acid/bases
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
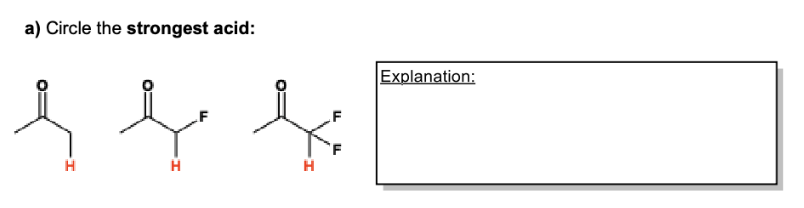
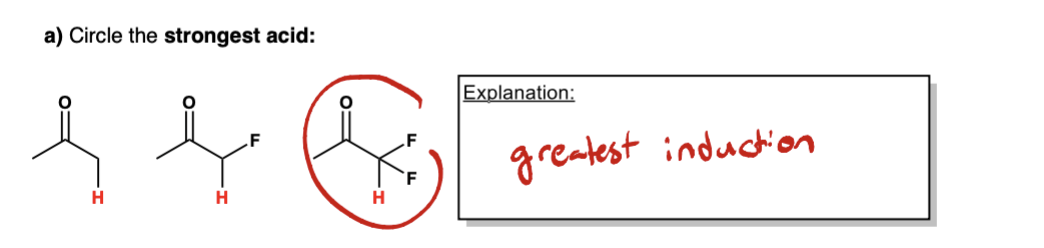
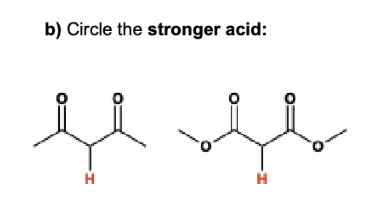
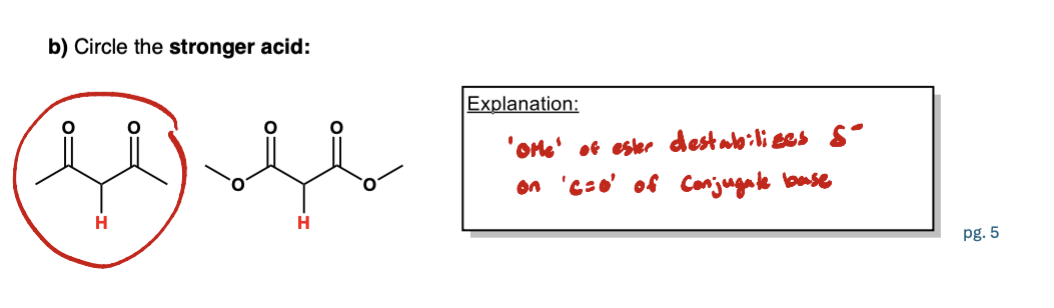

Define the following:
BRONSTED ACID
BRONSTED BASE
BRONSTED REACTION

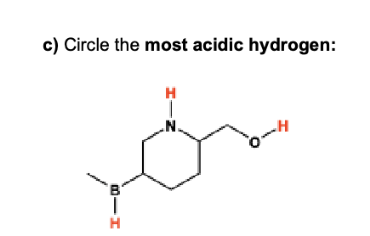
