Skeletal System Anatomy (With Pictures)
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Will add all pictures soon -Jan 26 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
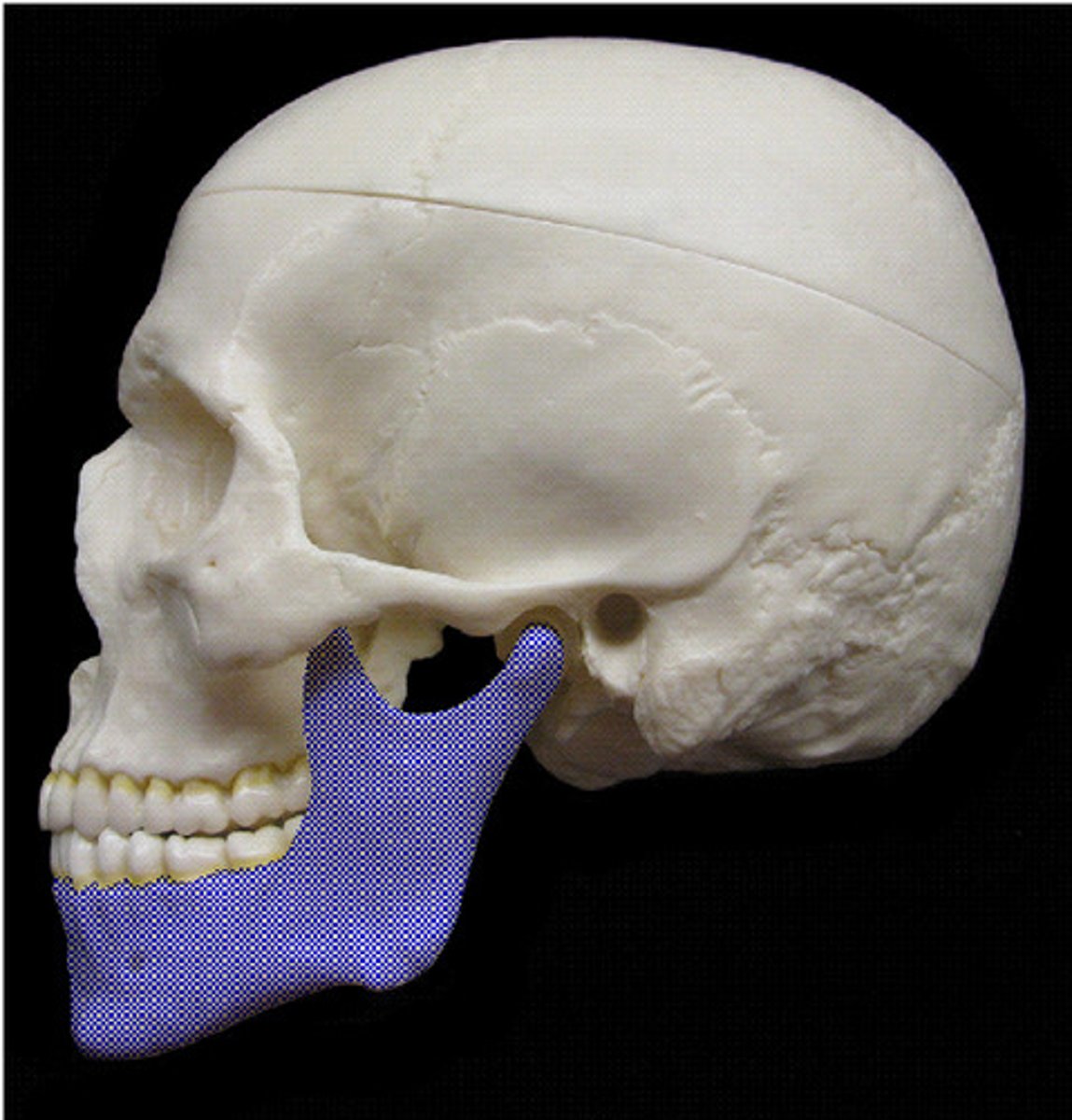
Mandible
lower jaw bone, only bone of the skull not joined by sutures
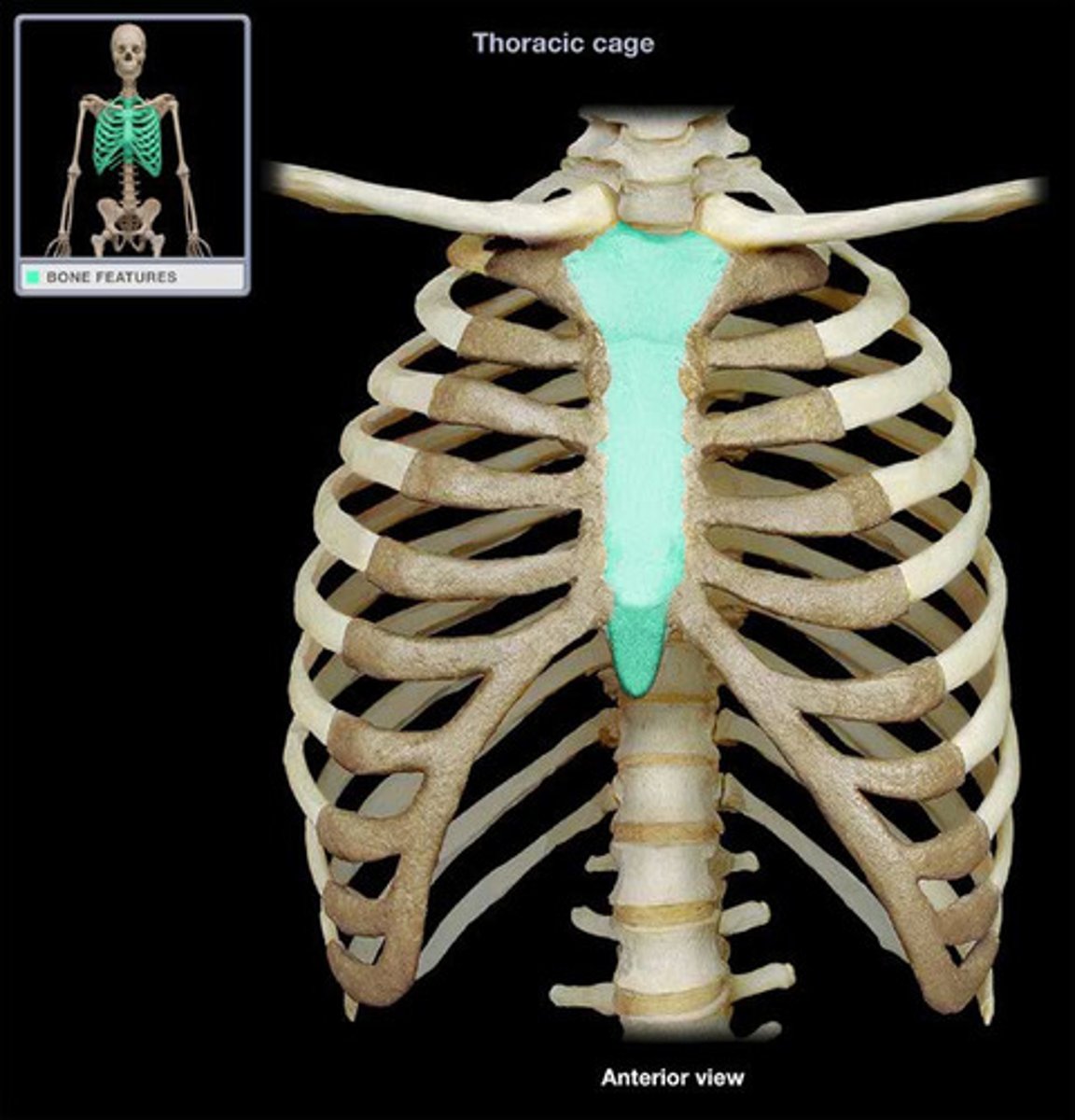
Sternum
breastbone, forms the middle of the front of the rib cage and is divided into three parts
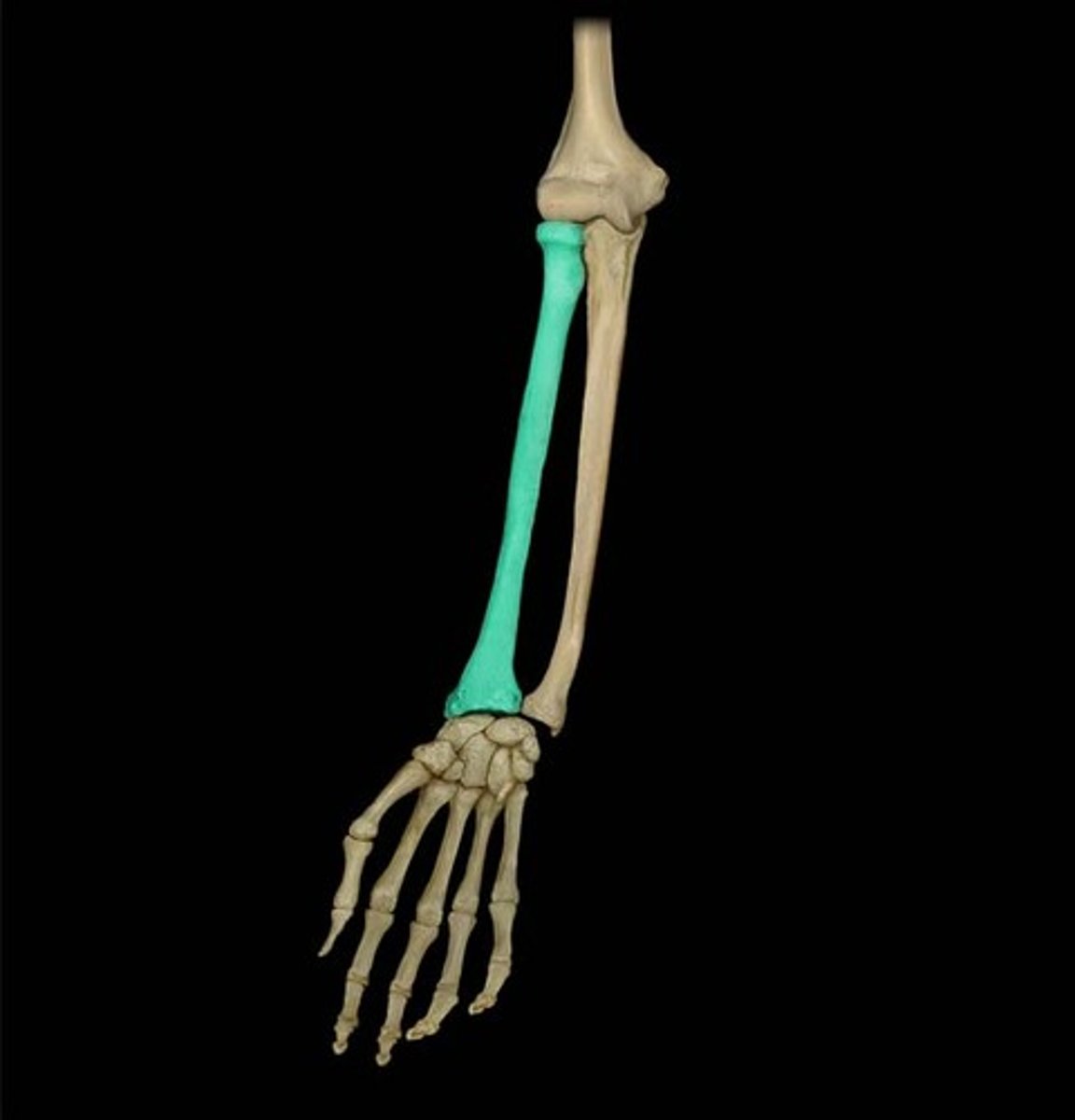
Radius
the thicker and shorter of the two bones in the forearm, "on the thumb side"
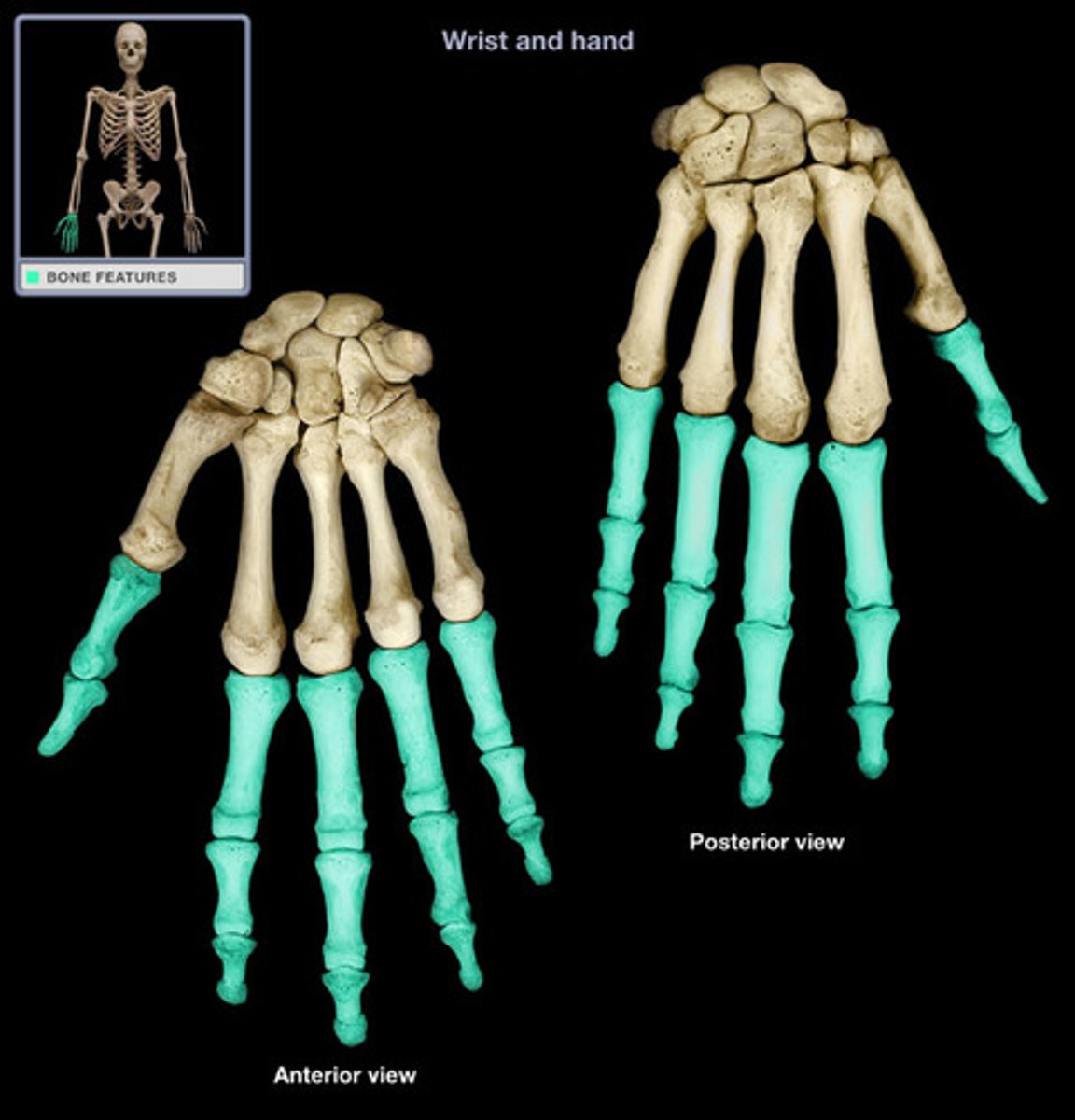
Phalanges
bones of the fingers and toes
Ribs
form the thoracic cage, 12 pairs
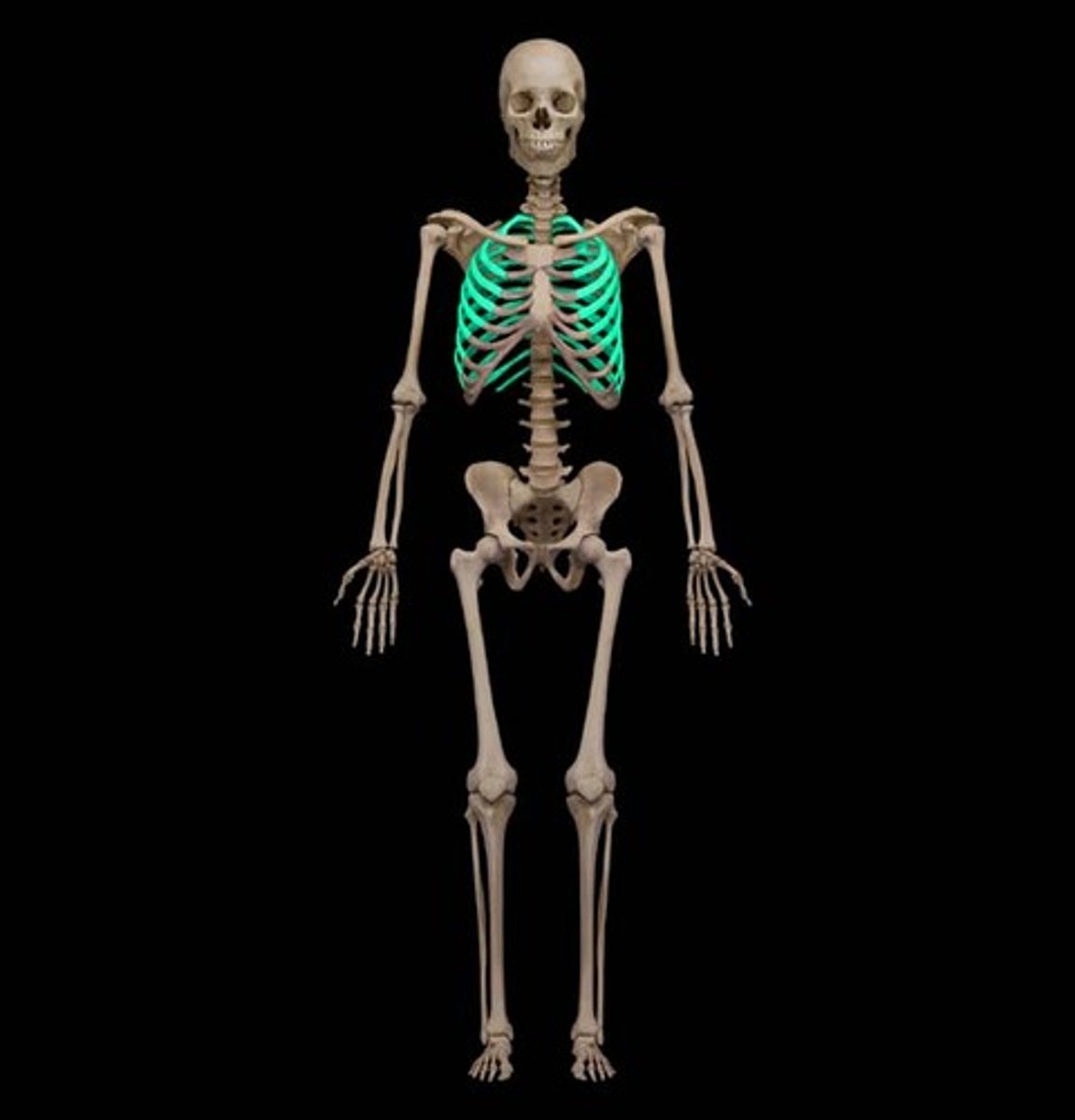
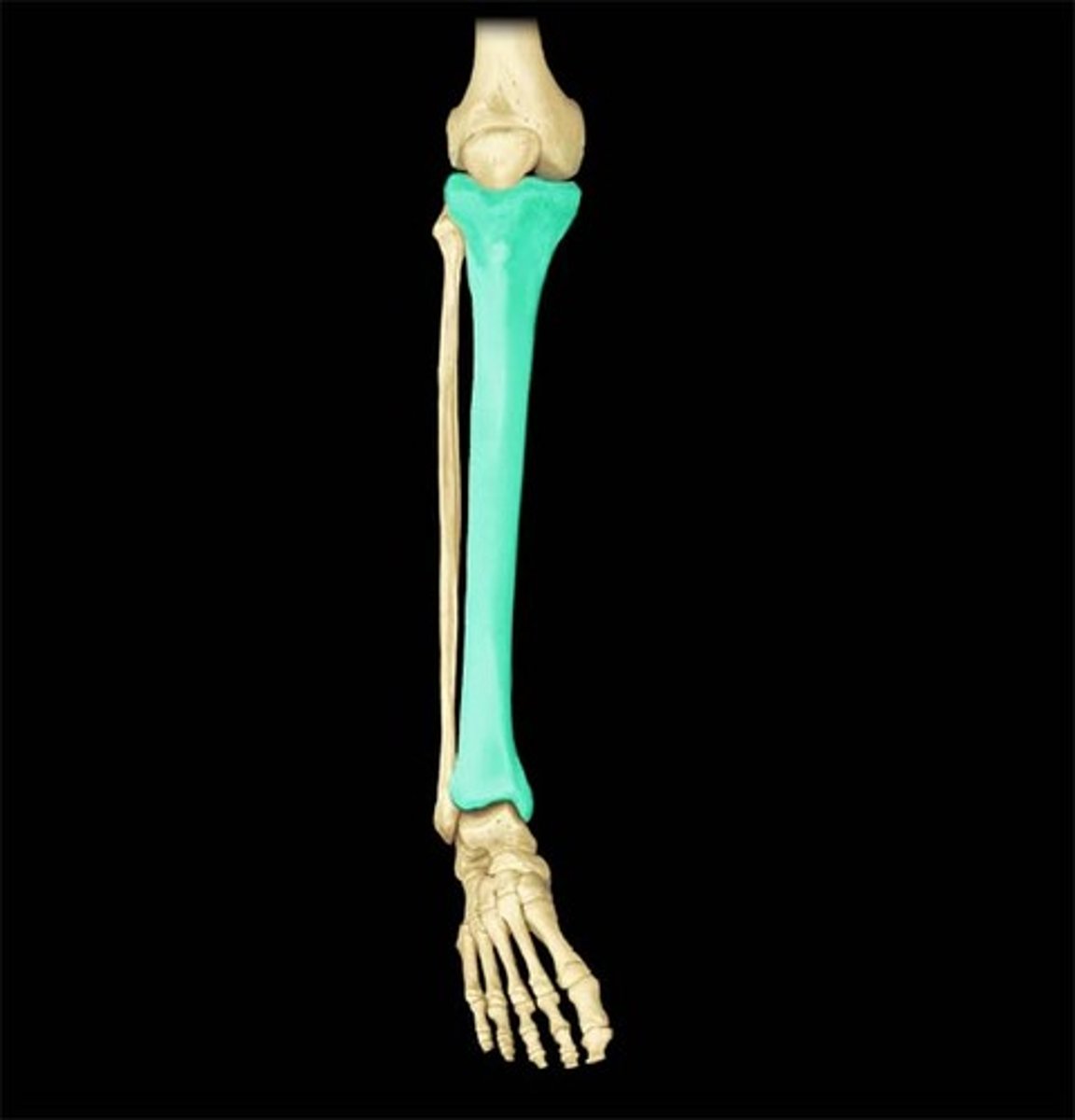
Tibia
the thicker and innermost of the two bones in the lower leg, "shin bone"
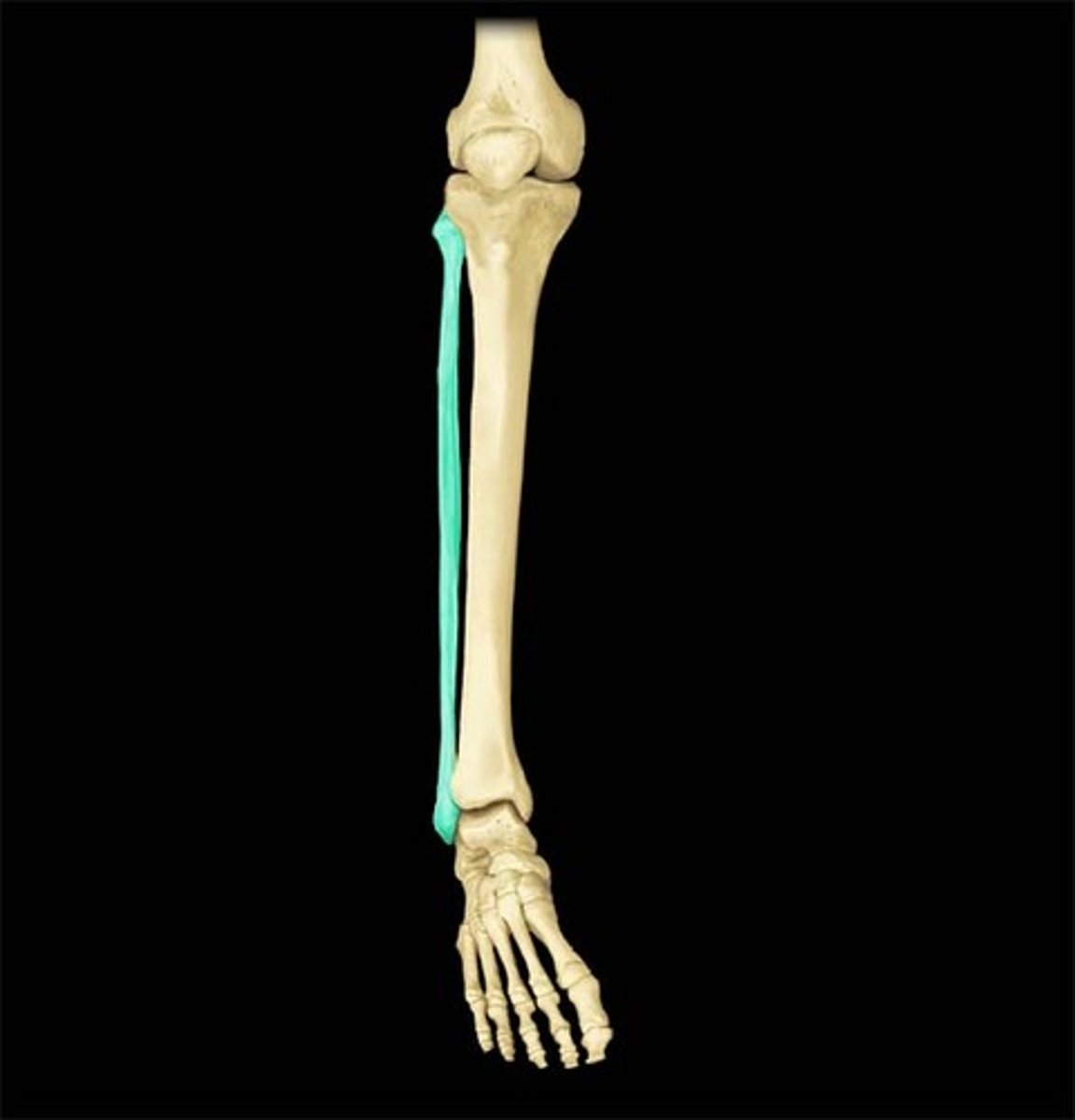
