TEAS Science
4.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
305 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomical position
Standard positioning of the body as standing; feet together; arms to the side; with head, eyes, and palms of hands forward.
2
New cards
Cells
The basic structural unit of an organism from which living things are crated.
3
New cards
Cellular functions
Processes that include growth, metabolism, replication, protein synthesis, and movement.
4
New cards
Directional terminology
Words used to explain relationships of locations of anatomical elements (distal, posterior, medial, etc.)
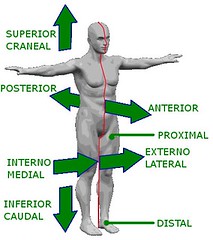
5
New cards
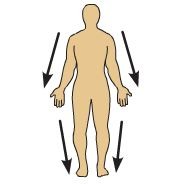
Distal
Farther from the trunk of the body
6
New cards
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
7
New cards
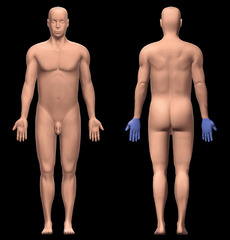
dorsum of hand
top of hand
8
New cards
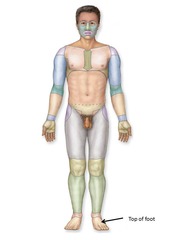
dorsum of foot
Top of foot
9
New cards
posterior
Back of the body
10
New cards
medial
Toward the midline of the body
11
New cards
anterior
Located towards the front of the body
12
New cards
inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
13
New cards
Organ system
A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions.
14
New cards
Organelle
A specialized part of a cell that has a specific function.

15
New cards
Organ
A self-contained part of an organism that performs a specific function.
16
New cards
Reference planes
Planes dividing the body to describe locations: sagittal, coronal, and transverse.
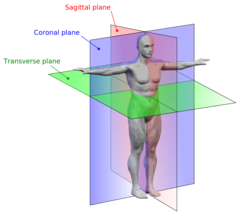
17
New cards
Tissue
A group of cells with similar structure that function together as a unit, but at a lower level than organs.
18
New cards
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
19
New cards
Asthma
A lung disease characterized by inflamed, narrowed airways and difficulty breathing.
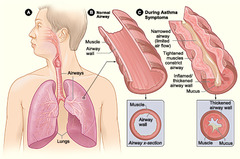
20
New cards
Bronchi
The main passageways directly attached to the lungs.

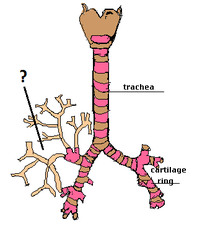
21
New cards
Bronchioles
Small passages in the lungs that connect bronchi to alveoli.
22
New cards
cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder that affects the lungs and other organs, characterized by difficulty breathing, coughing up sputum, and lung infections.
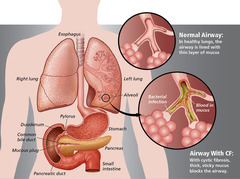
23
New cards
perfusion
The passage of fluid to an organ or a tissue.
24
New cards
pleura
A membrane around the lungs and inside the chest cavity.
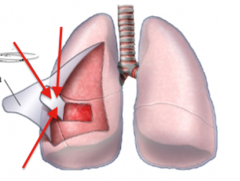
25
New cards
Surfactant
a lipoprotein secreted by the alveoli that lowers the surface tension in the alveoli, reduces the amount of pressure needed to inflate the alveoli, and decreases the tendency of the alveoli to collapse.
26
New cards
tidal volume
Amount of air inhaled and exhaled during normal breathing
27
New cards
trachea
The windpipe; tube leading from the larynx to the lungs; a passage through which air moves in the respiratory system
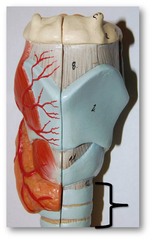
28
New cards
ventilation
The movement of air in and out of the body via inhalation and exhalation.
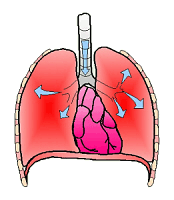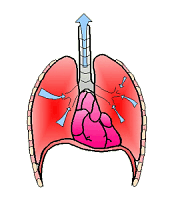
29
New cards
pulmonary loop
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
30
New cards
systemic loop
Carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and back to the heart
31
New cards
arteries
Blood vessels that deliver blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
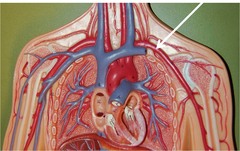
32
New cards
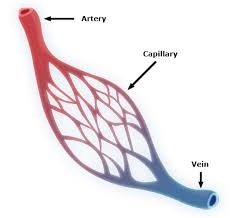
capillary
Small blood vessels that connect arterioles to venules.