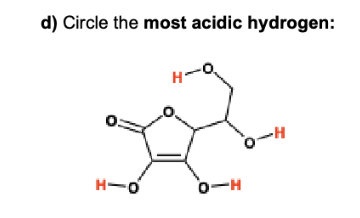
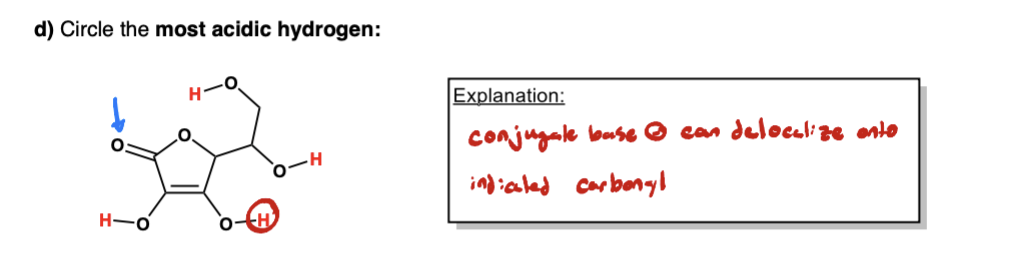
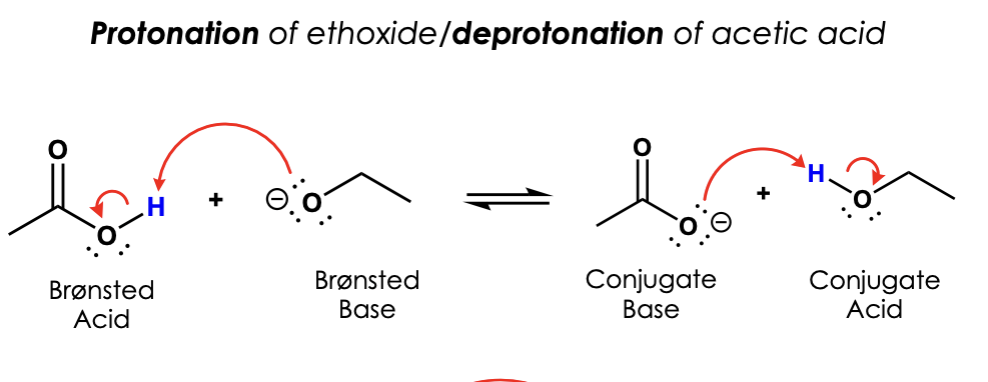
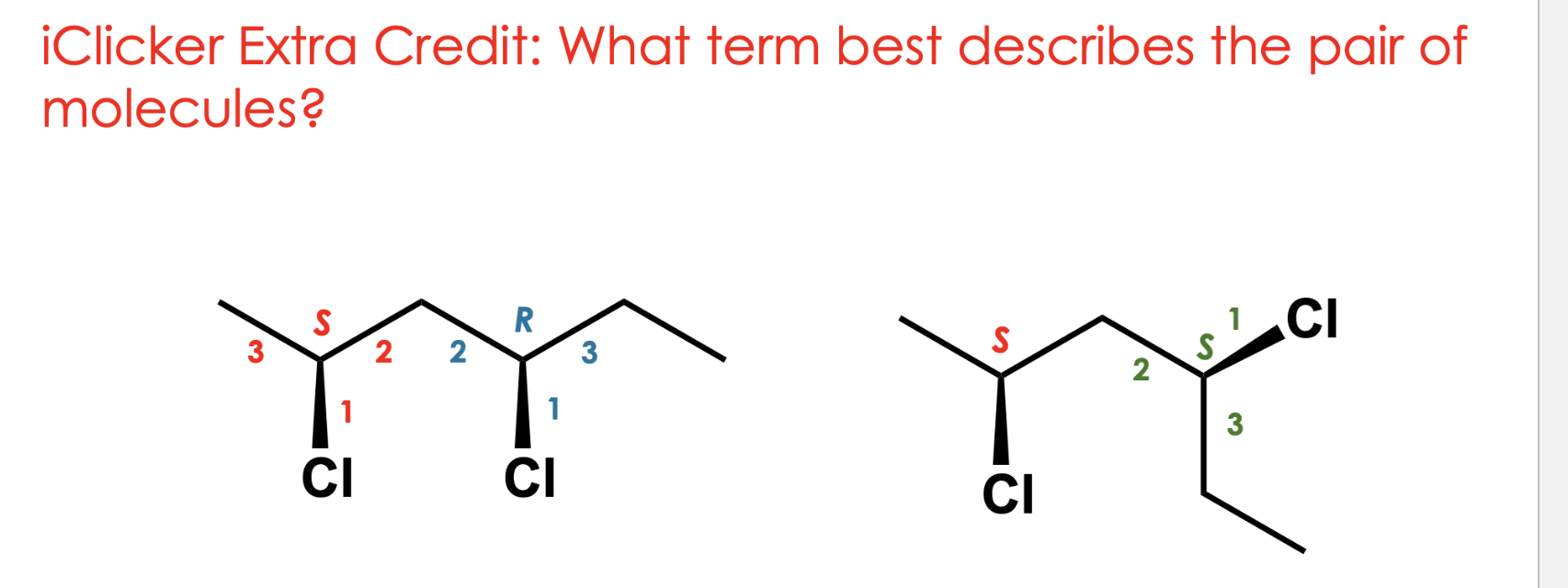
label them according to the bronsted definition
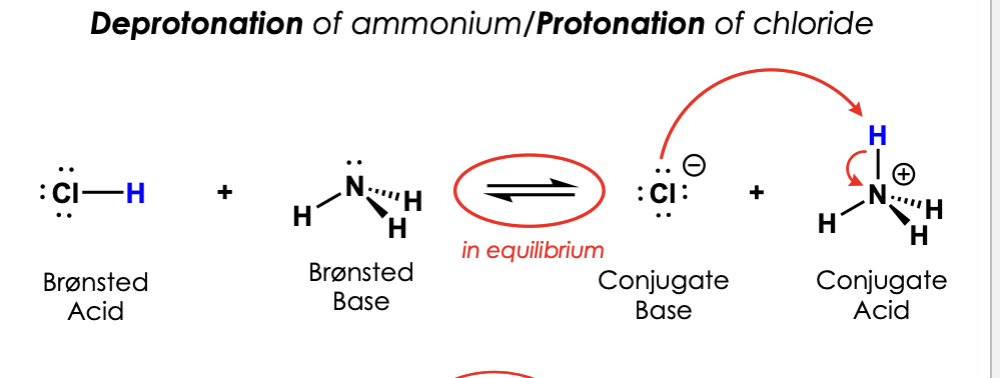
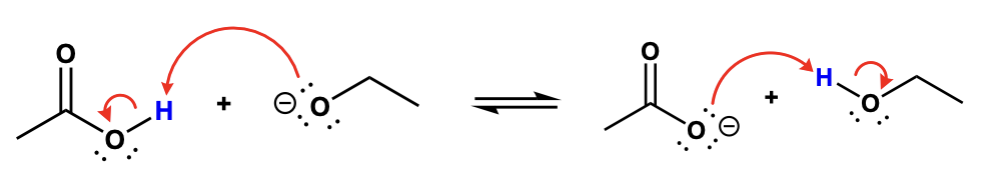