Fibula
the thinner and outermost of the two bones in the lower leg, "calf bone"
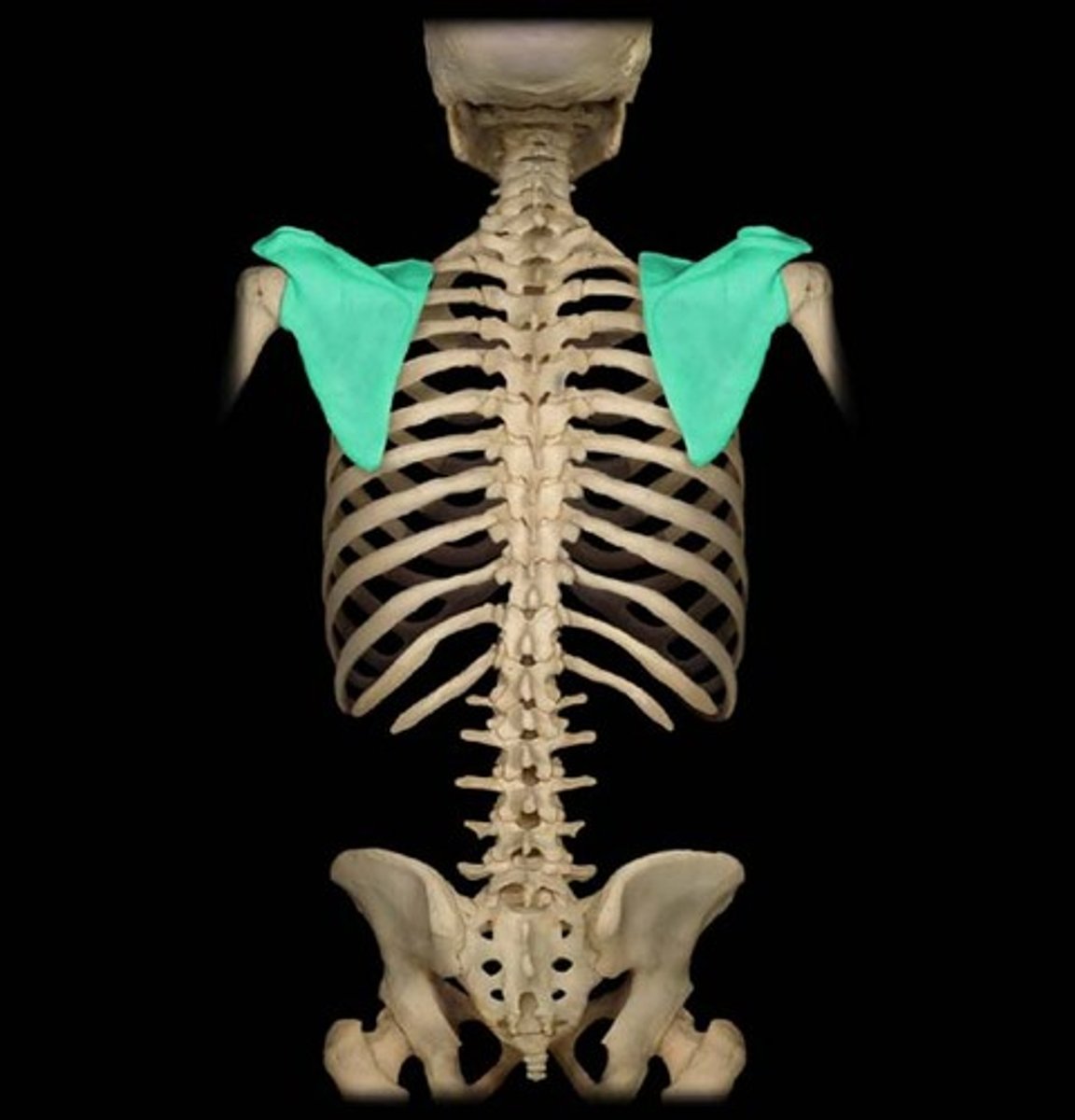
Scapula
shoulder blade
Carpals
wrist bones
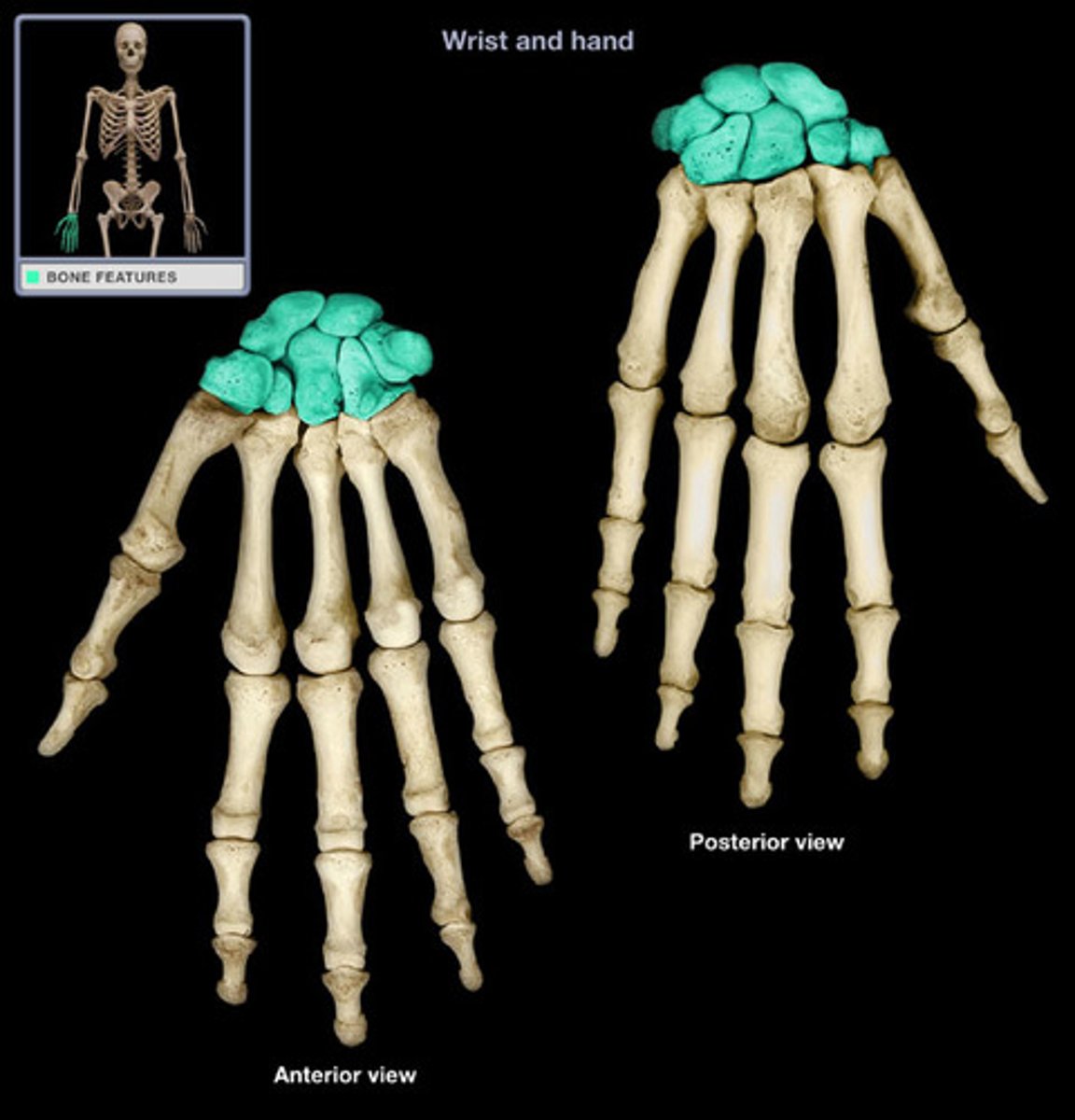
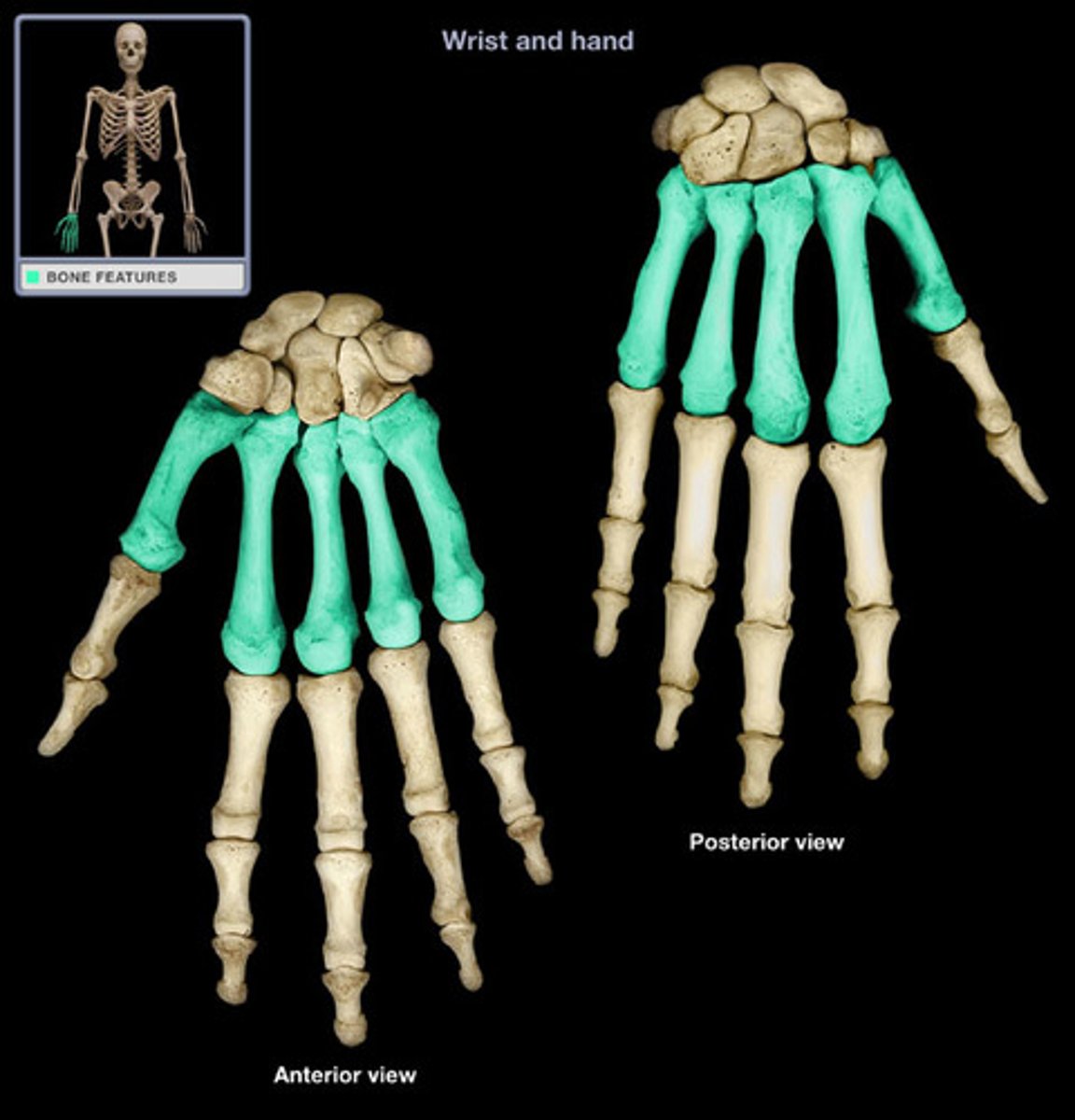
Metacarpals
bones of the palm
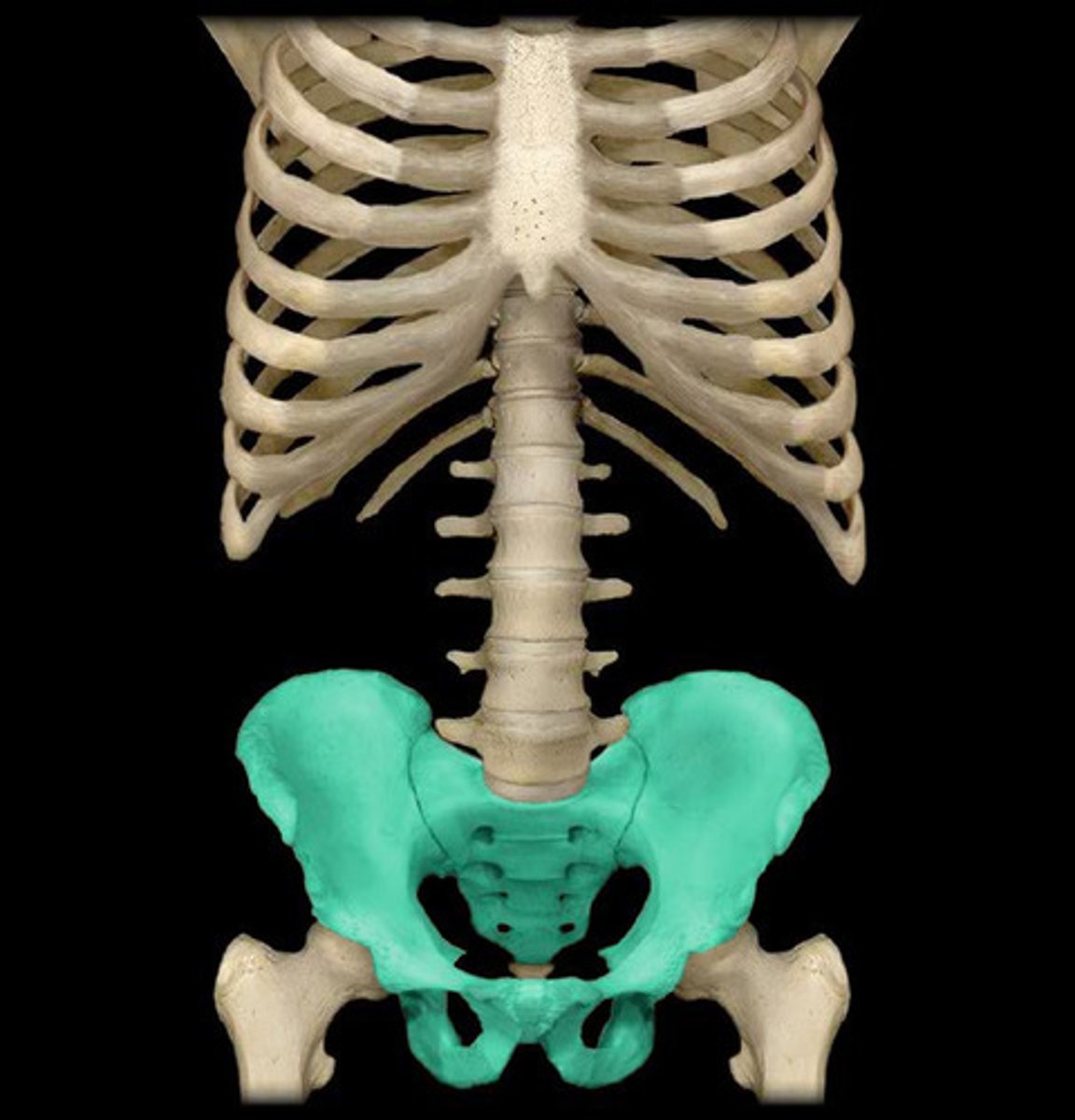
Coxal
hip bone
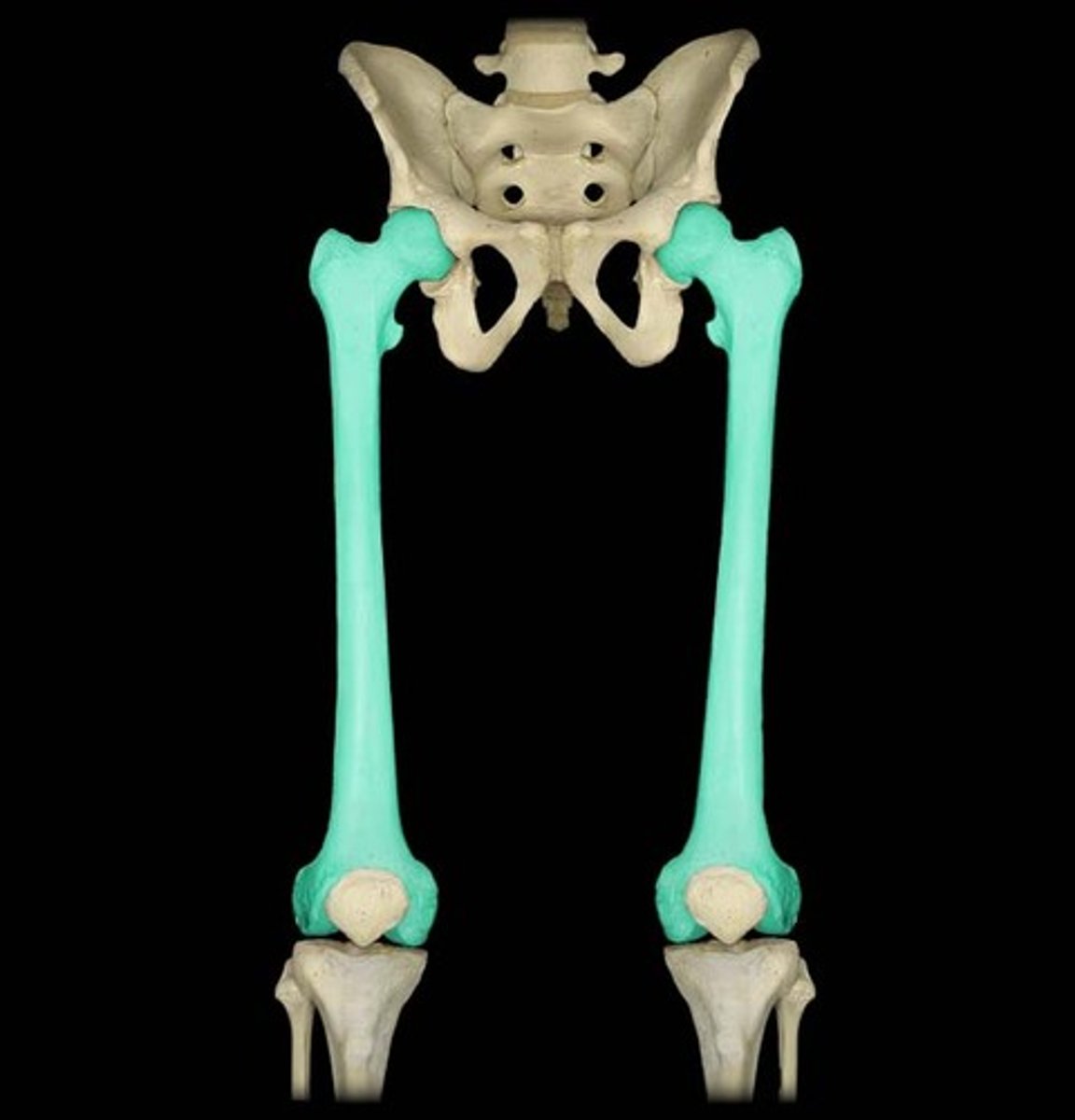
Femur
largest bone in the body, "thigh bone"
Tarsals
ankle bones
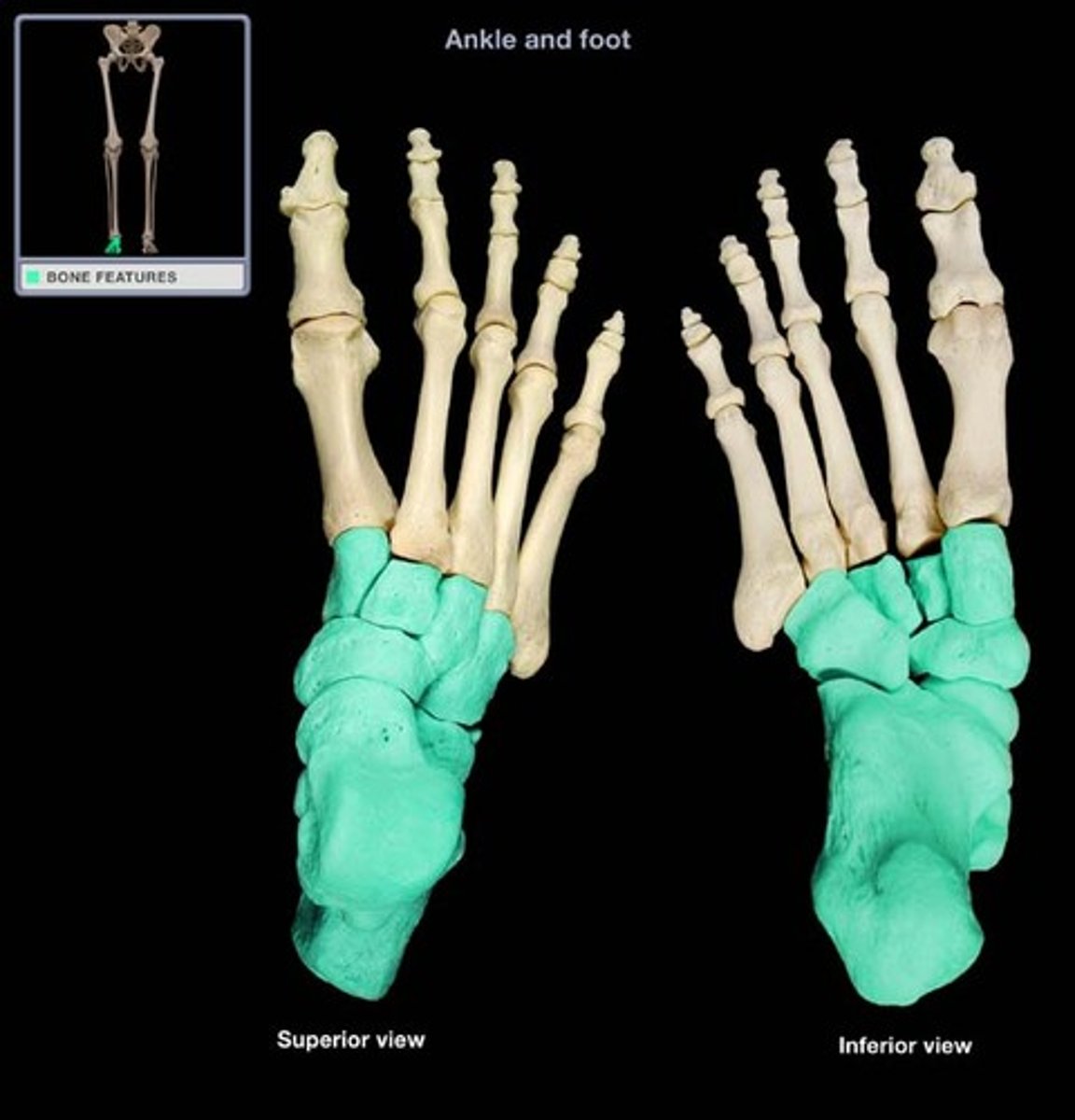
Metatarsals
bones of the foot
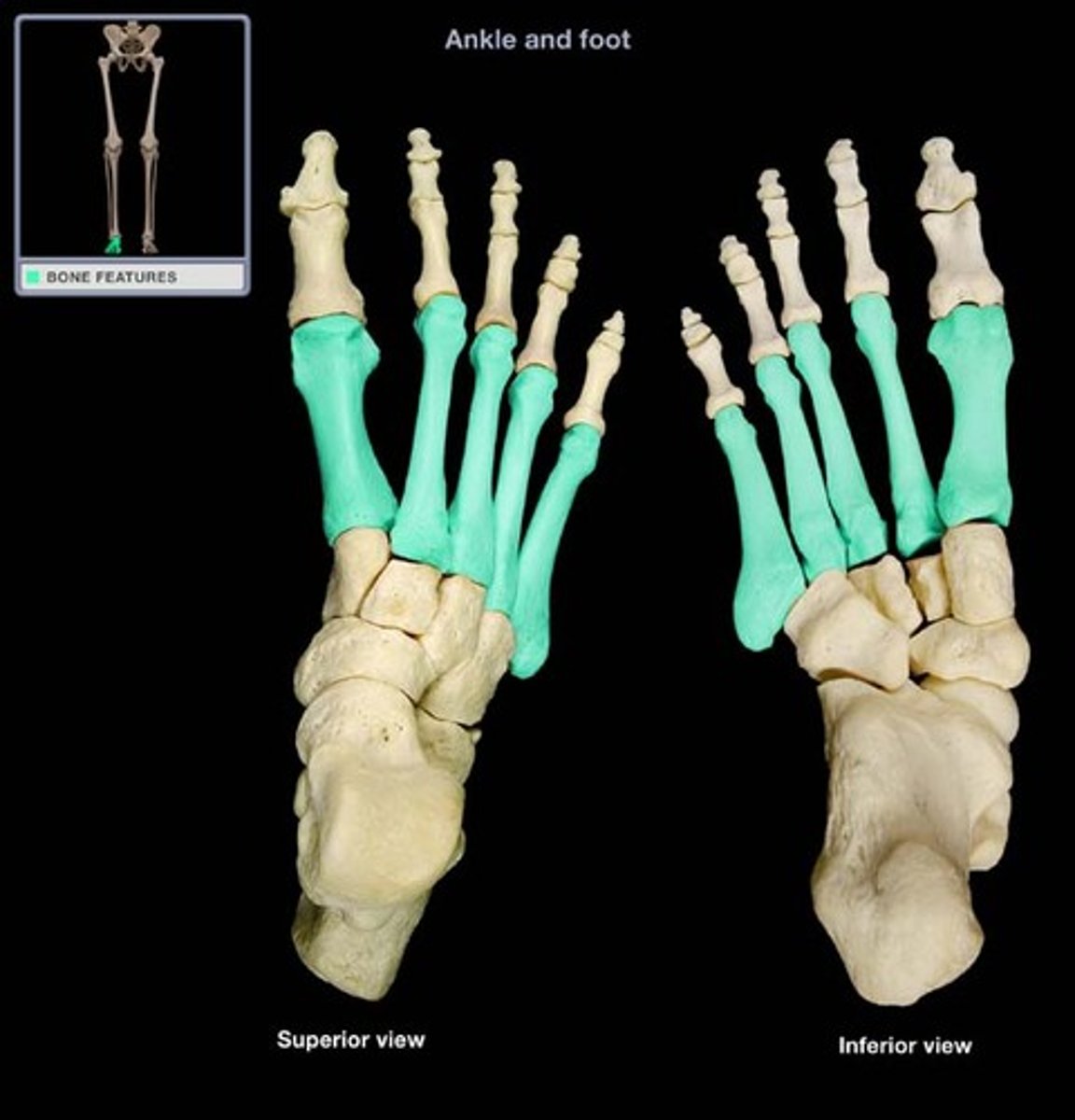
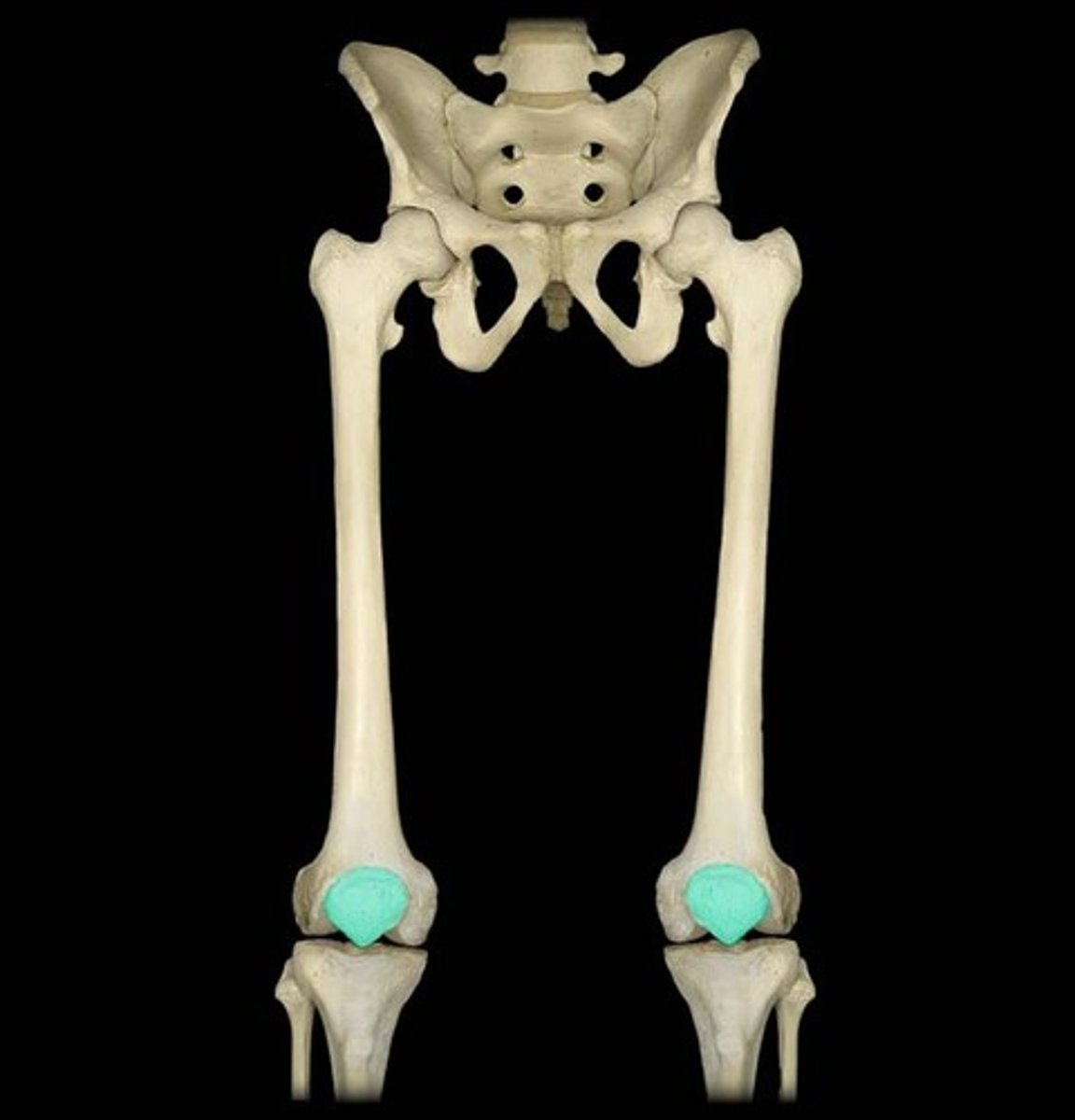
Patella
knee cap
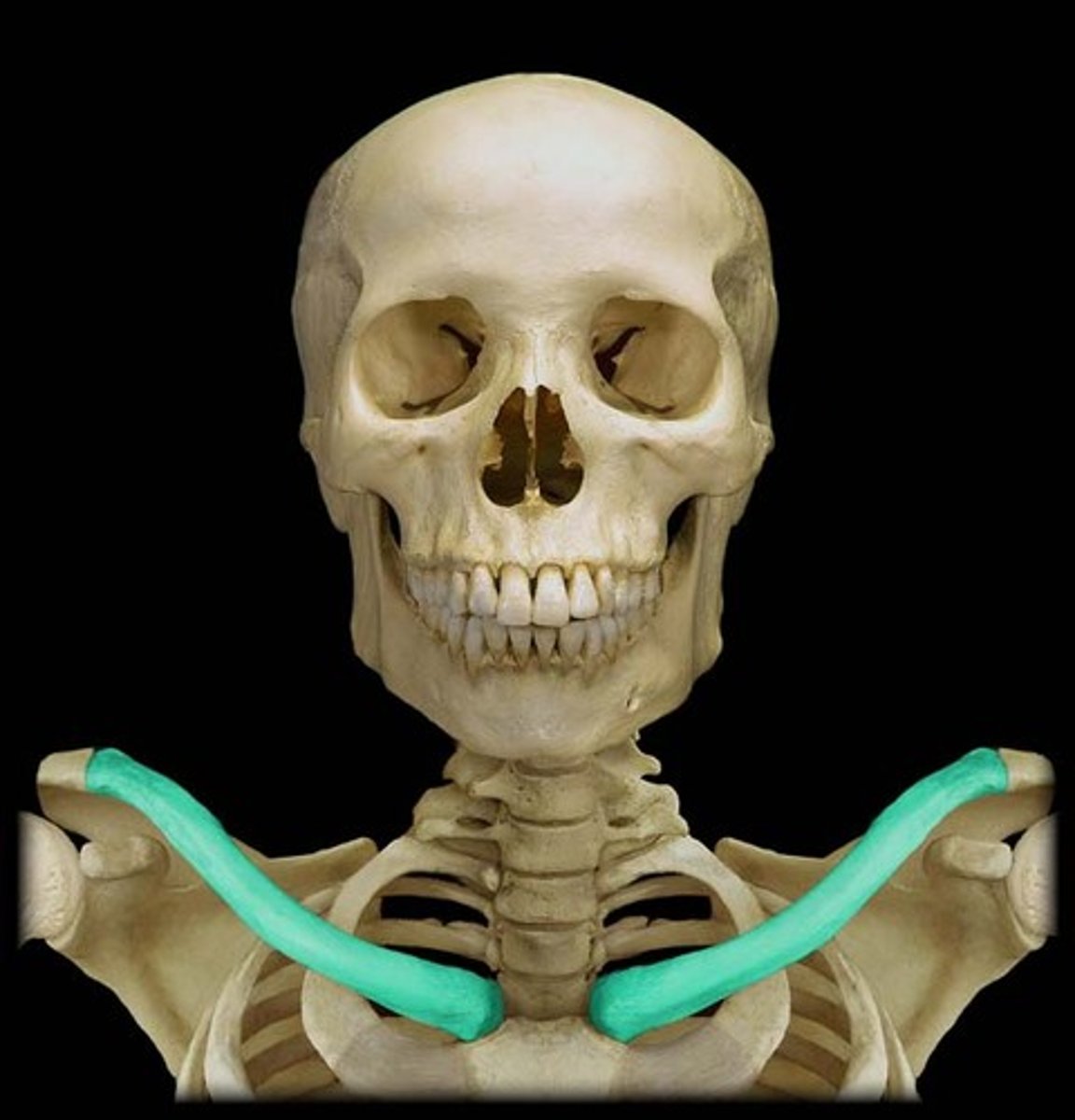
Clavicle
collar bone
Humerus
upper arm bone
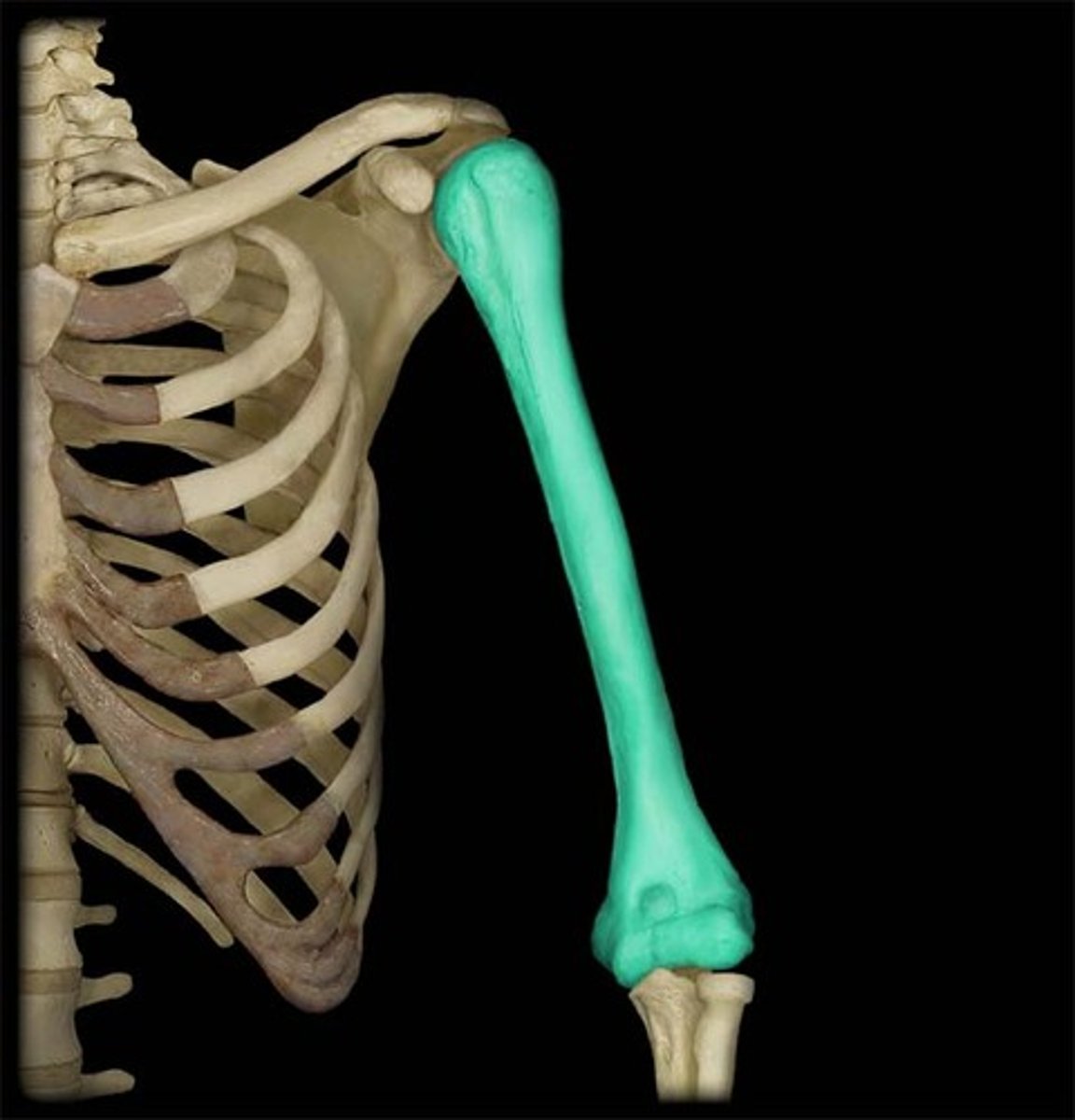
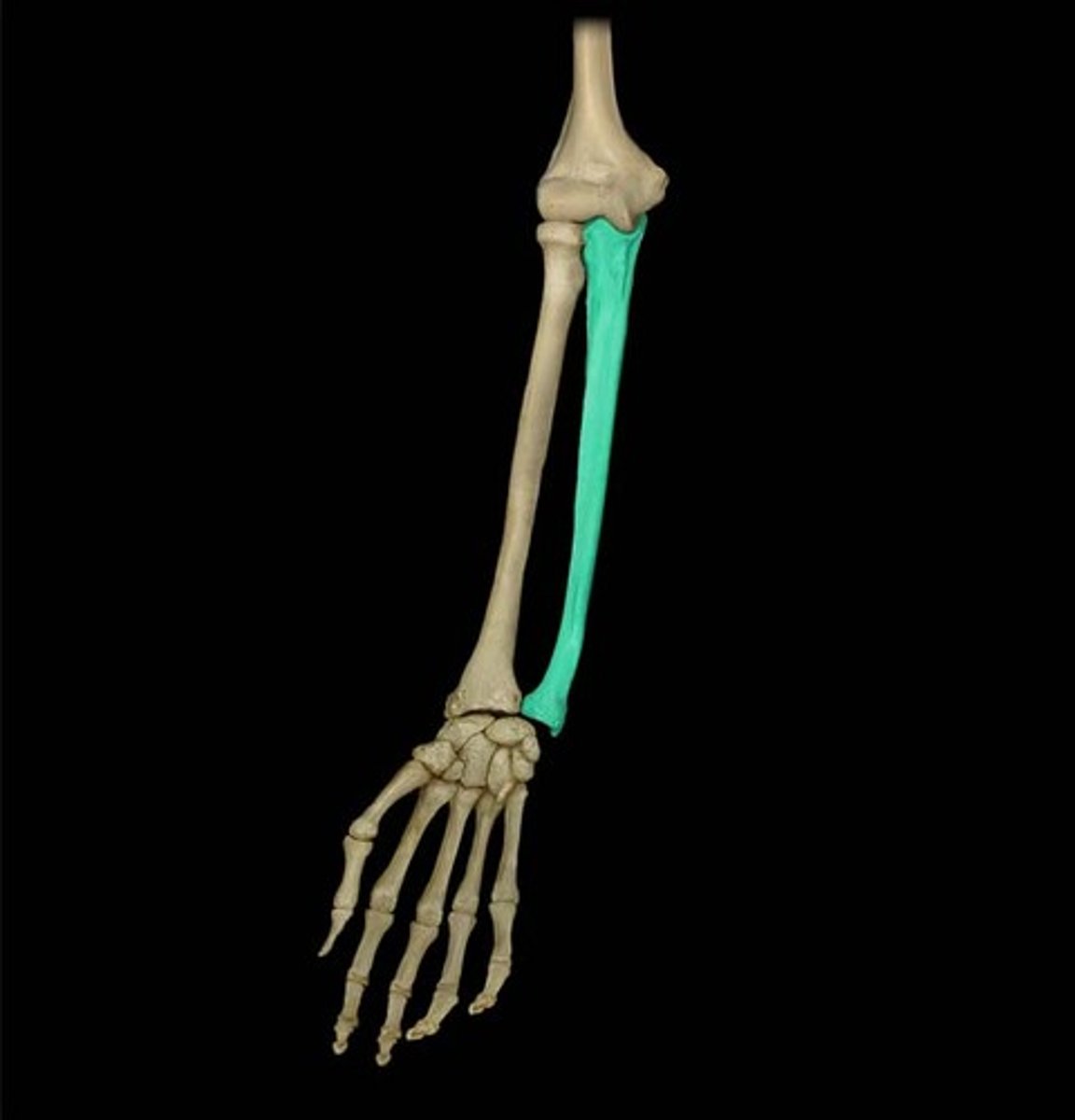
Ulna
the thinner and longer of the two bones in the forearm, "on the pinky side"
