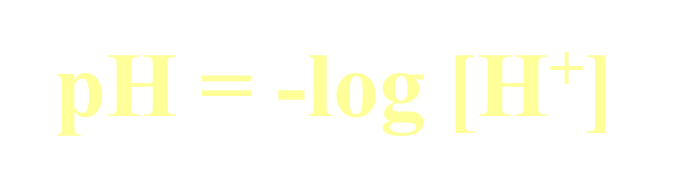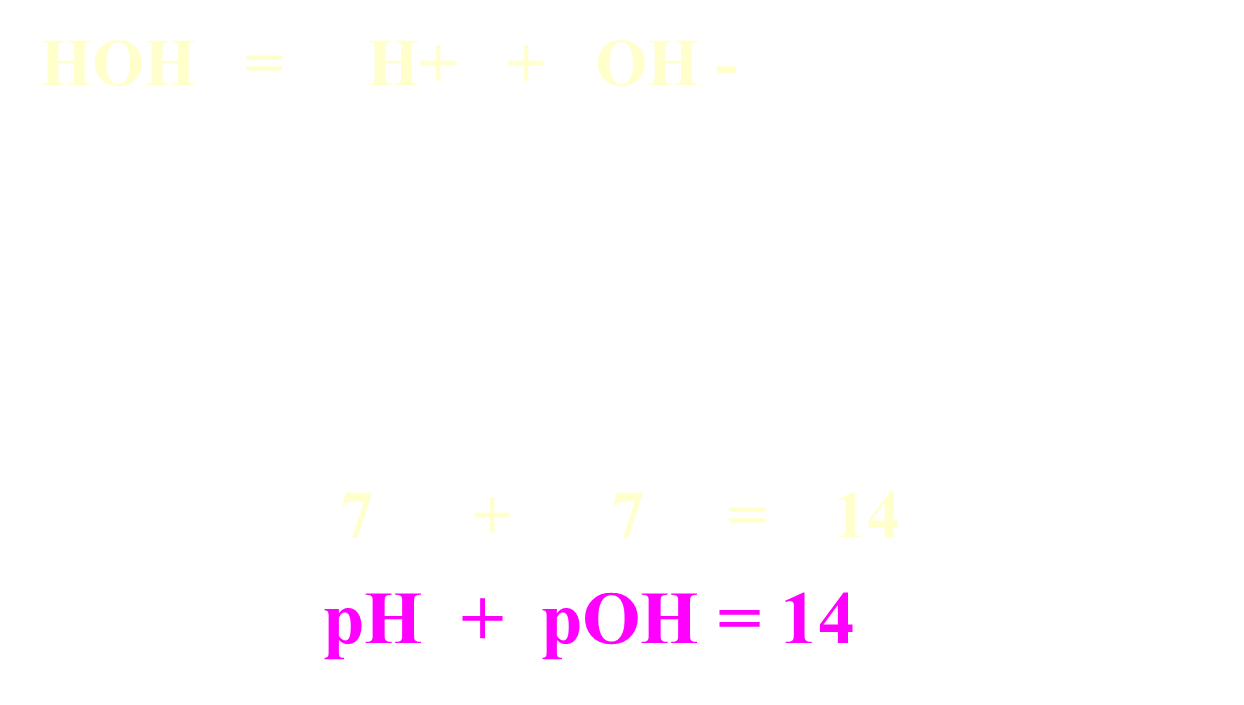L1: pH of Common Solutions
Hydrogen Ions and Activity
To test a diagnosis of a patient, the doctor orders several tests (urinalysis, blood banking).
Results from the test will be expressed in units of pH.
