Bio 230W Exam 4 (Quizlet Practice Exam)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
(Q001) Which of the following types of cell signaling is long range and uses hormones as signals?
endocrine
(Q002) What type of cell response would take the longest amount of time (on the scale of minutes to hours) to execute?
one that involves a change in gene expression
(Q003) The first step in a signaling pathway that responds to a molecule that stays in the extracellular space is
binding of the signal molecule to a receptor.
(Q004) Which of the following describes negative feedback regulation?
A component late in the pathway inhibits an enzyme early in the pathway.
(Q005) Enzymes that add a phosphate group to a switch protein are called
kinases.
(Q006) One of the two types of GTP-binding proteins, often called G-proteins, are membrane bound. These are the
trimeric GTP-binding proteins.
(Q007) The active form of a monomeric GTP-binding protein is the
GTP-bound form.
(Q008) Which type of cell-surface receptor(s), when activated, catalyze(s) a reaction inside the cell?
enzyme-coupled receptors
(Q009) When activated, a G-protein has a structure that
is bound to GTP.
(Q010) Which of the following would produce the fastest response to G-protein activation?
ion channel activation
(Q011) Which of the following correctly matches a G-protein-activated enzyme with the second messenger molecule it produces?
phospholipase C à diacylglycerol
(Q012) Which cAMP-mediated signaling pathway would take on the order of minutes to hours for a response to develop (as opposed to seconds)?
a response where cAMP leads to the activation of a transcriptional regulator
(Q013) Calcium ion release triggers all of the following biological processes EXCEPT
action potential transmission along an axon.
(Q014) Which of the following depicts the correct order of steps involved in nitric oxide (NO) signaling to trigger smooth muscle relaxation?
acetylcholine receptor activation à activation of NO synthetase à NO diffusion into neighboring cells à activation of guanylyl cyclase à cGMP production
(Q015) Shown is a schematic of the light-induced signaling cascade in rod photoreceptor cells. At which step(s) does the response become amplified so that one photon stimulates a multifaceted response?
cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase hydrolyzing cGMP molecules
(Q016) How does the binding of a signal molecule activate an RTK for downstream signaling?
The RTK forms a dimer and cross-phosphorylates itself.
(Q017) Which of the following is NOT an intracellular signaling protein activated by an RTK?
G-protein
(Q018) If Ras contains a mutation that leads to a defect in GTP hydrolysis, this could fuel uncontrolled proliferation in cancer because
Ras is able to signal to downstream pathways inappropriately.
(Q019) Steroid hormones trigger transcription of target genes by
binding to nuclear receptors that act as transcription factors for specific genes.
(Q020) Shown below is a diagram of how theoretical intracellular signaling pathways could integrate incoming signals to produce a coordinated cell response.
signals A and D
(Q001) Which of the cytoskeletal structures are made up of protein subunits that are fibrous?
intermediate filaments
(Q002) Which of the following is an important function of intermediate filaments?
providing tensile strength to the cell and the nucleus
(Q003) How do the intermediate filament proteins keratin, vimentin, and neurofilaments differ from each other?
They are different at the head and tail domains that are exposed at the surface.
(Q004) In terms of structure, if cytoplasmic intermediate filaments are described as ropes, nuclear lamins could be best described as
mesh.
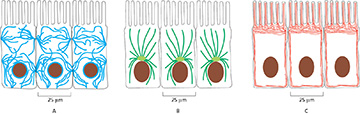
(Q005) Which of the following represents the placement of microtubules in an epithelial cell?
B
(Q006) Microtubules extend from organizing centers in the cell. Which is an example of an organizing center?
basal body of a cilium
(Q007) Microtubules are made up of 13 ___________ that are linear chains of ___________.
protofilaments; tubulin dimers
(Q008) The end of the microtubule that has /alpha-tubulin exposed is the
(-) end.
(Q009) Shown below is a diagram of a centrosome and associated microtubules. What is the identity of the structure in red, indicated by the black dashed arrow?
/gamma-tubulin ring complex
(Q010) Microtubules are inherently unstable unless they are
stabilized by a (+) end attachment.
(Q011) Taxol and colchicine are used to treat cancer because they arrest dividing cells in mitosis. What is the mechanism of action of these drugs?
Both drugs constrain the dynamic instability of microtubules.
(Q012) Microtubules participate in the spatial polarization of nerve cells because
microtubule (-) ends originate near the cell body allowing (+) end-directed transport along the axon.
(Q013) Which motor protein is an ATPase, has two globular heads, moves toward the (-) end of a microtubule, and generally interacts with cargo via an adaptor protein?
cytoplasmic dynein
(Q014) Which of the following actin-binding proteins prevent polymerization of actin monomers?
thymosin and profilin
(Q015) At the leading edge of a cell, ARP proteins help form new branches on actin filaments to push the leading edge forward using the force of the polymerization, as shown in the figure below.
at the plus ends of newly polymerized actin filaments
(Q016) Which of the following motor proteins has one head domain, moves along actin toward the plus end, and is found in all cell types?
myosin-I
(Q017) A ___________ is a long structure found in abundance in the cytoplasm of a single skeletal muscle fiber, and is composed of many bundles of actin and myosin filaments that are arranged in repeating units.
myofibril
(Q018) The binding of ATP causes a conformational change in myosin that
releases the myosin head from the actin filament.
(Q019) When an action potential excites a muscle cell, where do the calcium ions come from?
both the extracellular space and the sarcoplasmic reticulum
(Q020) How is muscle contraction reversed?
Calcium ion pumps in the sarcoplasmic reticulum reduce the cytosolic calcium levels and tropomyosin blocks the myosin binding site on actin.
(Q021) How do calcium ions stimulate contraction in nonmuscle cells and smooth muscle cells?
Calcium ions bind to troponin and lead to a conformational change in tropomyosin that exposes the myosin binding sites on the actin filament.