label them according to the bronsted definition
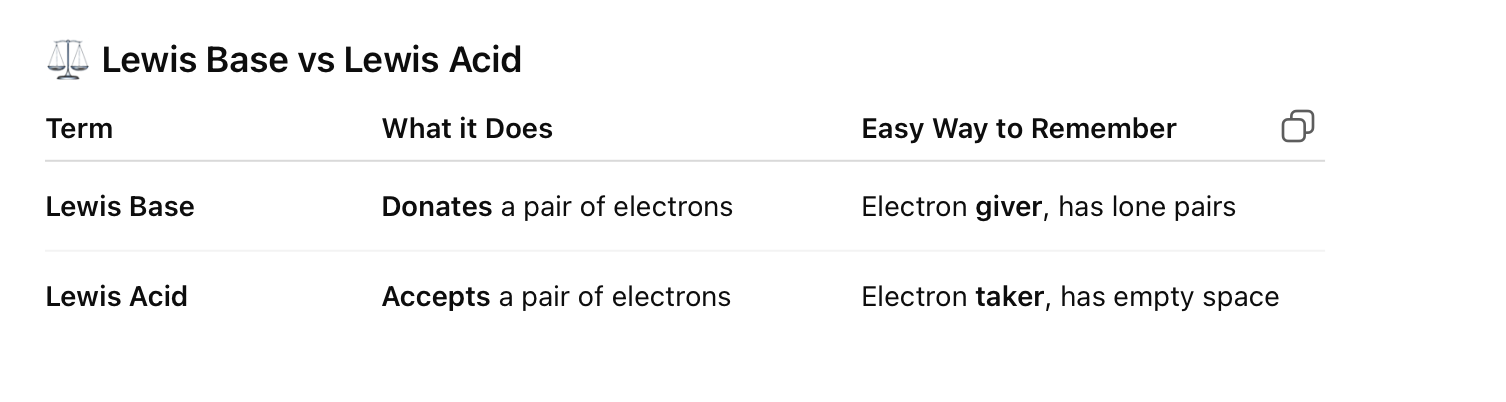
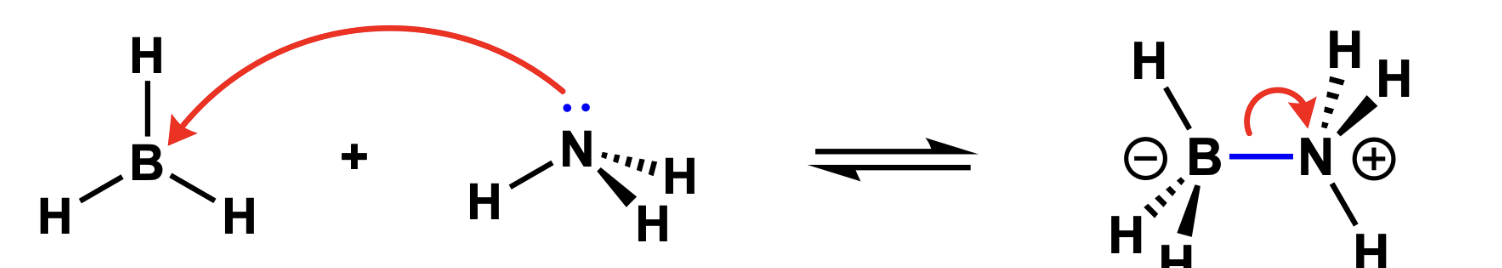
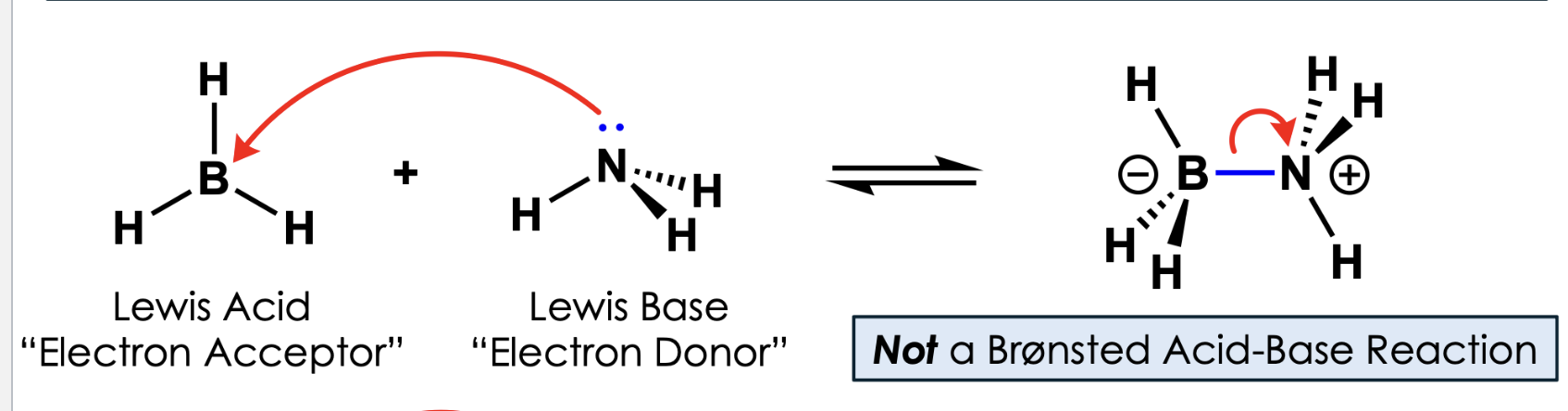
Lewis Base vs Lewis Acid
✅ Quick Memory Trick:
“Base = Brings Electrons”
Lewis Base = Brings or Gives electron pair
DIA
label it
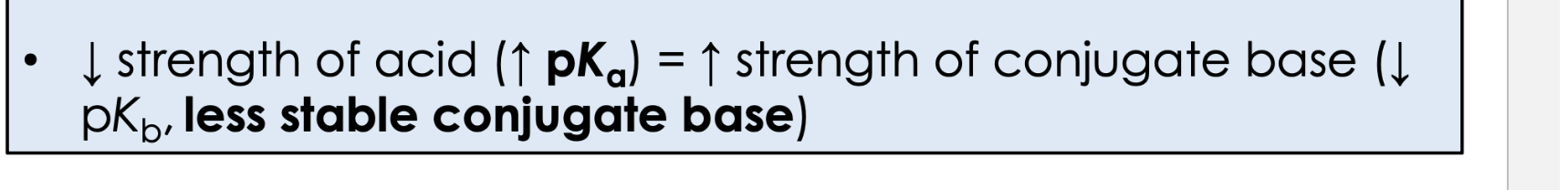