33
New cards
diastole
The portion of the cardiac cycle in which the heart refills with blood.
34
New cards
heart
The muscle that pumps blood throughout the body.
35
New cards
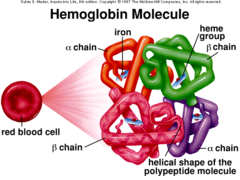
Hemoglobin
The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
36
New cards
leukocyte
White blood cells, which protect the body against disease.
37
New cards
lymph
Clear fluid that moves throughout the lymphatic system to fight disease.
38
New cards
lymphocyte
A subtype of white blood cell found in lymph.
39
New cards
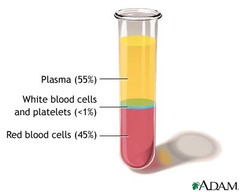
plasma
The pale yellow component of blood that carries red blood cells, which blood cells, and platelets throughout the body.
40
New cards
systole
The portion of the cardiac cycle in which the heart expels blood.
41
New cards
vein
Blood vessels that carry blood to the heart.
42
New cards
sinoatrial node
pacemaker of the heart
43
New cards
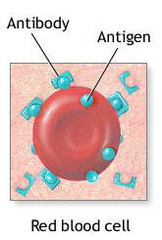
Antibodies
An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response.
44
New cards
Anus
The opening of the rectum from which solid waste is expelled.
45
New cards
bolus
A mass of food that has been chewed and swallowed.
46
New cards
chyme
The semifluid mass of partly digested food that moves from the stomach to the small intestine.
47
New cards
enzymatic digestion
The break down of food by enzymes for absorption.
48
New cards
gall bladder
The organ that stores bile.
49
New cards
large intestine
Also known as the colon, where vitamins and water are absorbed before feces is stored prior to elimination.
50
New cards
liver
The organ that produces bile, regulates glycogen storage, and performs other bodily functions.
51
New cards
mouth
The oral cavity at the entry to the alimentary canal.

52
New cards
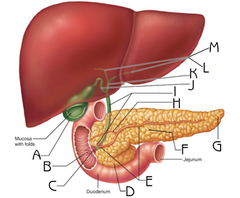
pancreas
The gland of the digestive and endocrine systems that produces insulin and secretes pancreatic juices.
53
New cards
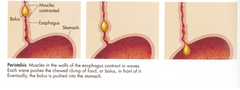
peristalsis
A series of muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
54
New cards
rectum
The last section of the large intestine, ending with the anus.
55
New cards
saliva
The clear liquid found in the mouth, also known as spit.
56
New cards
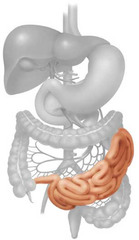
small intestine
The part of the GI tract between the stomach and large intestine that includes the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, where digestion and absorption of food occurs.
57
New cards
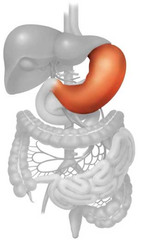
stomach
The organ between the esophagus and small intestine in which the major portion of digestion occurs.
58
New cards
salivary amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch
59
New cards
salivary lipase
What is the enzyme present in saliva that breaks down fats?
60
New cards
gastric lipase
Enzymes produced in the stomach that cleaves fatty acids from glycerol molecules.
61
New cards
pepsin
An enzyme in the stomach that breaks down protein
62
New cards
HCl
Which acid is in the stomach?
63
New cards
Gastrin
Digestive hormone that stimulates sustained secretion of gastric juice from the stomach
64
New cards
ghrelin
A hunger-arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach
65
New cards
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles. it's stored in the gallbladder.
66
New cards
Pancreatic juice
contains trypsin, chymotrypsin, amylase, lipase and bicarbonate, it is secreted by the pancreas.
67
New cards
Proteases
Pancreatic enzymes that complete protein digestion.
68
New cards
amylase
An enzyme that digests starch into disaccharides. Amylase is secreted by salivary glands and by the pancreas.
