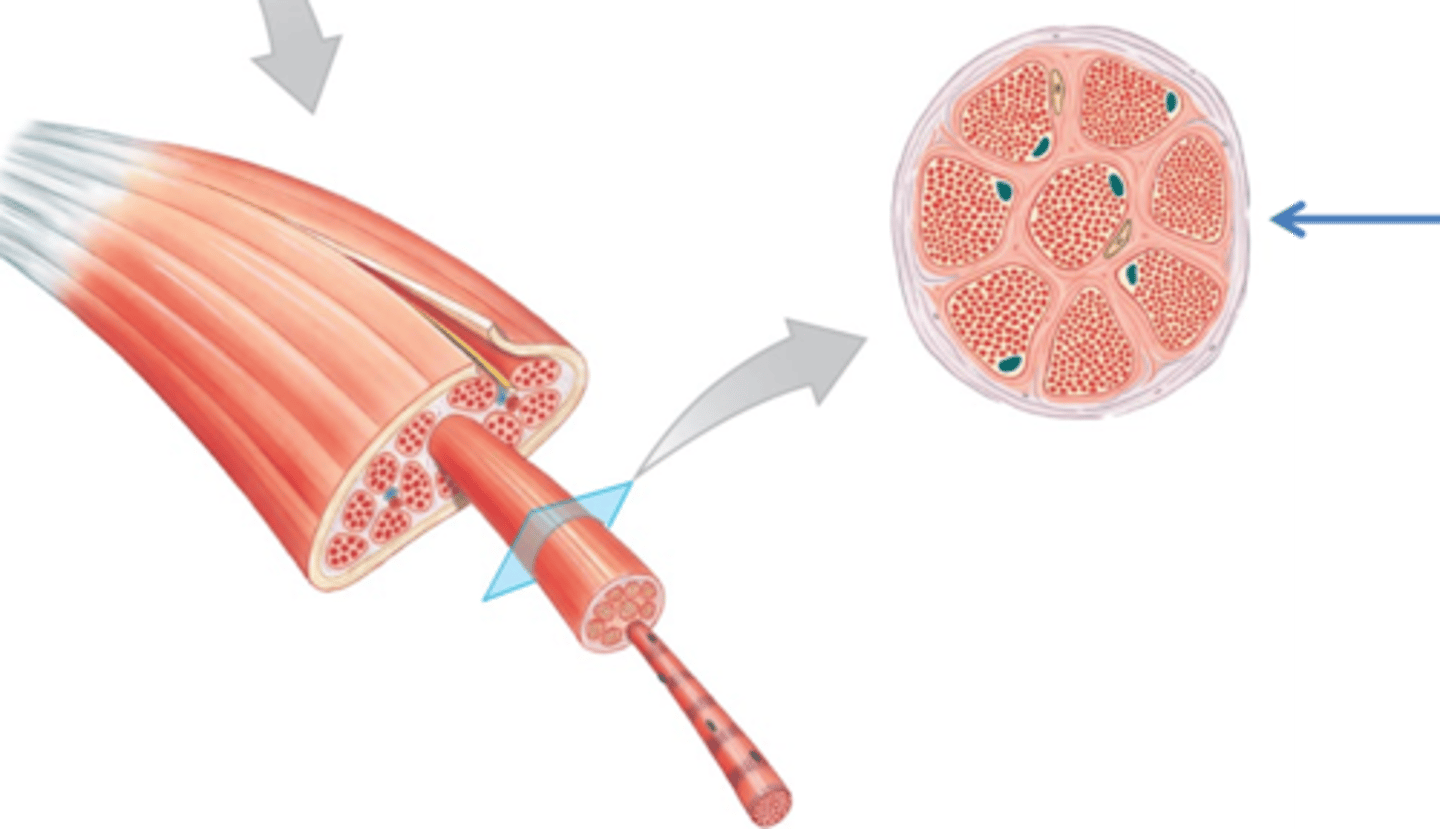
Myofibrils
cylindrical structures extending the entire length of the muscle fiber
Mitochondria along myofibrils
Myofilaments
bundles of protein filaments within myofibrils
Thick and thin filament
thick filaments
primarily composed of myosin
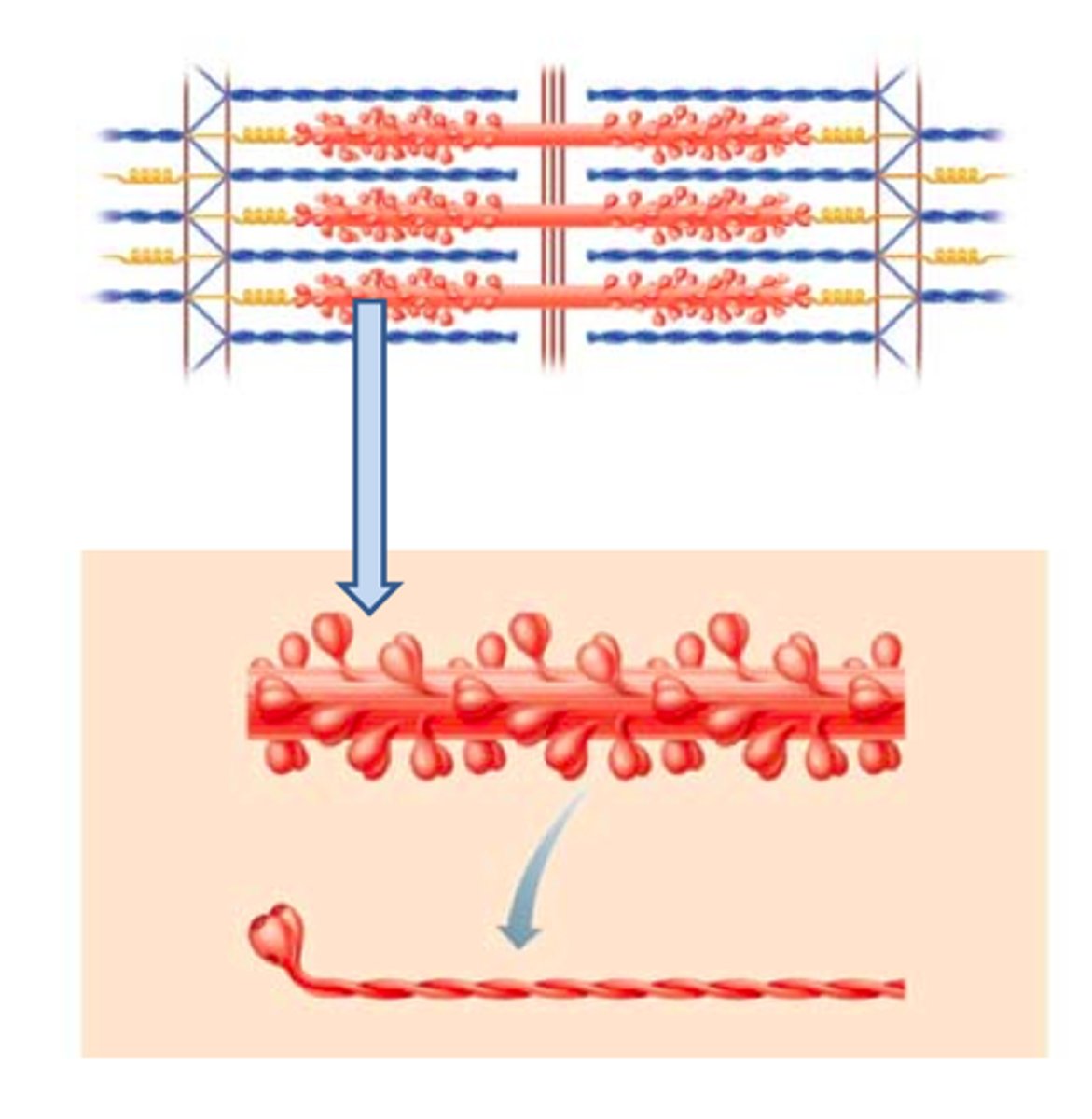
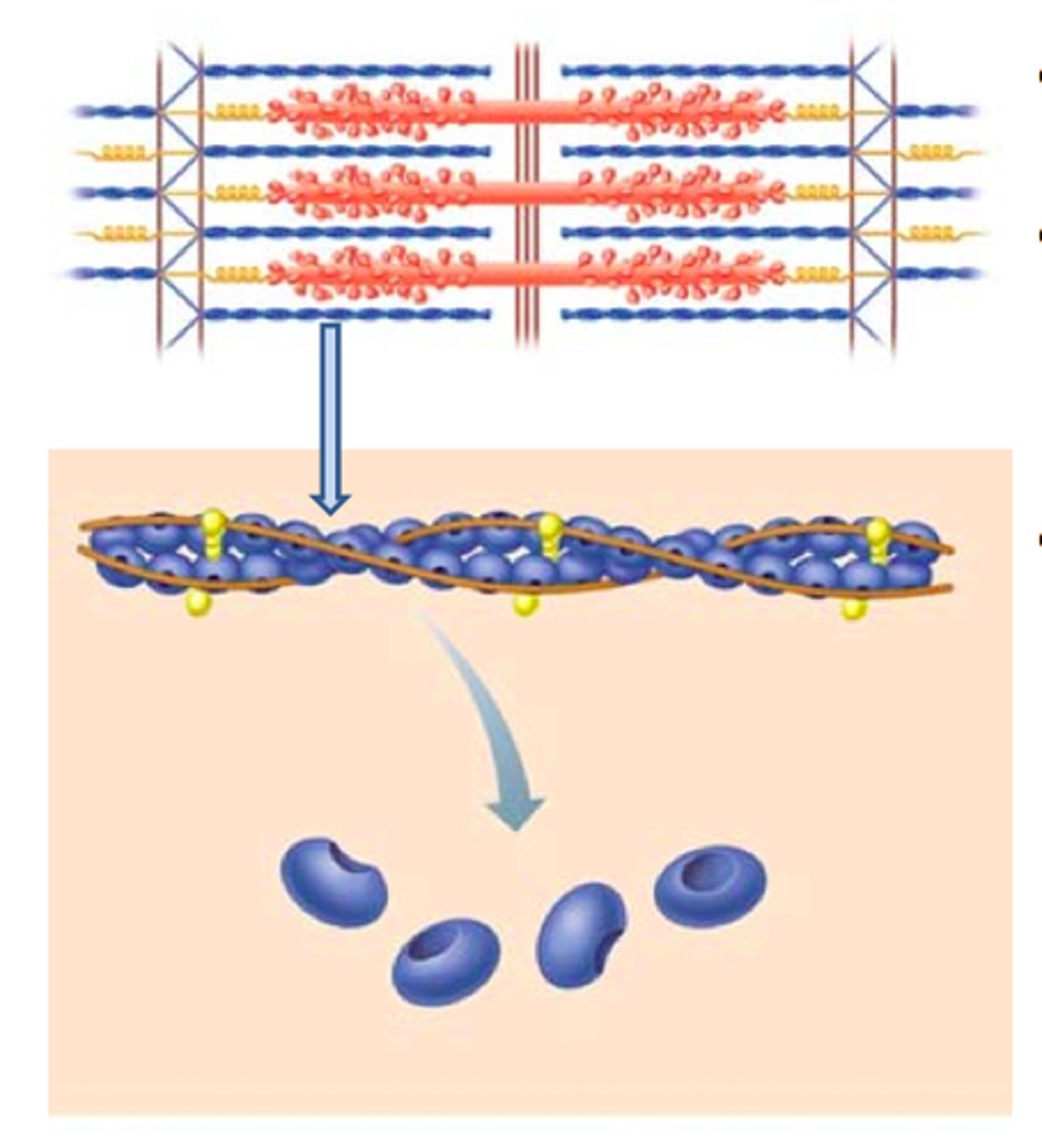
thin filaments
primarily composed of actin
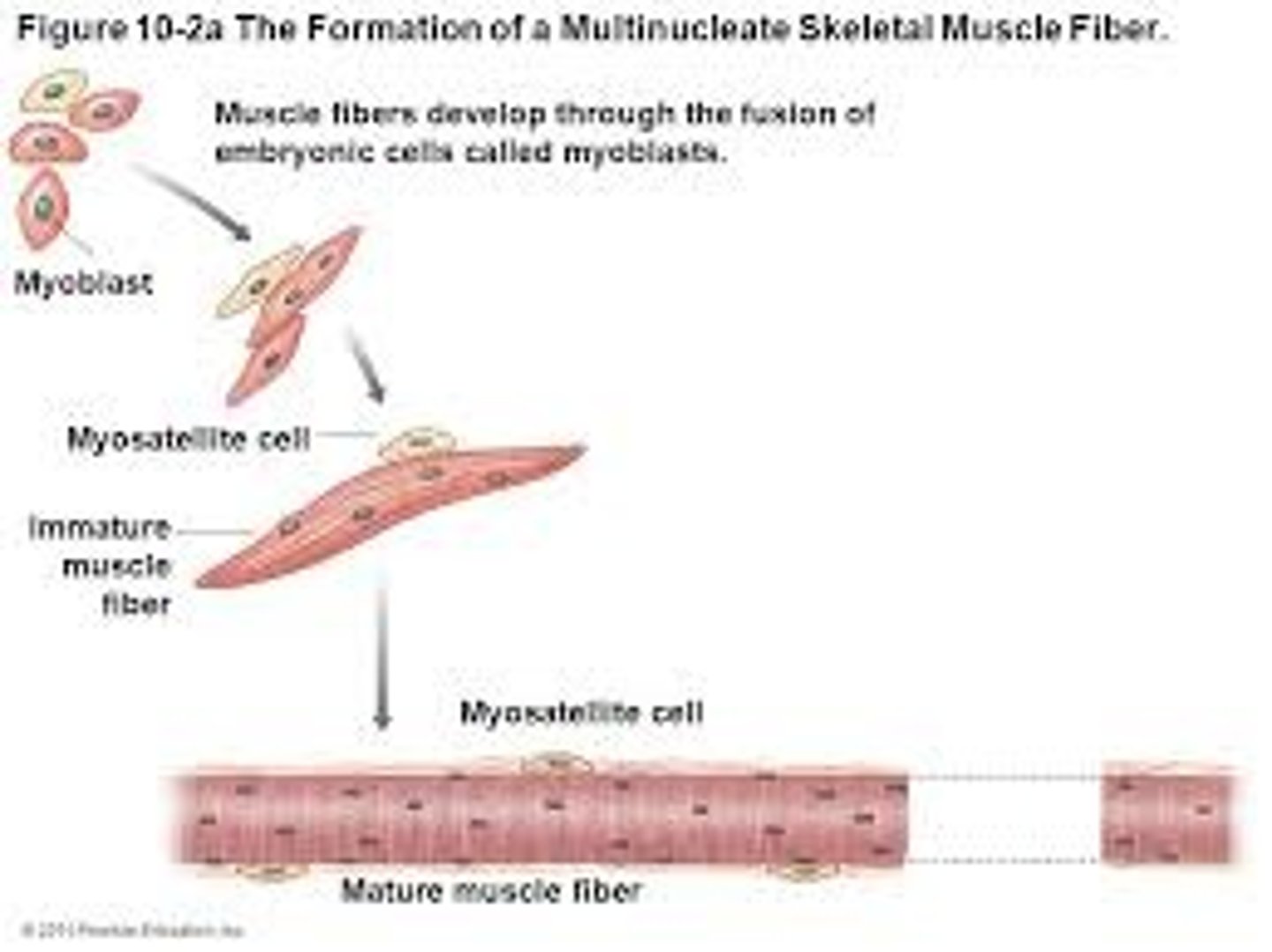
myosatellite cells
stem cells that help repair damaged muscle tissue
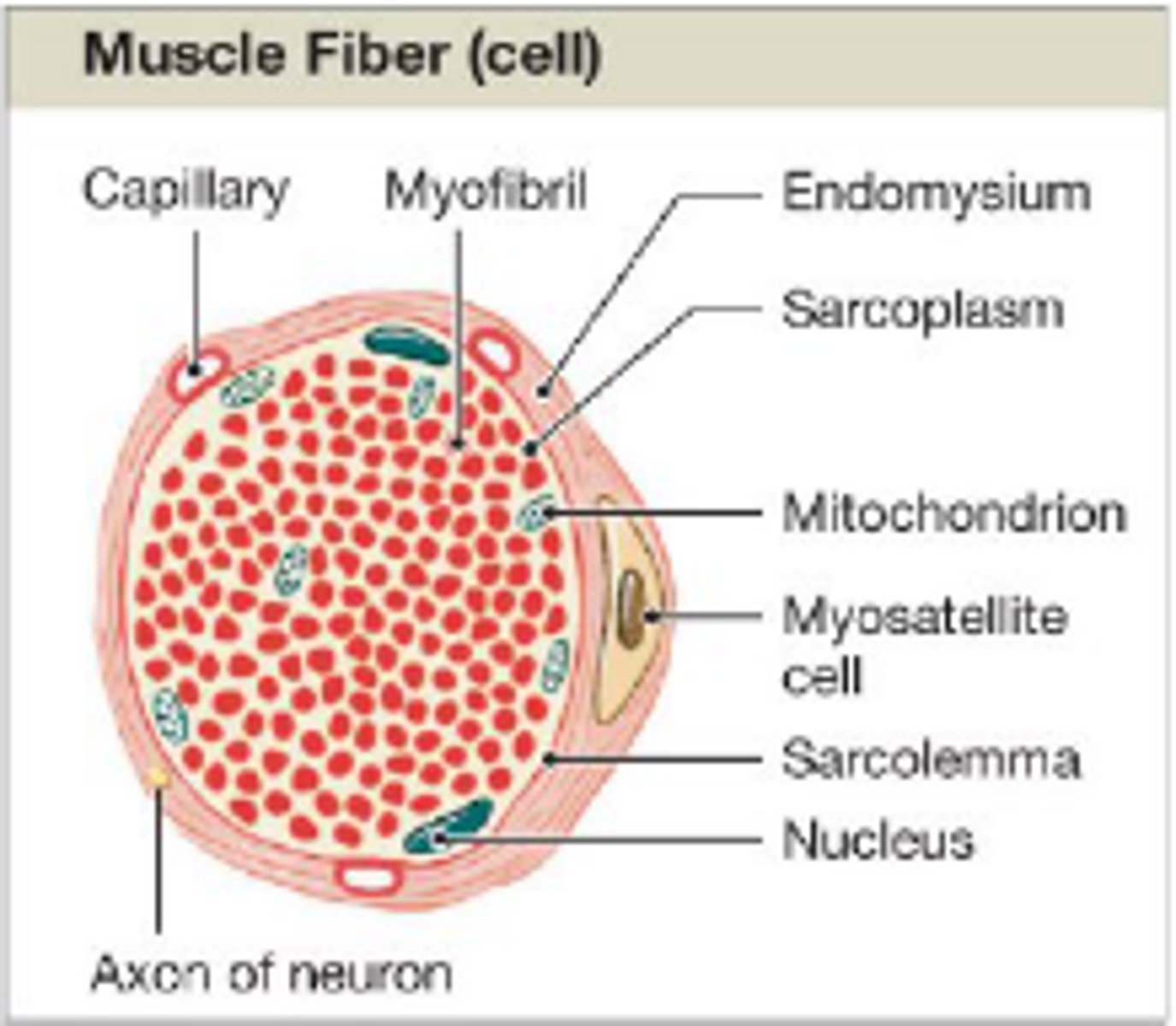
endomysium, perimysium, epimysium
are each continuous with tendons and aponeurosis