stronger KA means what?
stronger acid
smaller pka means what?
stronger acid
1 pka unit= …. change in acidity
10x change in acidity
lower pkb means what?
stronger base
higher strength of an acid means what in terms of pka and PKB?
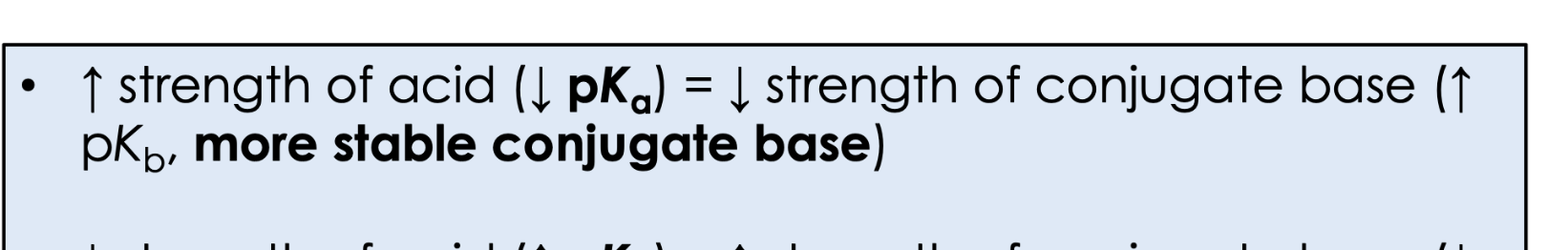
lower strength of an acid means what in terms of pka and PKB?