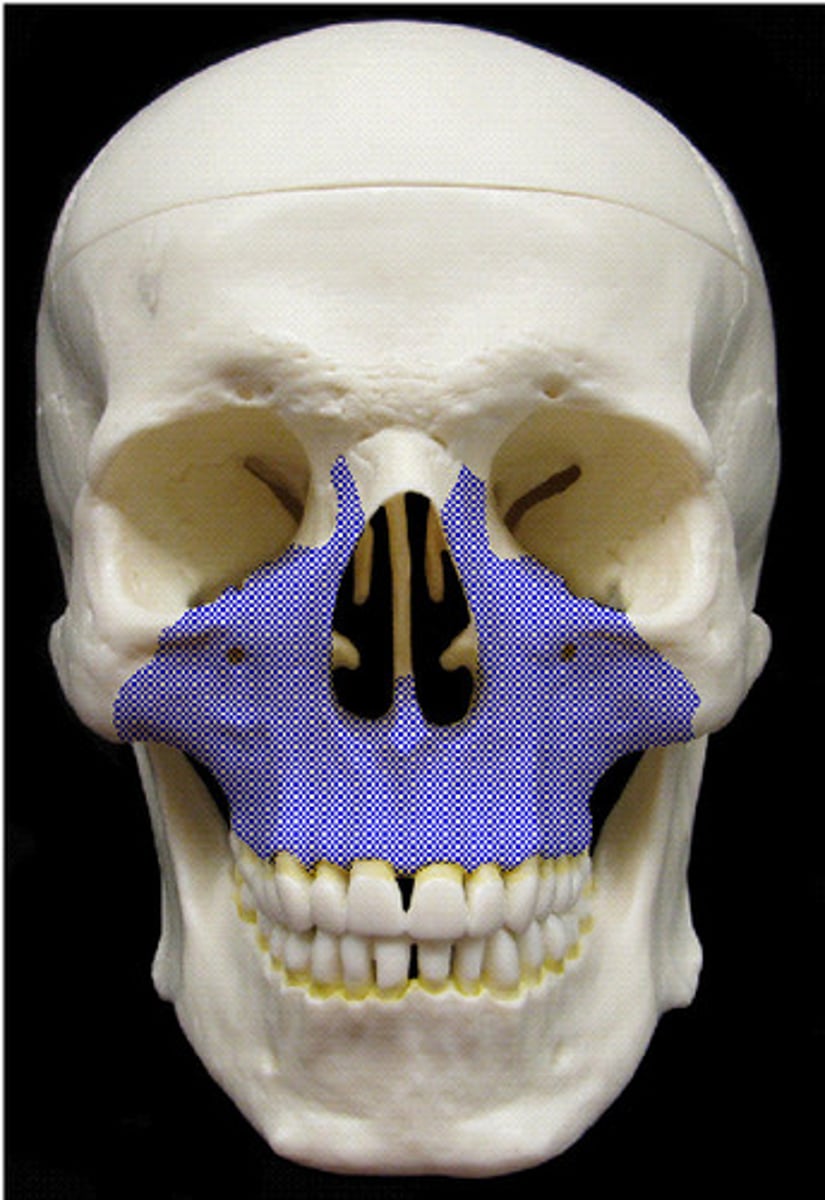
Maxilla
upper jaw bone
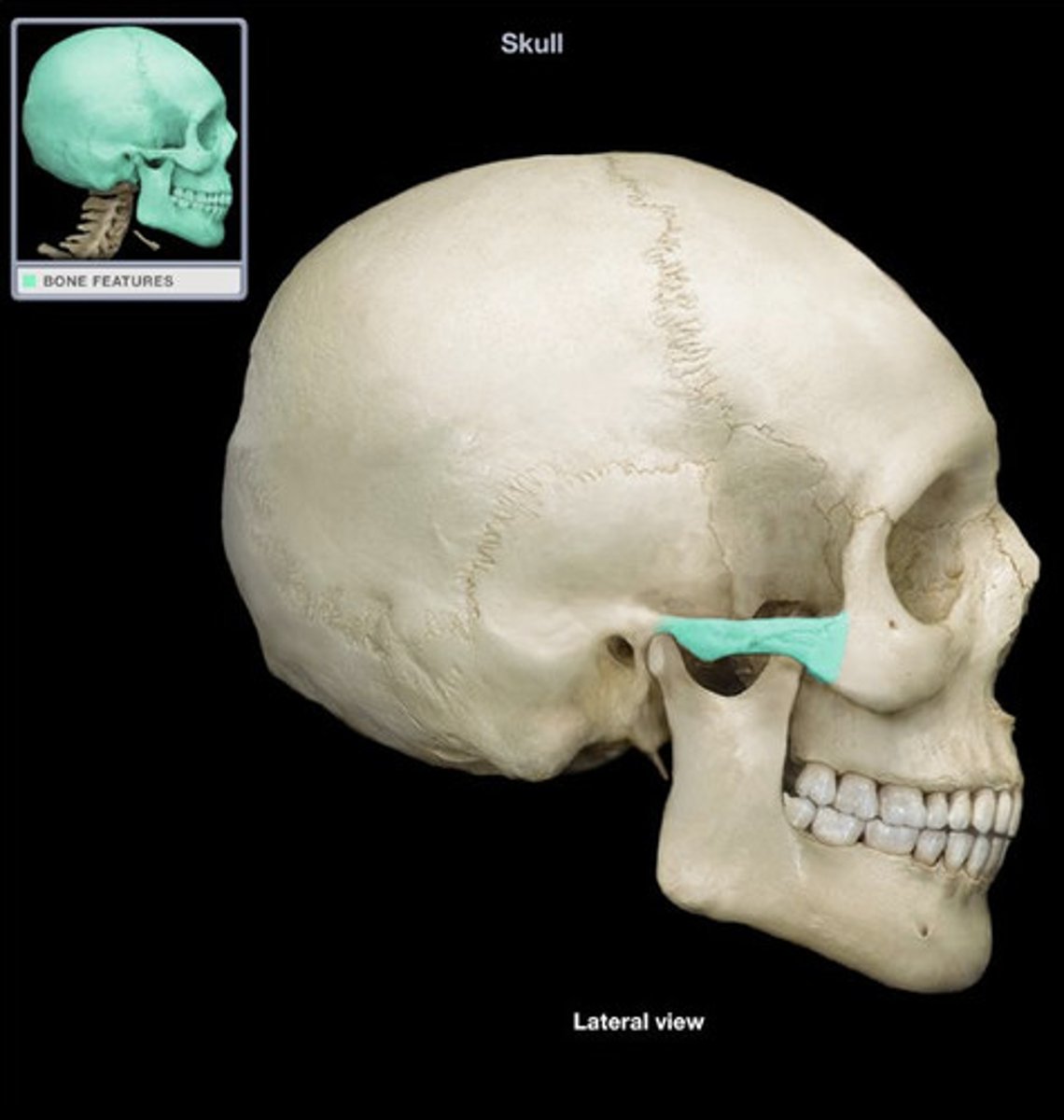
Zygomatic
a projection of the temporal bone, found on each side of the maxilla
Frontal
forehead bone
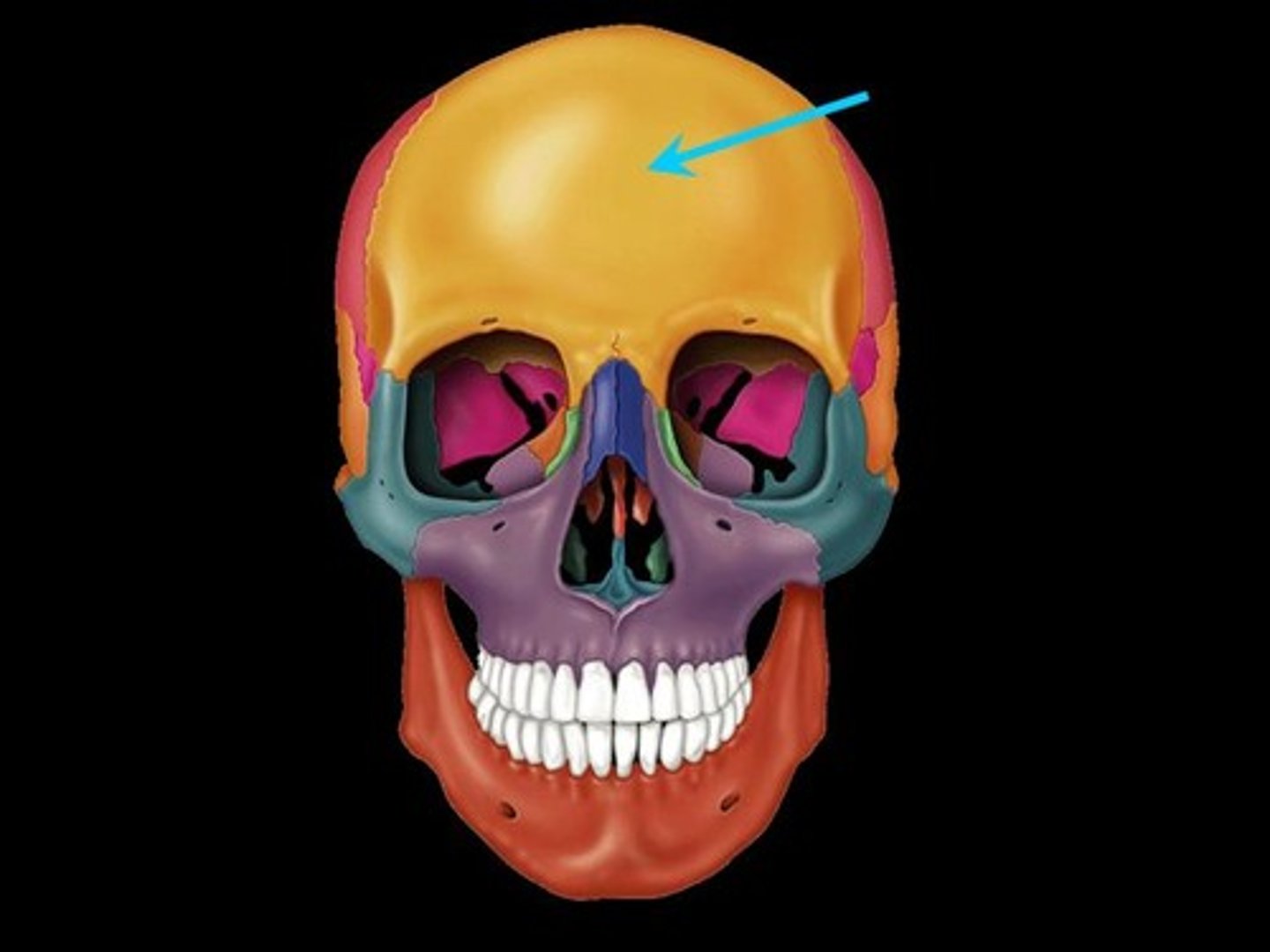
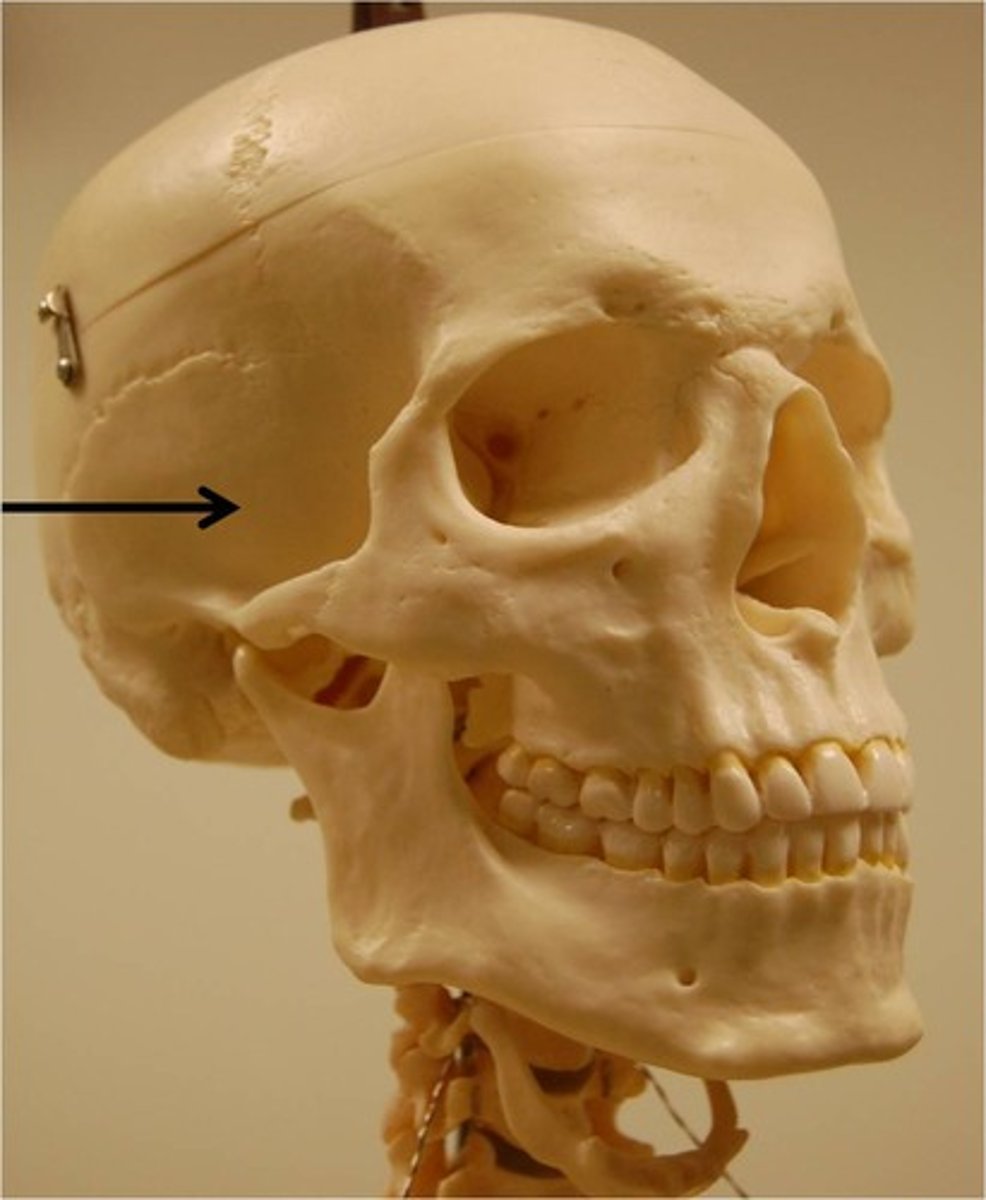
Temporal
two bones on each side of the head that form the lower portion of the skull
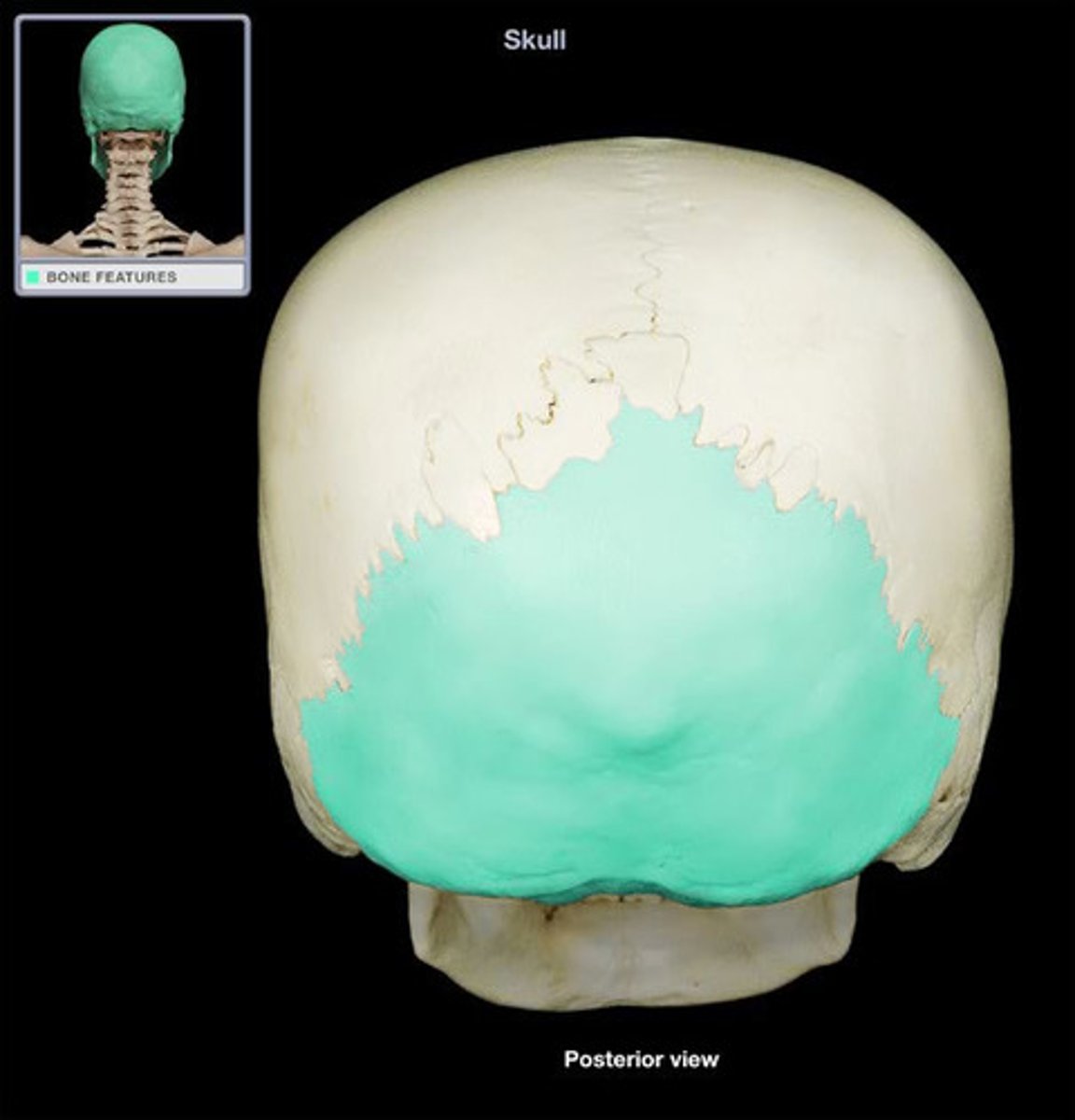
Occipital
bone that forms the back of the skull
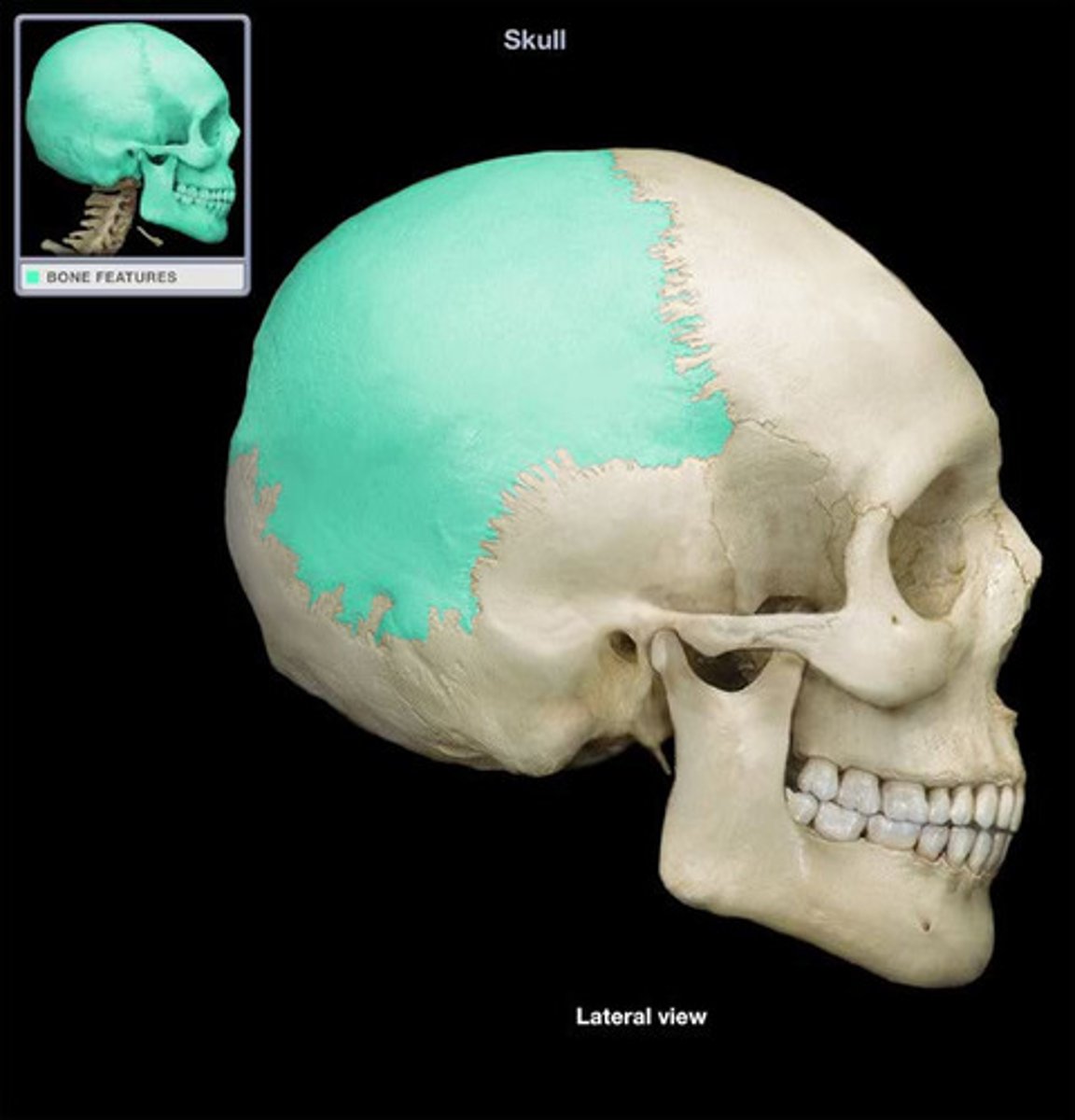
Parietal
two bones on each side of the head that form the upper portion of the skull
Ilium
the upper, wing-shaped portion of the hip bone
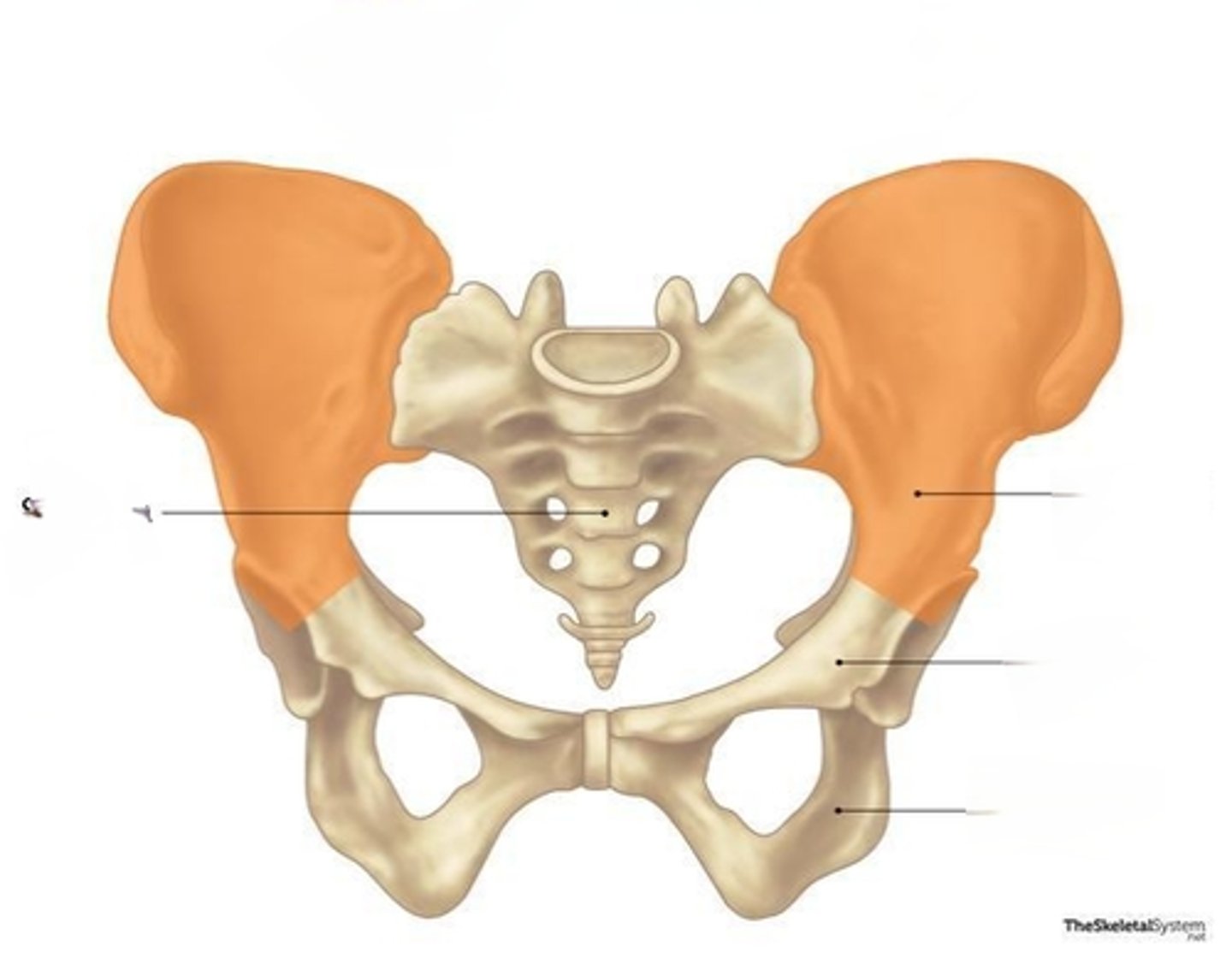
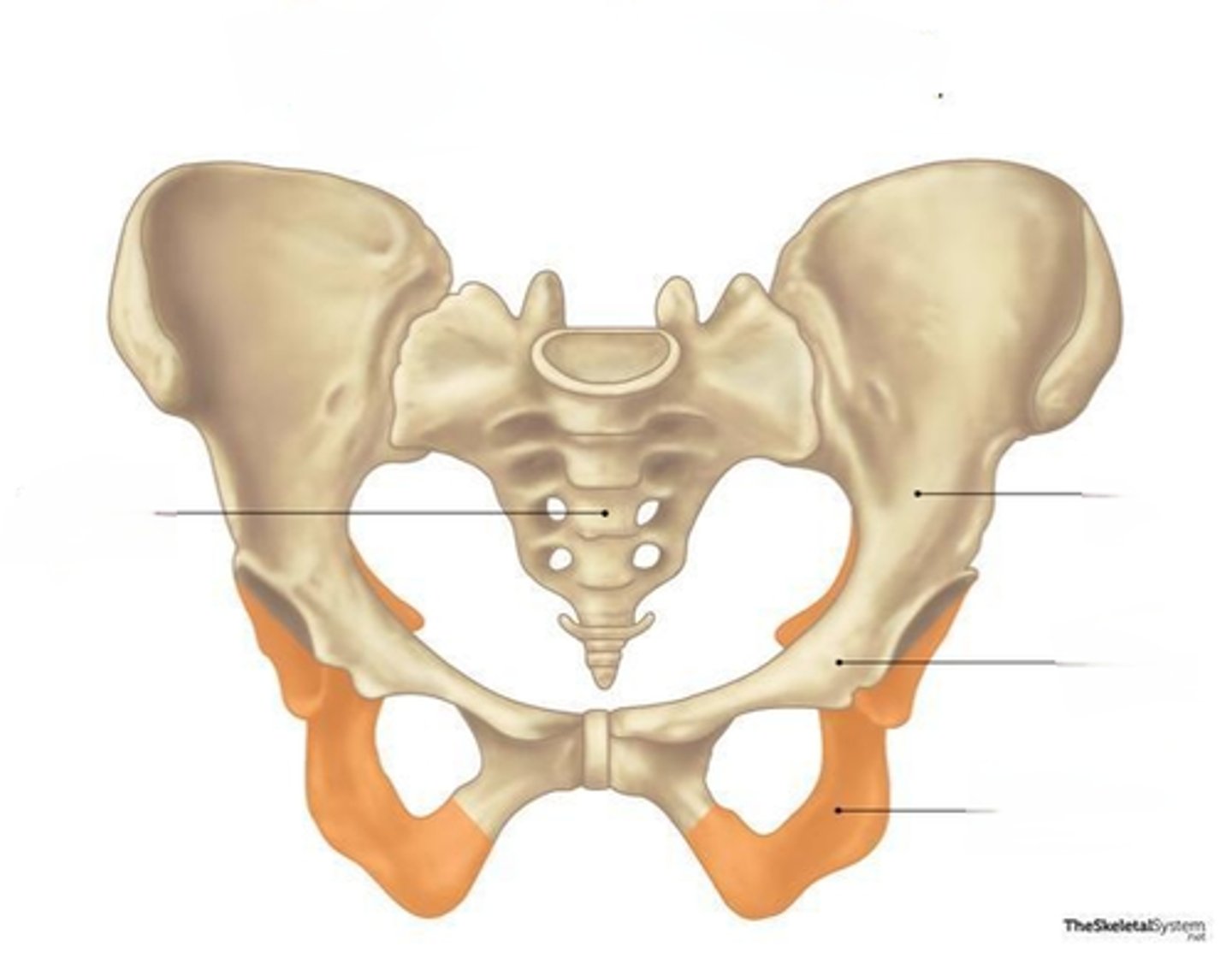
Ischium
the lowest portion of the hip bone, connects to the pubic symphysis
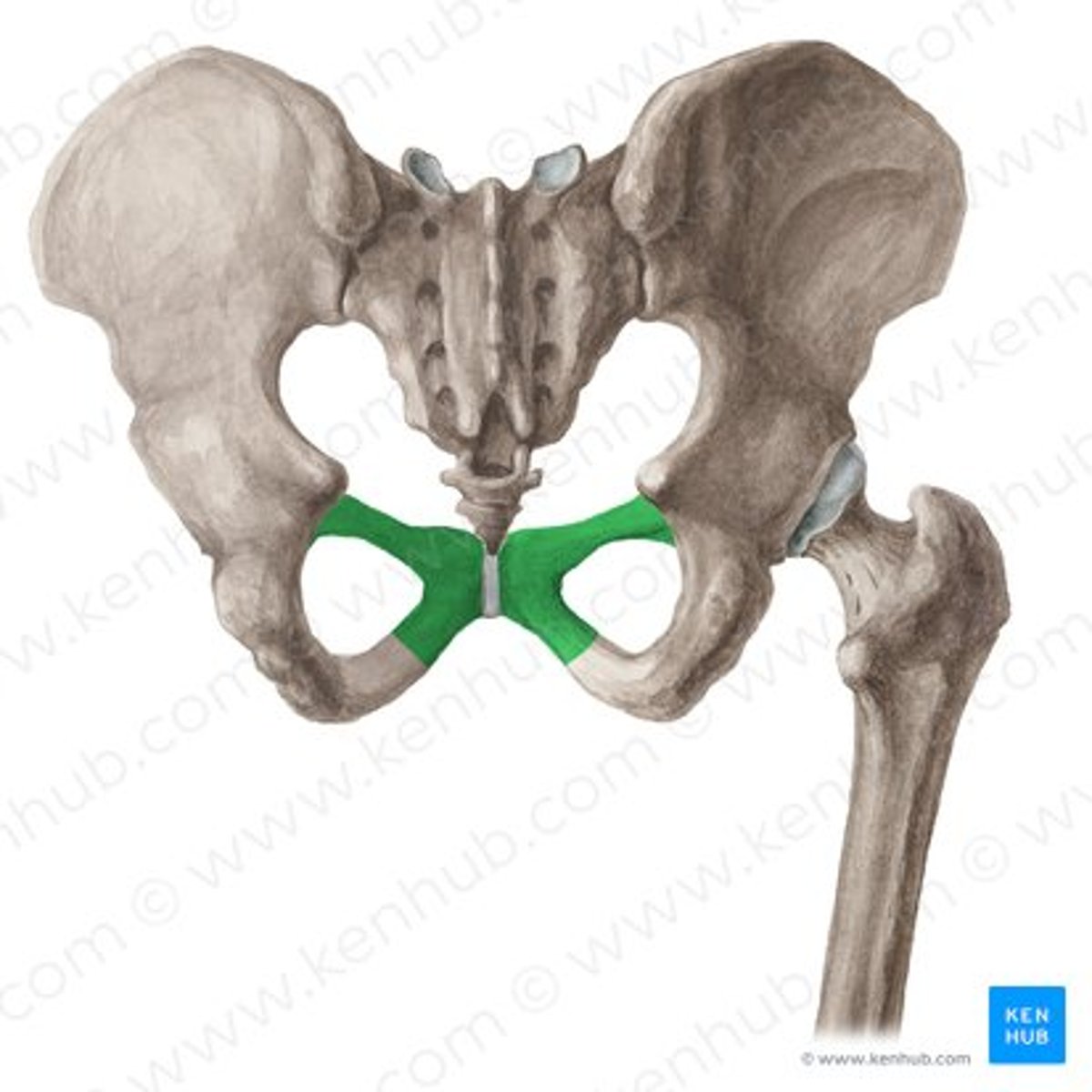
Pubis