tendons
Connect muscle to bone
Aponeurosis
strong sheet of tissue that acts as a tendon to attach muscles to bone
skeletal muscle development
myoblasts fuse to form muscle fibers, myoblasts that do not fuse remain in the endomysium and turn into myosatellite cells
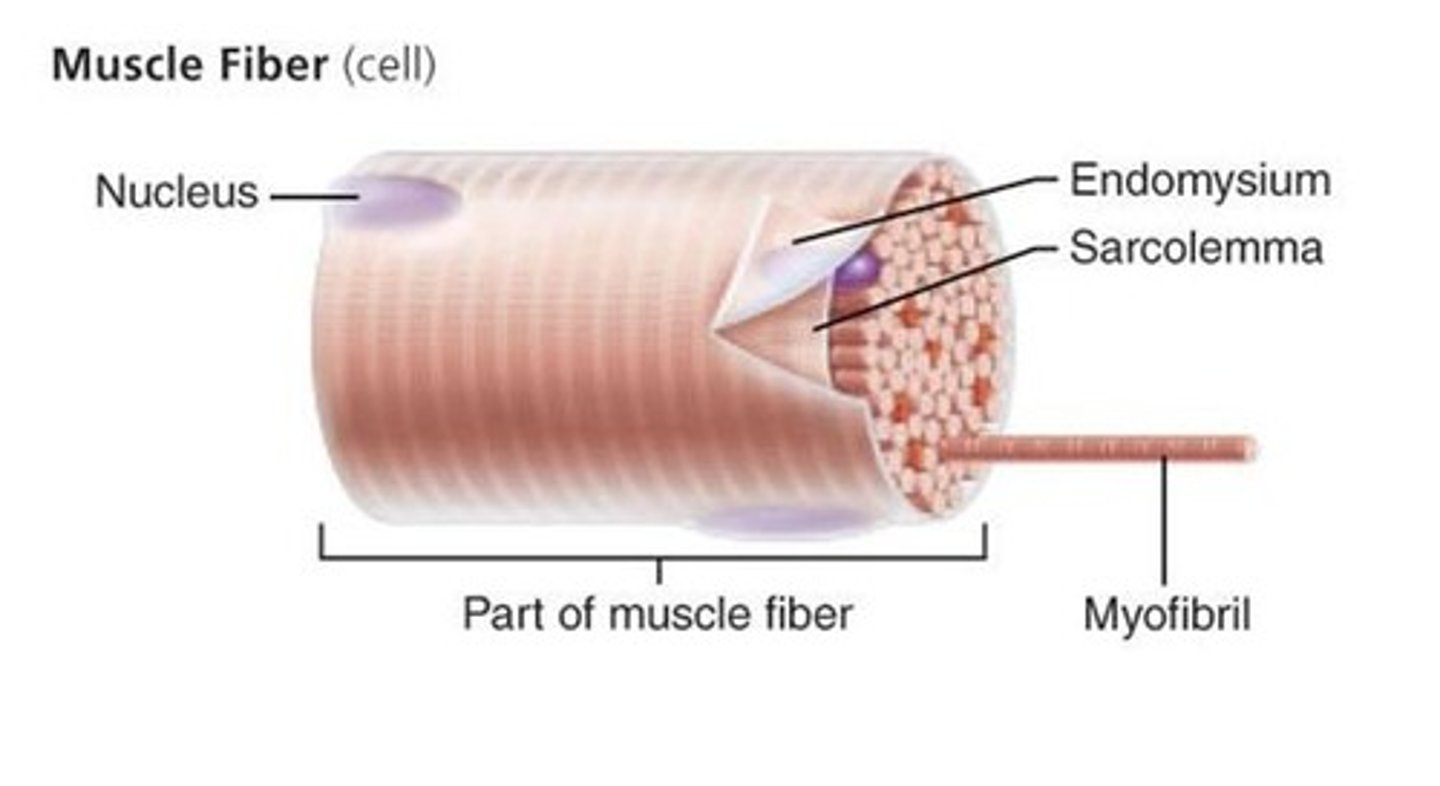
special terms for skeletal muscle fibers
sarcolemma and sarcoplasm
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber
selective permeability = uneven +/- charges
reversal of charge is step 1 in muscle contractions
motor neuron initiates change in charge
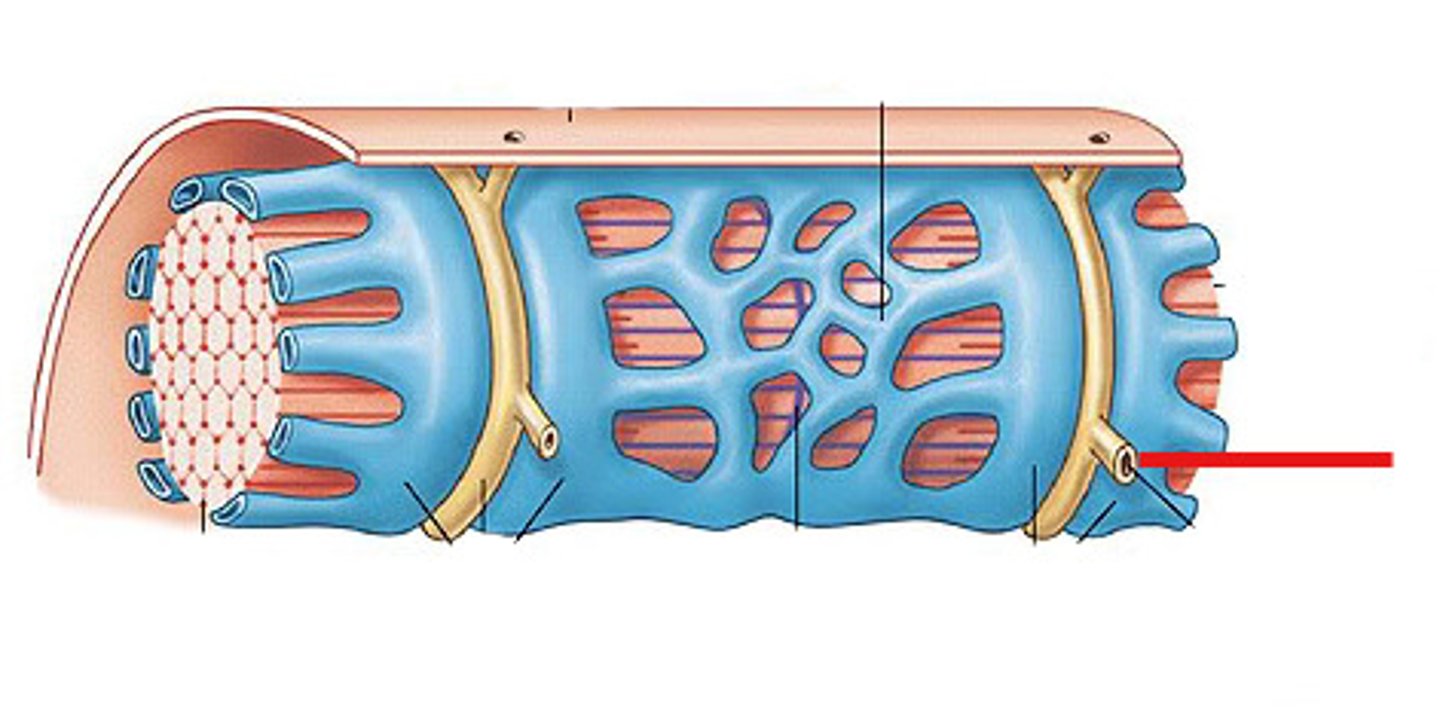
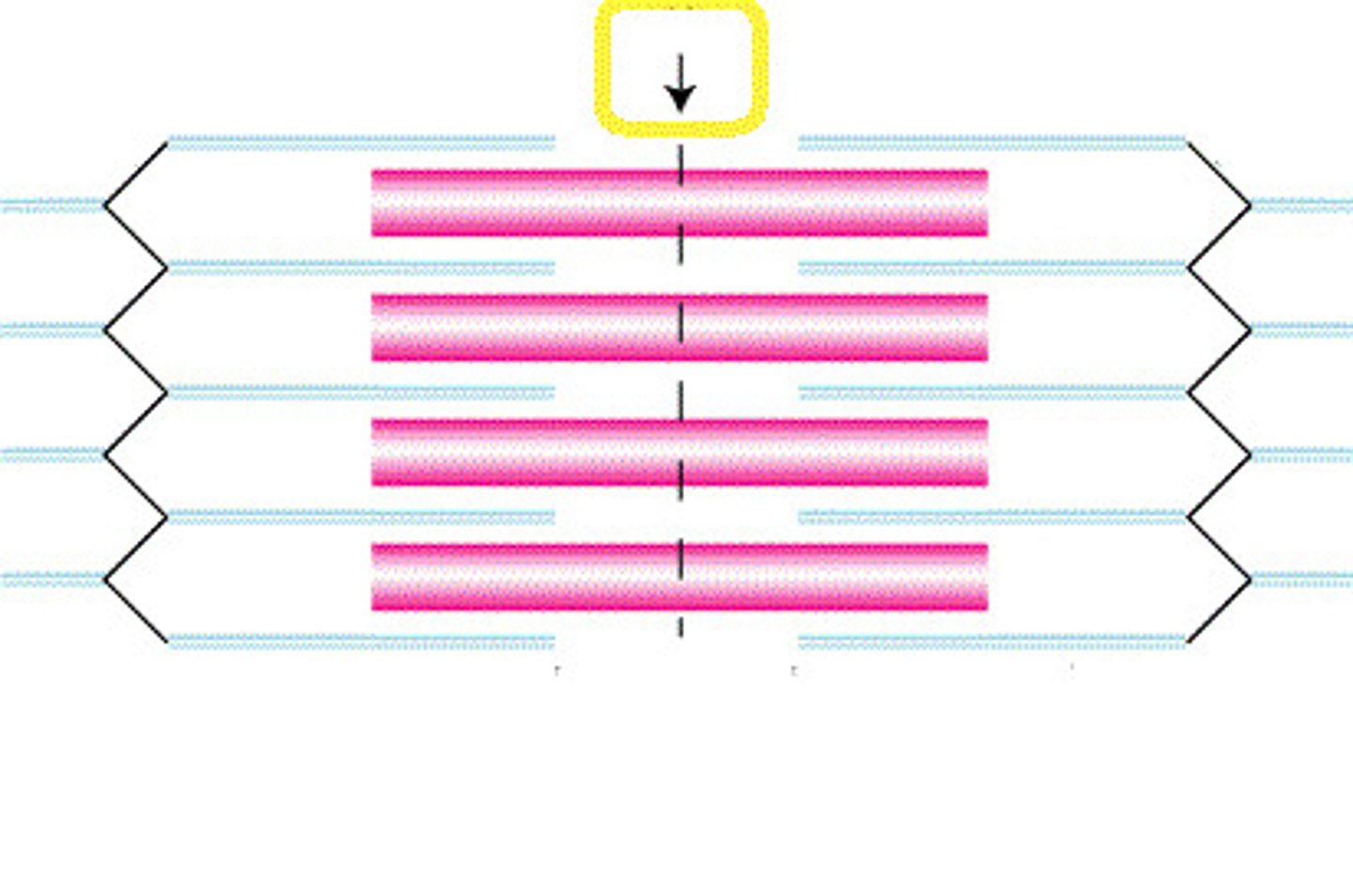