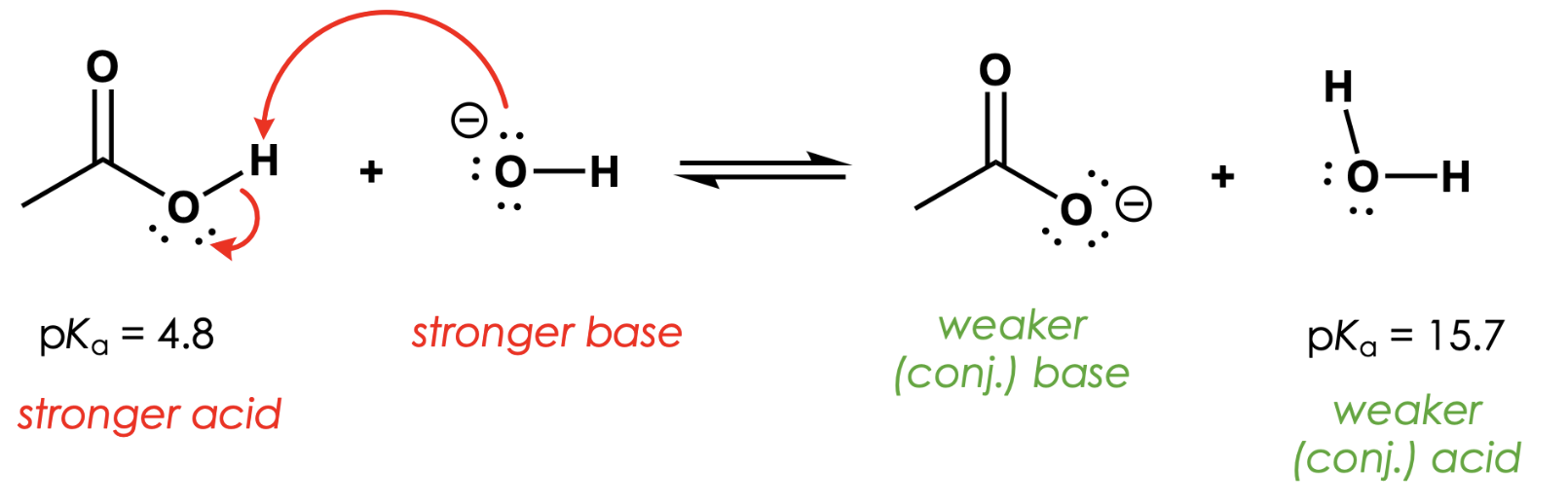
which side of the equation is preferred?
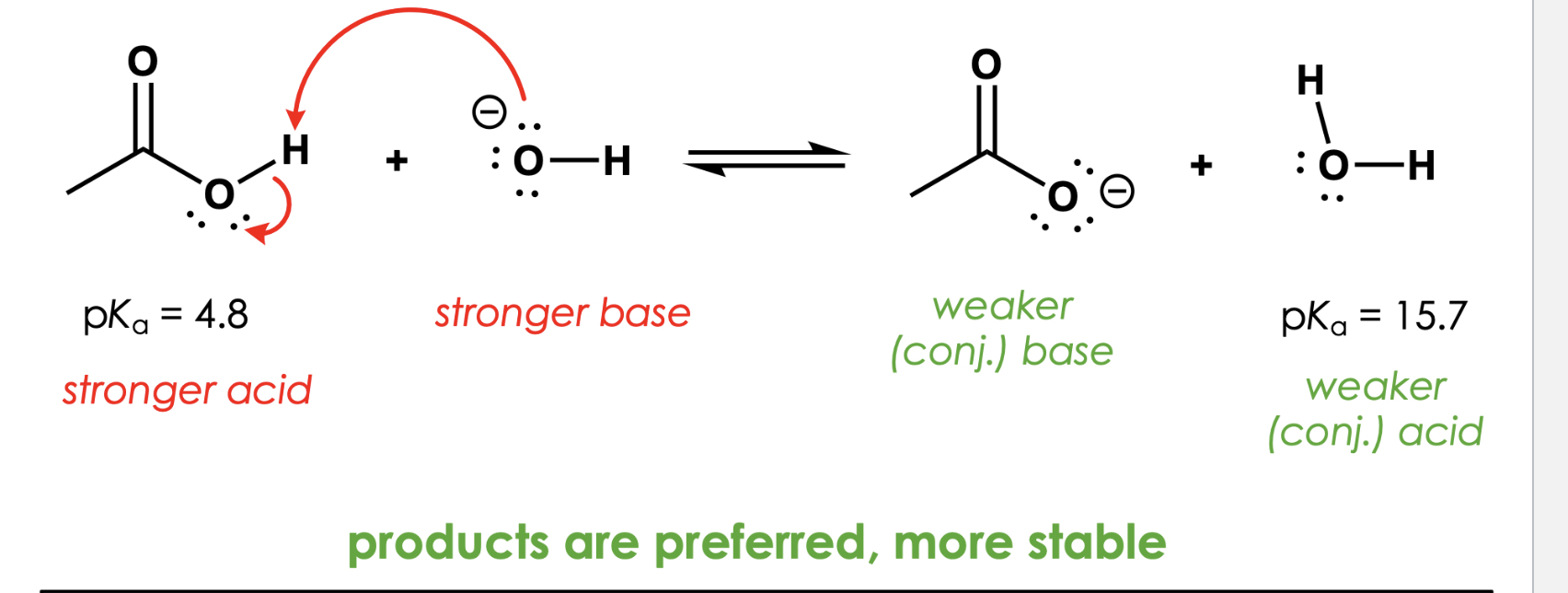
"Equilibrium favors the more stable side of the equation" means what
This means:
In a reaction, the system will shift toward the side with more stable molecules.