Purpose of pH scale
measure the acidity/basic of solution
H+ (hydrogen ion) or H3O+ (hydronium ion) - acid
OH- (hydroxide) - base
ACID
pH is less than 7
neutralizes bases
Forms H+ ions in solution
Corrosive
reacts with most metals to form hydrogen gas
Good conductors of electricity
bc of ions generated
Generate ions
ex. HNO3 + H3O → H3O+ + NO3
Weak and Strong Acids
Weak Acids
do not ionize partially:
ex. Acetic, Boric, Nitrous, Phosphoric, Sulfurous
Strong Acids
ionize completely:
ex. Hydrochloric, Nitric; Sulfuric, Hydriodic
Common Acids
HCl (hydrochloric) stomach acid
H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) car batteries
HNO3 (nitric acid) explosives
HC2H3O2 (acetic acid) vinegar
H2CO3 (carbonic acid) sodas
H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) flavorings
BASE
pH greater than 7
Feels slippery
Dissolves fats and oils
Usually forms OH- ions in solution
Neutralizes acids
Weak and Strong Base
Weak Bases
ammonia (NH3)
urea (CO(NH2)2)
Strong Bases
sodium hydroxide
barium hydroxide
calcium hydroxide
Common Bases
NaOH (sodium hydroxide) LYE soaps, drain cleaner
Mg(OH)2 (magnesium hydroxide) antacids
Al(OH)3 (aluminum hydroxide) antacids, deodorants
NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide) ammonia
Reaction with Indicators
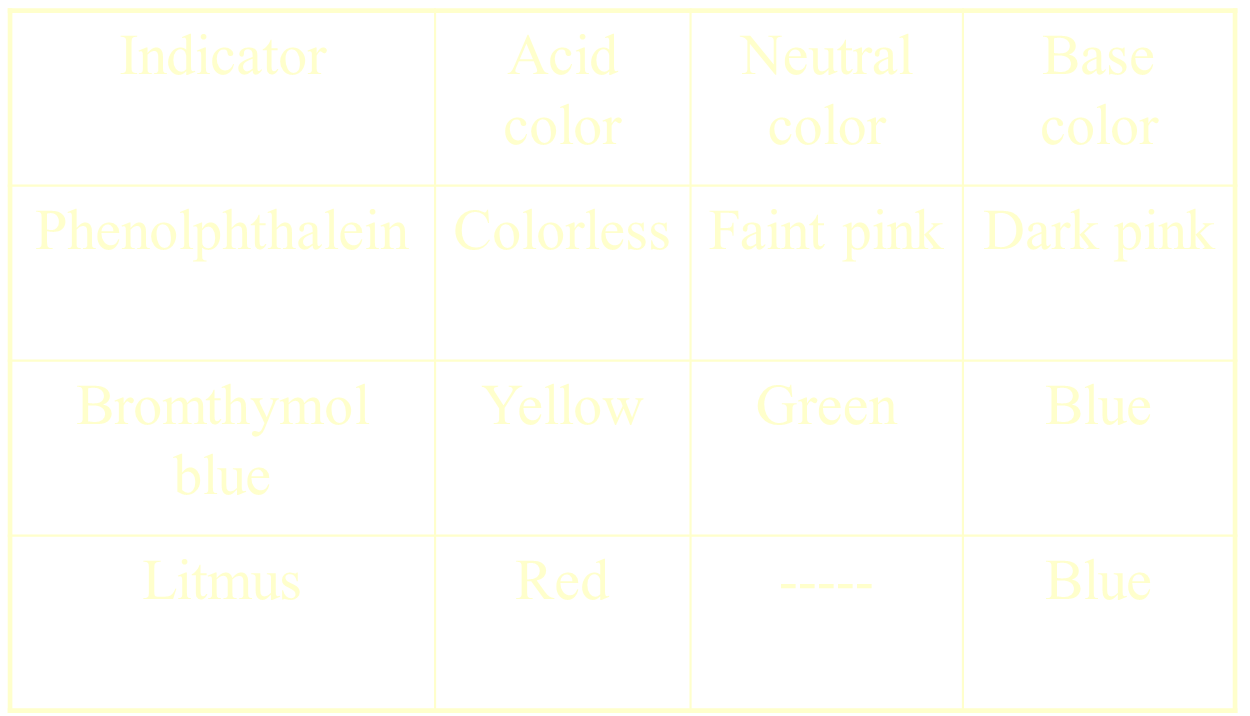
Measuring pH
pH meters
pH paper
changes color to indicate a specific pH value
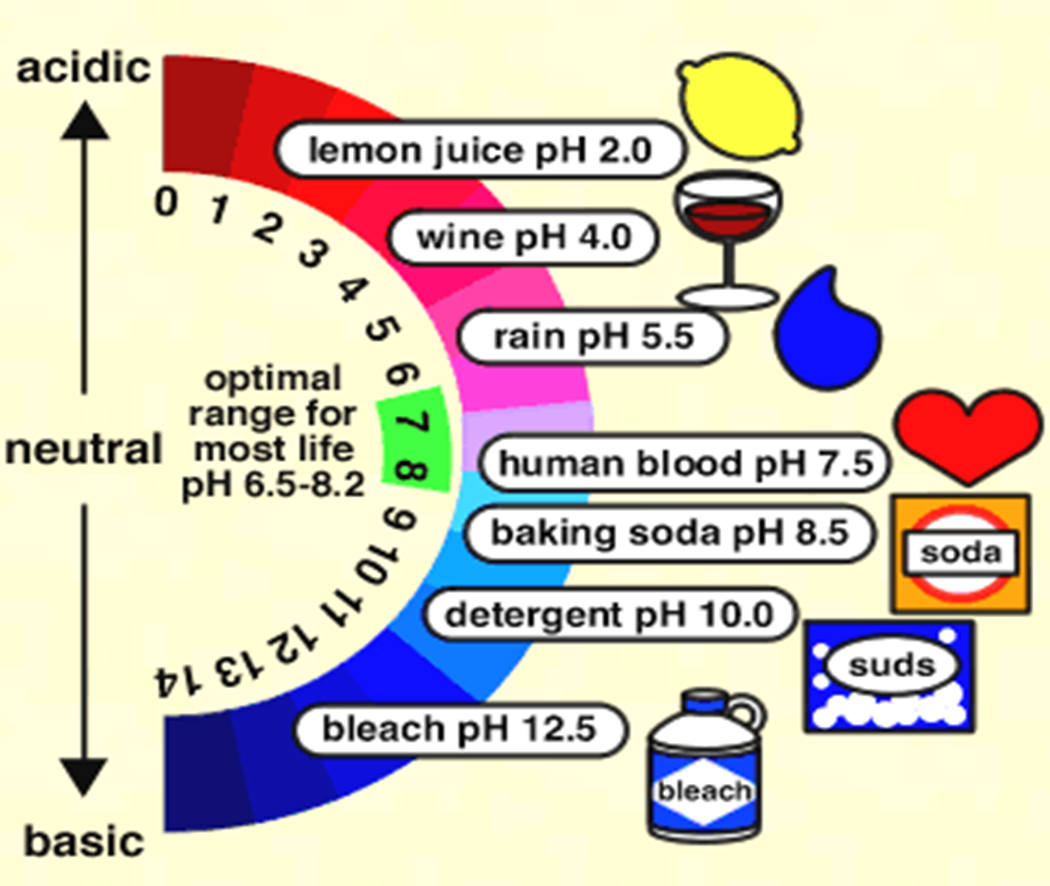
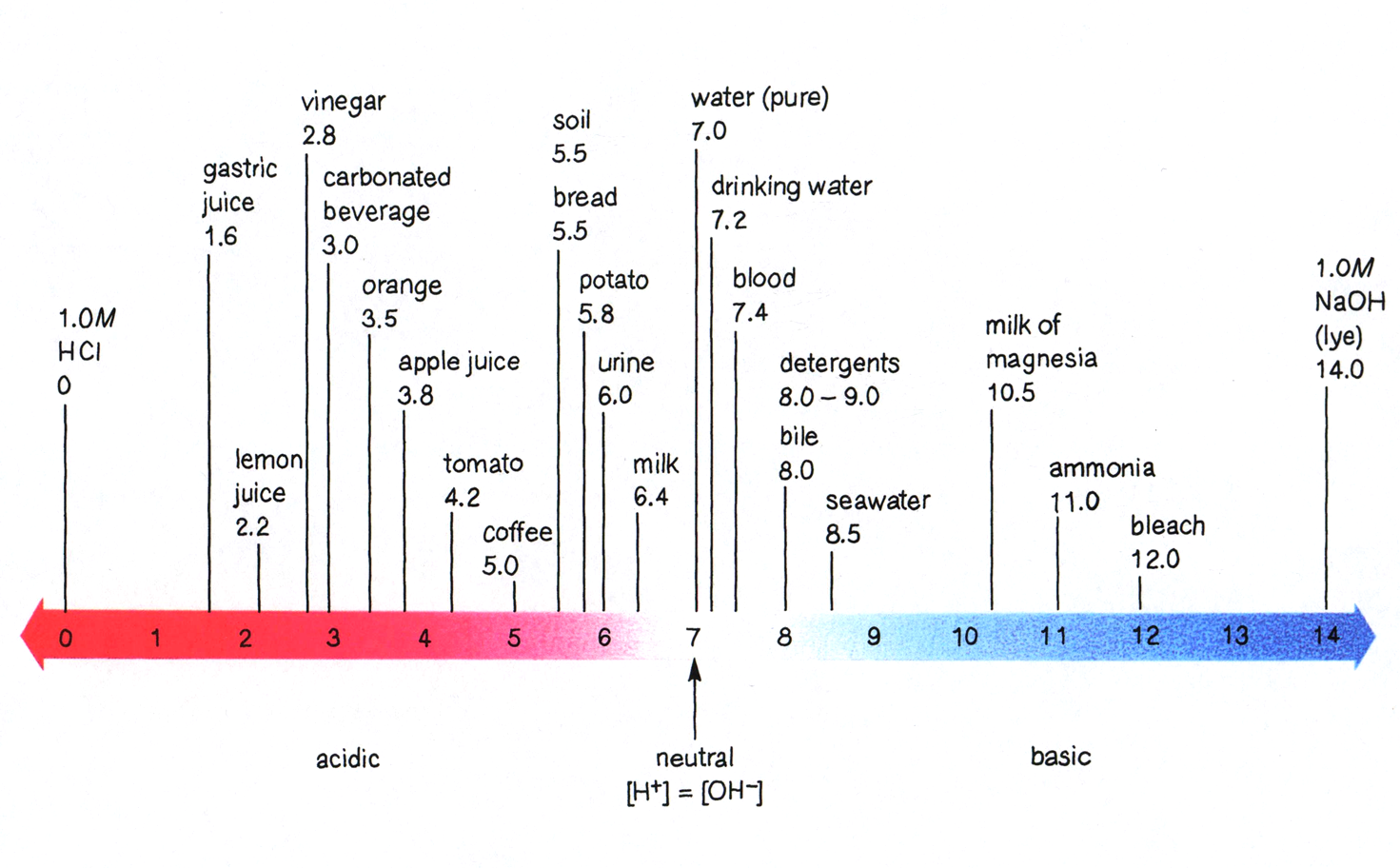
pH Scale
pH of Common Substances
pH Scale