Transverse tubules (T-tubules)
continuous with sarcolemma, extend into sarcoplasm
form passageways through muscle fiber and encircle sarcomere
(The yellow structure)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
similar to smooth ER
stores Ca ions that are actively pumped from the cytosol
have terminal cisternae on either side of the T tubule
terminal cisternae
enlarged areas of the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding the T tubules.
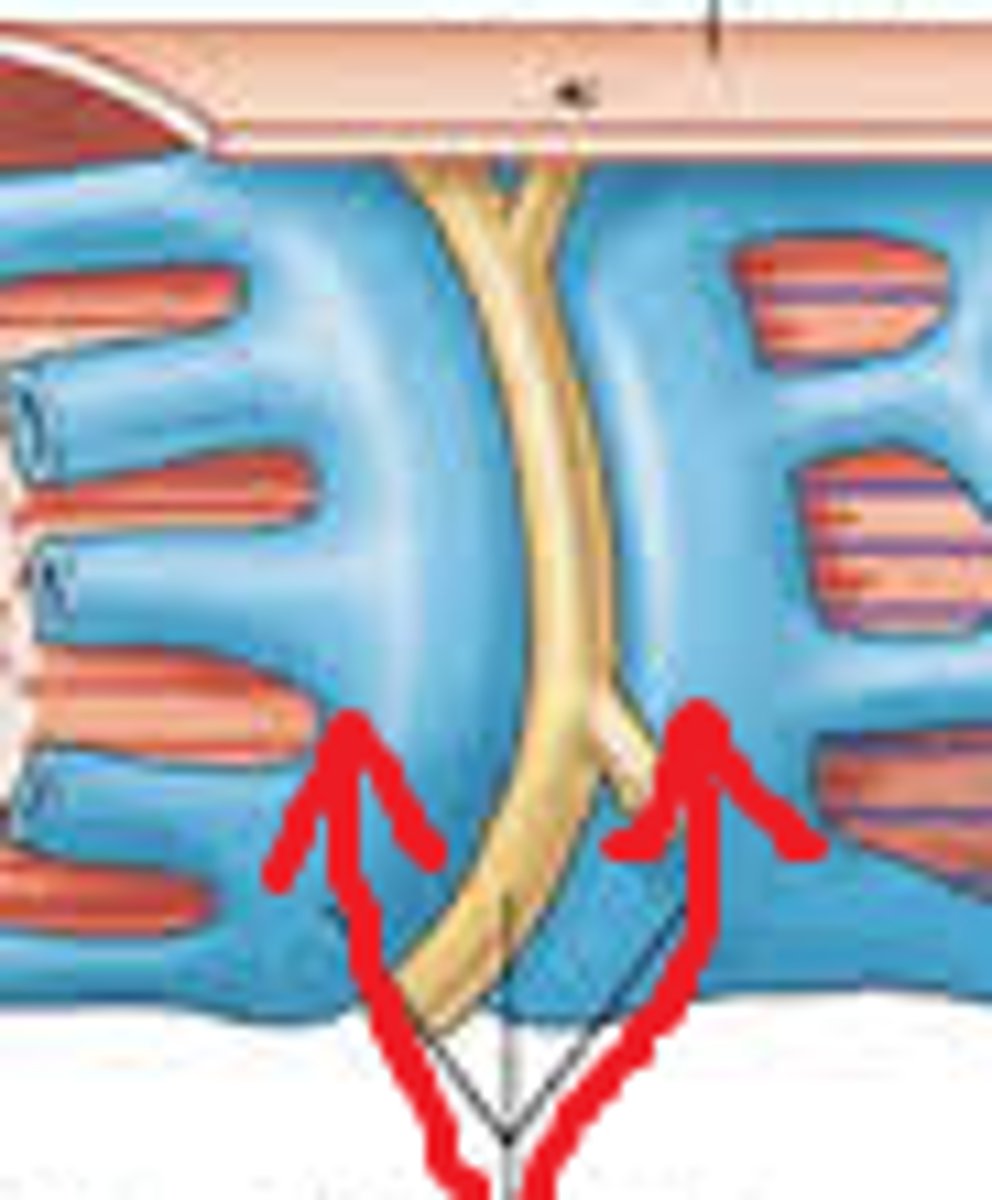
Triad
pairs of terminal cisternae and one T tubule
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell found between myofibrils