Stable = lower energy = favored.
Strong acids/bases are blank stable + why
Weak acids/bases are more stable + why

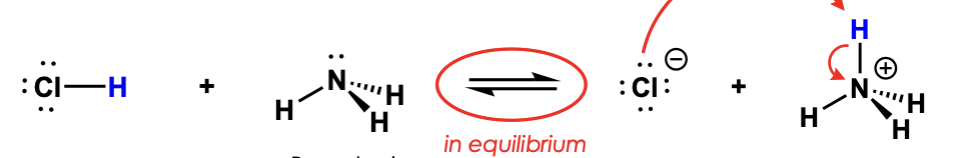
HA + B⁻ ⇌ A⁻ + HB
Left side: strong acid (HA) + strong base (B⁻) → less stable
Right side: weak acid (HB) + weak base (A⁻) → more stable
WHERE WILL IT MOVE
✅ So equilibrium shifts toward the weaker acid/base side (right).
1. What makes an acid stronger?
Answer:
→ If its conjugate base is more stable.
Why?
Because a stable conjugate base is okay holding the negative charge, so the acid is happy to give away H⁺.
2. How does conjugate base stability affect pKa?
Answer:
→ More stable base = lower pKa = stronger acid.
Why?
Stable base = acid gives H⁺ easily = stronger acid.
3. What makes a conjugate base stable? Name 2 things.
Answer:
→ Resonance and electronegative atoms (like oxygen).
Why?