the middle, thinnest portion of the hip bone
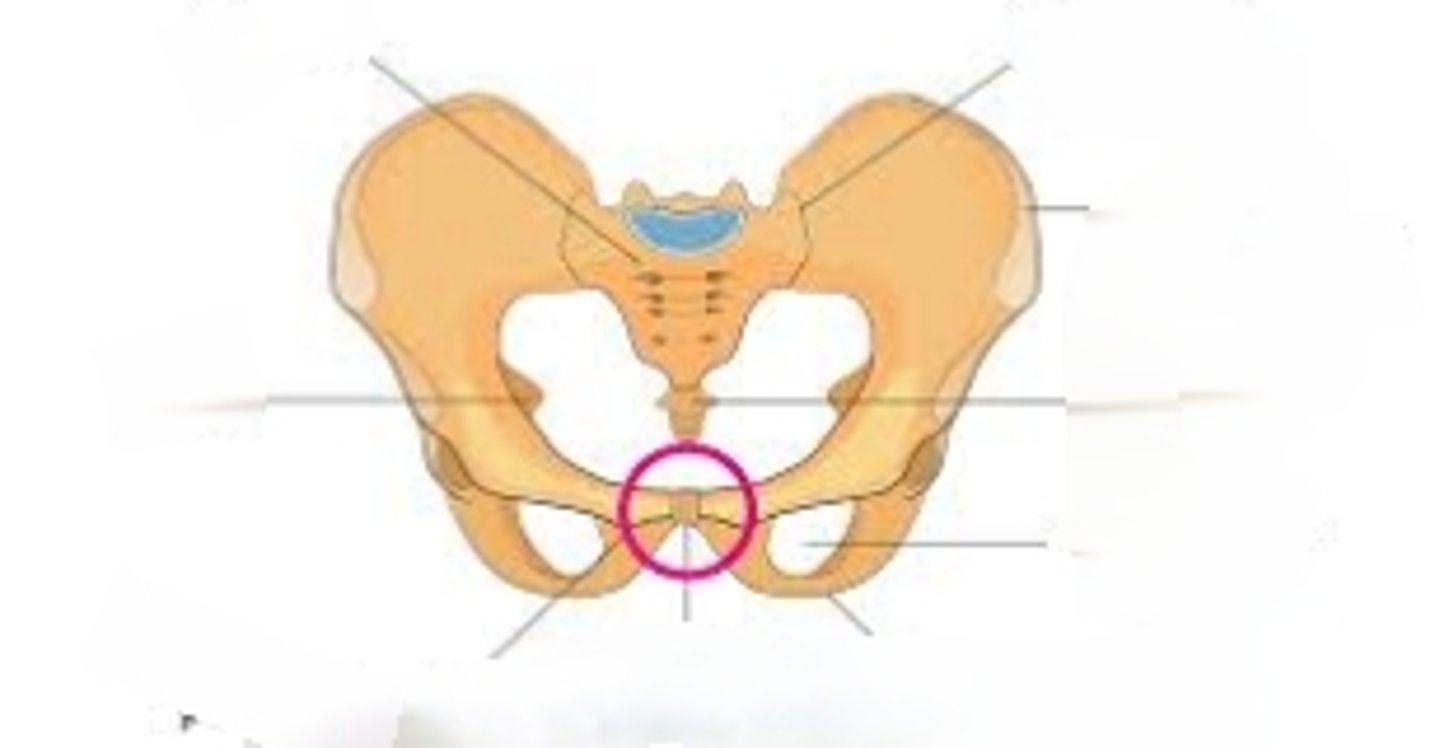
Pubis Symphysis
point where the right and left coxal bones join together
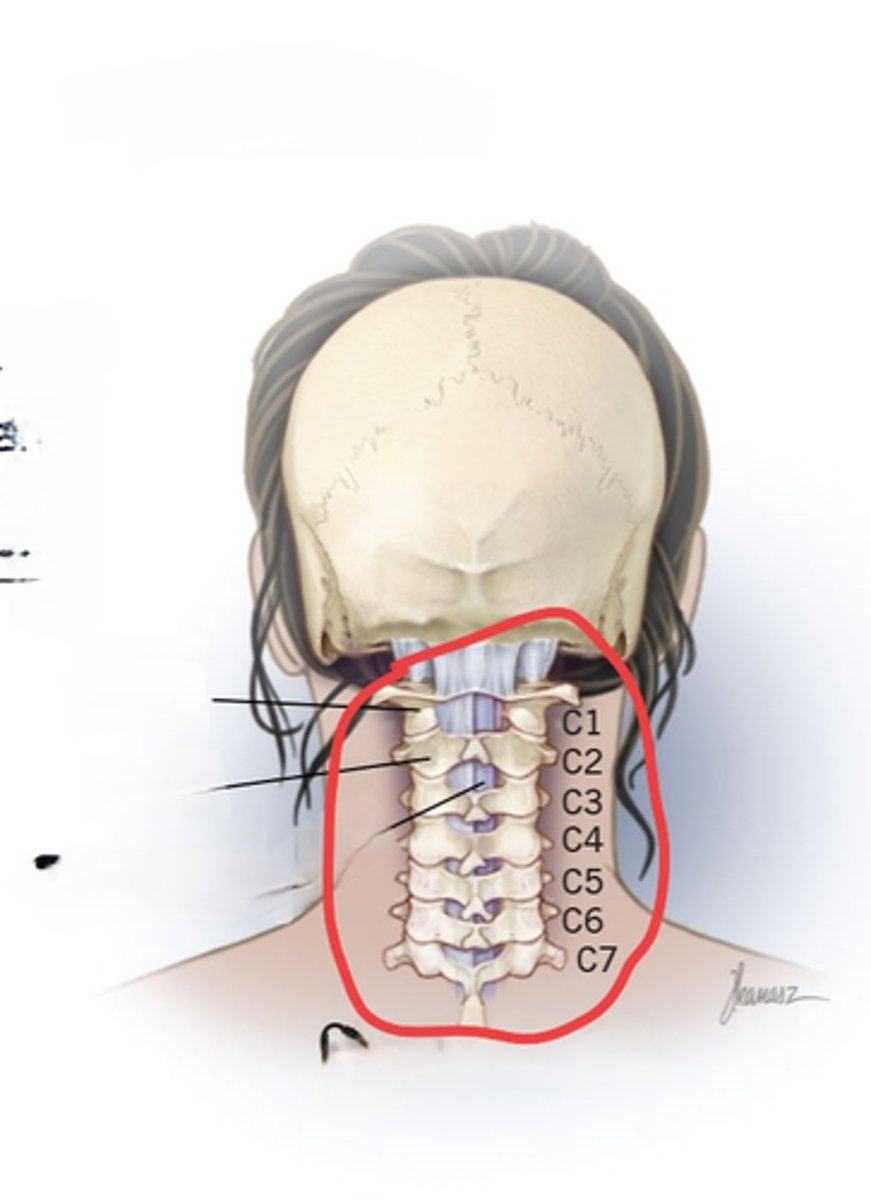
Cervical Vertebrae
Behind the neck, C1-C7
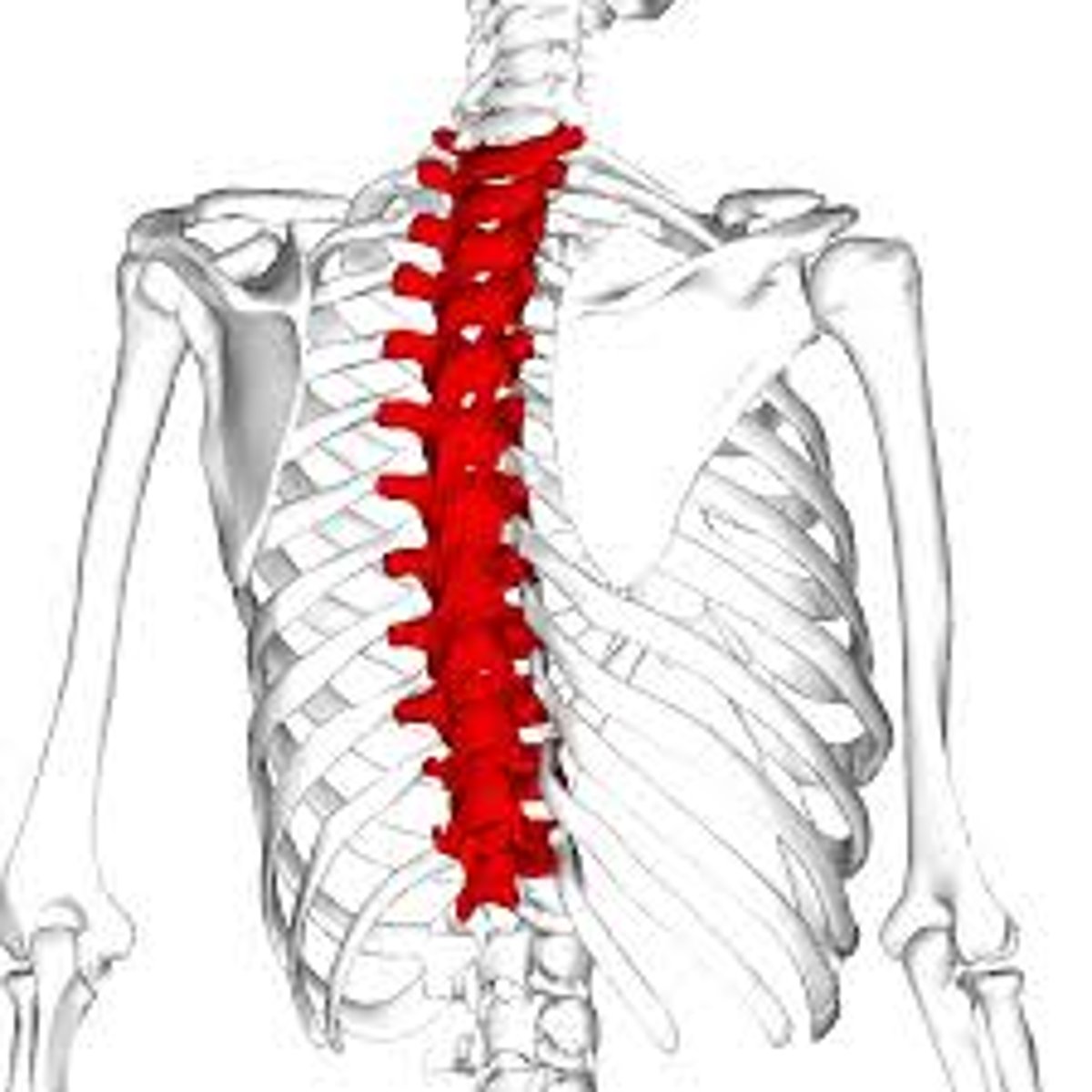
Thoracic Vertebrae
Behind the thoracic cage, T1-T12
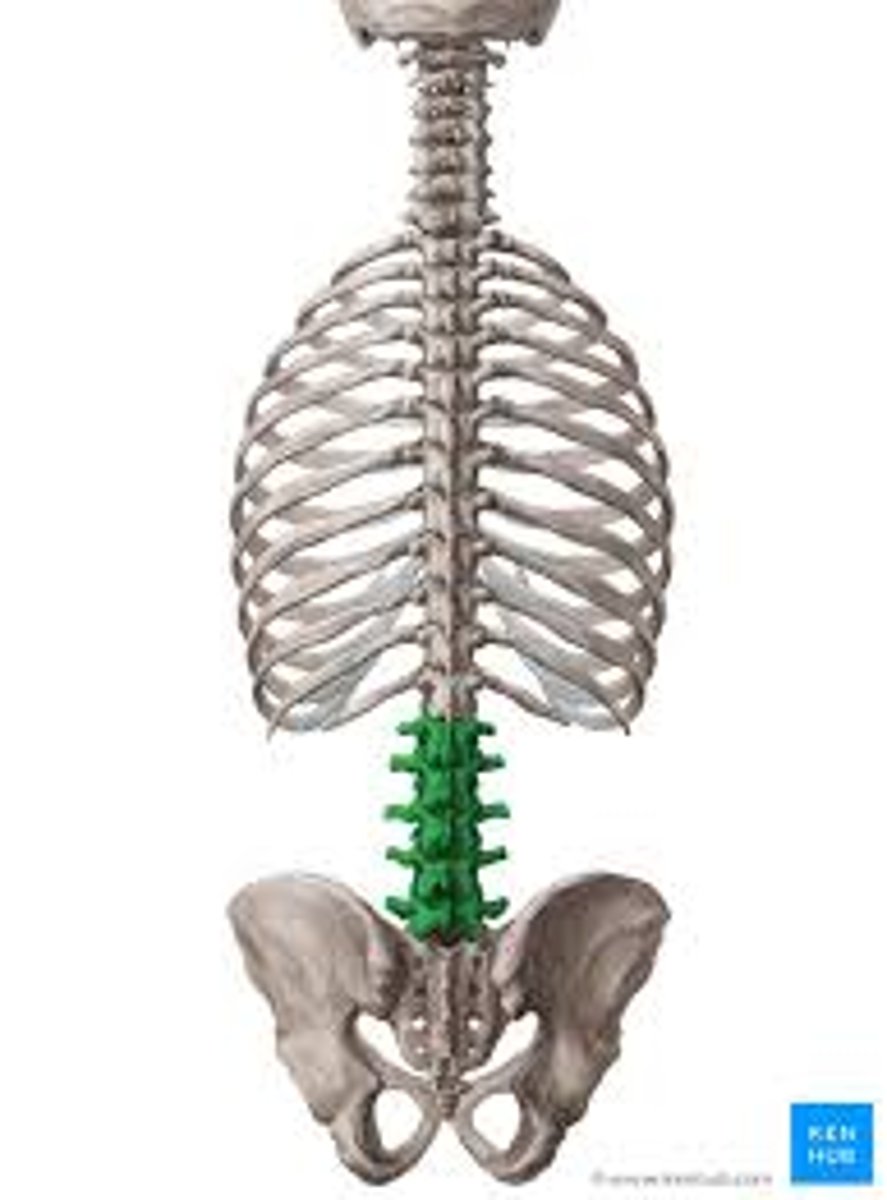
Lumbar Vertebrae
Behind the lower back, L1-L5
Atlas
1st cervical vertebra
Axis
2nd cervical vertebra
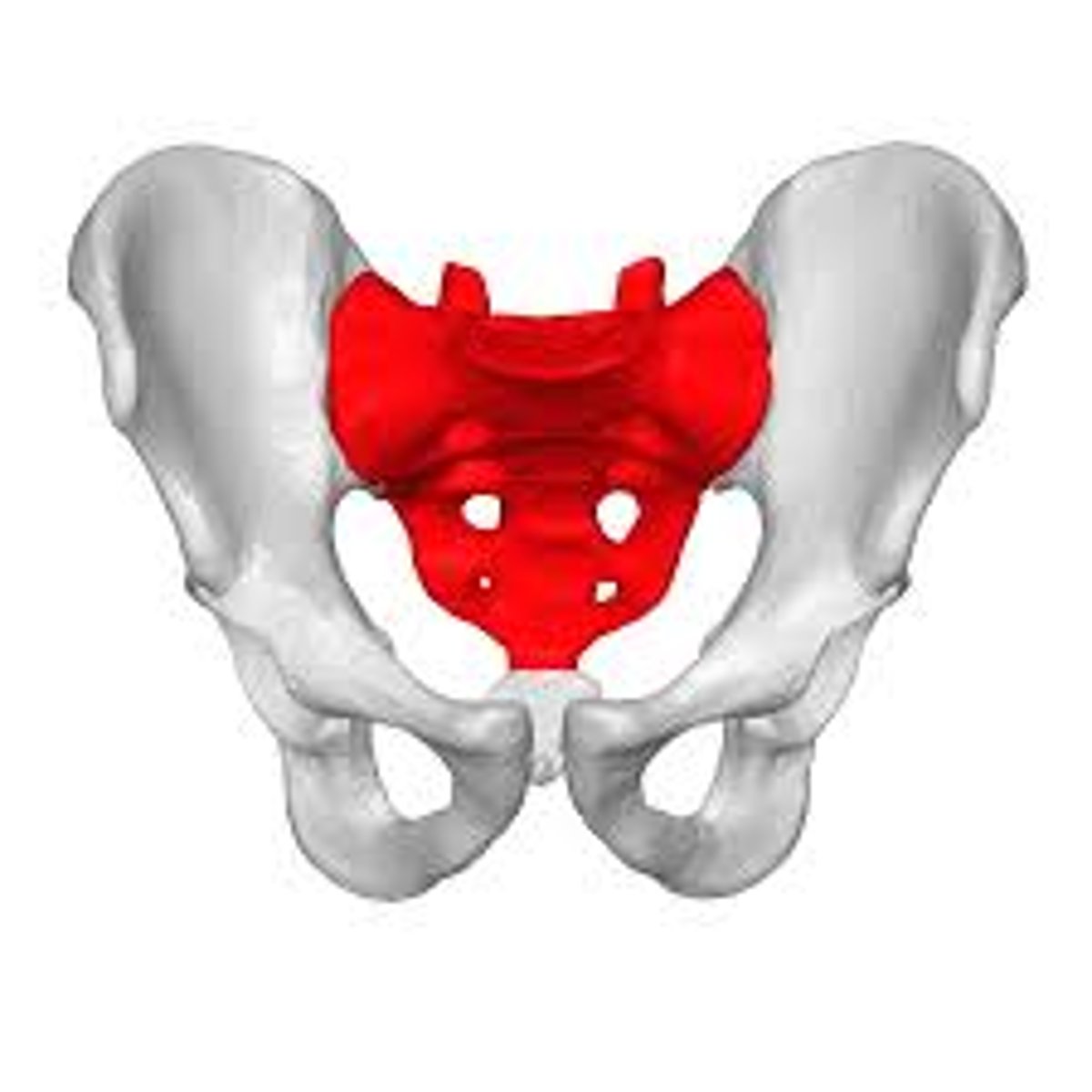
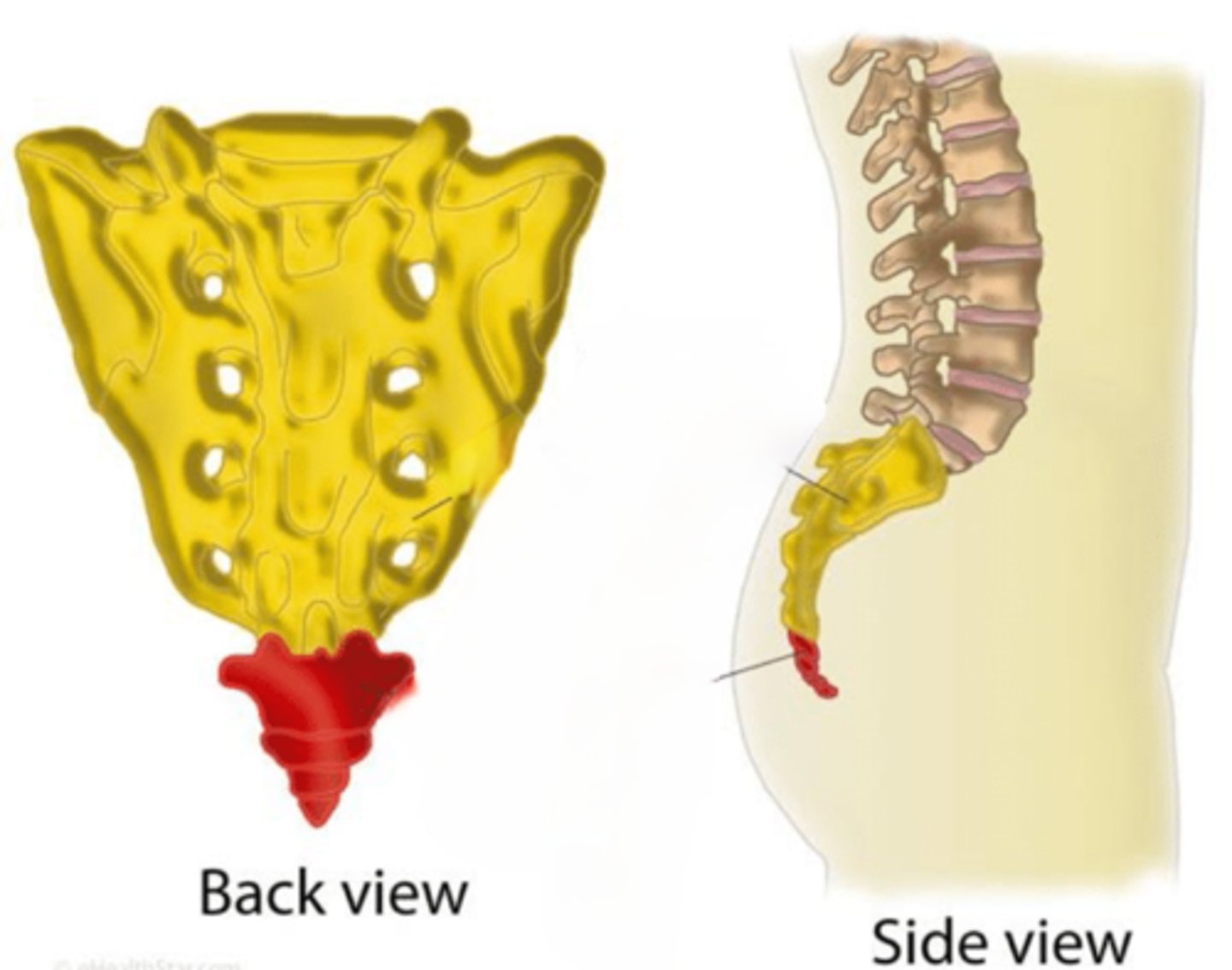
Sacrum
Formed by 5 fused sacral vertebrae
Coccyx
Formed by 4 fused coccygeal vertebrae, "tail bone"
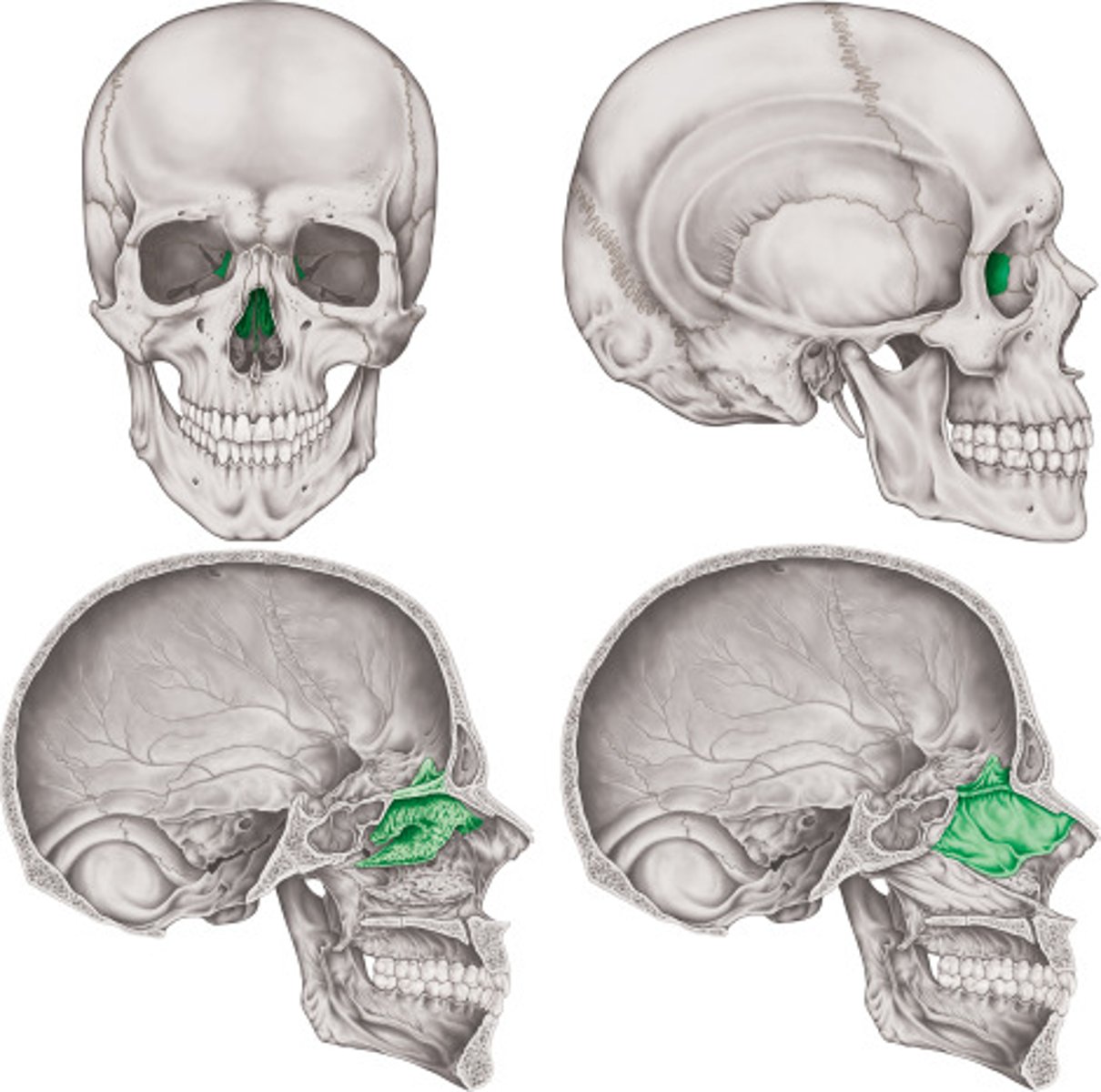
Ethmoid
located between the two eye sockets
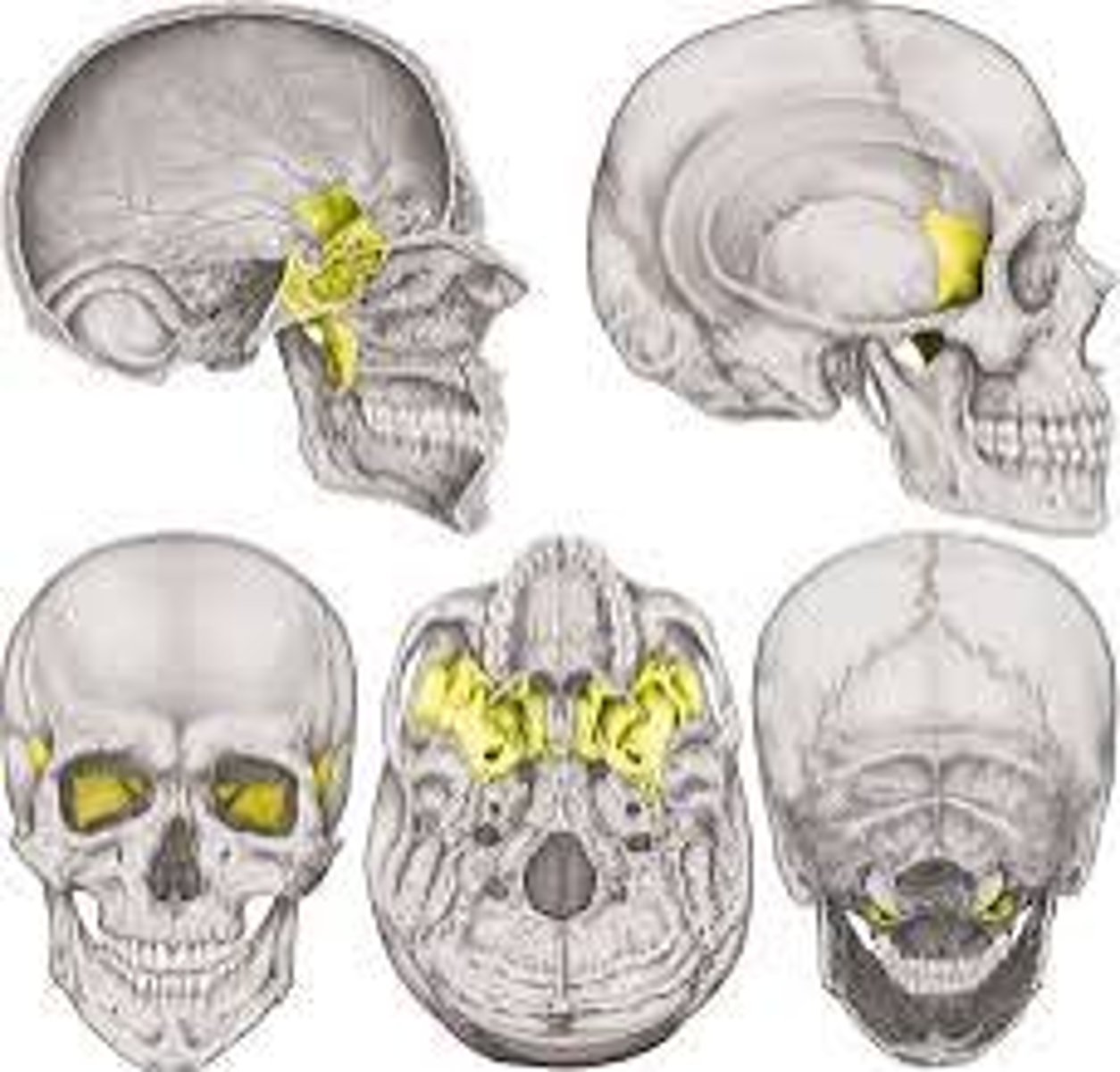
Sphenoid
two bones of each side of the head, anterior to the temporal bones