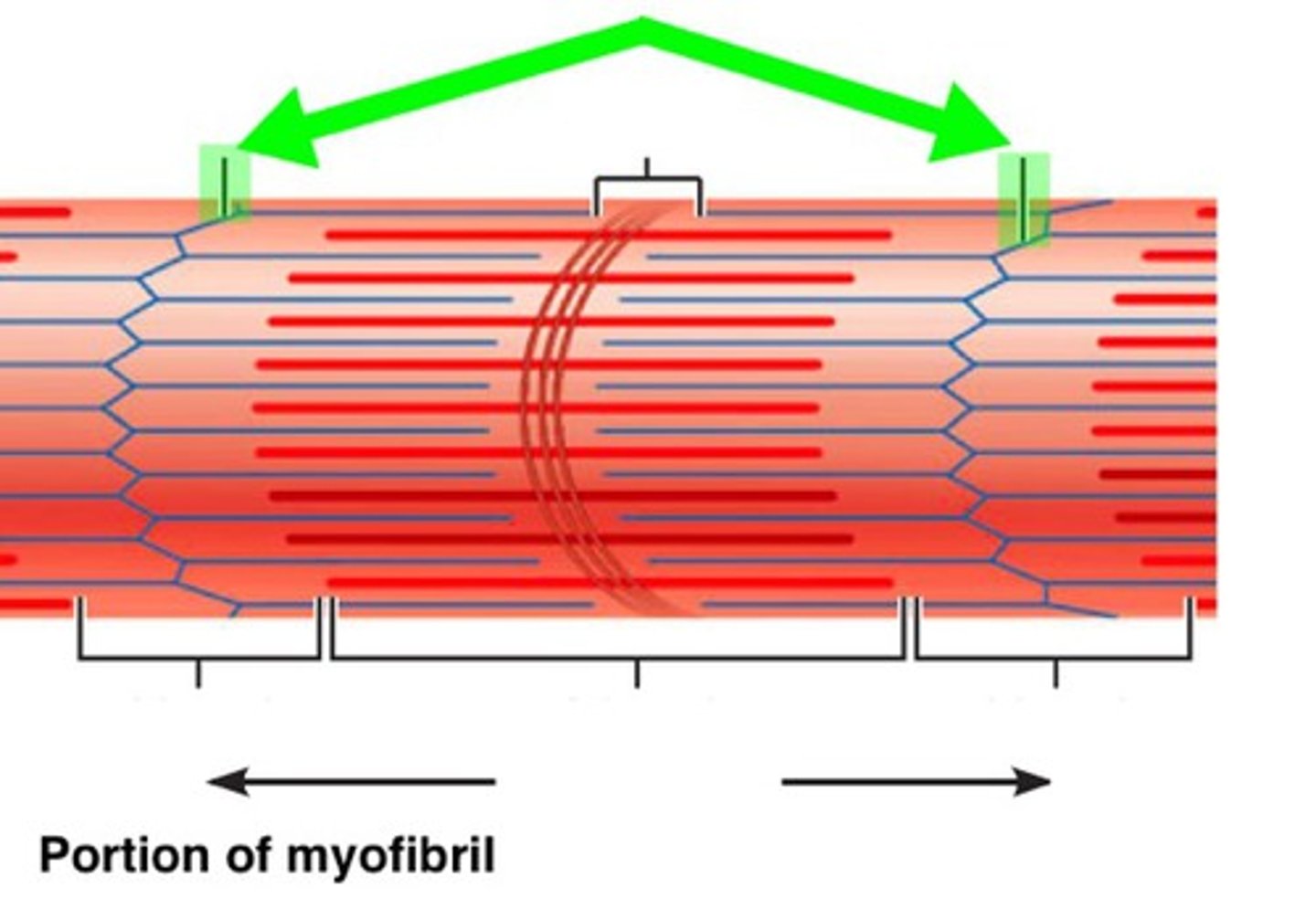
Sarcomere
functional unit of myofibril (region between z lines)
contains Z lines, I band, A band, zone of overlap, M line, and H band
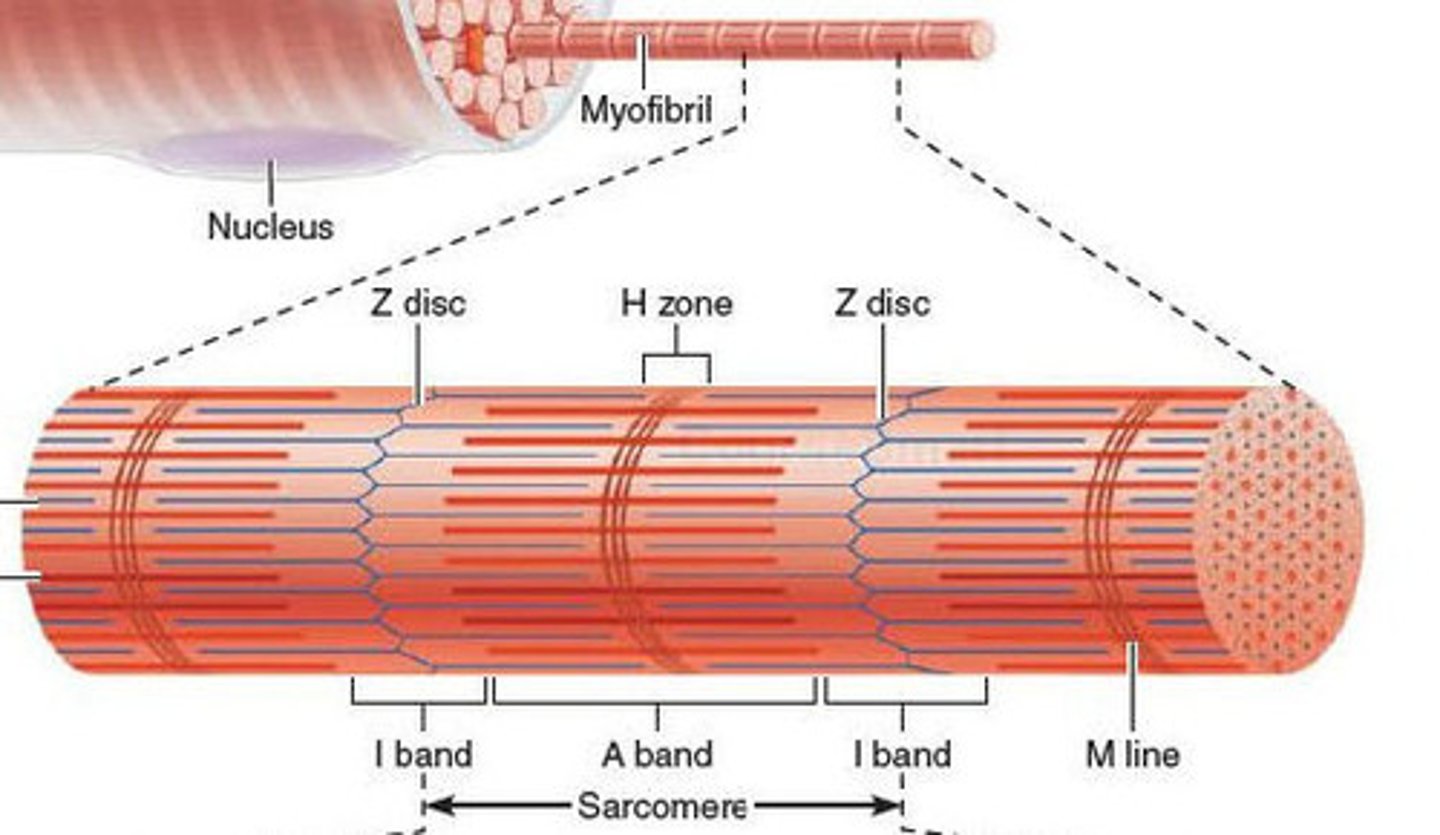
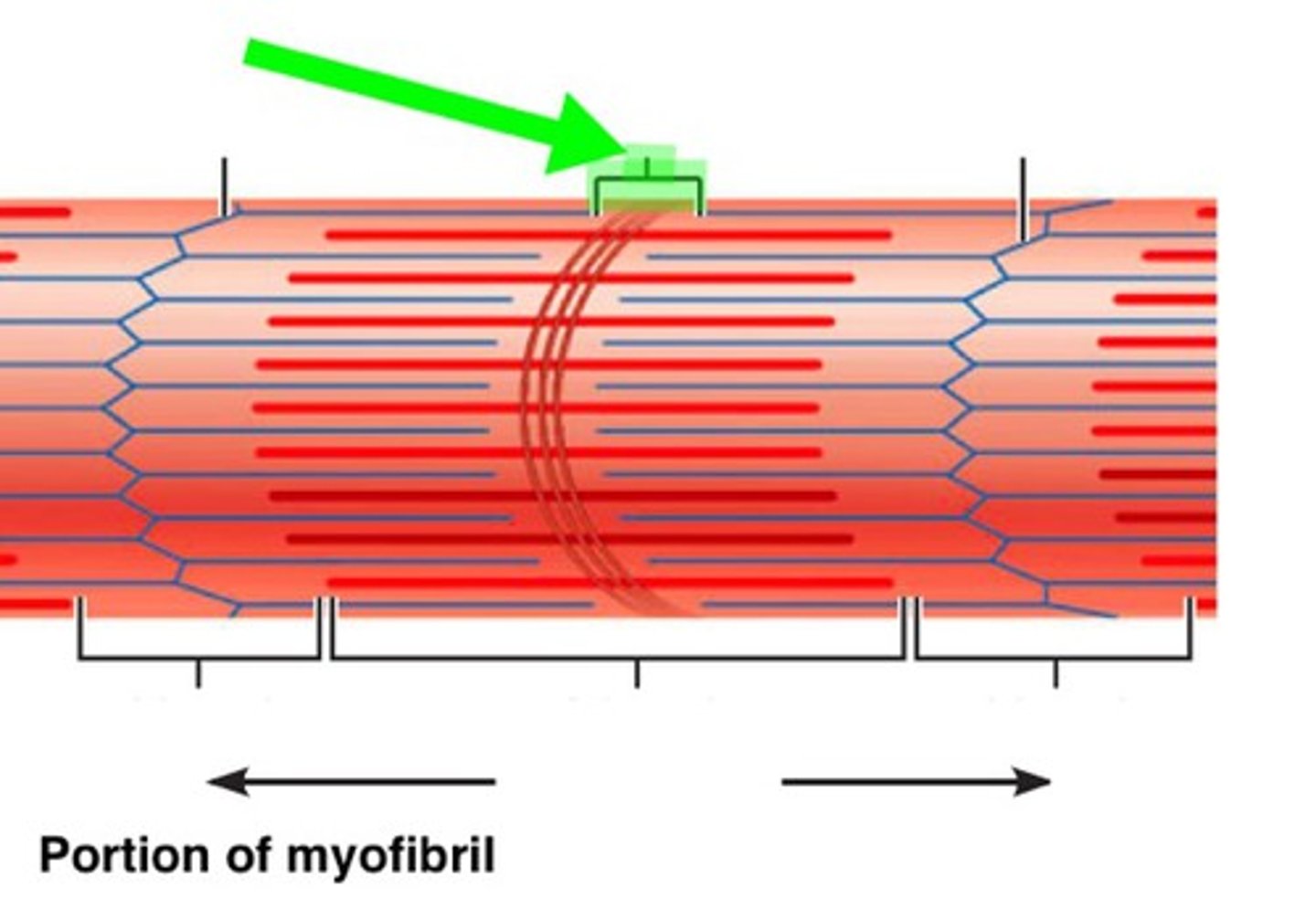
H band
The area around the M line
Has thick filaments but no thin filaments
M line
middle of sarcomere
zone of overlap
where thick and thin filaments overlap
A band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments
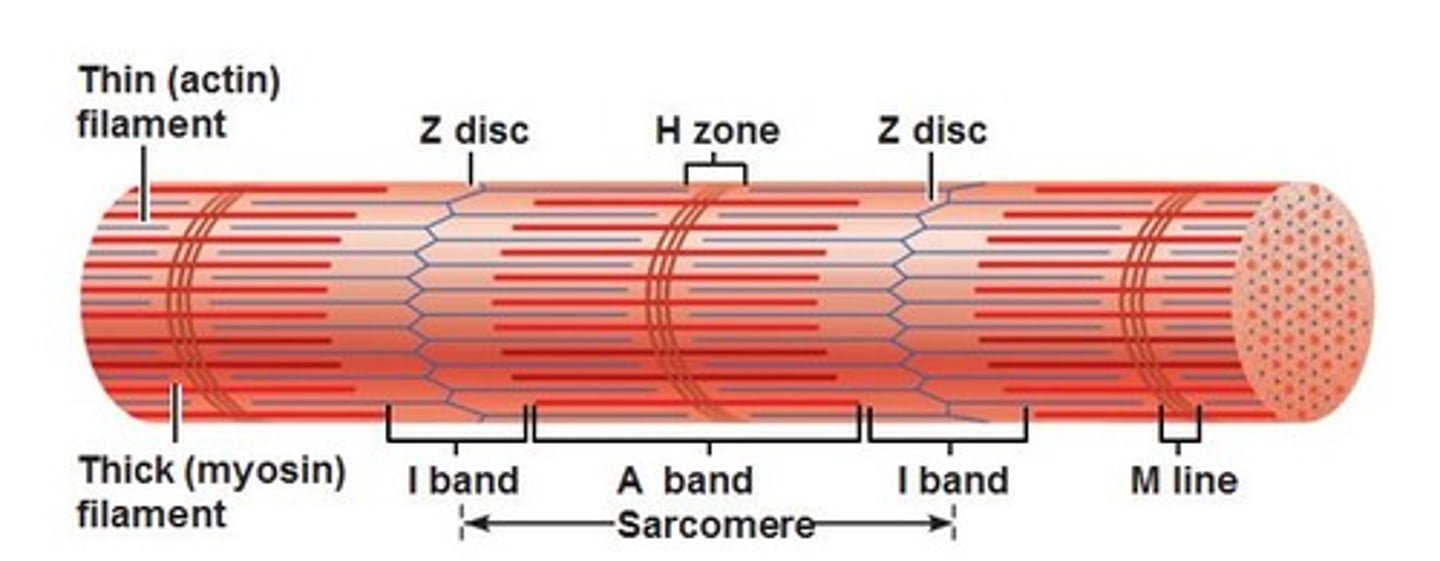
I band
thin filaments only (actin)
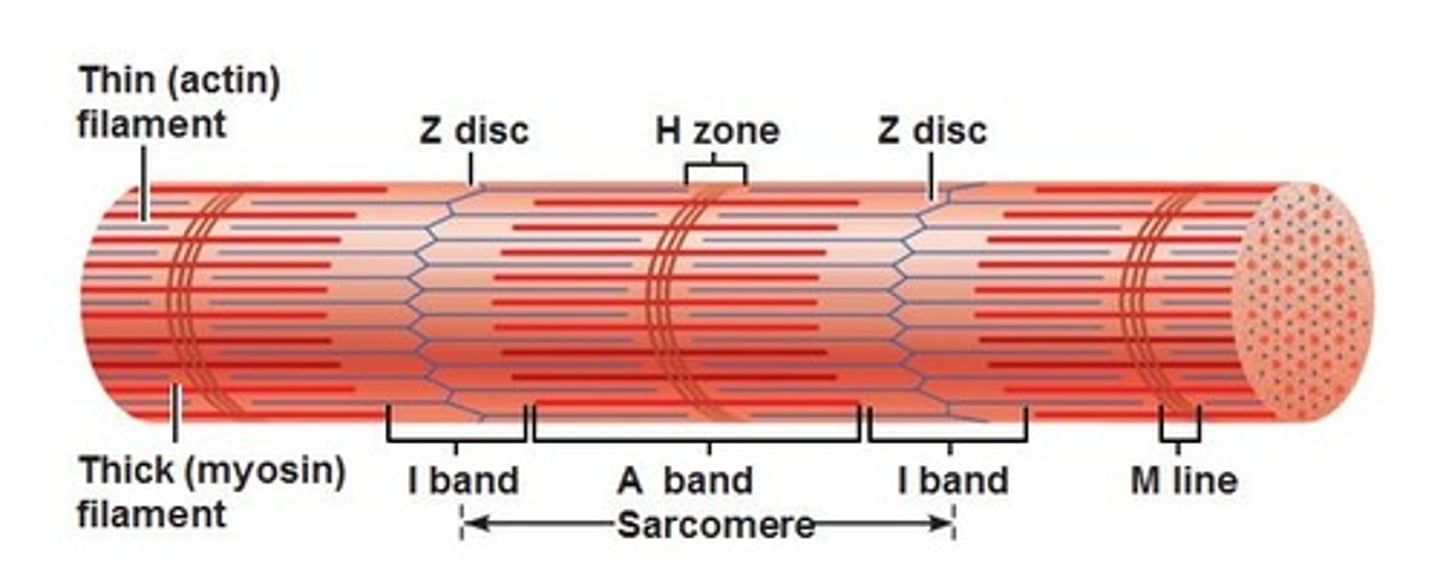
Z lines
The ends of a sarcomere.