They spread or hold the negative charge better.
6. What does a low pKa mean?
Answer:
→ Strong acid.
Why?
Low pKa = acid gives up H⁺ easily.
7. What does a high pKa mean?
Answer:
→ Weak acid.
Why?
High pKa = acid wants to keep H⁺ = conjugate base is unstable.
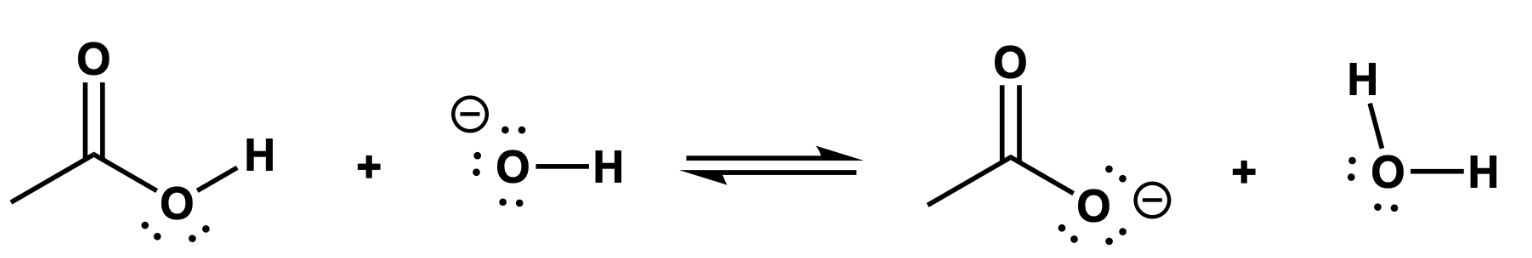
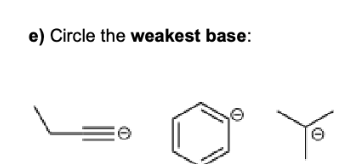
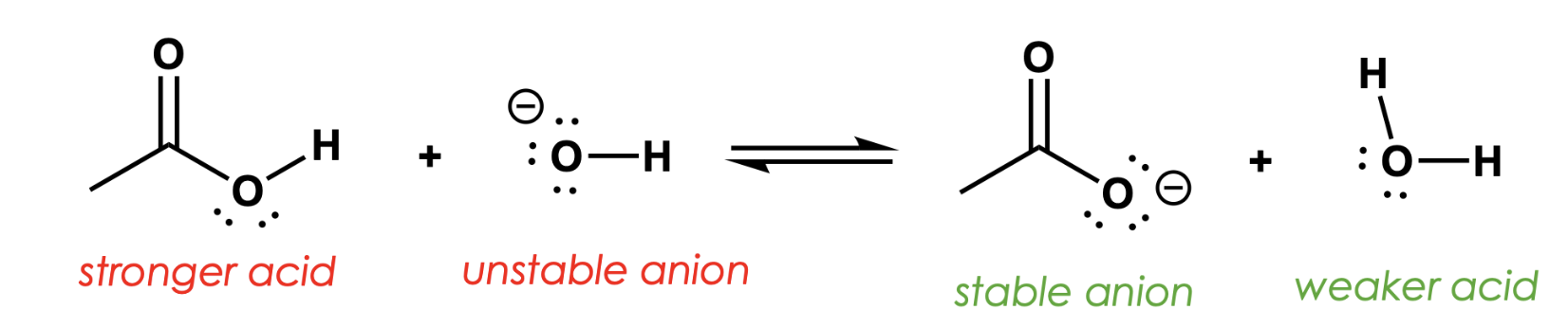
label them acids and anions (stronger + weaker)
ARIO?
atom

In the same row → more electronegative atom = is better at what holding blank charge? more/less base? weaker/stronger acid?
In the same row → more electronegative atom = better at holding negative charge = more stable base = stronger acid.
groups vs periods on periodic table

Bigger atom = better at holding negative charge = more stable conjugate base = stronger acid. but why?
🧠 Why does size matter?
A big atom spreads the negative charge out more (this is called polarizability).