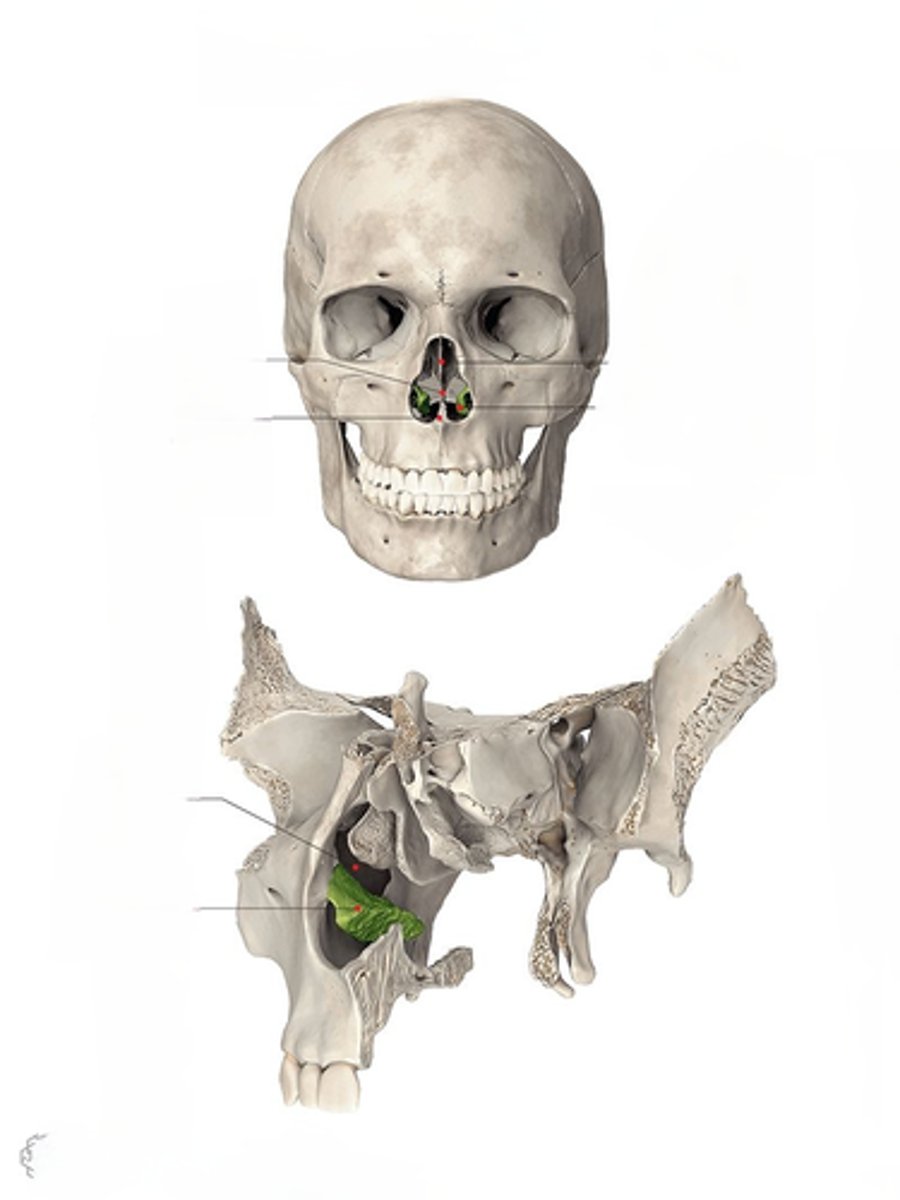
Inferior Nasal Concha
bones on the inferior lateral sides of the nasal cavity
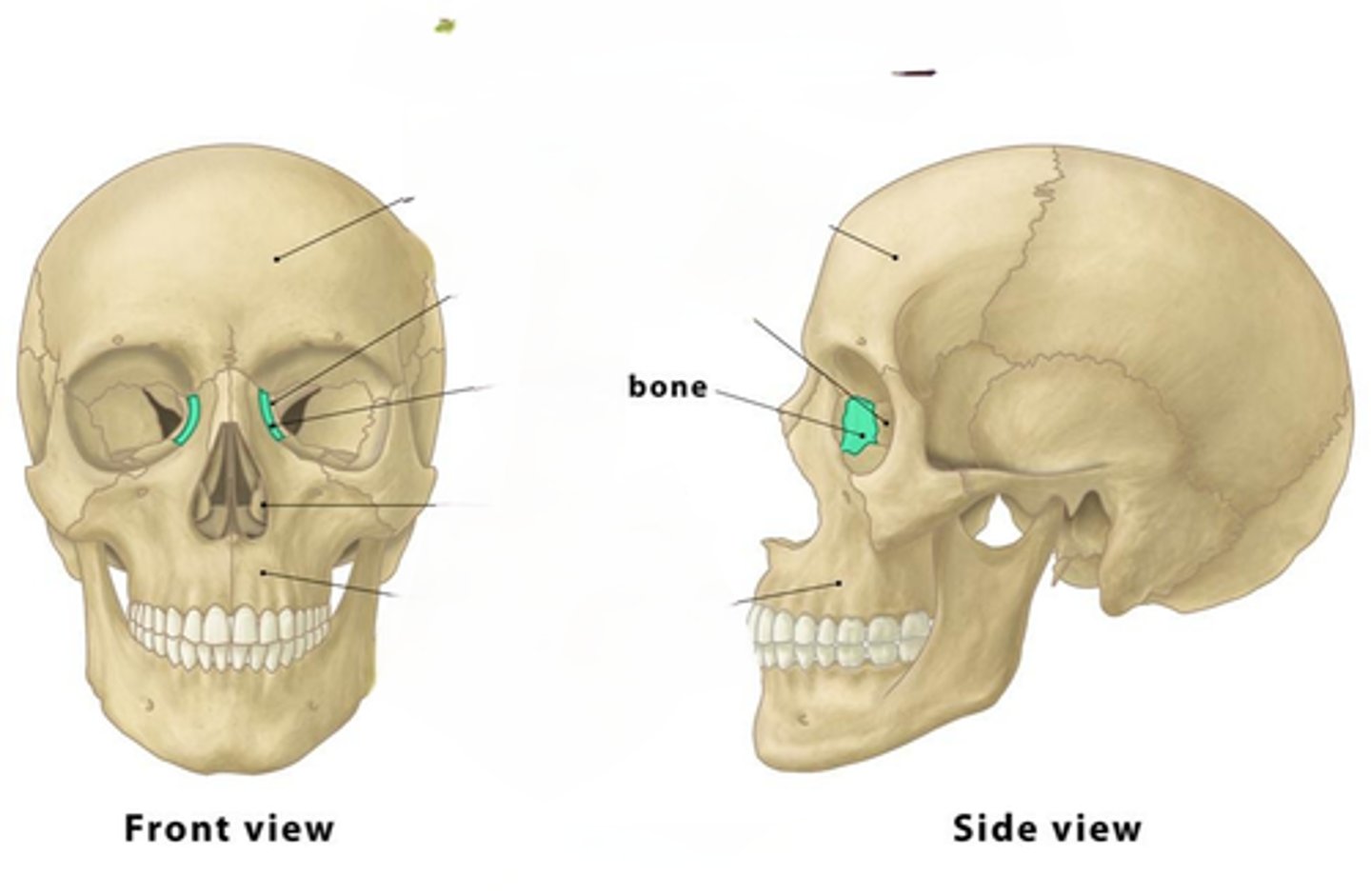
Lacrimal
teardrop shape bone on either side of the nasal cavity
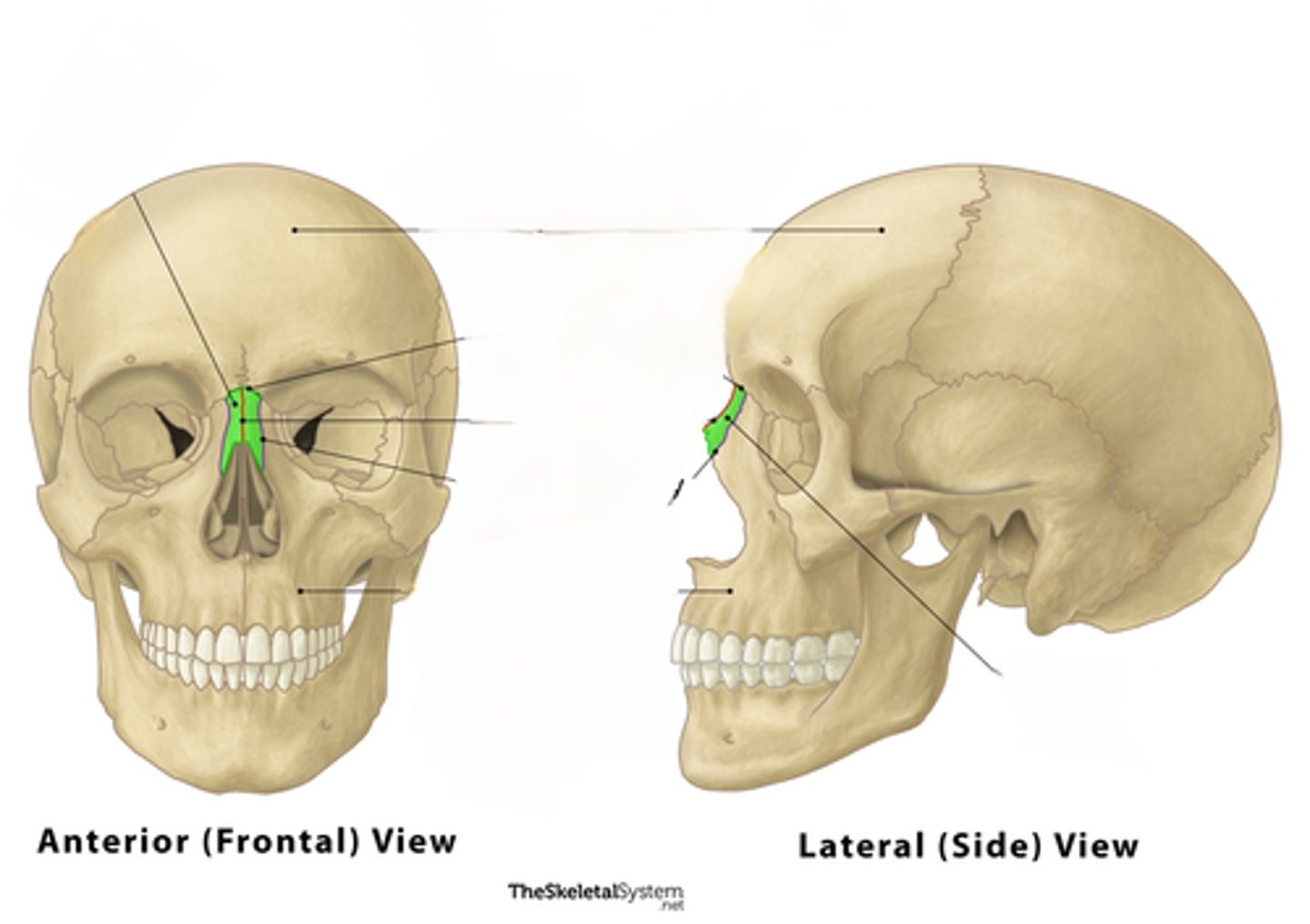
Nasal
bones that form the bridge of the nose
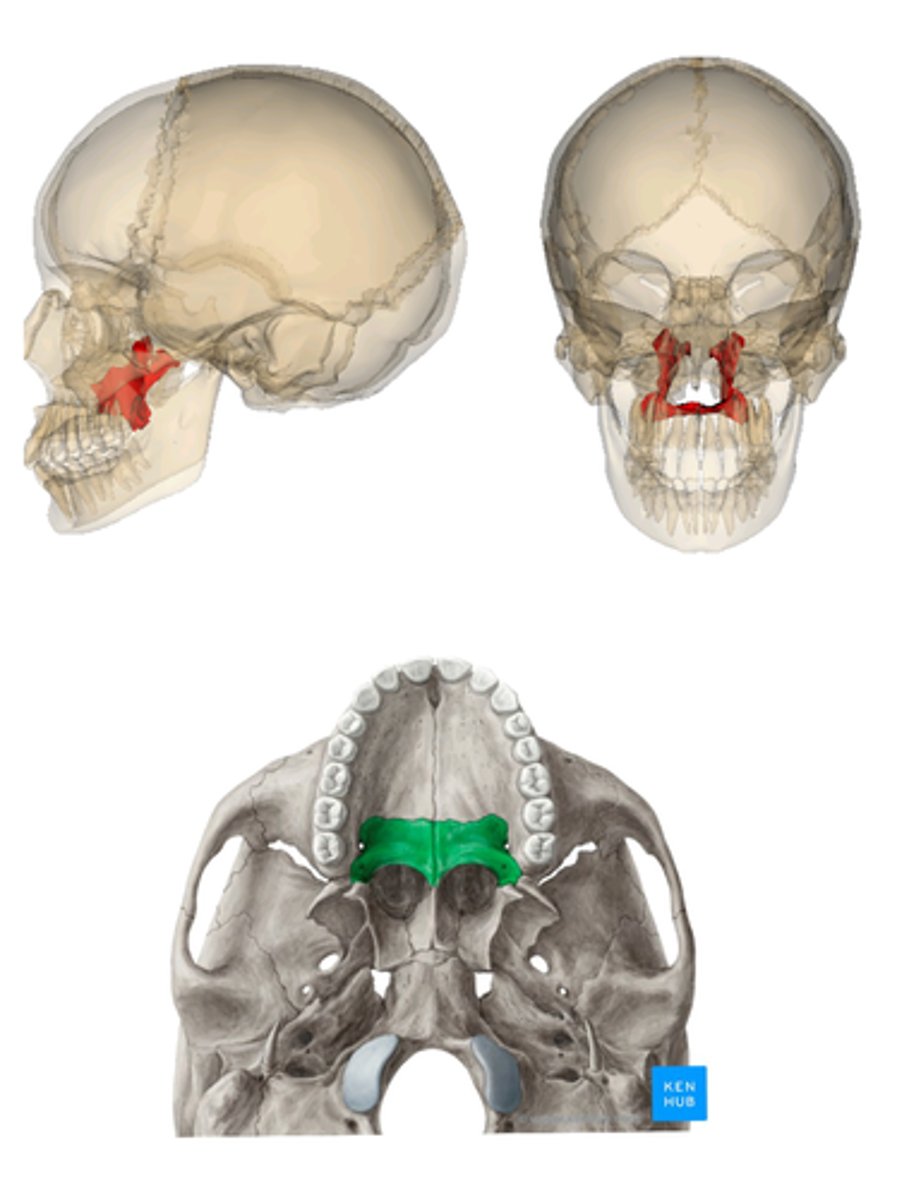
Palatine
bones on the superior medial portion of the nasal cavity
Vomer
the small, thin bone separating the right and left nasal cavities
206
number of bones in the skeletal system
appandicular skeleton
two large groups of the skeletal system
Protect and support the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs housed in the thorax
functions of the axial skeleton
Sutures
immovable joints of the skull
True Ribs
ribs attached directly to the sternum, pairs 1-7
False Ribs
ribs not attached directly to the sternum, pairs 8-12