contractile proteins
generate force during contraction (actin and myosin)
regulatory proteins
switch the contraction process on and off (tropomyosin and troponin)
structural proteins
keep thick and thin filaments in proper alignment (titin and nebulin)
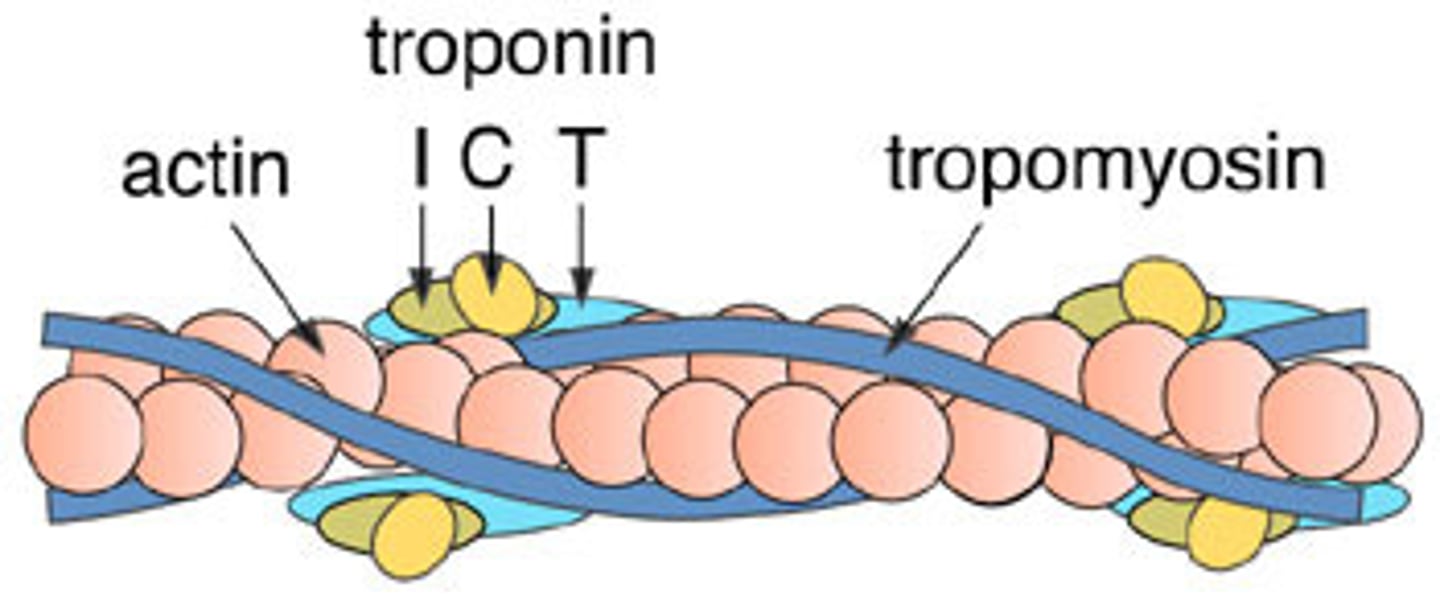
Structure of thin filaments
F-actin, Nebulin, tropomyosin, troponin
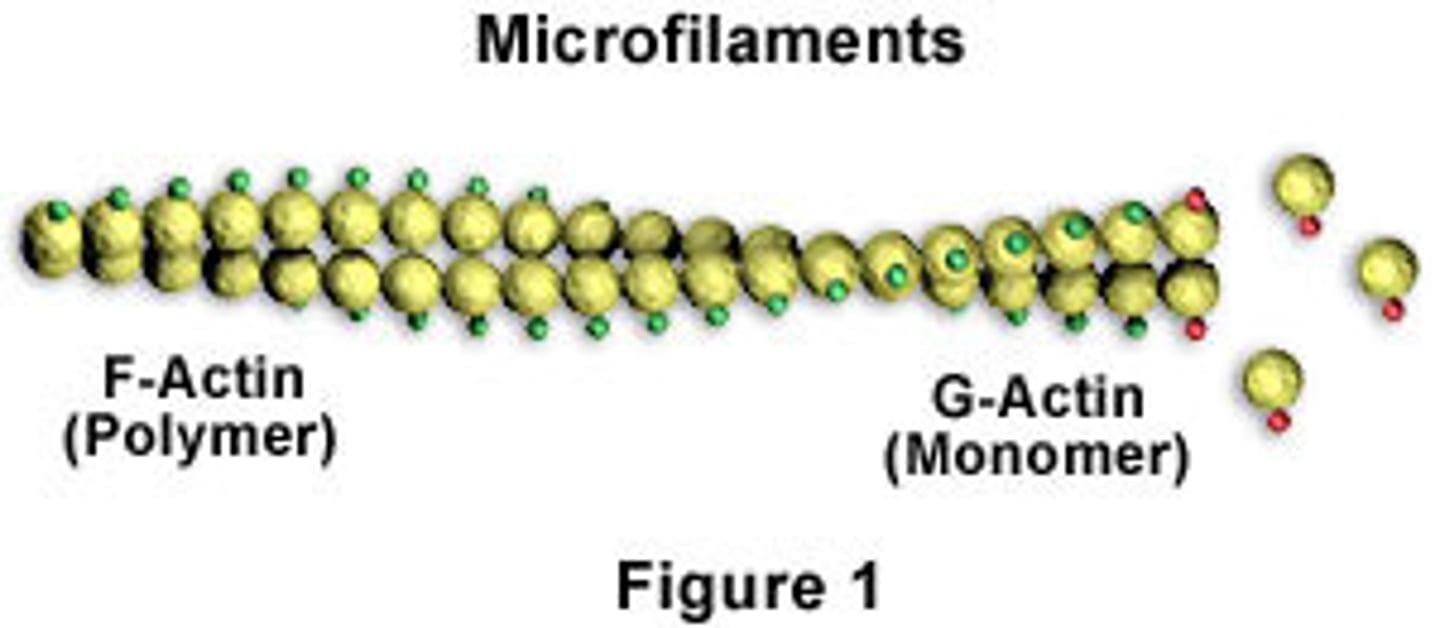
F-actin (filamentous actin)
two twisted rows of globular G-actin
active sites for binding myosin
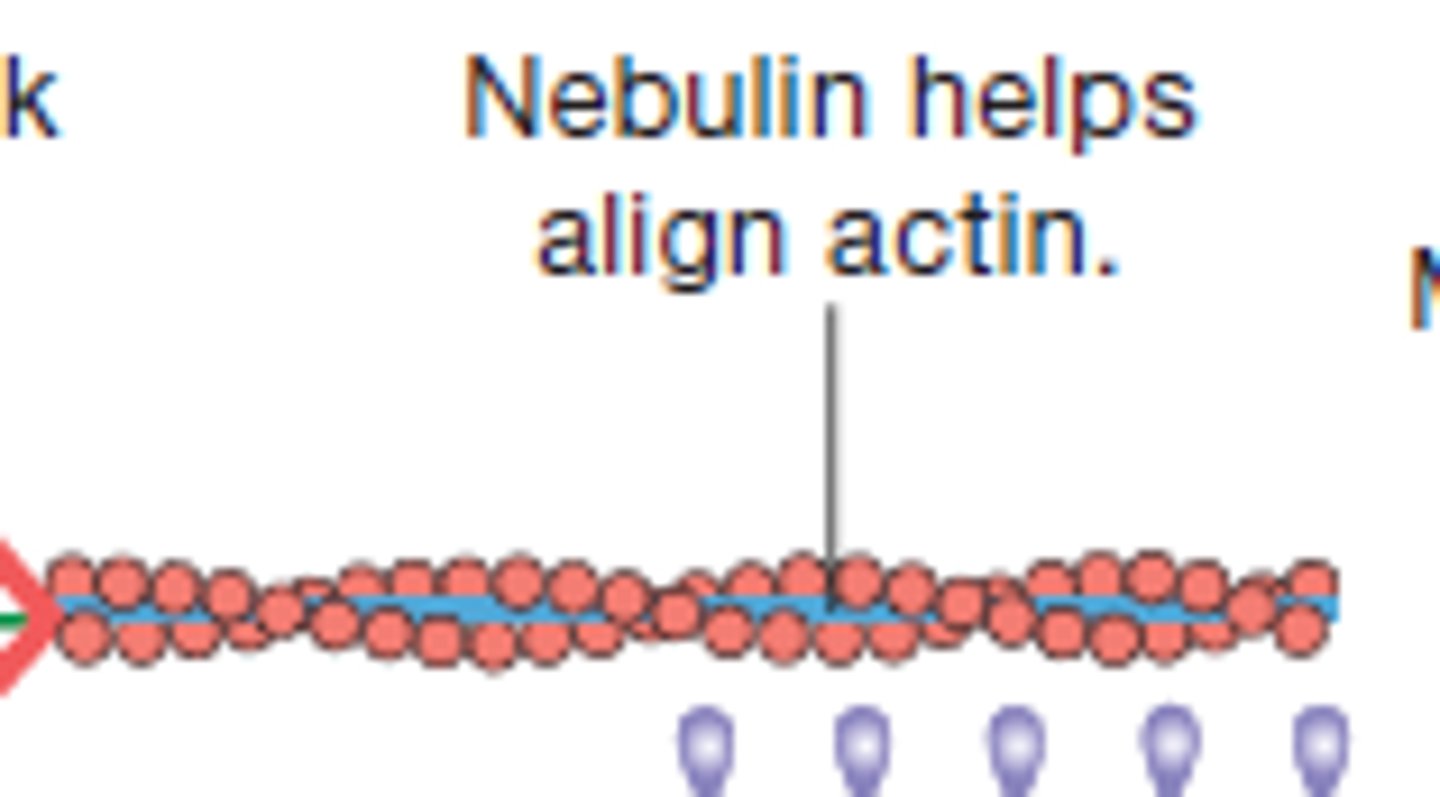
Nebulin
Holds F-actin strands together
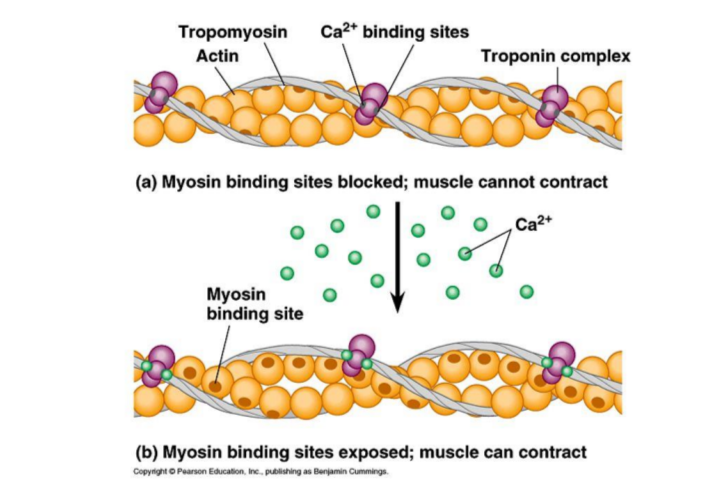
Tropomyosin
double stranded protein wrapped around F-actin
blocks myosin binding site on G-actin molecules in relaxed muscle
Troponin
holds the tropomyosin in place
has binding site for Ca2+
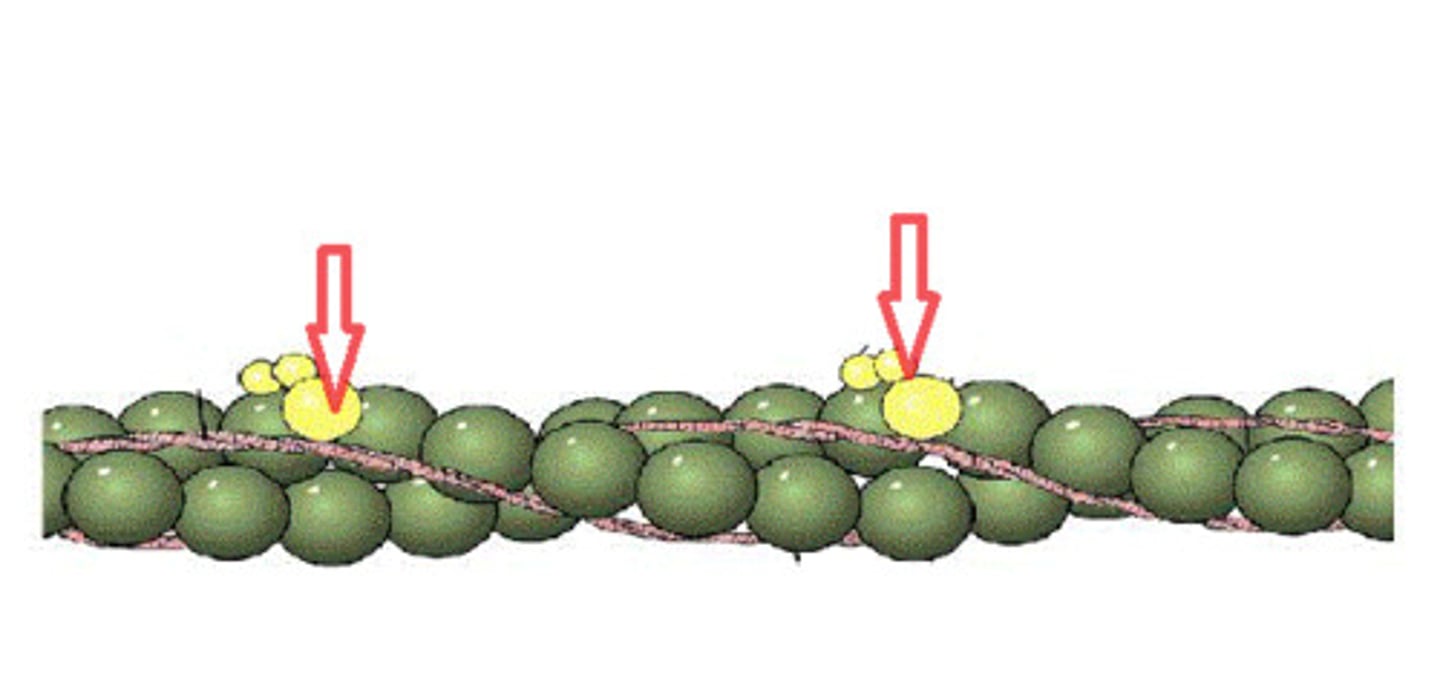
Thin filament in the presence of calcium
when Ca2+ is present it binds appropriate site on troponin
pulls the tropomyosin off of the F-actin, revealing myosin binding sites
allowing the muscle to contract
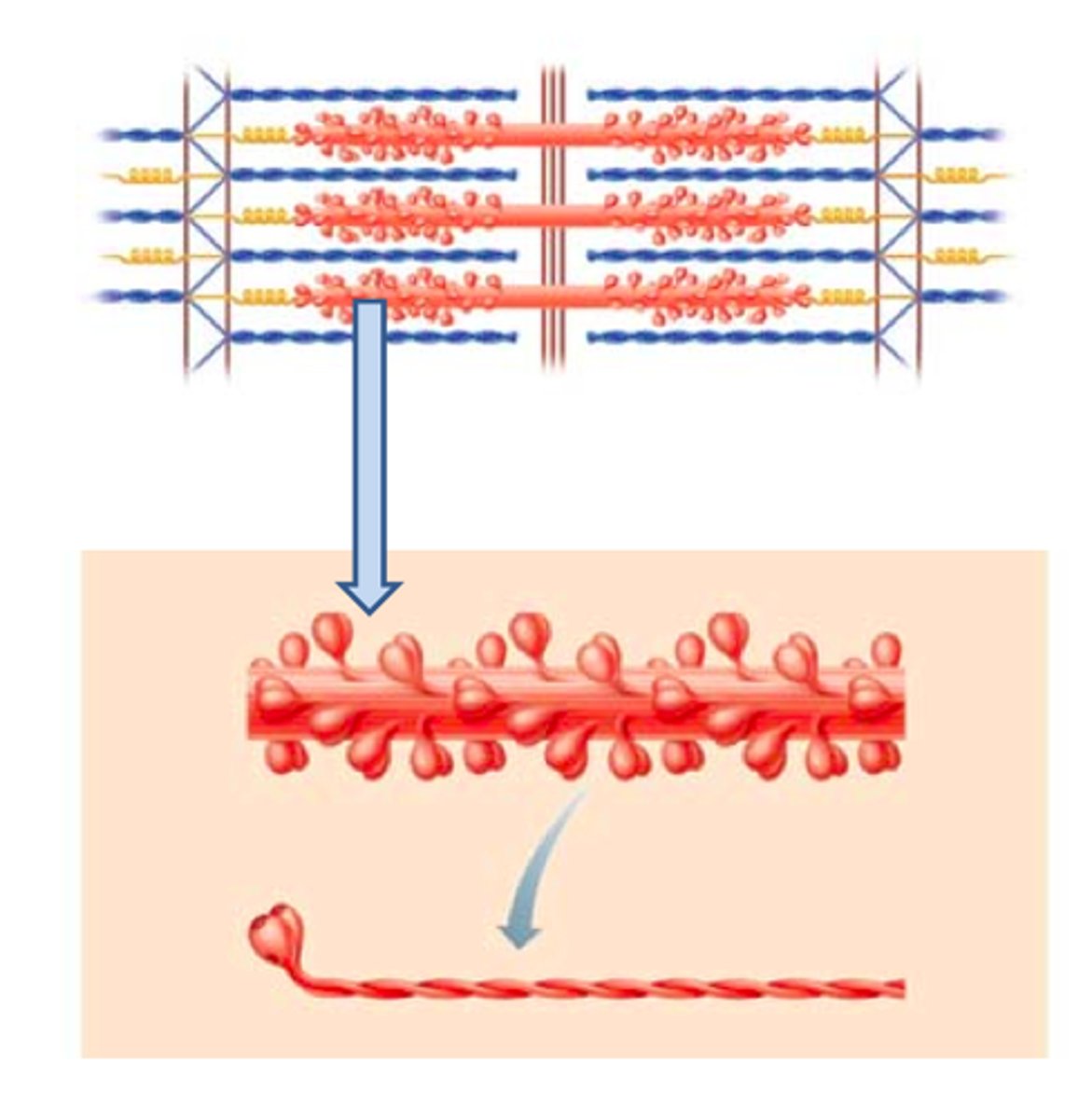
myosin molecule
2 twisted myosin subunits
free heads point towards thin filaments
forms crossbridges
Titin
connect thick filament to M & Z lines
elastic and extensive
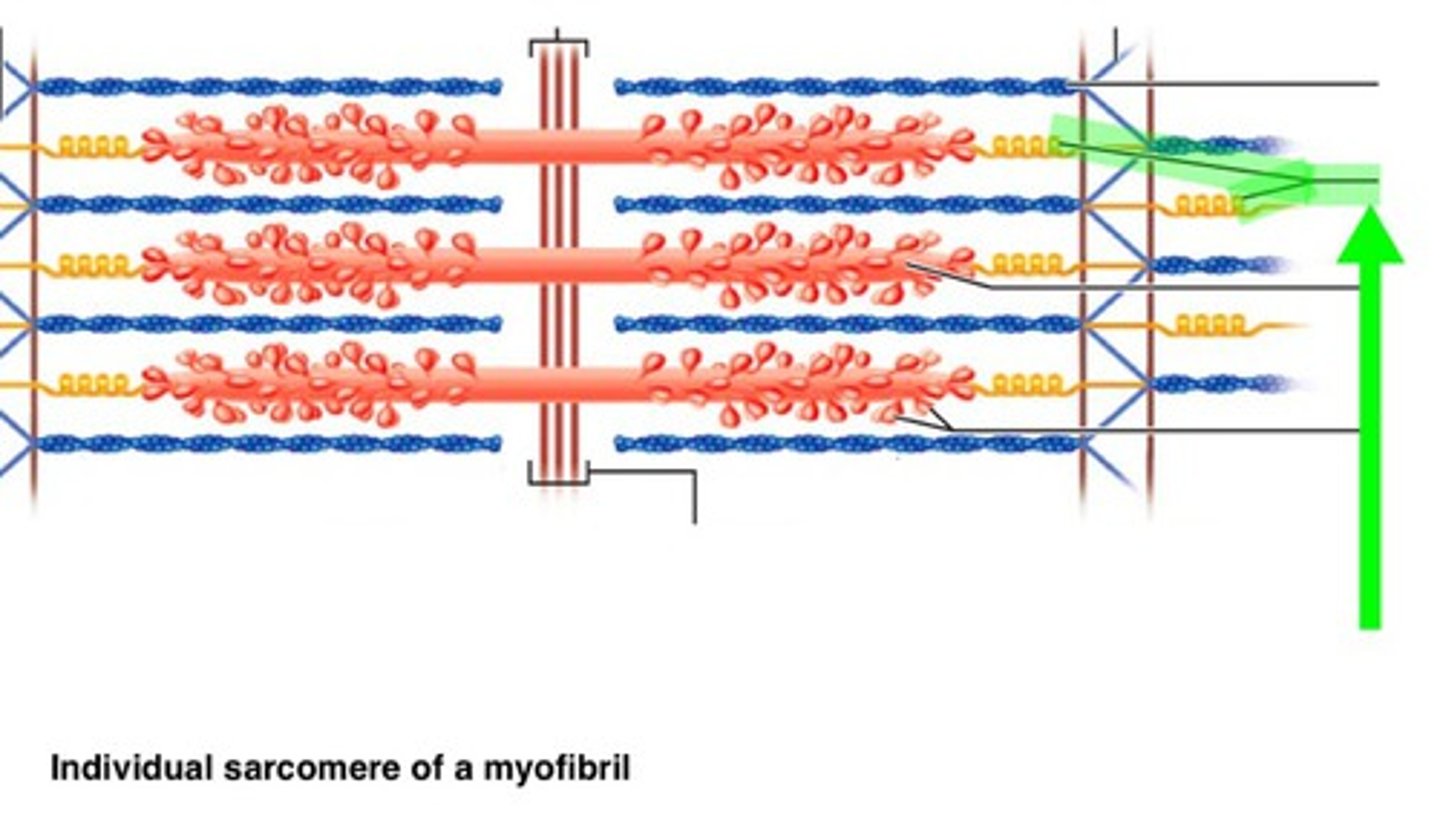
Thick + Thin filament together
Myosin head attaches to myosin binding site on F-actin and pulls to contract
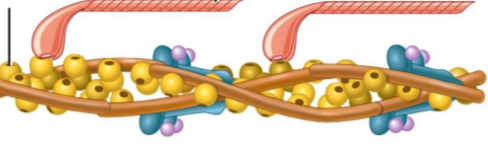
sliding filament theory
sliding occurs in all sarcomeres in each myofibril
Myofibrils shorten=muscle fibers shorten=muscle contraction
A band length stays the same
Plasma membranes
positive charges: contain more potassium (K+) inside the cell, and more sodium (Na+) outside the cell