69
New cards
secretin
Digestive hormone that stimulates the pancreas to release bicarbonate to neutralize acid in duodenum.
70
New cards
somatostatin
What hormone inhibits glucagon release and pancreatic exocrine secretions?
71
New cards
insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
72
New cards
glucagon
A protein hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells that raises blood glucose levels; an antagonistic hormone to insulin.
73
New cards
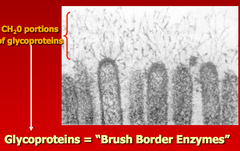
Brush border enzymes
Assist in digestion of carbohydrates and proteins in the small intestine; activate enzymes; break down small peptides into a.a.s in the small intestine. (proteases, lactase, disaccharidases).
74
New cards
Cholecystokinin
Following the ingestion of a fatty meal, what hormone is secreted by the duodenal mucosa to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder
75
New cards
motilin
A gastric hormone that activates duodenal/ jejunal receptors to initiate peristalis
76
New cards
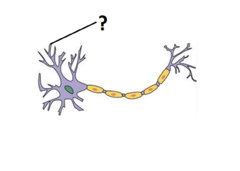
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
77
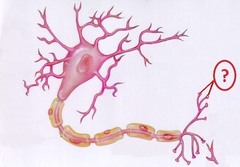
New cards
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
78
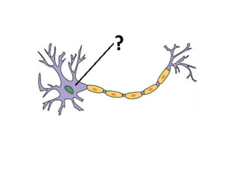
New cards
axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
79
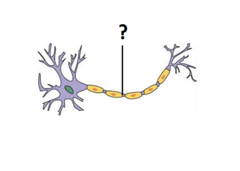
New cards
myelin sheath
A layer of electrical insulation that surrounds the axon.
80
New cards
axon terminal
terminal branch of an axon where neurotransmitters are stored
81
New cards
actin
A contractile protein that is part of the thin filaments in muscle fibers
82
New cards
myosin
A protein present in muscle fibers that aids in contraction and makes up the majority of muscle fiber
83
New cards
sarcomere units
each fibril is organized into these units, contraction takes place here. composed of regular overlapping thick myosin and thin actin
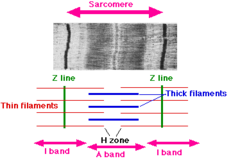
84
New cards
autonomic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates unconscious body functions such as breathing and heart rate.
85
New cards
contraction
Shortening or elongating a muscle to perform muscle actions.
86
New cards
involuntary
Without intentional control.
87
New cards
muscle
Soft tissue that produces force and motion to move the body.
88
New cards
nerve
A bundle of axons that transmits electrical impulses to peripheral organs.

89
New cards
reflex
An involuntary movement in reaction to a stimulus.
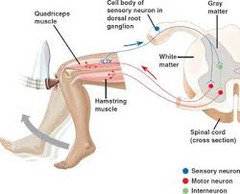
90
New cards
relaxation
Release of tension is also known as?
91
New cards
synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
92
New cards
voluntary
performed on purpose
93
New cards
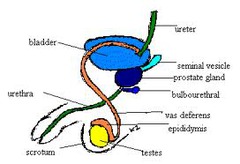
seminal vesicles
Paired sac-like male exocrine glands that secrete fluid (a major component of semen) into the vas deferens
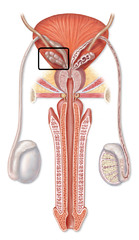
94
New cards
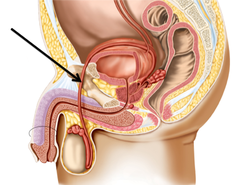
prostate
The gland in males that controls the release of urine and secretes a part of semen that enhances motility and fertility of sperm.
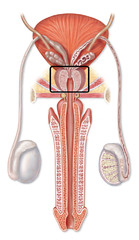
95
New cards
bulbourethral gland
A pair of exocrine glands near the male urethra. They secrete fluid into the urethra. Also called Cowper glands
96
New cards
vas deferens
The duct in which sperm moves from a testicle to the urethra.
97
New cards
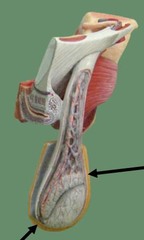
testicles
The organs that produce sperm; also called testes.
98
New cards
scrotum
The pouch of skin that contains the testicles.
99
New cards
cervix
The passage that forms the lower part of the uterus.
100
New cards
estrogen
Female sex hormones.