Floating Ribs
ribs that are only connected to the vertebrae, pairs 11-12
Involved in locomotion and the manipulation of the environment
functions of the appendicular skeleton
Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis
the 3 bones that fuse to form the coxal bones
Articulation
a location where two bone surfaces come together
Projection
a raised area that sticks out from the bone's surface. Projections are also known as processes and are attachment points for ligaments and tendons.
Tubercle
small, rounded process or bump
Tuberosity
rough process, larger than a tubercle
Spine
sharp process
Crest
ridge
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial
3 major types of joints
Flexion
decreases the angle of a joint
Extension
increases the angle of a joint
Hyperextension
increases the angle of a joint beyond normal range
Abduction
movement away from the median plane
Adduction
movement toward the median plane
Rotation
the turning of a structure around its axis
Pronation
movement that positions body parts to the back/down
Supination
movement that positions body parts to the front/up
Plane joints
produce multiaxial and gliding movements, restricts rotation, bones are flat or slightly curved
Examples of plane joints
intercarpal and intertarsal joints, articular processes between vertebrae
Hinge joints
produce uniaxial movements, one bone moves while the other remains stationary
Examples of hinge joints
elbow and knee joints
Pivot joints
produce uniaxial movements, a projection or process on one bone fits into and rotates within an opening on another bone
Examples of pivot joints
atlantoaxial and radioulnar joints
Saddle joints
produce biaxial movements, concave and convex portions of bones fit together
Examples of saddle joints
carpometacarpal joints
Ball-and-socket joints
produce multiaxial movements, provides the greatest range of motion
Examples of ball-and-socket joints
shoulder and hip joints
Condyloid joints
produce biaxial movements, modified ball-and-socket joints (oval shape versus spherical)
Examples of condyloid joints
metacarpophalangeal and atlantooccipital joints
Head
prominent rounded surface
Facet
flat surface
Condyle
rounded surface
Holes
opening or groove in a bone that allows blood vessels and nerves to enter or pass through the bone
Sulcus
groove
Canal
passage in bone
Foramen
hole
Sinus
air-filled space
Dorsiflexion
decreases joint angle between the front of the leg and the top of the foot, "flexing the foot"
Plantar Flexion
decreases joint angle between the back of the leg and the sole of the foot, "pointing the foot"