Relationship between pH and pOH

Formulas:
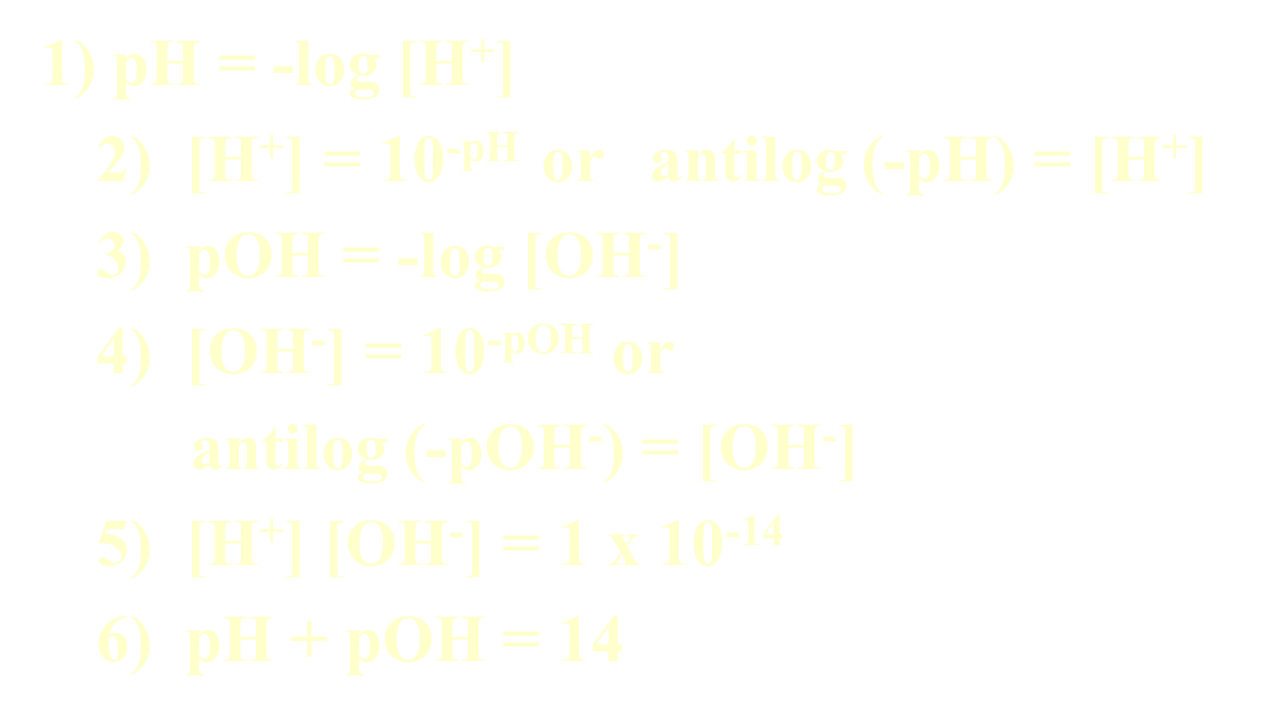
BUFFERS
a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acids and bases are added
Types of Acids and Bases
(concepts based on reactions of aqueous solution 1800’s)
Svante Arrhenius developed a concept of acids and bases relevant to reactions in H2O
Arrhenius acid
produces hydrogen ions in water
Arrhenius base
produce hydroxide ions in water
broader modern concept of acids and bases were developed later
Bronsted-Lowry acid
donates a hydrogen ion in a reaction
Bronsted-Lowry base
accepts a hydrogen reaction
Conjugate acid
compound formed when a base gains a hydrogen ion
species formed when a base has accepted proton
Conjugate base
compound formed when an acid loses a hydrogen ion