A small atom holds the negative charge tightly in one spot → more unstable.
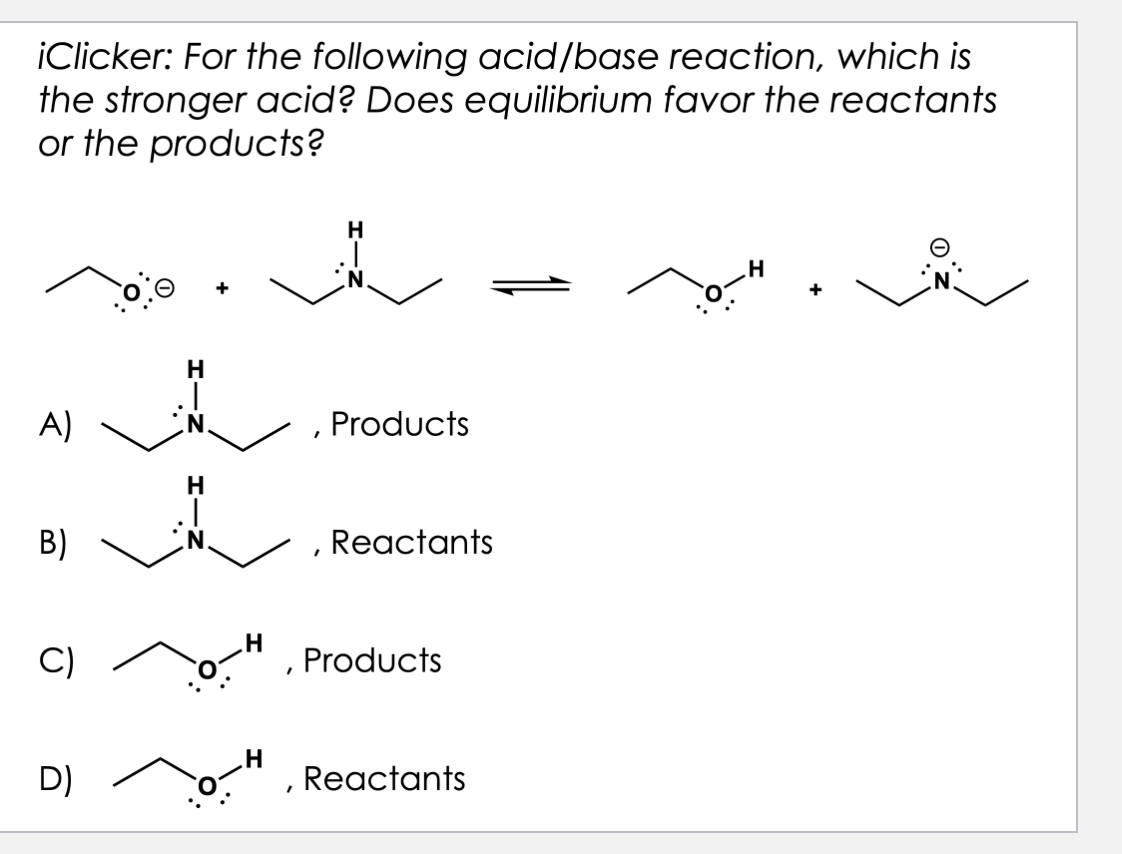
D
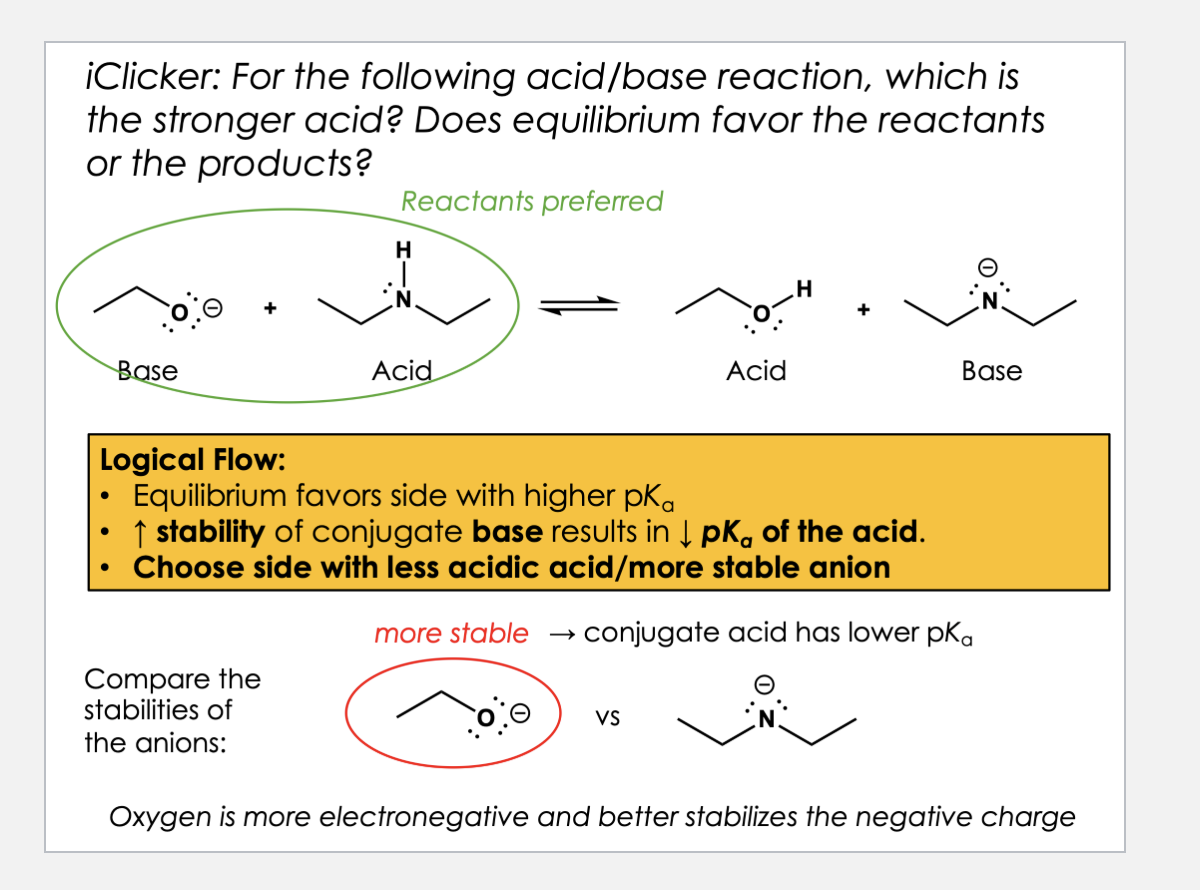
More stable anion → weaker base but why?
💡 Think about what a base does:
A base wants to grab a proton (H⁺).
If the conjugate base (anion) is very stable, it is happy just staying as it is.
So it doesn’t want to react or grab H⁺ → meaning it is a weak base.
less stable anion --> stronger base why?
Because…
A less stable anion (negatively charged ion) is uncomfortable holding that negative charge.
To feel more stable, it wants to get rid of that negative charge.
The easiest way to do that is to grab a proton (H⁺).
A molecule that really wants to grab a proton is called a strong base.
The inductive effect is
affected by
electronegativity,
2. # of electronegative
atoms
3. distance