Negative charges: Mostly proteins inside the cell, can't cross plasma membrane, more Cl- outside in extracellular fluid
resting membrane potential
inside of cell slightly more negative than outside
Neurons resting potential=-70 mv
skeletal muscle fibers resting potential=-85 mv
leak channels
channels that are always open and allow ions to move along their gradient
Sodium potassium ion pumps
constantly work against concentration gradients
3 Na+ out of cell, bring 2 K+ ions in
maintains resting membrane potential
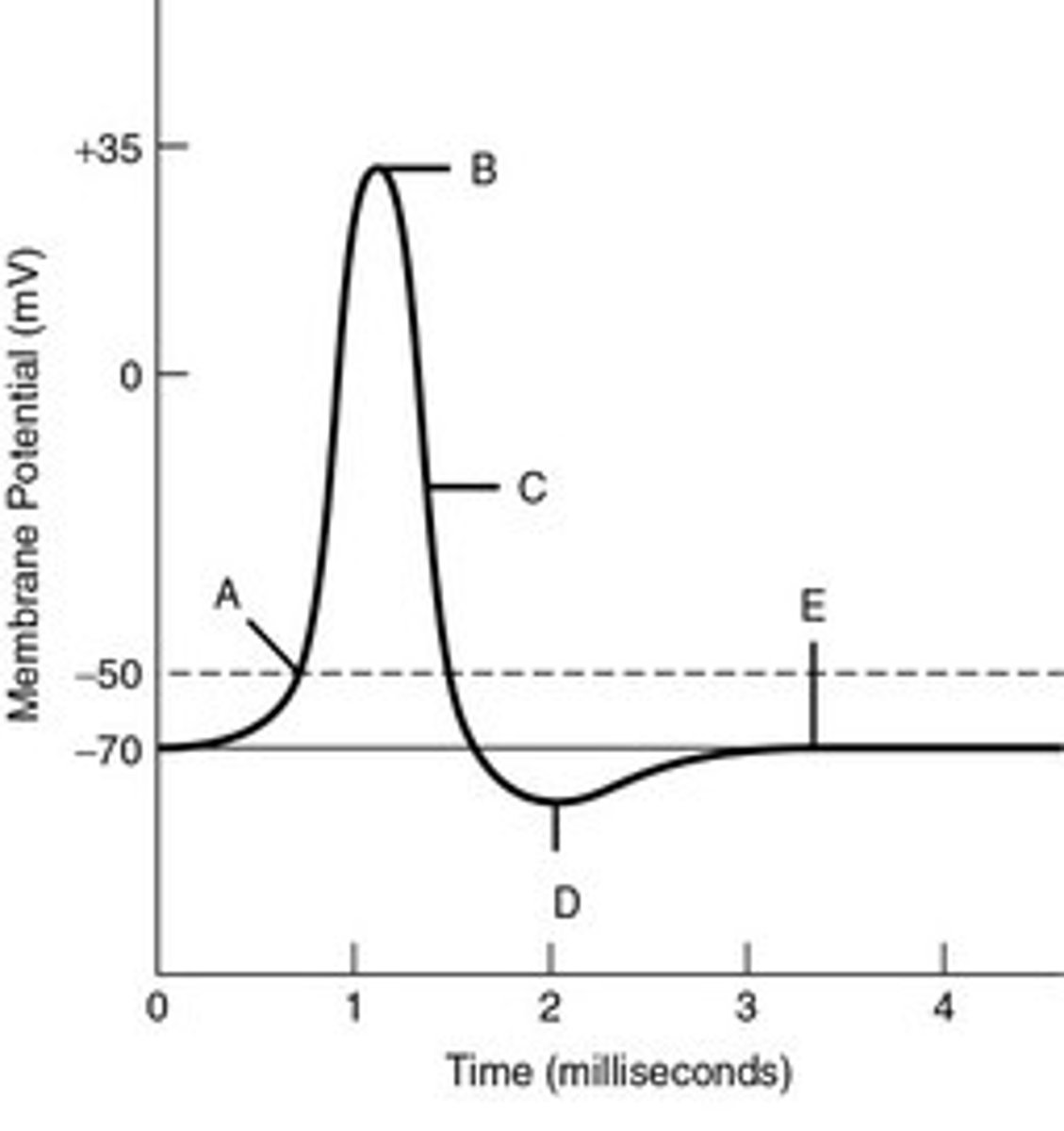
action potential (AP)
A: Na+ into the cell (increases mv)
B: Na+ channels close and K+ channels open (at peak)
C: K+ leaves cell (decreases mv)
D: K+ channel closes but overshoots
E: Na+ K+ pump brings back to resting membrane potential
Neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
where motor neuron controls skeletal muscle fiber
1 NMJ per muscle fiber
1 NMJ may branch out and control multiple muscle fibers
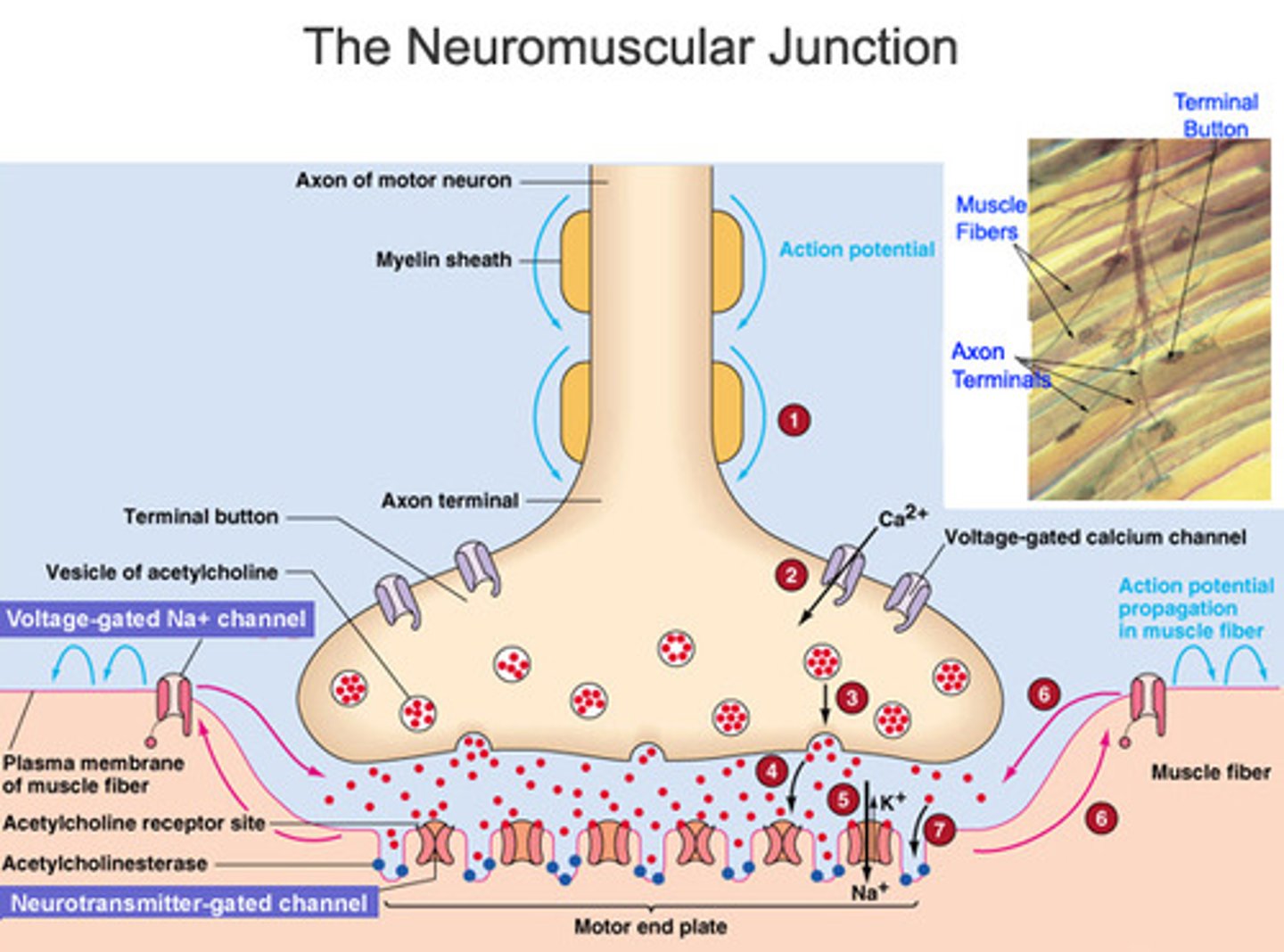
NMJ components
axon terminal, synaptic cleft, motor end plate
axon terminal (synaptic terminal)
has vesicles with acetylcholine (neurotransmitter)
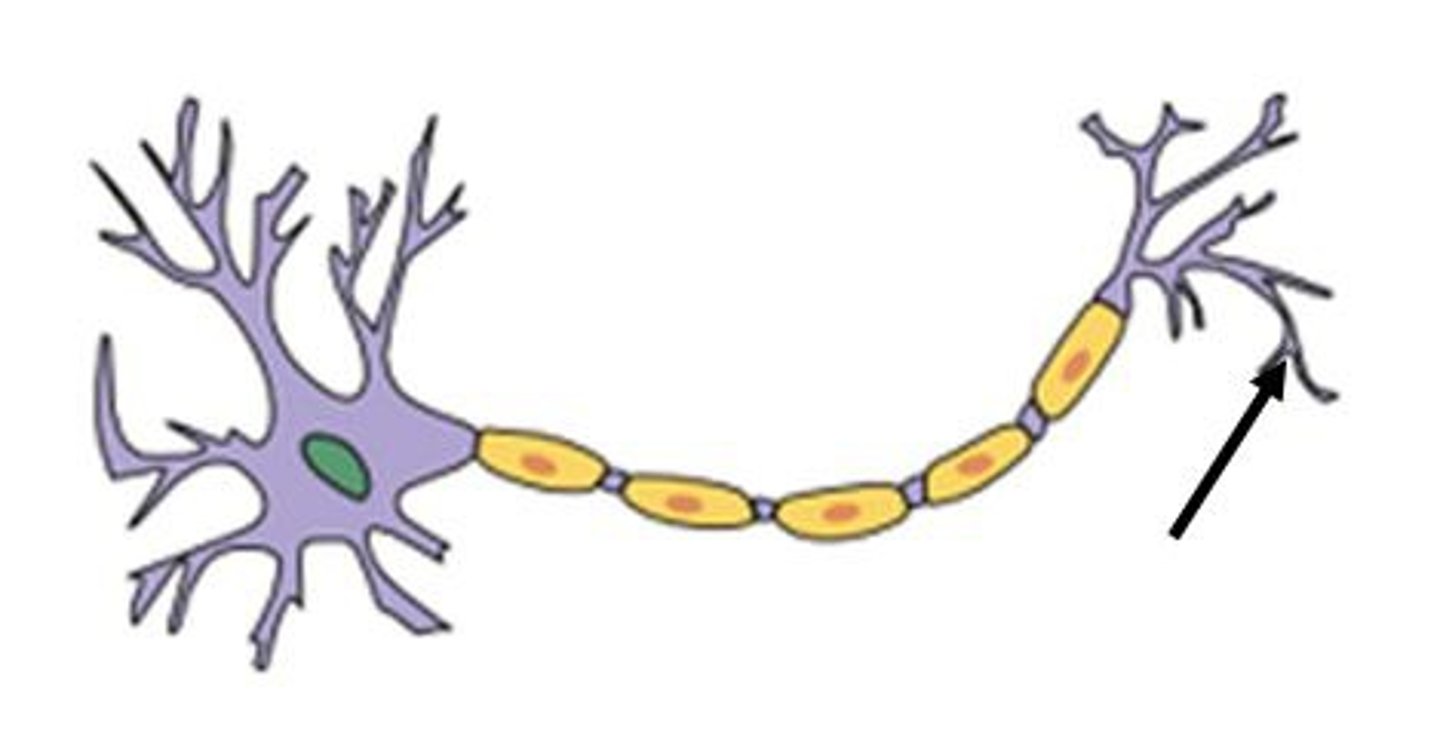
synaptic cleft
space between axon terminal and motor end plate
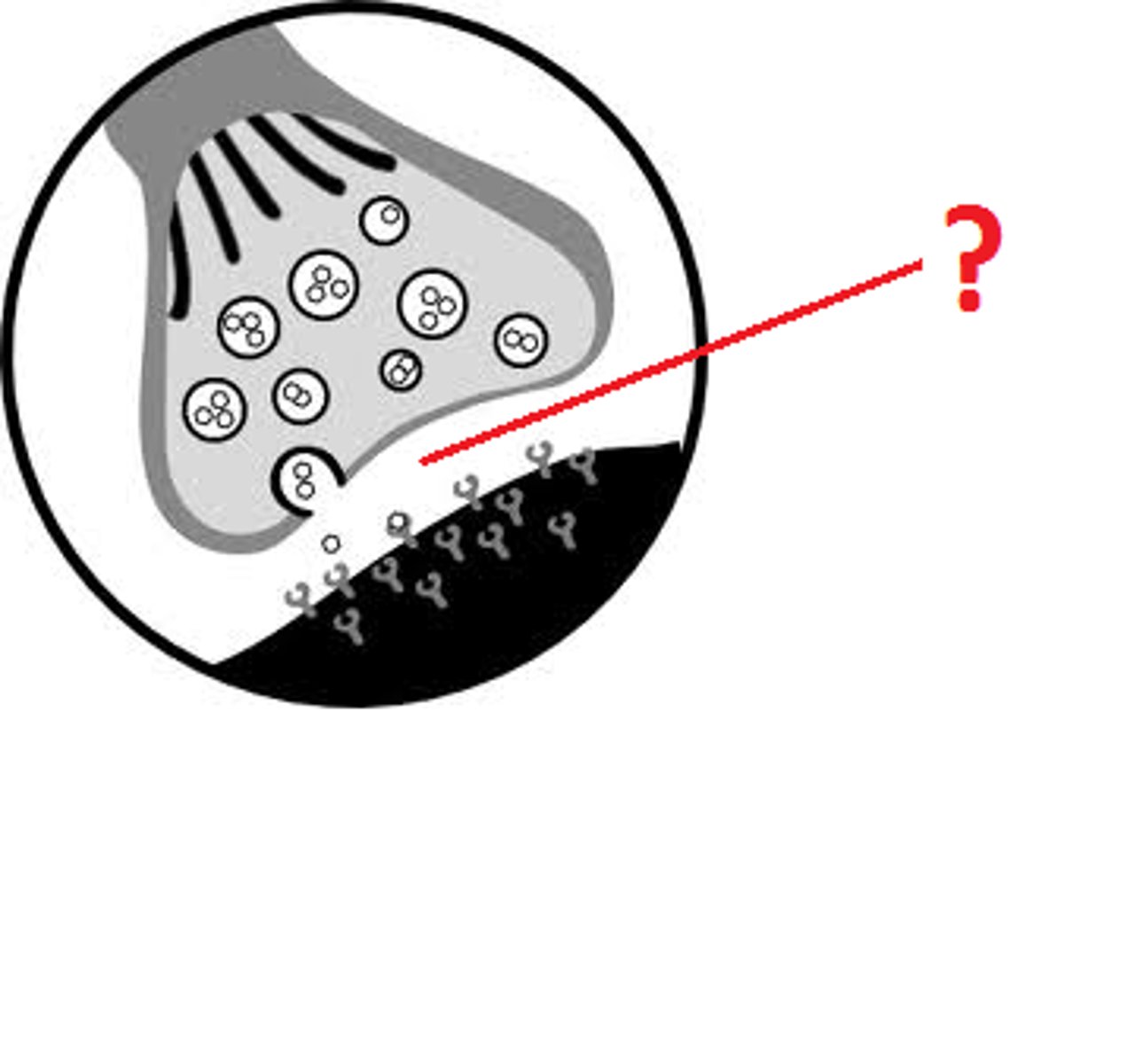
motor end plate of muscle fiber
junctional folds that increase number of acetylcholine receptors
contains acetylcholinesterase, breaks down acetylcholine
Activities at the neuromuscular junction
1. electrical impulse arrives at axon terminal, acetylcholine (ACh) is released via exocytosis
2. ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft, binds to ACh receptor membrane channels at motor end plate, changes sarcolemma Na+ permeability, Na+ enters muscle fiber sarcoplasm
3. Na+ influx generates action potential
4. AP generated at motor end plate immediately spreads across entire sarcolemma
5. AP moves down T-tubules between terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
6. SR releases stored Ca2+ into sarcomeres beginning contraction (excitation contraction coupling)
Steps of Excitation-Contraction Coupling
1. Neural control: AP in motor neuron starts process at neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
2. Excitation: AP causes ACh release from motor neuron which leads to AP in sarcolemma
3. Calcium ion release: muscle fiber action potential travels through T-tubules and triggers release of Ca2+
4. Contraction cycle begins
-4a: Myosin heads are energized and cocked
-4b: Contraction cycle begins, Ca2+ ions arrive from SR
-4c: Active sites exposed, calcium binds to troponin, troponin changes position and moves tropomyosin which exposes the active site on actin
-4d: cross bridges form; myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin
-4e: myosin heads pivot towards M-line (center)=power stroke, and adp + p are released
-4f: cross bridges detach, a new ATP attaches to each myosin head, myosin releases from actin
-4g: Free myosin head splits ATP into ADP+P, and that released energy is used to recock the myosin head
5. Sarcomere shortens: thick + thin filaments interact (Sliding filaments) which shortens sarcomeres by pulling the ends of the muscle fiber closer together
6. Muscle tension produced: shortening of muscle fibers causes entire muscle to shorten. This muscle contraction produces a pull, or tension on tendons
motor unit