species formed when an acid has donated or removes a proton
ex. Acetic Acid ionizes according to the ff. chemical reaction:

Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
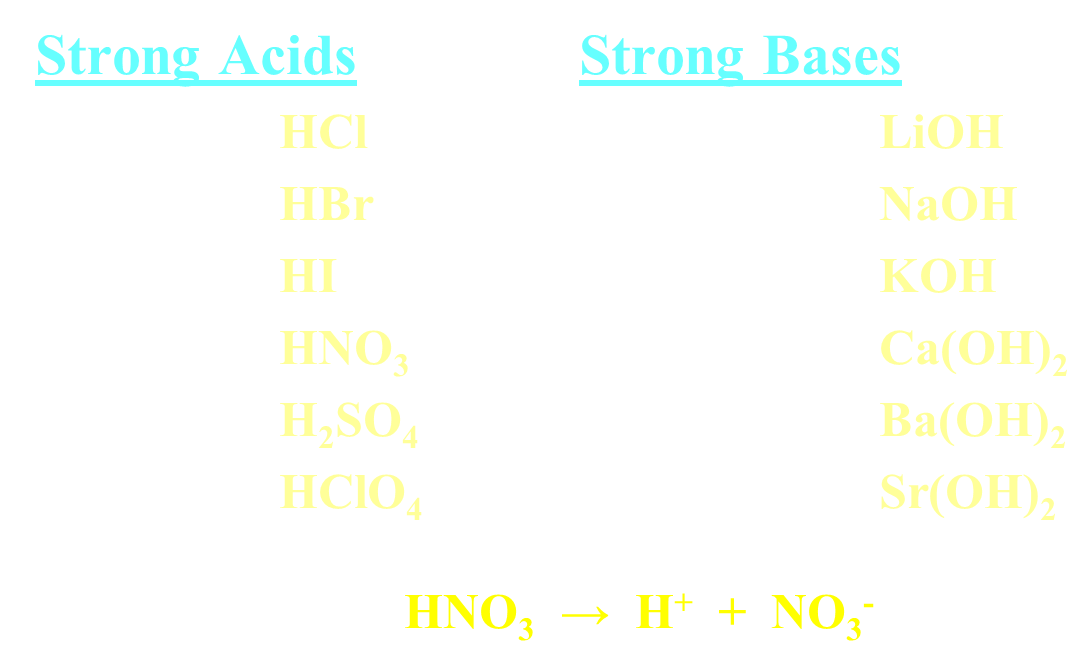
Strong Acids and Bases
Goes 100% ionization
normally shown with single-headed arrow
Weak Acids and Bases
Partially dissociate or ionize, reaching some dynamic equilibrium state.
double-headed arrow
significant in biological systems
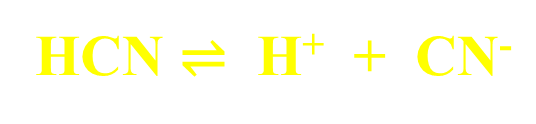
Buffer Systems
Carbonates
carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion
Phosphates
sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium hydrogen phosphate
Proteins
hemoglobin
transports O2 when Inhaled
transports CO2 when exhaled
Cation (+)
Anion (-)