Week 6 Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:59 AM on 5/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
When would you consider the autoionization of water?
when pH is 6-8
2
New cards
when does dissolving salts result in a neutral solution?
when salts have a strong acid and strong base
3
New cards
when does dissolving salts result in a basic solution?
when salts have a strong base and/or weak acid
4
New cards
when does dissolving salts result in an acidic solution?
when salts have a strong acid and/or weak base
5
New cards
What is Kw in relation to Ka and Kb
Kw=KaKb
6
New cards
What happens when a salt is derived from both a weak acid and base? How is acidity determined?
both the cation and anion hydrolyze, aciditiy is determined by whether Ka or Kb is larger
7
New cards
lower temperature on pH and Kw (explain in chatalier’s principle)
pH rises above 7 but is still neutral, Kw lowers because heat, a reactant, is reduced, causing a shift to reactants
8
New cards
higher temperature on pH and Kw (explain in chatalier’s principle)
pH lowers below 7 but is still neutral, Kw raises because heat, a reactant, is increased, causing a shift to products
9
New cards
What is the order of Ka when polyprotic acids are ionized? What is the exception?
Ka1>Ka2>Ka3, second ionization doesn’t affect pH too much except sulfuric acid
10
New cards
when two strong acids are combined, what happens?
the stronger acts as an acid while the weaker acts as a base
11
New cards
how does the common ion affect equilibrium?
since there are more ions in products, it will shift to reactants, preventing further ionization
12
New cards
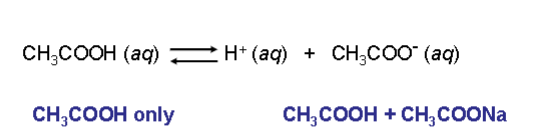
look at the following reaction. describe what happens with CH3COOH + CH3COONa?
there will be more ions in products than H+ protons, thus shifting equilibrium to the left, and decreasing Ka
13
New cards
what is the henderson-hasselbalch equation?
pH=pKa+log(conj base/acid)
14
New cards
buffer solutions
resist change in pH up to a point
15
New cards
imagine a buffer of HA and A-. describe what happens if a strong acid is added
the proton of the strong acid will combine with A-, the weak base, and results in more HA than A-
16
New cards
imagine a buffer of HA and A-. describe what happens if a strong base is added
the proton from HA will be taken by the stong base, resultins in more A- than HA
17
New cards
what is and isn’t a simple buffer solution generally made of?
a weak acid/base with its conjugate base/acid , no strong acids/bases
18
New cards
how to calcualte pH of buffers?
pH = pKa+log(initial conjugate base conc/initial acid conc)