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
motor unit recruitment
activation of more motor units for more tension
muscle tone
resting tension in skeletal muscle
some motor units are always active to produce low level tension (not movement),
done subconsciously
concentric contraction
muscle tension rises until it exceeds load
as muscle shortens, tension is constant
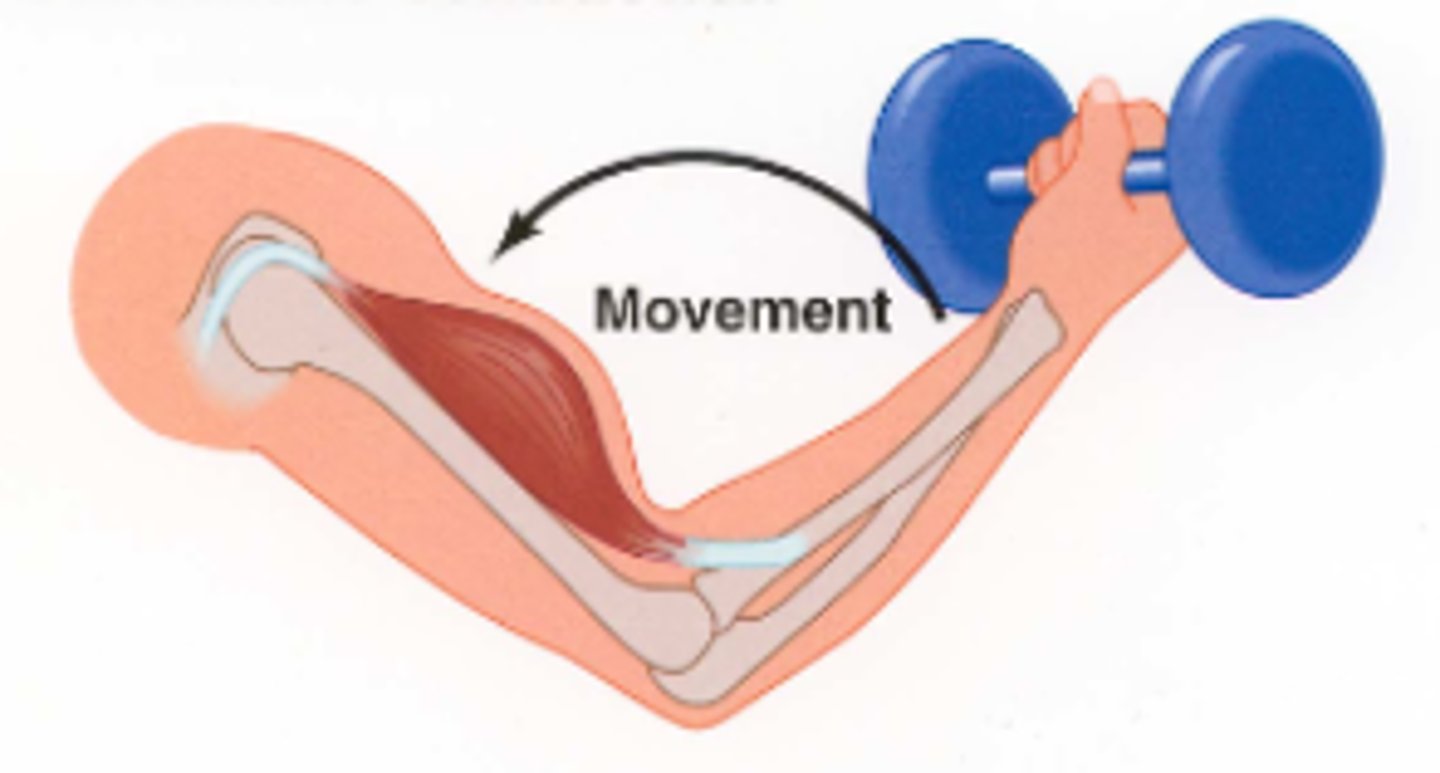
eccentric contraction
peak tension produced is less than load
muscle lengthens/elongates
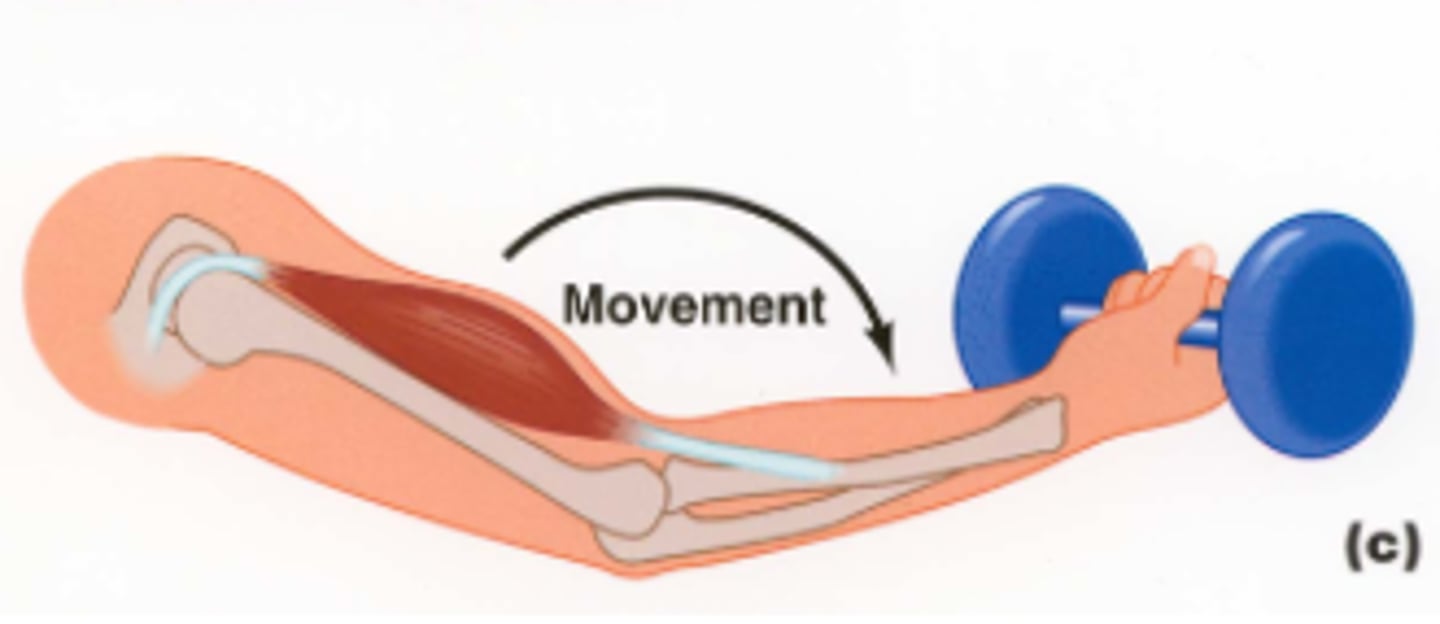
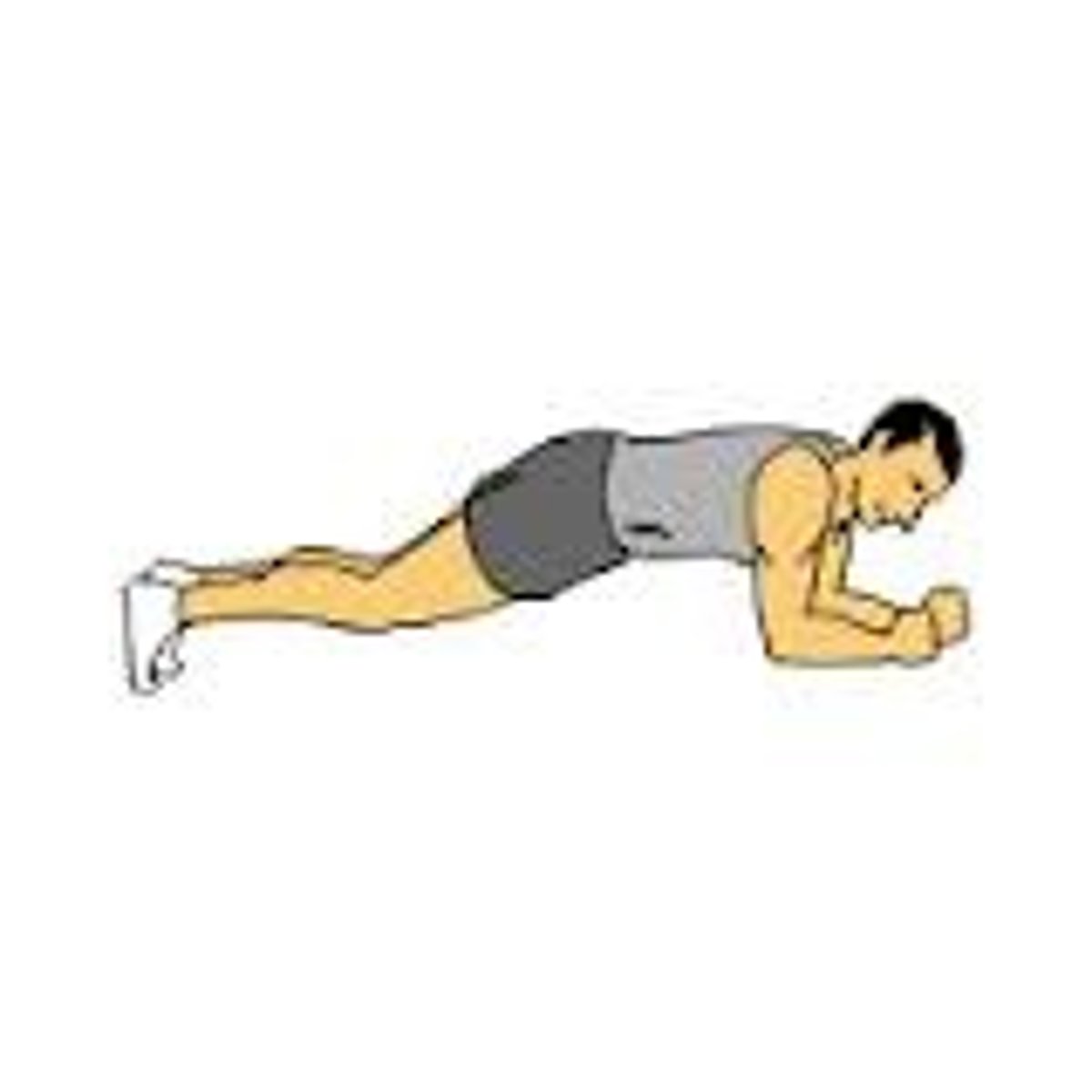
isometric contraction
Muscle length does not change
tension never exceeds load
Ex: planks

muscle fatigue and recovery
fatigue: muscle can no longer perform at required level
recovery period: time needed to return conditions in muscle fibers to pre-exertion levels
fast fibers
pale color
large in diameter
large glycogen reserves
few mitochondria
powerful contractions
fatigue rapidly
Ex: weight lifting, anaerobic exercise
slow fibers
red color
smaller diameter
longer sustained contraction
resist fatigue
large amount of O2, myoglobin, capillaries
Ex: marathon running
intermediate fibers
little myoglobin
pale
more capillaries & fatigue resistant than fast fibers
Can be aerobic or anaerobic exercise
hypertrophy
muscle enlargement from repeated, exhaustive stimulation
more mitochondria
more glycogen
more/wider myofibrils
more myofilaments
steroid hormones
atrophy
decrease in muscle size, tone, and power
decreased stimulation or inherited diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy
muscular dystrophy
group of hereditary diseases characterized by degeneration of muscle and weakness (sex linked, males only)