Organic Chemistry
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
When finding hybridization always remember about what
resonance structures which determine hybridization
sp hybridization has what geometry and bond angle
linear and 180
sp2 hybridization has what geometry and bond angle
trigonal planar, 120
sp3 hybridization has what geometry and bond angle
tetrahedral, 109.5
Oxygen exists normally with how many bonds and lone pairs
2 bonds and 2 lone pair
Nitrogen exists normally with how many bonds and lone pairs
3 bonds and 1 lone pair
Phosphorous exists normally with how many bonds and lone pairs
3 bonds and 1 lone pair
Sulfur exists normally with how many bonds and lone pairs
2 bonds and 2 lone pairs
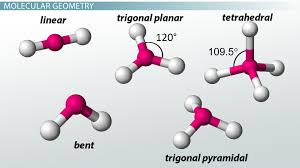
MEMORIZE
What are Lewis Acids
compounds that serve as electron acceptors
What are Lewis Base
compounds that serve as electron donors
What is Bronsted Lowry Base
are proton acceptors
What is Bronsted Lowry Acid
proton donors
The lower the pKa, the _acid
stronger
What are the 7 strong acids
HClO3,
HBr,
HCl,
HI,
HNO3,
HClO4,
H2SO4
High Ka means
high Ka means strong acid. High Ka means lower pKa value
High pKa means
low Ka value. Also means weakest acid
What happens to acidity as we go down a column in the periodic table
Acidity increases because atomic size increases
In an acid-based reaction, what kind of acid is favored for production?
the formation of a weaker acid is favored
For an amino acid, what happens to the amino and carboxyl group depending on how high or low pH is
If the pH is higher than functional group’s pKa, then carboxyl group will be in base form (COO-) no Hydrogen. If pH is lower than pKa, carboxyl group will gain proton COOH. If pH is greater than pKa, amino group will be the same (NH2). If pH is less than pKa, amino group will gain proton NH3+
If atoms like Fluorine group are closer to carboxylic acid what does this mean in terms of how strong the molecule is
Groups like Fluorine when close to carboxylic acid, are electron withdrawing groups so they will stabilize the negative charge of the conjugate base of the chosen molecule, resulting in stronger acid.
Which ones are stronger acid one with carboxylic acid or only alcohol group
Carboxylic acid because the conjugate base of carboxylic acids are MORE STABLE
A bigger atom does what to acidity
increases acidity
Electron withdrawing groups like F, Cl, Br, I do what to acidity
increase
What are some electron withdrawing groups resulting in increasing acidity
From Greatest to smallest:
nitro (NO2), (SO3H), cyano (CN), carbonyls (CHO, C=O, COOH, COOR), halogens,
When determining which molecule is the most acidic: Use CARDIO
C → carboxylic acid is strongest acid
A → atom size the bigger the size of atom the more acidic
R → resonance! must be able to be resonance stabilized or do resonance (SO no cyclic rings without double bonds inside)
DI → dipole induction. Which groups are the most electron withdrawing?
O → lok at orbitals. sp most acidic, then sp2, and sp3 is least acidic
Strong conjugate base means..
weak acid (low Ka, high pKa)
weak conjugate base means
strong acid (High Ka, low pKa)
strong conjugate acid means…
weak base
weak conjugate acid means
strong base
What makes a molecule more basic in terms of what kind of functional group must be there and characteristics?
electron donating groups like NH2, NHR, N, OH, OR are strongest, then NHCO-, OCO-, lastly weakest is Ch3, CH2CH3